Micronutrients & Bioactive Compounds
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
should someone take this Vit C supplement for a cold?
-comes into body and filter a lot out in urine; tradeoffs?: money; no physical harm?
-supplements not regulated like food; x11 RDA (men); halfway to UL (so prob safe)
-dif nutrition status and time indoors w/ dif seasons
-Immune +: added Vit D
-*astrik: doesn’t mean couldn’t provide immune support, just not enough evidence
-Article Antartica Study: did or didn’t get Vit C product; Results- no dif between groups, but physical labor group’s cold was ½ day shorter (other study also not powerful)
-Own Marquette Study: baseline level? Dif length of sickness? How incentives? Determine?
Reminder of Micronutritents
-Vitamins and Minerals
-No kcals
-mg or micro grams of something/can’t see (vs macro=g and can see)
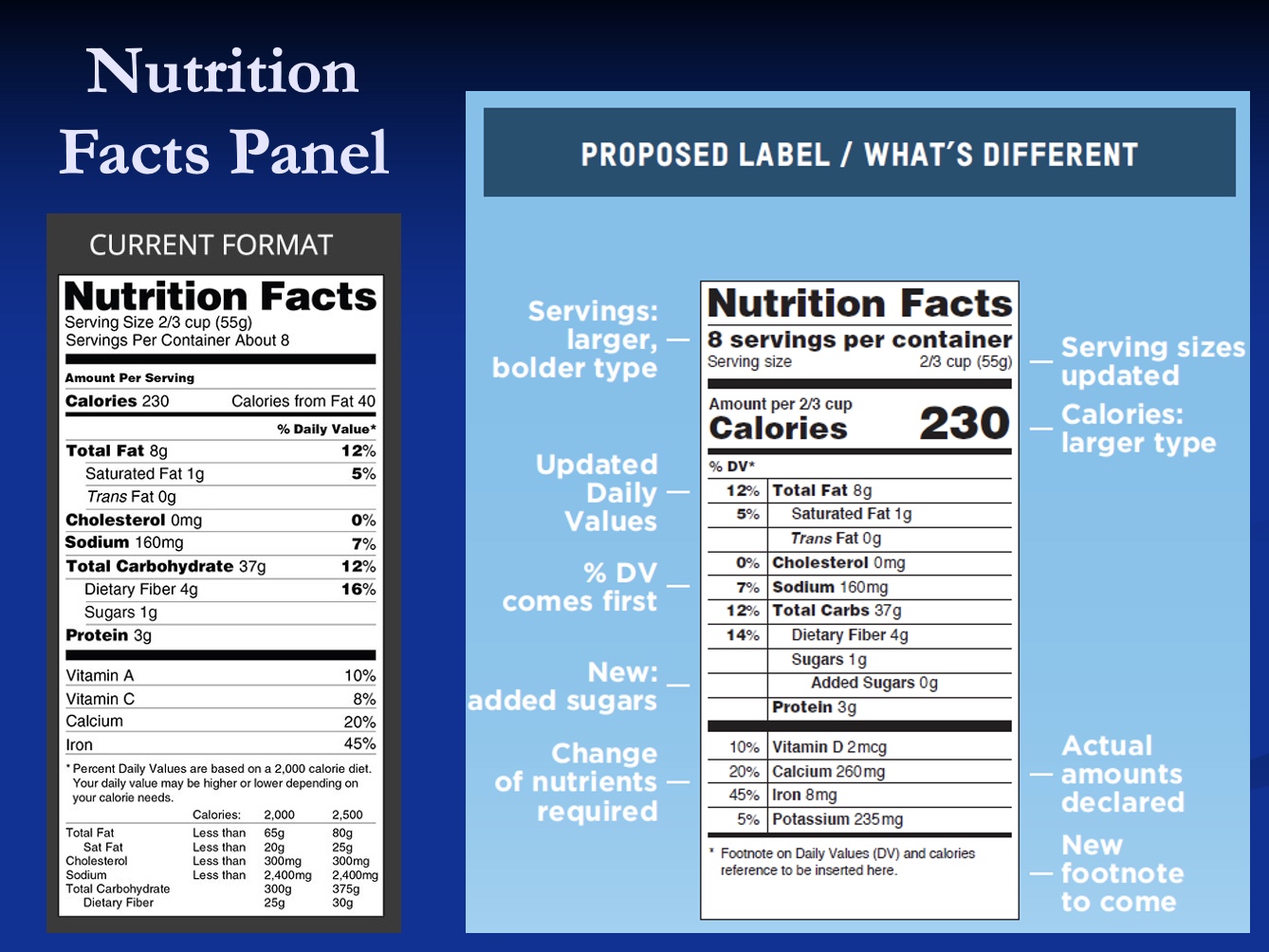
Micronutrients on Nutrition Label
-Listed required nutrients: Ca and Iron always on, Vit D and Potassium added (nutrients hard for Americans to get though diet)
Ca, Vit D, Iron, K
-actual amounts declared (always had %)
Estimated Sources of Calories in US Diet: Micronutrient analysis
-added sugar: no micro
-refined grains: if enriched flour get B-vit, otherwise low-quality w/ regards to micro
-potatoes, whole grains, and other carbs: have micros, but thin wedges (~100 kcal for fruits and veggies?)
