Retail Management Chapters 1-2
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What are some examples of Direct to Consumer Companies?
warby parker
versed
curology
ritual
caspar
What is retailing?
set of business activities that adds value to the products and services sold to consumers for their personal or family use
what is a retailer?
a business that sells products and/or services to consumers for personal or family use
What are some examples of retailers?
Kohls, Wendys, Amazon, Wells Fargo
What are some firms that are retailers and wholesalers?
office depot
home depot
bank of america
costco
Nike
Amazon
Apple
What are some issues in retailing today?
how can we best serve our customers while earning a fair profit or just profit?
How can we stand out in a highly competitive environment where consumers have many choices?
How can we grow our business, while retaining a core of loyal customers
How can we evolve and maintain as an Omnichannel retailer?
How can we survive on increasing global competition and a changing marketing environment
Evolving Supply Channel Changes
What is vertical integration?
when firms performs in more than one set of activities
What is an example of vertical integration?
Victoria’s Secret, Bath and Body Works, Mast Industries
What is Backward integration?
retailer performs some distribution and manufactering activities
What are some examples of backward integration?
JCPenney sells Arizona jeans (Private Label)
Buckle (BKE jeans)
Harry’s (Razors)
what is forward integration?
manufacturers undertake retailing activities
What are some examples of forward integration?
Nike
Apple
Sherwin Williams
How do retailers add value?
break bulk (get quantities customers want)
Hold inventory (hold it at a convenient place when you want it
Manage risk (buy inventory, easy returns)
Provide assortment
other services (get credit, layaway, returns)
What is the social and economic significance of retailing?
Community Support
Over $6.5 trillion in annual US Sales
Employs approx. 15 million people
Management training opportunities
Entrepreneurial opportunities
How has retailing become globalized?
source merchandise from around the world
walmart operates in US, China, Mexico, UK, Argentina
Carrefour has stores in 25 countries
Retailers from around the world are in the US market physically and digitally
What makes Retailing a high tech industry?
selling merchandise digitally
digital marketing
using internet to manage supply chains
data analytics for decision making
merchandise planning and prediction
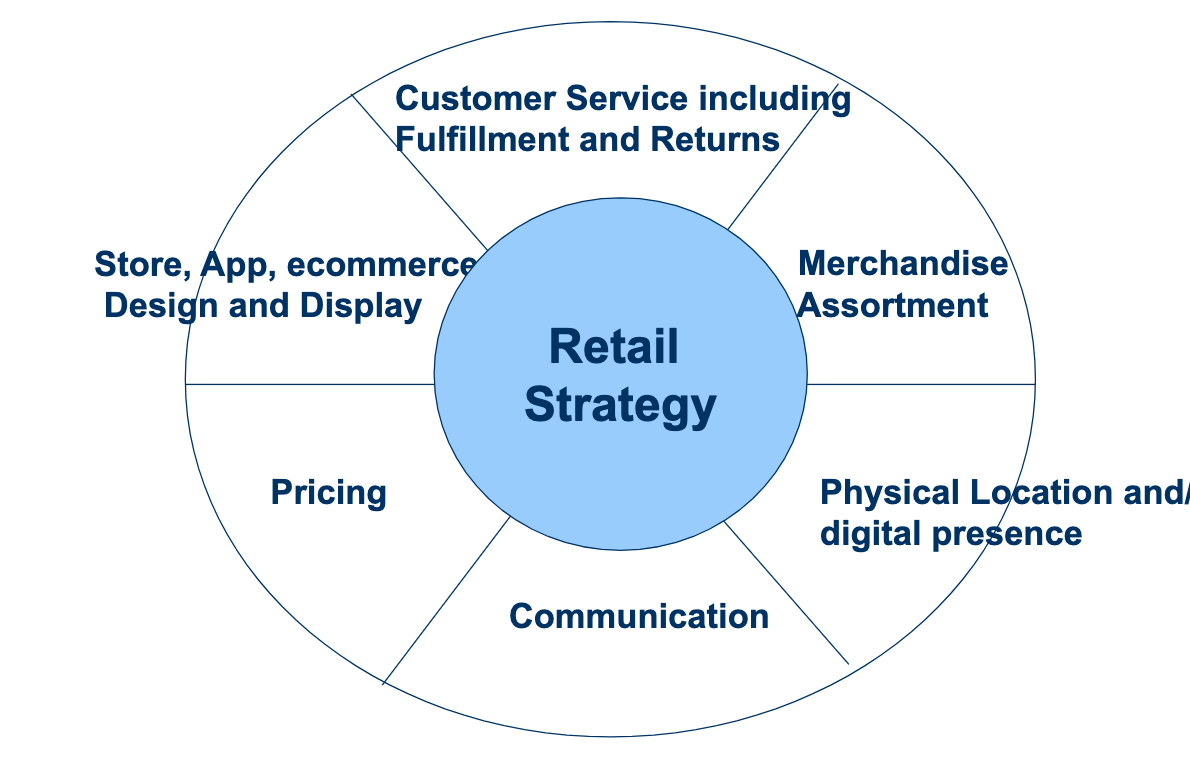
What are the decision variable for retailers?
