MACRO Unit 1 Multiple Choice
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Which of the following is not an assumption of the productions possibilities frontier?
a. A country produces only two goods or types of goods.
b. Technology does not change.
c. The amount of available resources does not
change.
d. There is a fixed quantity of money.
a. A country produces only two goods or types of goods.
b. Technology does not change.
c. The amount of available resources does not
change.
d. There is a fixed quantity of money.
ANSWER: d
(there is a fixed amount of resources, but not money)
Which of the following areas of study typifies microeconomics as opposed to macroeconomics?
a. the impact of minimum-wage laws on employment in the fast food industry
b. the effect of changes in household saving rates on the growth rate of national income
c. the impact of faster money growth on the rate of inflation
d. a comparison of alternative tax policies and their respective impacts on the rate of the nations economic growth
a. the impact of minimum-wage laws on employment in the fast food industry
b. the effect of changes in household saving rates on the growth rate of national income
c. the impact of faster money growth on the rate of inflation
d. a comparison of alternative tax policies and their respective impacts on the rate of the nations economic growth
ANSWER: a
Draw a demand curve for music downloads. What happens to it in each of the following scenarios? Why?
1. The price of iPods falls
2. The price of music downloads falls
3. The price of music CDs falls
Answer:
1.The demand curve will shift to right (complement goods).
2. The quantity demanded of music downloads increase due to a fall in its own price.
3. The demand curve will shift to left (price of the substitute good declines.)
When quantity demanded has increased at every price, it might be because
a. the number of buyers in the market has decreased.
b. income has increased, and the good is an inferior
good.
c. the costs incurred by sellers producing the good
have decreased.
d. the price of a complementary good has decreased.
a. the number of buyers in the market has decreased.
b. income has increased, and the good is an inferior
good.
c. the costs incurred by sellers producing the good
have decreased.
d. the price of a complementary good has decreased.
Answer: d
If the price of a good is low,
a. firms would increase profit by increasing output.
b. the quantity supplied of the good could be zero.
c. the supply curve for the good will shift to the left.
d. firms can and should raise the price of the product.
a. firms would increase profit by increasing output.
b. the quantity supplied of the good could be zero.
c. the supply curve for the good will shift to the left.
d. firms can and should raise the price of the product.
Answer: b
The adage, "There is no such thing as a free lunch," means
a. even people on welfare have to pay for food.
b. the cost of living is always increasing.
c. people face tradeoffs.
d. all costs are included in the price of a product.
ANSWER: c
Ramona decides to spend two hours taking a nap rather than attending her classes. Her opportunity cost of napping is
a. the value of the knowledge she would have received had she attended class.
b. the $24 she could have earned if she had worked at her job for those two hours.
c. the value of her nap minus the value of attending class.
d. nothing, since she valued sleep more than attendance at class.
ANSWER: a
Any point on a country's production possibilities frontier represents a combination of two goods that an economy