-protein and fat: dairy=micro
***Americans don’t have a rich diet in micronutrients
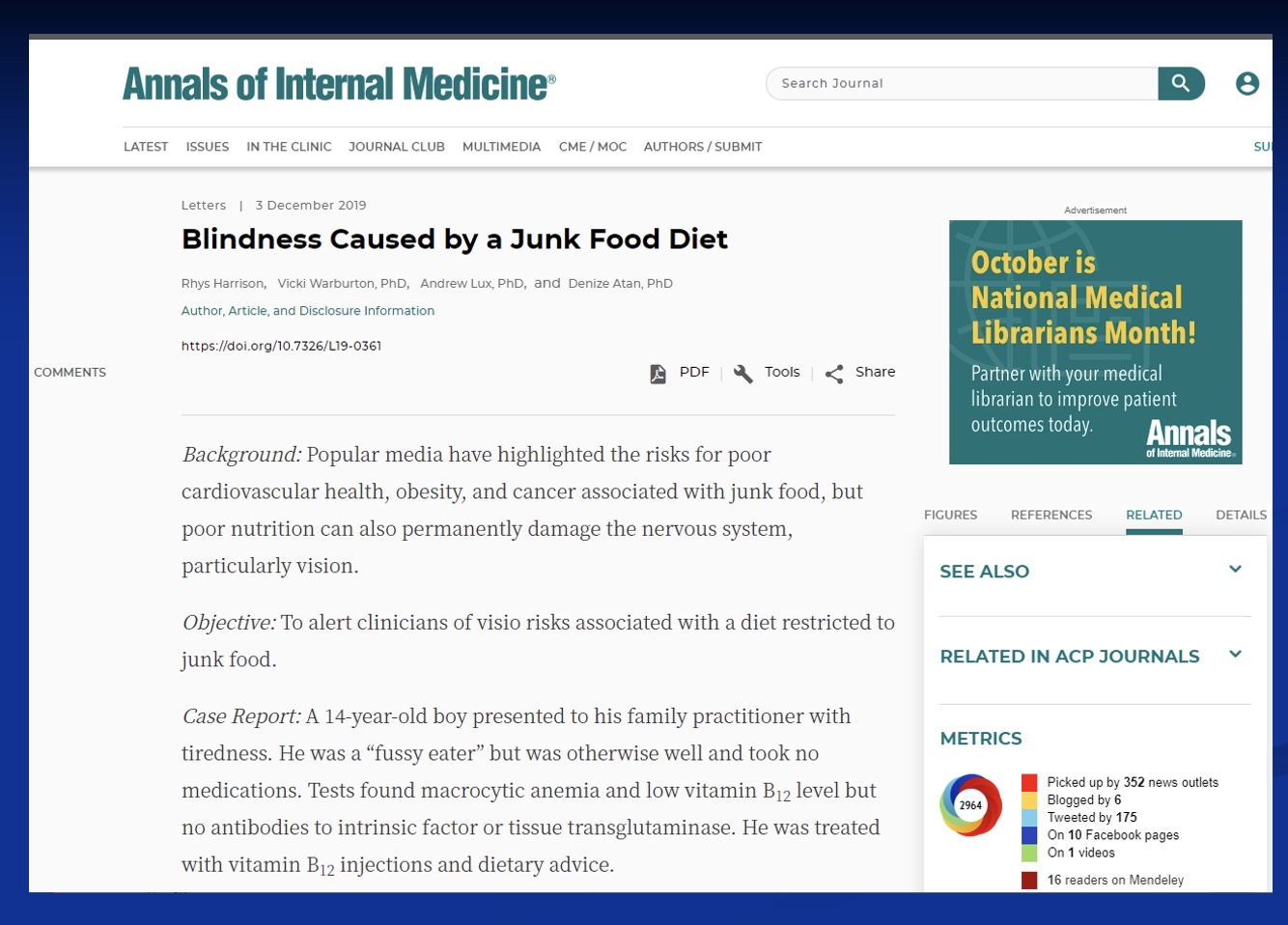
Case Study: How limiting diets restrict vitamins and minerals
-Boy was tired and a fussy eater, otherwise healthy
-test found macrocytic anemia (low O2 carrying capacity bc B12 deficiency/not bc iron) and low vit B12, but no antibodies for intrinsic factor (allows B12 absorb) or tissue transflutaminase (like celiac disease/something wrong w/ gut/bad absoprtion)
-treated with vit B12 injections and dietary advise (eat less fat, more fruits and veggies)
Results
-permanent hearing and vision loss
-he only ate the same 5 foods
-extreme levels some things, deficiency in others (expected)
Analysis
-cells still functioning, but not normal (function at dif rates)
-tired bc physiology distorted by his diet
what micronutrients are in these foods?
-squash, peppers, black beans or quinoa
-mushrooms, sour cream, wild rice or beef
-think: would it make a nice dish?
-if eat a diversity of whole foods, vitamins and minerals generally come along for the ride
*processed meats: hard to determine nutrition just by looking
micronutrients function
-Process regulators (of many things)
regulating enzymes/their rates
minerals incorporated into enzymes; ex: Mg and Thiamin/B-vit in mito (decarboxylate so go to Krebs)
-structural
bones high mineral base (Ca, iron, P, selenium)
and repository for minerals (ex: put lot Ca in blood → osteoporosis)
elements=
minerals
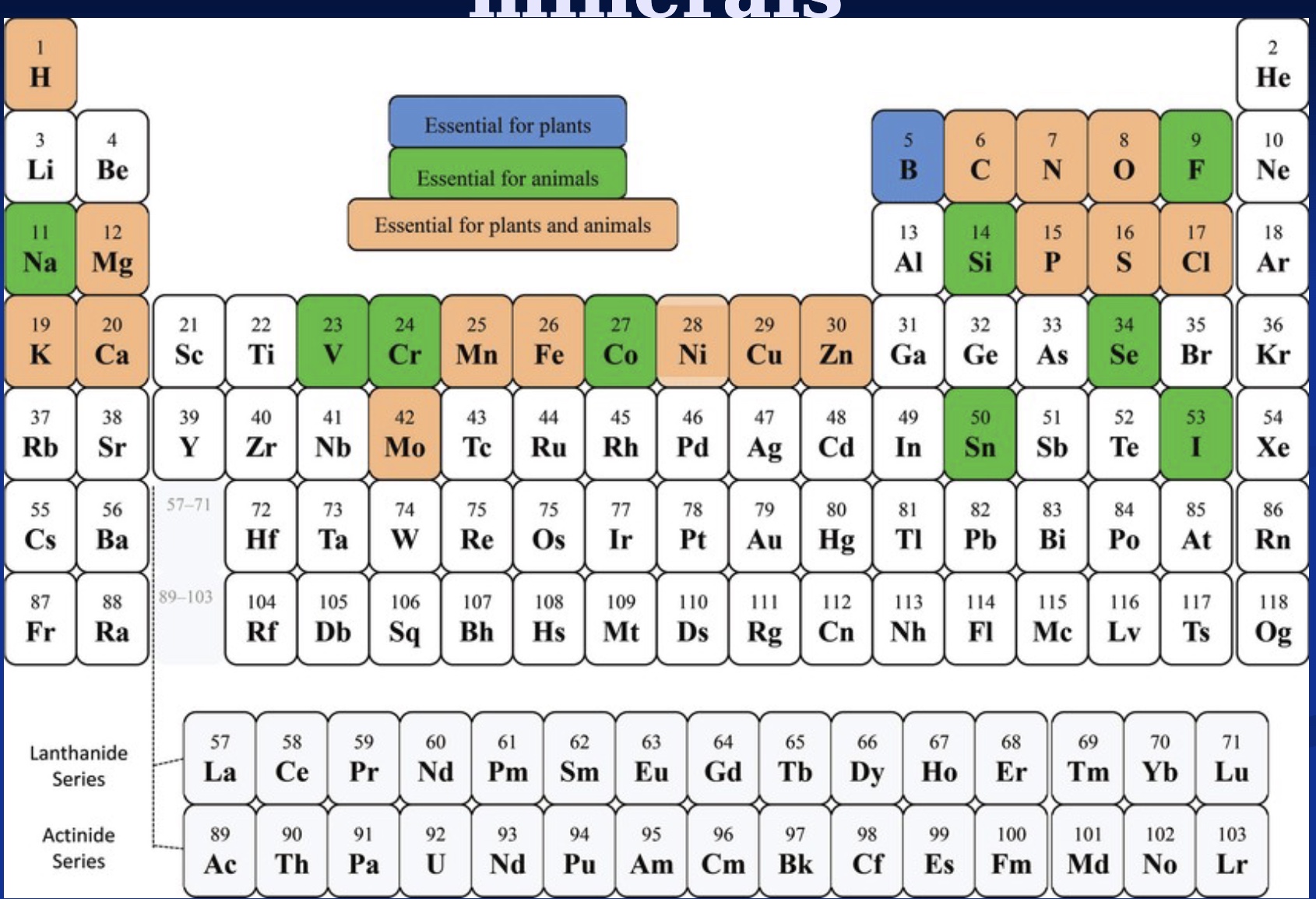
Micro DRI’s
*don’t have to memorize, but have sense of what micro’s are in food groups (ex: Ca in dairy)
-most are RDA’s (vs AI)
-some change in units overtime
-Vit D RDA: what need if no sunlight (some people can just get from sun; Milwaukee in winter not enough so need from food, can store in body)
-”ND”=no upper limit; lot of water soluble vitamins (bc easily filtered into urine)
Fat Soluble Vitamins
ADEK
-better absorbed when consume fats
-can be stored