customer service including fulfillment and returns
merchandise assortment
physical location and/or digital presence
communication
pricing
store, app, e-commerce design and display
What are some more aspects of retailing?
retail is creative
retail is detail
retail is fast, lack of speed kills
retail is highly competitive
retail keeps score everyday
nothing happens until something gets sold
reality in retailing is perception
always dealing with customer expectations
focus on customer behavior (trends)
What are some perceptions about careers in retailing?
don’t need college
low pay
long hours
boring
dead-end job
no benefits
everyone is part time
unstable environment
Why should you consider retailing?
entry level management positions
department manager or assistant buyer/planner
manage and have P&L responsibility on your first job
starting pay average to above average w/ great benefits
Some retailers pay graduate school
no 2 days are alike
buying for creative/financially oriented people
management for people who like working with people
no glass ceiling
What are some of the types of careers found in retailing?
store management
data analytics
accounting and finance
technology
real estate
hr management
supply chain management
marketing
public affairs
information systems
loss prevention
visual and graphic design
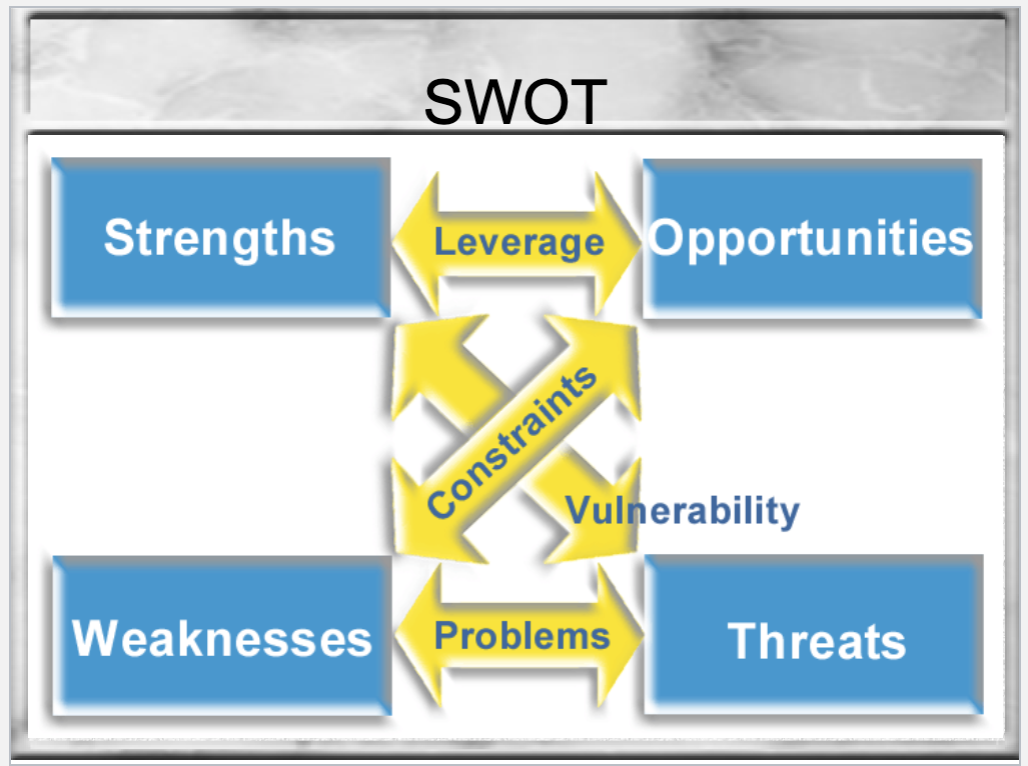
How does SWOT Work?