a. will never be able to produce.
b. can produce using all available resources and technology.
c. can produce using some portion, but not all, of its resources and technology.
d. may be able to produce in the future with more resources and/or superior technology.
ANSWER: b
On the production possibilities frontier shown, which point or points are efficient?
a. a,b,c,e
b. d
c. a,b,c
d. e
ANSWER: c
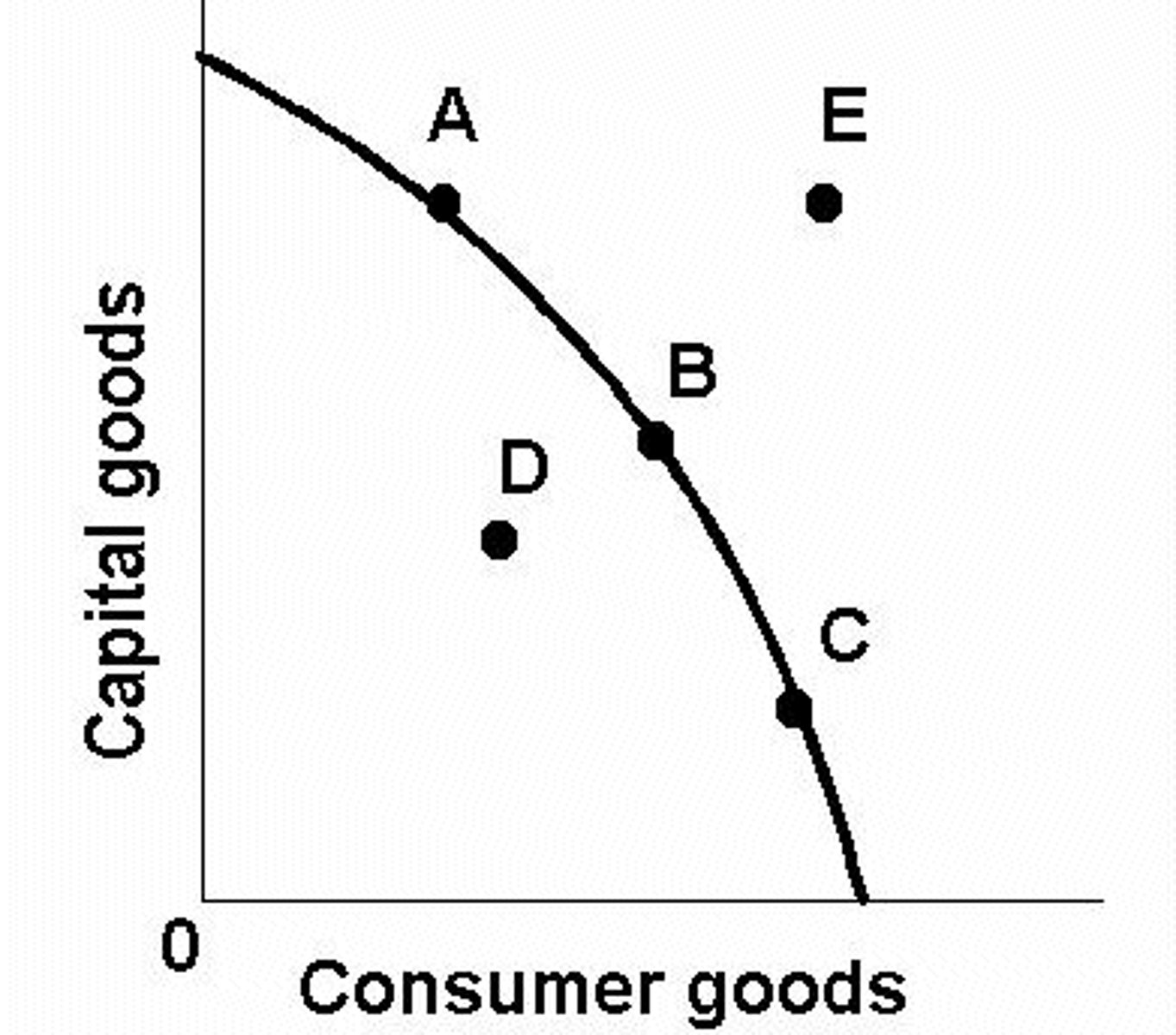
The production possibilities frontier illustrates
a. the combinations of output that an economy should produce.
b. the combinations of output that an economy should consume.
c. the combinations of output that an economy can produce.
d. All of the above are correct.
ANSWER: c
A production possibilities frontier is a straight line when
a. the more resources the economy uses to produce one good, the fewer resources it
has available to produce the other good.
b. an economy is interdependent and engaged in trade instead of self-sufficient.
c. the rate of tradeoff between the two goods being produced is constant.
d. the rate of tradeoff between the two goods being produced depends on how much of each good is being produced.
ANSWER: c
Regan grows flowers and makes ceramic vases. Jayson also grows flowers and makes vases, but Regan is better at producing both. In this case, trade could
a. benefit both Jayson and Regan.
b. benefit Jayson, but not Regan.
c. benefit Regan, but not Jayson.
d. not benefit Jayson nor Regan.
ANSWER: a
The producer that requires a smaller quantity of inputs to produce a certain amount of a good, relative to the quantities of inputs required by other producers to produce the same amount of that good,
a. has a low opportunity cost of producing that good, relative to the opportunity costs of other producers.
b. has a comparative advantage in the production of that good.
c. has an absolute advantage in the production of that good.
d. should be the only producer of that good.
ANSWER: c
Currently you purchase 6 packages of hot dogs a month. You will be graduating in December and will start your new job January 2nd. You have no plans to purchase hot dogs in January. For you, hot dogs are
a. a "college-only" good.
b. a normal good.
c. an inferior good.
d. a consumer good.
Answer: C
An example of complementary goods would be
a. hamburgers and hot dogs.
b. lawnmowers and automobiles.
c. hamburgers and fries.
d. Coke and Pepsi.
Answer: C
Alyssa rents 5 movies per month when the price is $3.00 each and 7 movies per month when the price is $2.50. Alyssa has demonstrated the
a. law of price.
b. law of supply.
c. actions of an irrational consumer.
d. law of demand.
Answer: D
Which of the following is NOT a determinant of demand?
a. the price of a resource
b. the price of a complementary good
c. the price of the good next month
d. the price of a substitute good
Answer: A
Suppose roses are currently selling for $40.00 per dozen. The equilibrium price of roses is $30.00 per dozen. We would expect a
a. shortage to exist and the market price of roses to increase.
b. shortage to exist and the market price of roses to decrease.
c. surplus to exist and the market price of roses to increase.
d. surplus to exist and the market price of roses to decrease.
Answer: D
Which of the following changes would not shift the demand curve for a good or service?
a. a change in income
b. a change in the price of the good or service
c. a change in expectations about the future price of the good or service
d. a change in the price of a related good or service
Answer: B