*hang out more/absorbed in fat tissue (so have more UL, but the UL are lower than water-soluble)
Water Soluble Vitamins
-Vitamin B’s (8)
*collection; # based on when discovered
-Vitamin C
-Travel freely in blood (don’t have to be bound to anything)
-Excess excreted (why lot don’t have as many UL, or the UL they have is higher than fat soluble)
*ex: 1 B-vit gives off bright color in urine
true or false: we generally absorb minerals well
false
Vitamins Function and Source: Vit A
-Vision/skin
Vit A in rods, light sensing pigment (“eat carrots→ good night vision”)
“heatlhy skin” (DNA regulator, medication acutane)
-yellows/oranges/reds/greens
common in low-fat foods (fruits and veggies; B-caratine)
sweet potato, red bell pepper, pumpkin
leafy greens like spinach or kale (chlorpihille covers up)
-toxicity issues
1 nutrient of concern (especially w/ supplements; why on meds for short time; not bc of B-caratine)
UL low for Vit-A
Beta Caratine
-Becomes Vit A in your body; body regulates how much convert (*dif compound than Vit A; Vit A harder to find in diet)
-In fruits and veggies
*supplements have Vit A itself (not B-caratine)
Vitamins Function and Source: Vit D
-Ca & immune
acts on GI to regulated/improve Ca absorption (also promotes break down of bones to promote Ca release from bones)
Lot of Ca in blood promotes building up of bone, thus “need Vit D for strong bones”
regulates/supports immune; binds with WBC and excites or quiets them
-sunlight!/seafood/fortified: dairy, products
less pigment (lighter skin)=less time to make Vit D; further from the equator= higher rhumotoidarthritis, type I diabetes, MS, and autoimmune; thus don’t need from food
high in Vit D (evol further from coast=ligther skin); dif levels depend on what fish eat (ex: farmed salmon lower levels)
not a good source unless fortified; where Americans get most Vit D
*other “products”=Ken’s mushrooms, more UV light increase Vit D (but not in active form)
Vit D sources
-sunlight/UV light
-food or supplements
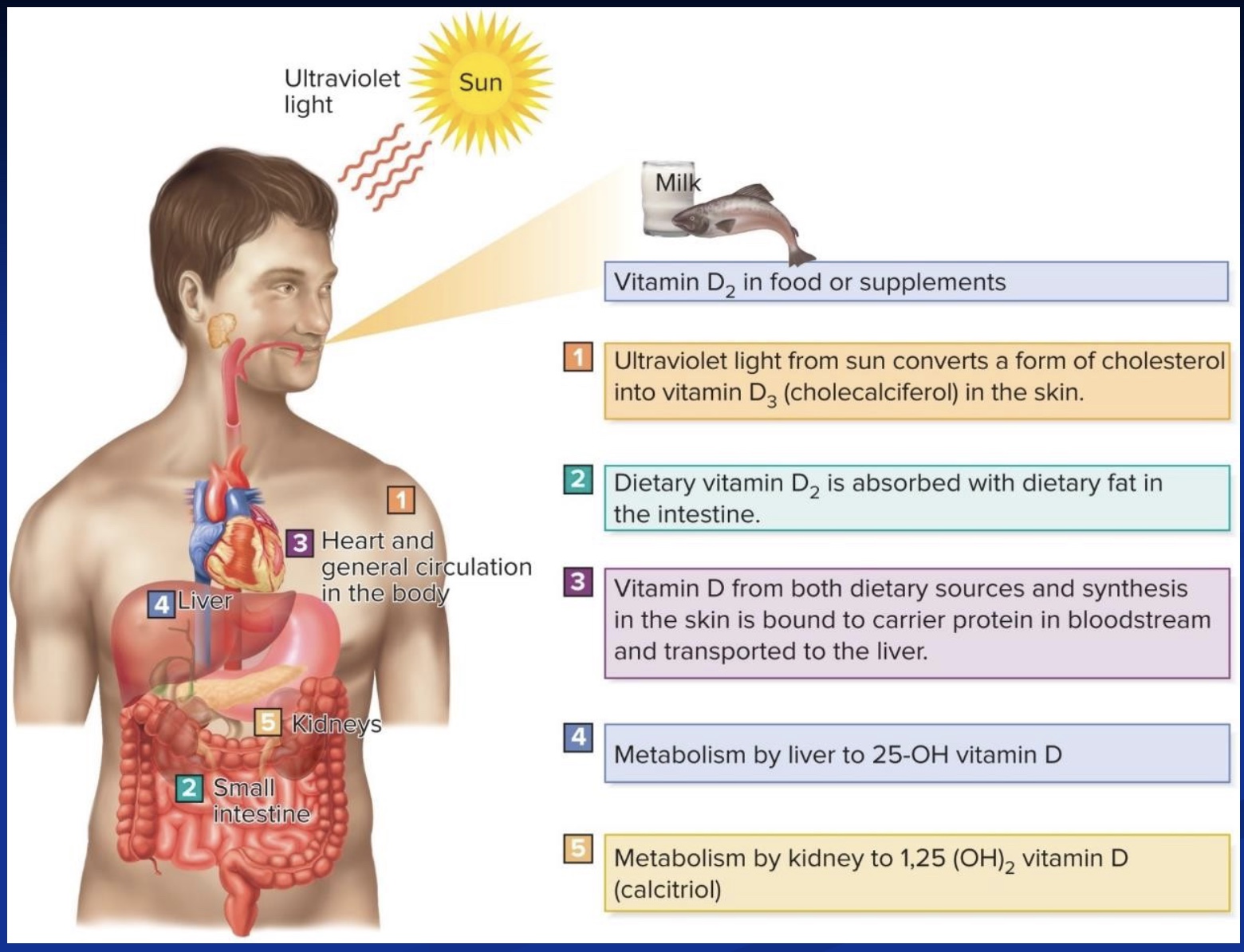
How does Vit D get to its active form?
