The Behaviourist Approach
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What does the behaviourist approach look at?
Behaviour that can be observed and measured, rather than mental processes
What do behaviourists believe?
All behaviour is learned
A baby is a ‘blank slate’
All basic learning is the same in all species → animals replace humans as experimental subjects
What are the two types of learning?
Classical and operant
What is classical conditioning?
Learning through association
What is operant conditioning?
Behaviour is shaped and maintained by its consequences
What did Pavlov experiment?
To show how dogs could be conditioned to salivate at the sound of a bell when presented with food
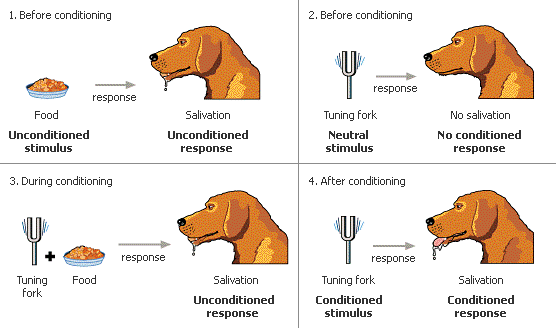
What was the procedure of Pavlov’s experiment?
The dogs heard a bell when presented with food
Gradually they learned to associate the sound of the bell with food
Whenever hearing the sound, they would salivate
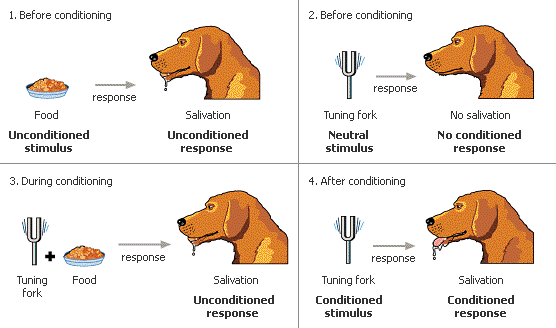
What did Pavlov find in terms of stimuli?
Bell (neutral stimulus) + food (unconditioned stimulus) = conditioned stimulus