You should leverage strengths and opportunities, understand the constraints of weaknesses when paired with opportunities, Understand the vulnerability of strengths when paired with threats, and Understand how when weaknesses are paired with threats they become a problem.
what are some general trends in retailing?
growth in digital, omni-channel retailing by new and traditional retailers
increased use of technology to reduce cost; increase value delivered
growth in services retailing
new types of retailers
new types of retailers
globalization
How can retailers be different?
using different retail mixes
Type of offering
Product or Service
Industry
Merchandise
design, visual merchandising
location
pricing
infinite variations
What is merchandise?
variety (breadth)
assortment (Depth)
Availability (In Stock)
What is variety or breadth of merchandise?
the number of merchandise categories
Wide vs. Narrow
What is assortment or depth of merchandise?
the number of items in a category (SKUs)
deep vs. shallow
What is availability in terms of merchandising?
the percentage of customers who want to buy a product can get it
What does QSP stand for?
Quality
Service
Price
What does SKU stand for?
Stock keeping Units
How does service differ for retailers
retailers differ in the services they offer customers
Cycleworks offers assistance in selecting the appropriate bicycle as well as bicycle repairs
Walmart does not have any additional services but you will get a bike at a lower cost
What are some types of food retailers?
supermarkets
cars, highways, and tv to build brands
knowledgeable customers - self service
perishable vs. packaged goods
big box retailers
Warehouse Clubs
Costco
Amazon
Supercenters (Target and Walmart)
Convenience Stores
Limited Assortment Groceries
Digital Retailers
Natural/Organic Emphasis Grocers
Non-Grocer Grocers
Supermarkets
conventional supermarkets account for less than 45% of food sales
Offer Services: pharmacies, health care, banks, coffee
Want customers to think of it as a place to “hang out”
Online ordering, delivery, pick up at door
Online Grocery Retailers
Customers willing to pay more to save time
online retailers continues to expand
about 30% of orders are for nonfood items
paper products, cleaning items
slim profit margins continue to be a problem, fulfillment costs are high
large growth during the pandemic
Differentiate Strategy
Walmart = low price, huge variety and good value, convenience, and e-commerce
Target = more fashionable, focus on digital commerce, stores as fulfillment centers, branding
Costco = low price, unique product mix
Specialty Stores
concentrate on limited number of complementary merchandise categories
deep but narrow variety
sales associate expertise
DTC
Slowing down in specialty stores during the pandemic
Resale stores
thrift stores
consignment
Issues in specialty store retailing
digital stand alone and mall-based retailers: decline in mall shopping and apparel sales
Lifestyle formats: Banana Republic, American Eagle, Buckle, Foot Locker, Finish Line, Supreme
Local Boutiques: Specialty Shoe, Jewelry, and Niche Sports (Skater Style Stores) Athletic Equipment
Omnichannel opportunities
Category Specialists
Deep and Narrow Assortments - Destination Stores
Low price and Average Service
Wholesaling to business customers and retailing to consumers
Increased Competition with National Expansion and Consolidation
Huge increase in DIY
Department Store Retailing
broad variety
deep assortment
customer service
merchandise displayed into distinct departments
soft goods
hard goods
Issues in department store retailing
competition
discount stores on price
digital on price and assortment
specialty stores on service, depth of assortment
Lower cost by reducing services
centralized cash wraps
More Sales
trained customers to wait for sales
Categories of department stores
discount
moderate
luxury
Department Stores are:
attempting to increase the amount of exclusive merchandise they sell
increase private-label merchandise, change merchandise mix
Change pricing model
expand multichannel and social media presence
What is a challenge of Department stores?
