CHEM 261
1/191
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
192 Terms
Arene
Aromatic ring
Haloalkane
C-X (x= halogen)
Alcohol
C-OH
Ether
C-O-C
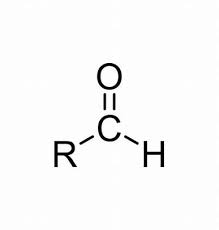
Aldehyde
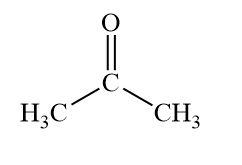
Ketone
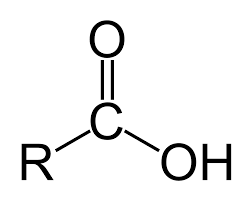
Carboxylic Acid
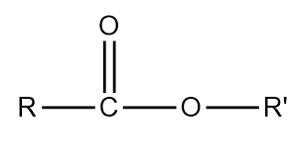
Ester
Acid Halide
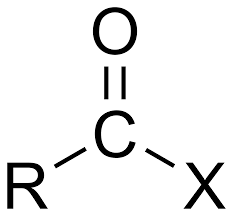
Anhydride
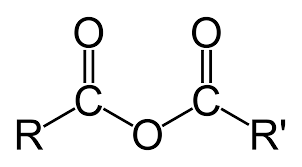
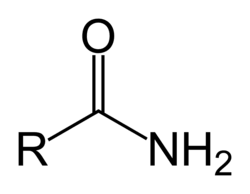
Amide
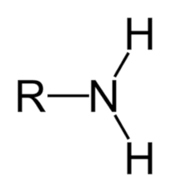
Amine
Primary Carbon
1 substituent on carbon
Secondary Carbon
2 substituent on carbon
Tertiary Carbon
3 substituent on carbon
Quaternary Carbon
4 substituent on carbon
Covalent Bonding
Sharing of electrons between atoms
SP3 Hybridization
tetrahedron, bond angles are 109°
SP2 Hybridization
planar, bond angles are 120° (double bond)
SP Hybridization
linear, bond angles are 180° (triple bond)
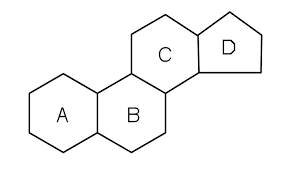
Steroid Molecule
Decane
C10H22
Undecane
C11H24
Dodecane
C12H26
Tridecane
C13H28
Tetradecane
C14H30
Pentadecane
C15H32
Hexadecane
C16H34
Heptadecane
C17H36
Octadecane
C18H38
Nonadecane
C19H40
Eicosane
C20H42
Triacontane
C30H62
Tetracontane
C40H82
Pentacotane
C50H102
Hexacotane
C60H122
Structural isomer
same molecular formula as another molecule but a different arrangement
Stereoisomer
same molecular formula and connectivity of atoms but different three-dimensional arrangement of atoms
Chemistry
Study of matter
Organic Chemistry
Study of compounds containing carbon
Atomic Number
Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom (Z)
Atomic Weight
Mass of protons (p+) and neutron (n) (unit: amu)
Molecular Weight
Mass of atoms in a molecule
Isotopes
same element that contain equal number of protons but different number of neutrons
s-Orbital
Spherical shaped cloud of electrons (electron density)
p-Orbital
Dumbbell-shaped cloud of electrons (Three orientations: placed on the x, y and z-axis)
Isoelectronic
same electronic structure
Ionic Bonding
positive and negative species are bonded to each other
Hybridization
Mixing of atomic orbitals (with the wrong geometry for bonding) to form hybrid orbitals with the correct geometry for bonding
sigma orbital
molecular wave function (orbital) made by linear combination of atomic orbitals having an s component
enthalpy
bond energy
pi orbital
molecular wave function (orbital) made by linear combination of two p atomic orbitals
electronegativity
desire (attraction) of an atom for electrons (negative charge)
London forces
intermolecular attraction due to temporary dipoles
Lewis acid
A substance that can accept a pair of electrons
Methyl Group
CH3
Methylene Group
CH2
Methine Group
CH
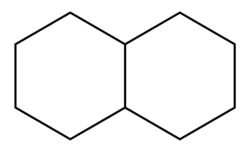
Decalin
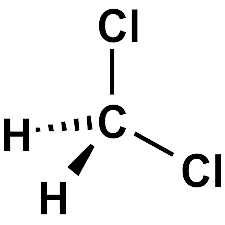
Methylene Chloride
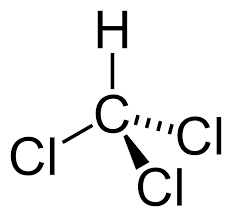
