Meiosis One pager
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Meiosis main goal
Produce gametes for sexual reproduction
Fertlization
Each parent donates one copy of each chromsomes
Diploid simple definition
2 copies of each chromosomes
Haploid simple definition
1 copy of each chromsomes
Germline Stem Cells
GMCs produce gametes that are haploid cells
Live in ovaries or testicles
What unique of meisosis
Includes two rounds of divsion that ultimatley produce 4 haploid cells
First step of meisosis
DNA replication within GSC’s
Germaine stem cells make an exact copy of their DNA
What happens to Germline stem cells after DNA replcication
Undergo two rounds of division
Meisosis I and Meiosis II
Meiosis I goal
to seperate the homologous chromsomes into two new cells
How is Meiosis I different from mitosis
Mitosis separates duplicated chromosomes while Meiosis I separates homologous chromosomes
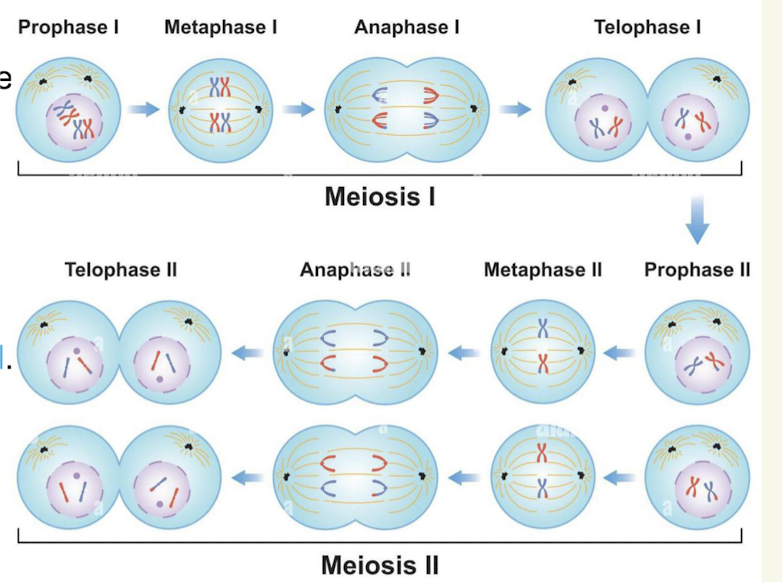
Prophase I
Replicated homogenous chromosomes are aligned together and can swap regions of DNA with eachother (crossing over)
Metaphase I
Homologous chrosmomes are aligned in the center
Anaphase I
Homologous chromsomes are pulled to the opposite ends of the cell
Telophase I
2 new cells are created containing a mixture of homologous chrosomes from each panret
Not genetically identical as parent cell
Crossing over signifinace
Increases genetic diversity
Increases the possible combination of genes inherited from each parent
Meisosis II goal
Resulting cells from Meiosis I divide again splitting up sister chromatids resulting in 4 haploid cells
No S phase
Metaphase II
New combination chromosomes are lined up again
Anaphase II
Sister chromatids (duplicated DNA) are seperated
Telophase II
Left with 4 total cells with 1 copy of 23 chromsomes
Overall image of Meiosis I and II
Both cells that were created in Meiosis I go through Meiosis II
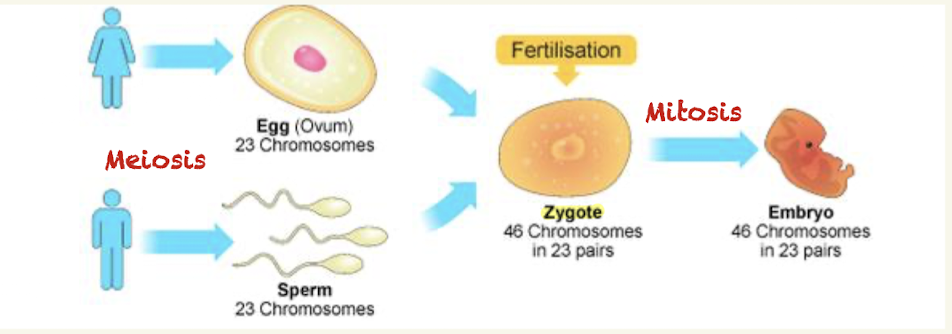
Goal of meiosis
Produce gametes (egg or sperm cells)
Crossing over signifance in reproduction
ensures that resulting zygote has a unique combination of DNA
What happens during fertilization
Egg and sperm combine to produce zygote with 2 copies of each chromsomes
What happens to problems in cell division
Carrys on to next generation
Non-Disjunction
Sister chromatids fail to seperate proeprly in meiosis II which can lead to offspring having an extra copy of a chromosomes (Trisomy 21)
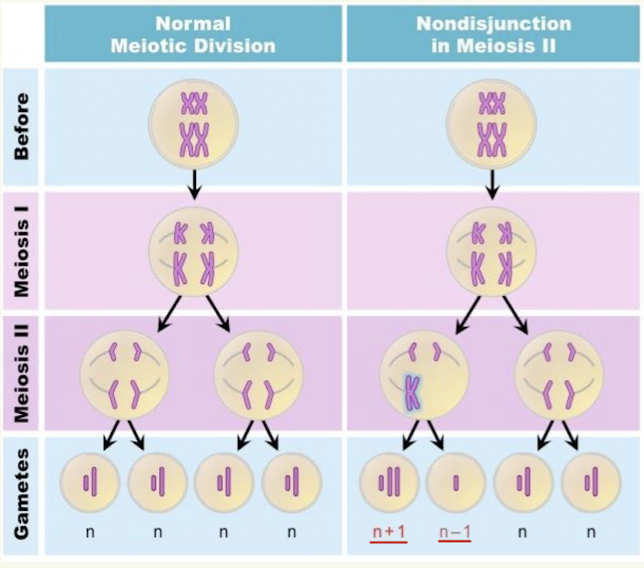
Trisomy 21
Extra #21 chromosomes and is strongest genetic link to down syndrome
Overall Mitosis
4 stages in total
Happens in somatic cells
Purpos is cell proliferation
produces 2 diploid daughter cells
Chromsomes number remains the same
genetic variation dosent change
Meiosis overall
8 stages in total
Happens in germline stem cell
Purpose is sexual reproduction
produces 4 haploids daughter cells
Simularties between Mitosis and Meiosis
Produce new cells
Similar basic steps
Start with a single parent cell