high end, semi-exclusive brands want to move away from dept. store distribution
What is drug store retailing?
specialty stores that concentrate on health and beauty care
consolidation
Walgreens, CVS
Competition
Evolution to a new format
stand alone sites with drive-thru windows
offering more frequent purchase food items
convenience stores
improved systems provide personalized service
What are off-price retailers?
inconsistent assortment of brand-name merchandise
significant price discounts (20-60% lower than suggested retail price)
closeouts
irregulars
outlet stores
factory outlets
flash sale sites
What are issues in off-price retailing?
Opportunistic Buying
High Growth Area
Buying First Line Merchandise
Sales down during the Pandemic
What is the off price retailing strategy?
pay vendor quickly with no promotional allowances, cooperative advertising funds, chargebacks, or markdown monies
do not promote brand name to no6 anger department and specialty shops, which are vendor’s traditional customers
Buy all of the vendor’s excess inventory, canceled orders, and returns regardless of color, size, or style distributions
Pay 10-20% of vendors’ traditional wholesale $500 jacket purchased for $50 and sold for $100 versus sold for $250 less allowances
Can also arrange for vendors to produce special goods for off-price retailers to reduce loss on fabrics, and to keep subcontractors busy
issues in extreme value retailing
customer base is changing
major challenges in this sector of retailing today
inconsistent product offering
What are some other retailers?
online
flea markets
vending machines
short term retailers - kiosks, pop up stores
variety stores
What are some examples of services retailing?
aging population having increased demand for health care and home services
young people are spending more time on health and fitness
busy families are using services like home cleaning, lawn services, and meal prep to balance lifestyles
What is the difference between service retailers and merchandise retailers?
intangibility
simultaneous production and consumption
perishability
inconsistency of offerings to customers
What are issues in catalog retailing?
low start up cost
evolution of multi-channel offering
electronic channel, stores
Increasing mail costs
clutter from other catalogs
What are some issues with direct selling?
completely bypasses retailers and wholesalers
manufacturers set up their own channels to sell their products directly to consumers
Party Plan System
Merchandise is demonstrated in a party atmosphere
Multi-level network
master distributors sell to distributors who sell merchandise
Pyramid Schemes
firm sells to other distributors and little if any merchandise goes to end users
Issues in Television Home Shopping
few consumers watch regularly
most purchases made by small proportion of viewers
customers can’t examine merchandise
customers must wait for merchandise to come on
sells predominately jewelry, apparel, cosmetics, kitchenware, and exercise equipment (but this is evolving)
host is key in selling process
What are the types of ownership in retail?
independent
chain
franchise
lease department
vertical marketing system
consumer cooperative
What are trends in ownership?
concentration on one format
growth in services franchising
What are Independent Advantages
flexibility
investment costs down
specialists
strong control
image
consistency
independence
entrepreneurial drive
What are some advantages of chains?
scale and scope
bargaining power
cost and operating efficiencies
technical abilities
Franchising
30-40% of US Retail Sales
Franchisee pays fixed fee plus % of sales
Franchisee implements program
What are reasons for franchising growth?
technological advances
profitable utilization of capital resources
attainment of the American “Ownership Dream”
demographic changes
product/service consistency
What are the types of franchising?
product/trademark
business format
What are benefits of franchisors?
national or global presence
ownership qualifications set
money obtained on delivery
stringent rules for franchisees
franchisee work incentive
royalties continue
What are problems with Franchisors?
damaged reputation
loss of customer loyalty
intra-franchise competition
reduced resale value
injured profitability
franchisee desire for independence
What are franchisee benefits?
small capital investment
brand awareness
operation procedures and management skills
cooperative marketing
exclusive selling rights
purchasing costs
What are Franchisee problems?
oversaturation
franchisor overselling
contract provisions
cancellation clauses
short duration
gross sales based royalties
What causes franchising failures?
inept management
fraudulent activities
market saturation
What are some trends for franchising in the 21st century?
sustained growth
enduring plus un-imagined applications
international expansion
increasing tensions