Slap an OH onto last carbon in the liver (still not active yet…)
Slap another OH onto the first carbon in the kidneys → and is now active)
*thus, if kidney or liver failure, may have Vit D deficency; Vit D based on cholesterol; steps 4 and 5 in picture
Vitamins Function and Source: Vit E
-antioxidant
added to lots of foods to preserve (so don’t go rancid)
-oils/nuts/avocado/butter
in oily foods in general; ex: chicken oil
supplements in gel capsule w/ oil
*aka “tocopherol”
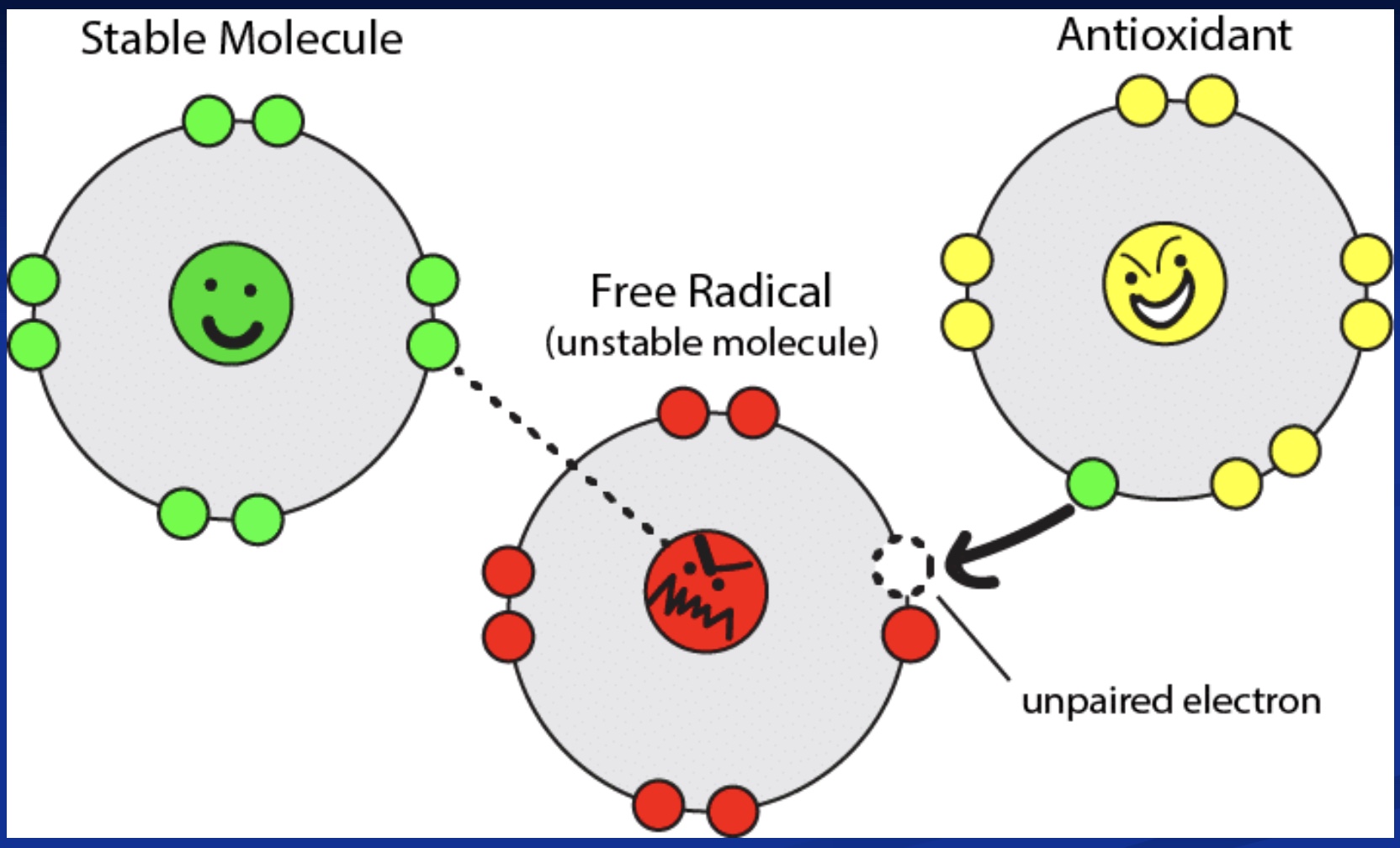
Free Radical vs. Antioxidant
-Free Radical: unstable molecule missing an electron and looking to steal one (so the stable molecule becomes a free radical; chain reaction)
*problem: what if stable molecule becoming a free radical is in the middle of transcribing a gene? what if it alters a protein?
-Antioxidant: has an electron to donate to free radicals to stop their process
*but still want certain amounts of free radicals, just not all the time (thus diet rich in antioxidants helpful); ex: when exercise, free radicals allow adaptations and better decision making
Vitamins Function and Source: Vit K (1 and 2)
Vit K1
-blood clotting
want to balance clotting (*slower=more easily bruise?)
-greens
ex: spinach, cabbage, kale
Vit K2
-bone metabolism
helps get Ca into bone
-microbiota
fermented foods high in K2; “probiotics”(where add microbiota to the foods you eat)
microbiota can convert K1→ K2 in body; thus leafy greens can help you get K1 and K2
Vitamins Function and Source: Vit B’s
-energy metabolism (synthesis AND catabolism)
ex: NAD and FAD
-many
collection; each do dif things
from many sources (not hard to find; not a lot of UL)
what 2 vitamins work together to do DNA synthesis?