Chloroform
CHCl3
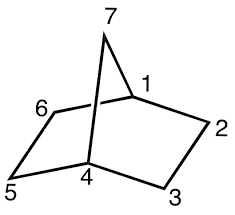
Norbornane
Chiral
has a non-superimposable mirror image
Achiral
not chiral, has a superimposable mirror image
Diastereomers
all stereoisomers that are not enantiomers
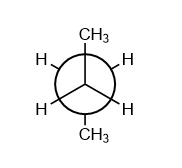
Anti Staggered
favoured, lowest energy
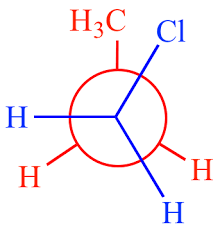
Staggered Gauche
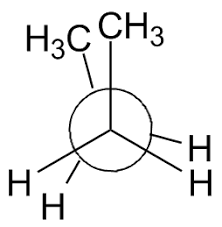
Syn Eclipsed
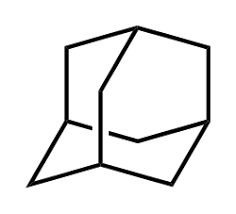
Adamantane
Diatomic molecules
F, Cl, Br, I
Hemolytic
One electron goes to each atom once the bond in broken. e.g. Free radical halogenation of alkanes
Heterolytic
(polar reaction): The electron pair goes to one of the atoms once the bond is broken. e.g. Addition reactions of alkenes; elimination reactions
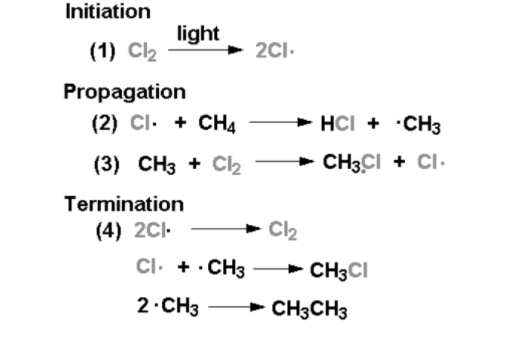
Mechanism of Halogenation
Hammonds Postulate
For an exothermic reaction, the transition state is closer in energy to the reactants and thus resembles them structurally. Conversely, for an endothermic reaction, the transition state is closer to the products in energy and has a structure that resembles them
Resolution
separation of enantiomers
Enantiomers
molecules that are stereoisomers and are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. Opposite stereochemistry at every chiral center.
Fischer Projection
A method of drawing chemical structures, where the horizontal components are coming towards you and the vertical ones are going back.
Meso Compounds
stereogenic centers but contain a plane of symmetry and are achiral
SN1
rate depends on 1 concentration
SN2
The rate is dependent on the concentration of the nucleophile and the electrophile (2 concentrations)
Stereospecific
stereochemistry of the starting material determines the stereochemistry of the product.
Concerted
The bonds of the starting material break at the same time as the product bonds form.
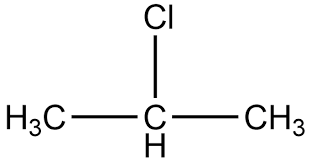
isopropyl chloride
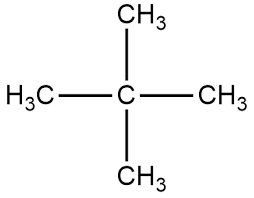
neopentane
Vinyl
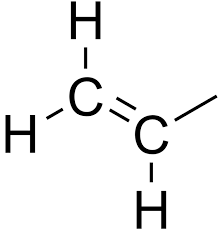
Allyl
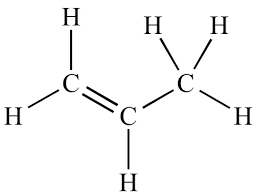
Phenyl
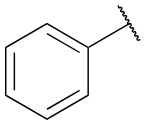
Benzene
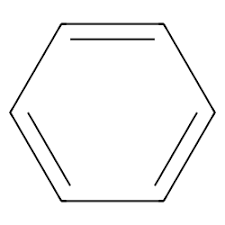
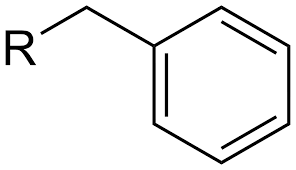
Benzyl
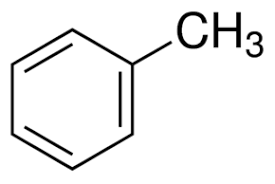
Toluene
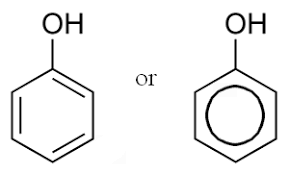
Phenol
R, Rectus
stereocenter that is right-handed, clockwise
S, Sinister
stereocenter that is left-handed, counterclockwis
Olefin
Another name for alkene
acetylene
Another name for alkyne
E
Entegegen - Opposite
Z
Zusammen - Together
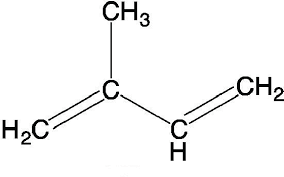
Isoprene
Terpenes
Natural products containing alkenes (units of C5)
Markovnikov’s Rule
In an addition reaction, the positive end of an A–B system (e.g. I–Cl) adds to the least substituted end of the double bond to make the more stable carbocation.