Conditioned stimulus elicits conditioned response - salivation
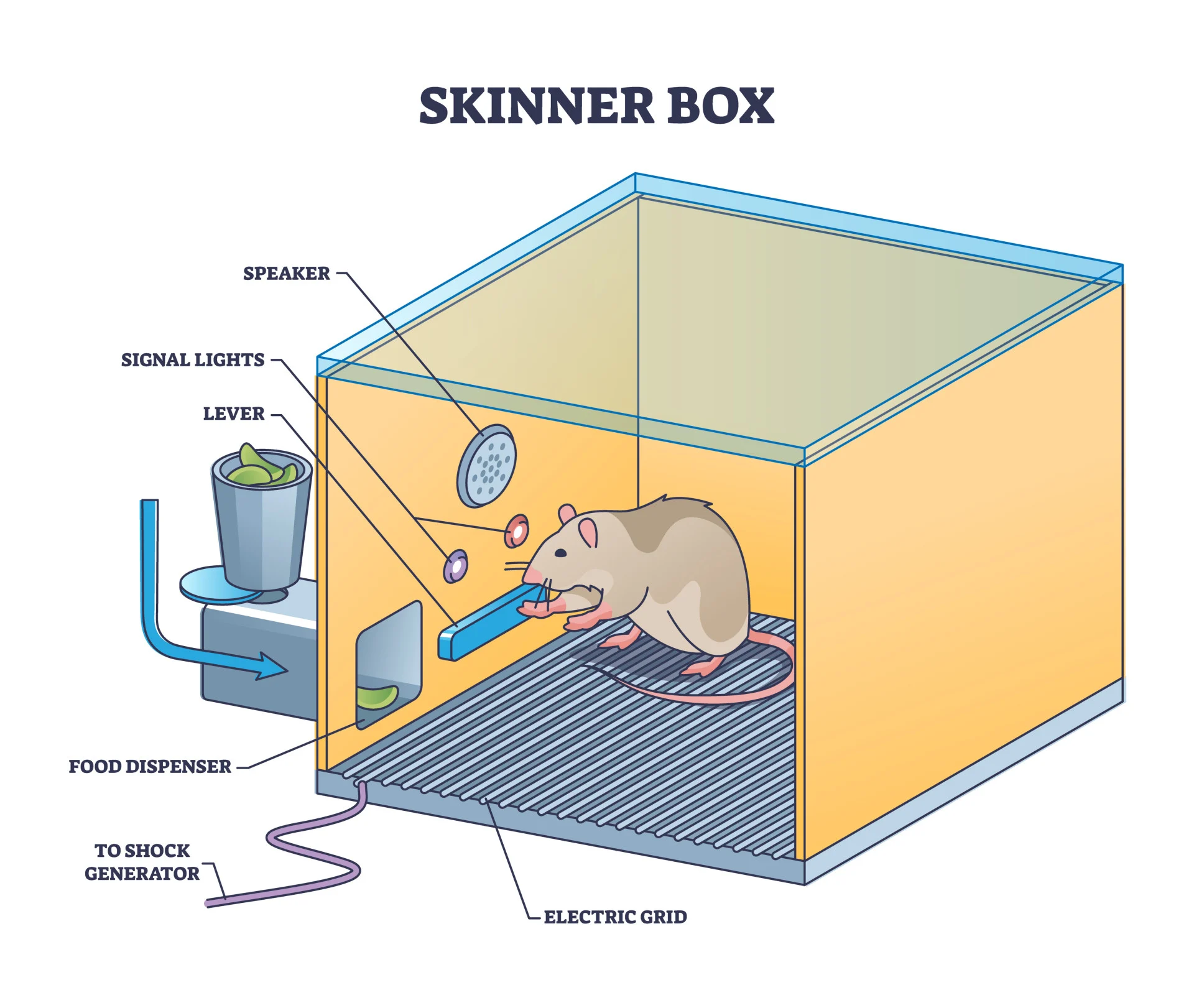
What was Skinner’s procedure?
Rats put in ‘Skinner’s box’
Every time rat activated a lever, it was rewarded with food pellet
Rat would continue behaviour to get more food and avoid electric shock (unpleasant stimulus)
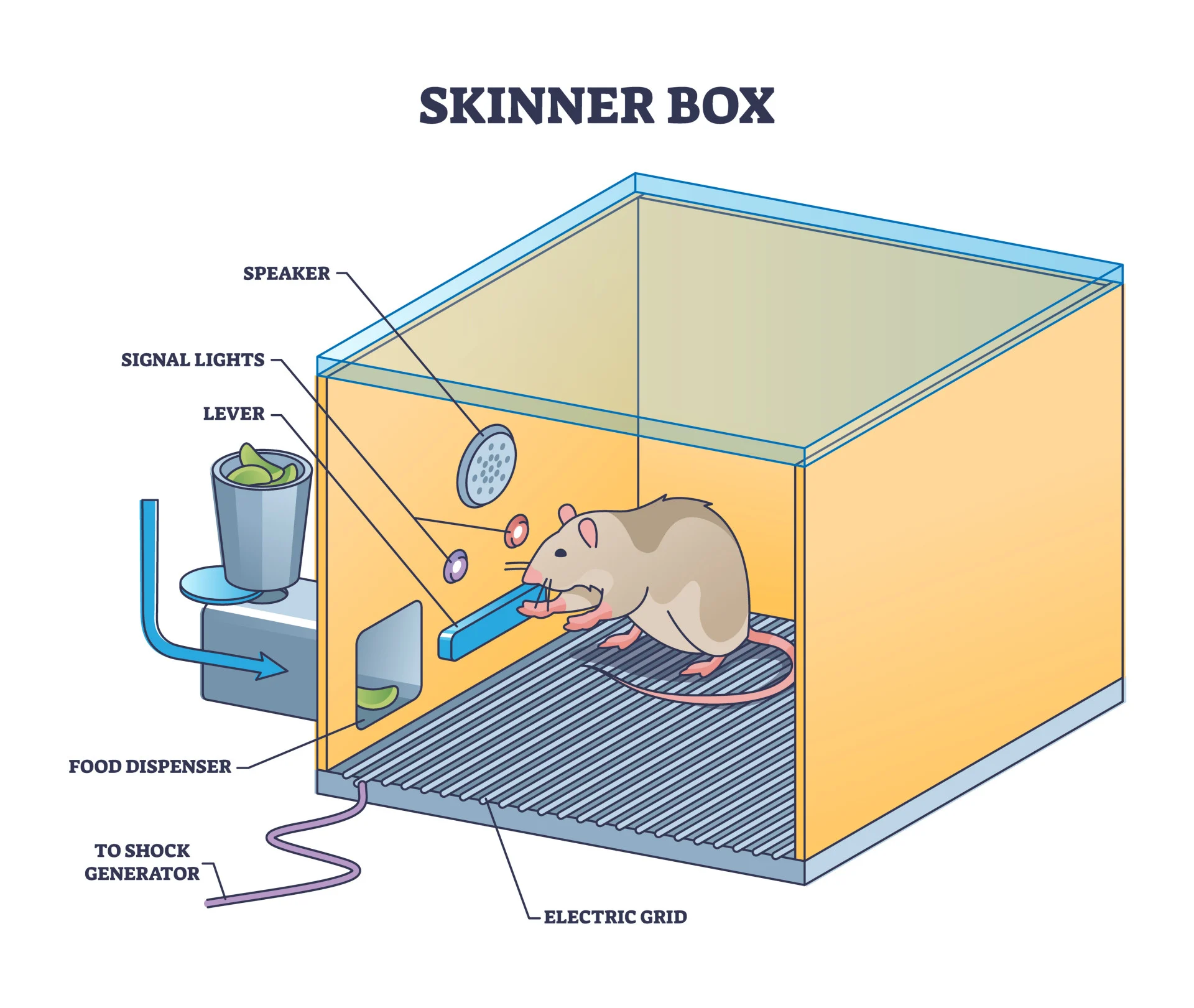
What did Skinner find?
If rat was rewarded every time it activated the lever, conditioned behaviour would die out quickly as rat was satiated
To combat this the food dispenser would only dispense after a random unpredictable number of activations
What are consequences that shape behaviour?
Positive reinforcement
Negative reinforcement
Punishment
What is positive reinforcement?
Receiving reward when certain behaviour is performed, increasing likelihood behaviour will be repeated
What is negative reinforcement?
Avoiding something unpleasant, with the outcome being positive
What is punishment?
Unpleasant consequence of behaviour - decreases likelihood of behaviour repeating
What are the strengths of the behaviourist approach?
Well-controlled research
Real-world application
What are the limitations of the behaviourist approach?
Oversimplifies behaviour
Ignores free will
Ethical issues
How is well-controlled research a strength?
Research is conducted within highly controlled lab settings
No extraneous variables, allowing cause-and-effect relationships to be established
How is real-world application a strength?
Operant conditioning has been the basis of token economy systems used in institutions - appropriate behaviour rewarded with tokens to be exchanged for privileges
How does the behaviourist approach oversimplify behaviour?
Oversimplified the learning process - does not consider the influence of human thought unlike SLT and cognitive approach
How does the behaviourist approach ignore free will?
Skinner believes that our past conditioning history determines everything we do - we do not make our own decisions
What ethical issues arise in the behaviourist approach?
Rats were housed in cramped conditions, kept below natural weight so they were always hungry
Cost-benefit analysis is needed - was animal treatment worth what we learned?