Folate (B9) and Vit B12
-deficient either= anemia= low O2 carrying capacity
*dif kinds of anemia, ex: CO poisoning, iron, B12 (=macroanemia) or folate deficient
Vitamins Function and Source: Folate
*is a B Vit (B9)
-DNA synthesis (cell growth)
including RBC (at ends of long bones)
-leafy greens/fortified
Law late 90’s: if grain is enriched or fortified, you have to include folate
bc deficiency → NTD; law decreased NTD by 33%; thus most notable vitamin in prenatal vitamins
-NTD
spine doesn’t close around the spinal cord; CSF leaks out
not common, but law helpful (but not everyone consumes foods with it)
Vitamins Function and Source: Vit B12
-Works in tandem with folate to do DNA synthesis (cell growth)
-found only in animal products
unless fortified plant products
but “if eating whole foods, and exclusively plant based → B12 deficency”
Vitamins Function and Source: Vit C
-Antioxidant/collagen fxn
diminishes free radical excessiveness
involved in enzyme processing making collagen; collagen is the most prominent protein in the body
Vit C deficient= “Scurvy”, w/ bleeding gums a symptom
-increase iron absorption
-fruits and veggies (pretty common)
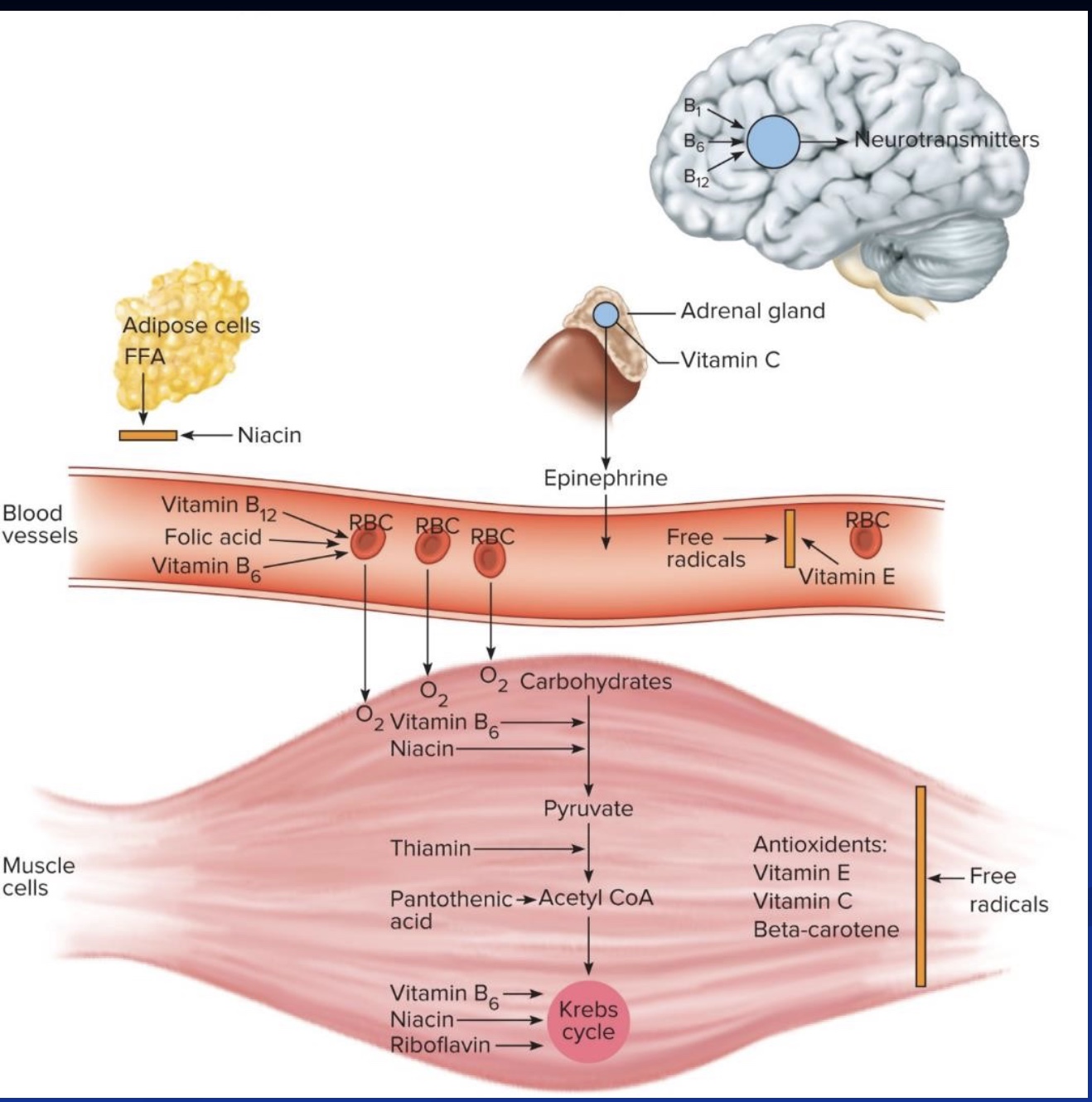
Summary photo of Vitamins various functions in the body
-antioxidants and free radicals
-B-vitamins and energy metabolism
-Vit B12 and Folate w/ RBC
Choline
-most recently added RDA (25 years ago)
-most common source= egg yolks
-choline becomes acetylcholine (neurotransmitter) by adding an acetyl group to choline
-Phosphatidylcholine= FA + FA + Phosphate + choline
common in cell membranes (like a phospholipid); allows water and fat to interact (emulsification)
ex “Lecithin”: in chocolate/candy coating and palm oil (so don’t melt), and mustard (so salad dressing doesn’t separate)
*side note: Ken’s pink chocolate bc fermented do dif pH
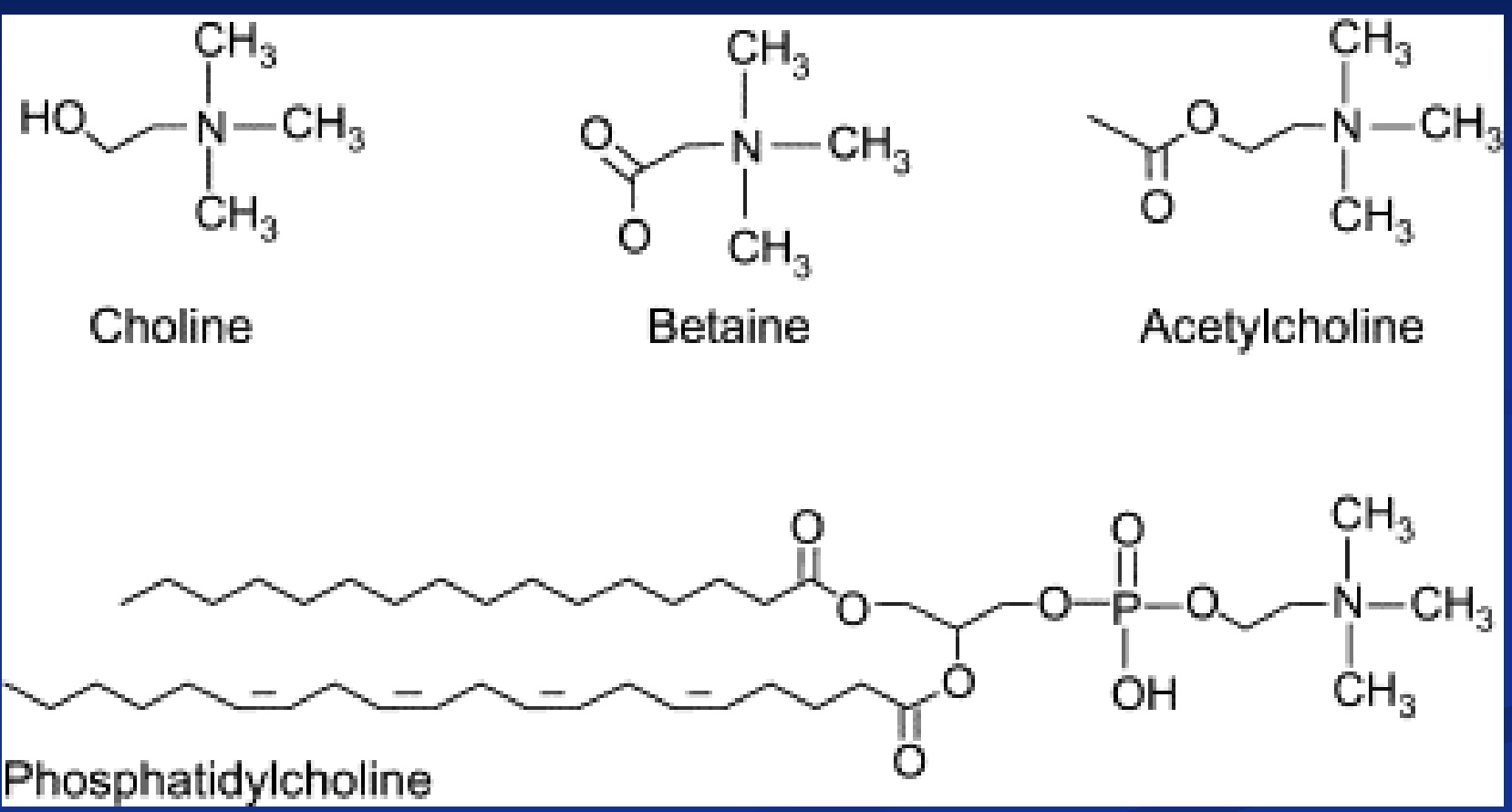
Table: how low of kcal total and still get RDA for all vitamins?
-1200kcal; mainly whole foods; amount= 100% RDA for all vitamins
-If eat 2000kcal/day and don’t hit the RDA, bc of empty calories
*Broccoli: Vit A and C; Maragrine: Vit E; Grape-nuts (minimally processed); Tuna: Vit D; *notice the milk is fortified

Mineral Function and Source (general)
-16+ essential minerals (unsure of trace levels)
-many functions (*not just for the skeleton)
-wide variety of sources (high in whole foods; more refined= lose minerals)
-low absorption (maybe 25%? but some absorb better than others)
Sodium
-goal <2300mg (~1tsp; most Americans eat 5000mg)
