AP bio unit 1
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
gene
unit of heredity
genome
all of an organism’s genetic information
cells
simplest self-reproducing unit that can exist independently
species
species
group of interbreeding organisms that can produce offspring
energetics
the study of energy and how it’s distributed through biological, chemical, or physical processes
dna
the carrier of genetic info for all organisms
biological system
system made up of both biotic and abiotic entities that interact
emergent property
property of a system that the individual parts do not have on their own (eg nest construction is possible if there’s many ants), EMERGES from interactions in a system
scientific inquiry
about the natural world. exploration → investigation → communication
controlled experiment
researcher sets up at least two groups to be tested; the conditions and setup of the groups are identical but the researcher introduces a single change to one group
percent change
(final-initial)/initial * 100
standard error of the mean
s / sqrt(n)
standard deviation
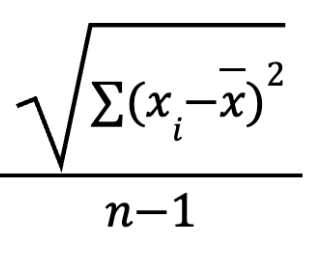
molecules
chemicals made up of two or more atoms
organic molecules
biological molecules that contain carbon
the three subatomic particles
proton (nucleus), neutron (nucleus), electron (electron shells/energy levels)
atomic number
the number of protons
isotopes
atoms of same element but different number of neutrons
ions
electrically charged atoms (cations are positive and anions are negative)
valence electrons
electrons on the outermost energy level
group/family
elements in the same column in the periodic table. column number is also the number of electrons
four most common elements
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen (also phosphorous)
covalent bond
when a pair of electrons are shared between two atoms. double bonds are if there’s two pairs shared. (typically nonmetal + nonmetal)
polar covalent bonds
electrons are not shared equally
electronegativity
atom’s ability to attract electrons (increases left to right, bottom to top on periodic table). in the example of h2o, since oxygen has higher EN and electrons are negative, it gains a partial negative charge
why are electrons shared unequally?
difference in EN
ionic bonds
two ions with opposite electrical charges bonded together (instead of sharing, the difference in EN was so high that one atom stole an electron from the other) (typically metal + nonmetal like NaCl)
why does NaCl dissolve?
the negatively charged ends of water molecules (o) are attracted to the positive sodium, and the positively charged ends of water molecules (h) are attracted to the negative chloride
chemical reaction
process by which atoms or molecules are transformed into different molecules. the things that’re changed are reactants and the molecules formed are the products. their bonding partners are changed.
why carbon so good??
of its six electrons, four r in outermost shell allowing it to form a lot of bonds
carbon can make compounds in many diff shapes (CH4 is a tetrahedron)
carbon atoms can link with other carbons to form chains or rings
four classes of organic molecules
proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and carbohydrates
polymers/monomers
polymers are long chains made up of smaller repeating subunits called monomers.
most of the organic molecules are polymers.
what do proteins do and what are they made up of?
speed up chemical reactions, deliver messages, and provide structural support for the cell.
they’re made of amino acids in peptide bonds.
all amino acids have nitrogen.
what do nucleic acids do and what are they made up of?
nucleic acids encode and transmit genetic information (DNA, RNA) and are polymers made up of nucleotides.
they are informational molecules.
all nucleic acids have nitrogen.
what’s another name for carbohydrates, what are they made of, and what do they do?
sugars.
they are polymers made up of monosaccharides.
they store energy.
what’s different about lipids and what do they do?
they’re hydrophobic, meaning nonpolar and don’t dissolve in water, while the other three are hydrophilic.
they’re also not polymers because they don’t consist of repeating subunits.
they make up the cell membrane, store energy and act as messengers.
hydrogen bond
a polar bond where a slightly pos hydrogen atom bonds with a more electronegative atom. they are weaker than covalent bonds.
cohesion
water molecules sticking to each other
adhesion
water molecules sticking to other things
surface tension
consequence of cohesion, strong bond on surface because surface molecules don’t have molecules surrounding them on every side
structures of ice, water and steam
ice: open crystalline lattices from each water molecule bonded to four others
water: water molecules move around and are closer together; bonds break and form (more dense than ice)
steam: water molecules move around even more rapidly, keeping them far apart and preventing most bonds
specific heat
the amount of energy required to change the temperature of a substance
motion increases as temp increases
why’s water more resistant to temp changes?
a lot of the energy heat provides goes into breaking hydrogen bonds so it takes longer for the temp to make any changes