generally recommend low Na, but some people more salt sensitive than other
lions share from processed foods; so recommend salt shaker bc then likely cooking, and Na on surface of food and can taste it more
-hypertension
if Na sensitive
“DASH Diet”= low NA (if salt sensitive)
Potassium
-joining bottom of facts panel
Americans have hard time reaching the RDA
-improves BP
higher K= lower BP (bc of Na/K pump?)
Calcium
-osteoporosis
Ca deficient= higher risk
to prevent: weight bearing exercise, nutrition, lifestyle
-supplementing???
studies find it doesn’t prevent fractures, even if taken with Vit D (actually showed moderate increase risk of CV events likely bc Ca not to bones and instead goes to arteries); funny that Vit K never even mentioned
in academia, do research but not telling people of this risk
Iron
-RDA higher for women (18 vs 8 mg/day)
Women RDA higher in reproductive years
-higher RDA for pre-teens and teens bc growing
-better absorbed if consumed with Vit C
*can put “iron fish” so leach iron into food while cook

study: effect of Vit D supplementation on musculoskeletal health
-does not prevent fracture or falls
-no differences between high and low doses
-little justification to use Vit D supplements
-Conclusion: this should be reflected in clinical guidelines, but takes a long time for clinicians to change their behaviors

Effects of Vitamin and Mineral Status on Physical Performance
-while know restricted effects restricted macros, limited info about impact of micronutrients
-physical active people generally meet recommendations (bc eating more, so less challenging to meet the RDA)
-when less than recommendation, some impairments occur; acute or short deprivation doesn’t impact performance; found sever deprevation folate and B12 results in anemia and decreased endurance
-iron deficiency with or without anemia (bc myoglobin in muscle and mito impacted, so Hb normal but ETC sagging) impairs muscle function and limits work capacity
-supplementation does not improve performance for those w/ adequate diets
-weight and aesthetic sports prone to nutrient deficiencies bc they restrict their intake

Individual Variation and Personalized Medicine
*think of genetic and functional variation
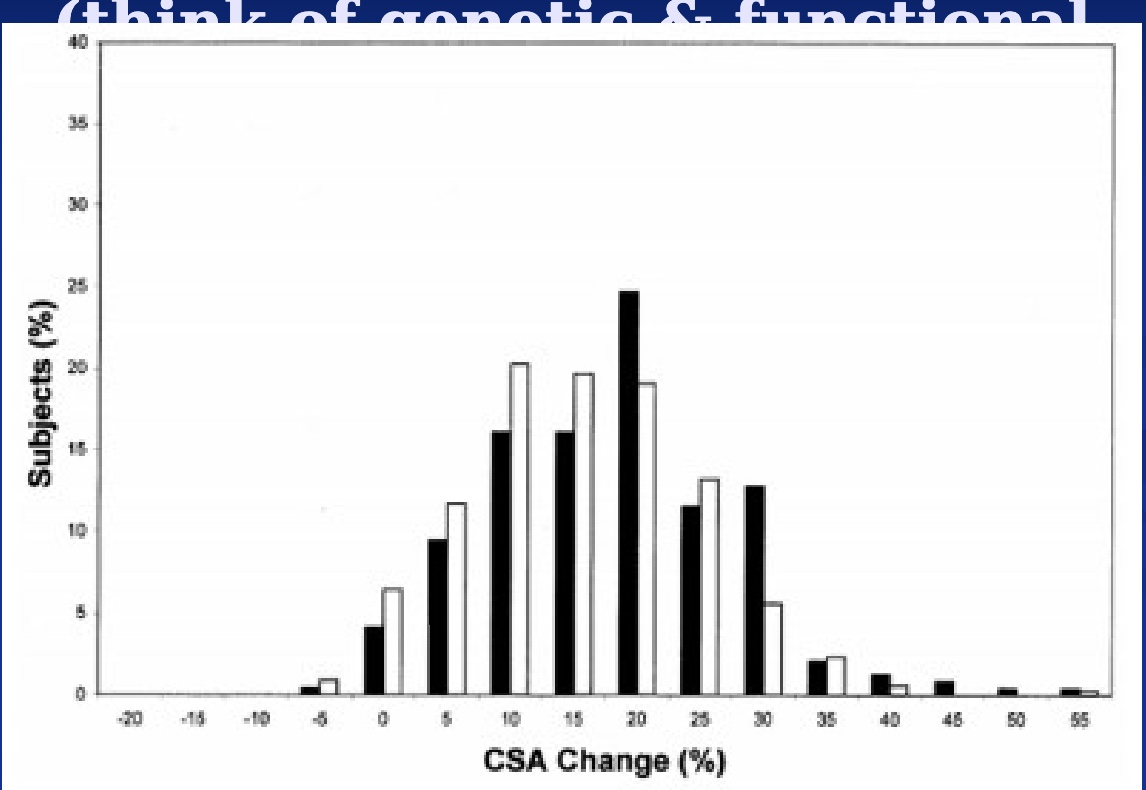
-Study: untrained people did single-arm bicep curls, looked to see if it increased their cross-sectional area
-Study Results: most people 15-20% increase (“hyper responders; bc more sensitive, genes turned on and off?), but some people had no change or got even smaller (“non responsive”; bc not consuming enough protein?)
-everyone is different/variation between people! think of variation to optimize health. we all react to differently to different stimulus
*Senior Center Study: exercise or not; error bars narrow suggest similar increases in exercise group that got more muscle strength, non-exercise group no change muscle strength (but still made sure to provide them w/ social component so didn’t feel left out)
Study: “Stop Wasting Money on Vitamins and Mineral Supplements”
*research doesn’t bare anything out
->50% of the US pop takes supplements
-in well-nourished (“insurance policy” /realtively healthy people) for chronic disease prevention
-nutrient status?
-increase needs? (for “normal people)
-misdirect from focus on diet? (we evolved to eat food, not supplements; supplements don’t come w/ anything else)
-Megadose? (not good); Daily? (instead randomly or on weekend? save $)
Position of Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics on Supplements
-Not recommended given lack of available scientific evidence
*certify’s RD’s
Study: Multi-Vitamins/Supplements “Bening Prevention or Potentially Harmful Distraction?”
-Set-up: >50% adults take supplements; lots of $
-The Appeal: people hear claims and think they will prevent chronic disease
-The Take Away: Waste money, and may be potentially harmful distractions (should focus more time on PA, cooking, “lower-risk and higher benefit activities”)
Study: Risk of mortality and supplements
-found not associated with benefits, but rather higher risk of mortality
*yet people still use; could be bc people who know they are sick take supplements to hopefully improve their status (and thus are in poorer health)
Study: Nutrients from food vs. supplements
-Nutrients from food, NOT supplements, liked to lower risks of death and cancer (getting same nutrients, so about how getting the nutrient)
-food is a complex thing w/ interactions that’s more likely to provide health benefits
Too much of a good thing? Green Tea Case Study
-16yr old girl looking to lose weight
-consumed green tea extract 3x/day
-developed ghondis (liver not clearing); acute hepatitis, no drugs or alcohol
-off tea for 48 hrs → got all better
-tea had something else in it, or was really condensed
Too much of a good thing? Antioxidants and Lung Cancer
-recruited people with higher risk of lung cancer
-gave them Vit A/E or not (Vit A also has antioxidants)
-Results: beta carotene made people 5% more likely to have cancer (beta caratine causing the cancer itself)
-what causes cancer? antioxidants?
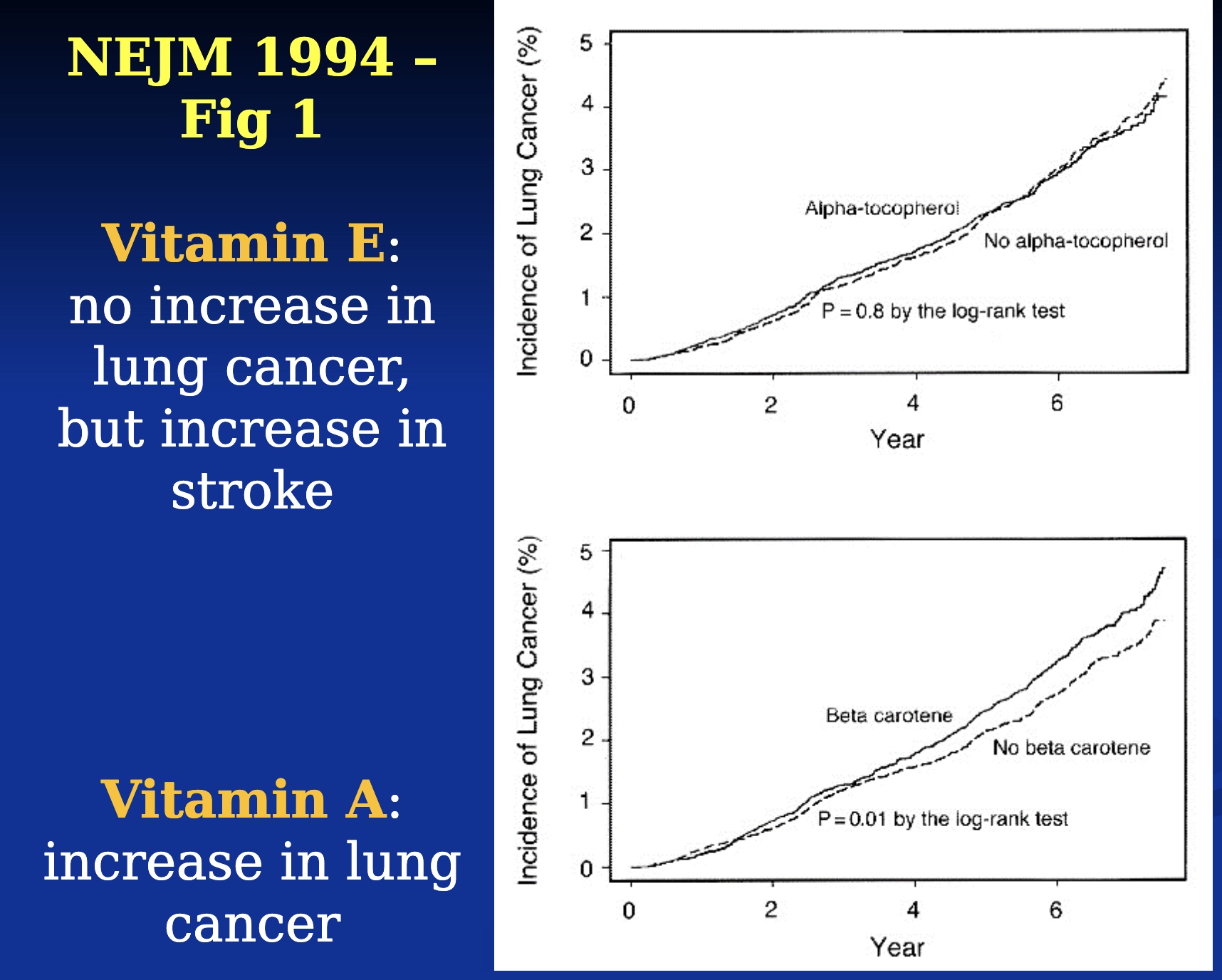
Too much of a good thing? oxidation and cancer
-Vit E associated w/ higher prostate cancer
-mouse study: injected mouse with skin cancer cells in the HPV, and antioxidants or not; mice who got antioxidant injection more likely to have metastasis
-other studies showed same results w/ oxidative stress and pro-oxidant
*antioxidants causing cancer?
too much of a good thing? key takeaways
-don’t label food as “good” or “bad”; think more about what context it’s coming in
-where go for health? (know deficiency)
-cancer cells are unstable, have dif metabolism (do more glycolysis), and generate lots of free radicals (which target immune system to damage the cancer cell???)→ do antioxidants stabilize free radicals?
Fish vs. Fish Oil Supplements (+Inuit people)
-from fish, seems protective/beneficial
Fish Oil Supplements
-10% of the pop
-Not protective for CAD (increase risk of a-fib; bc of oxidation/rancidity?)
-might increase risk of prostate cancer
-JAMA: surprise major publications show no benefit, but this has no effect on supplementation rates
Inuit
-live near the Artic circle area
-they consume a lot of omega 3’s and don’t have much prostate cancer
bc?: have uncommon gene mutations that down regulate omega-3 amount in blood

Case Study: acute hepatitis from common energy drink
-50 yrs old; anorexic and other health problems
-consumed 4-5 energy drinks daily for 3 weeks
-labs showed remarkable results: serum folate and Vit B12 levels exceeded quantifiable limits
*too much of a good think can be a problem!
Supplement videos
-”Doctor Show”: no evidence supplements prevent disease or common cold; influence from 1 guy/chemist (Pauling)
-Comedian: Twinkies regulated, but supplements not regulated the same
-Dr. Oz: “magic weight loss pill”, but later said need proper diet and exercise; more people wrote about supplement bill than Vietnam war
*Key Takeaways: not everybody is deficiency and thus not everybody needs supplements; healthy (not enough evidence saying healthy people should take supplements; personalized medicine) vs unhealthy; if get the RDA no deficiency; what is the optimal Vit D level? (know low Vit D= lower health, such as higher immune problems)
how are supplements regulated by the FDA?
-need to put what’s in the supplement on the label (no lieing)
-not evaluated before heading to the market
-FDA only gets involved and investigates if problems/complaints occur after
3 paragraphs: Regulating the Dietary Supplement Industry- taming of the slew (+RFK Jr)
-for over a decade there has been a call for change, bc so many people use supplements, yet still have no change
*Side note RFK Jr (head of HHS, which FDA is a part of; strong supporter of supplements)
Bioactive Compounds
-biochemical compounds from plants
-things in food, not on nutrition labels
-phytochemicals
Phytochemicals + examples
-Informally known as “nutraceuticals”; compounds active in plants
-Carotenoids: pre-cursor Vit A; antioxidant properties (megadose → cancer?)
lycopene: red compound in tomatoes/ketchup, watermelon
-Bioflavonoids: gives colors to berries/“supper foods”; plants make for themselves for protection (from UV light, pest, etc.)
Anthocyanin
Resveratrol: concentrated in skin of red grapes and wine; “helpful” bc extends life, but only in simple animal models
Phytoestrogen: in soybeans; gives subtle estrogen like effects
-Alkaloids
caffeine: coffee, chocolate, green and black tea
capsaicin: chili peppers; spicy/hot experience and flavor
*greens powder do have antioxidants, but evidence to be “healthy” not strong
*physiology expects these compounds vs artificial flavors/dyes (dif dose antioxidants, should expose self and let them have their effects)
Bioactive Compounds Special Topics
-epigenetic impact of cruciferous vegetables
-statins + grapefruit
-info in food from campus
-epigenetic impact of cruciferous vegetables (*if flower) on cancer prevention: regulated cell activity to minimize chance of cancer
-statins + grapefruit: 50%M and 49%F >65yrs take, lowers LDL chol; does grapefruit phytochemical turn off enzymes in the liver that are involved in detoxification? (would cause statin to circulate in higher levels bc liver can’t break it down)
-evaluating the phytochemicals for anti-cancer effects (NOT the fiber, omega-3’s, etc.)


seek diversity…
-so get a wide range of exposure, even in just 1 group
Diet Analysis of Vitamins and Minerals
-list the items in which you didn’t meet the RDA (more concerned if further away)
*look for green, “okay”, etc.
-What foods might you actually eat to improve these potential deficiencies? (eat what enjoy and have access to)
*oils: low in minerals, but high in Vit E; low fat diet=low in fat soluble vit’s? K+ common to be under RDA for (why on panel)