Bio 2 Exam 2 Chapter 29, 30, 31 - Fungi, Plant Diversity, etc
5.0(6)Studied by 147 people
Card Sorting
1/72
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For Niedzwicki's Biology 2 Lecture Class - answers outline questions and provides deeper understanding questions. If there are terms from the outline that you do not see on here, it is because we have not learned it in lecture yet.
Last updated 6:07 AM on 2/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
1
New cards
How do Fungi Make their Living?
they are heterotrophic, needs nutrition from complex substances
2
New cards
Fungi how many cells?
contains both single cells (yeast), and multicellular (molds)
3
New cards
hyphae
branching filaments that make up mycelium of a fungus, penetrates organisms and begins to eat
4
New cards
Chitin
cell wall for strength and support
5
New cards
mycelium
body of fungus that digests food
6
New cards
septet
divides cells in hyphae
7
New cards
Coenocytic Hypha
undivided cells in hyphae
8
New cards
Describe the life cycle of a fungi, when is it haploid, when diploid …and when is it heterokaryotic
haploid first and during spore production until plasogamy. Heterokaryotic until reaching karyogamy. Diploid in zygotic phase until meiosis
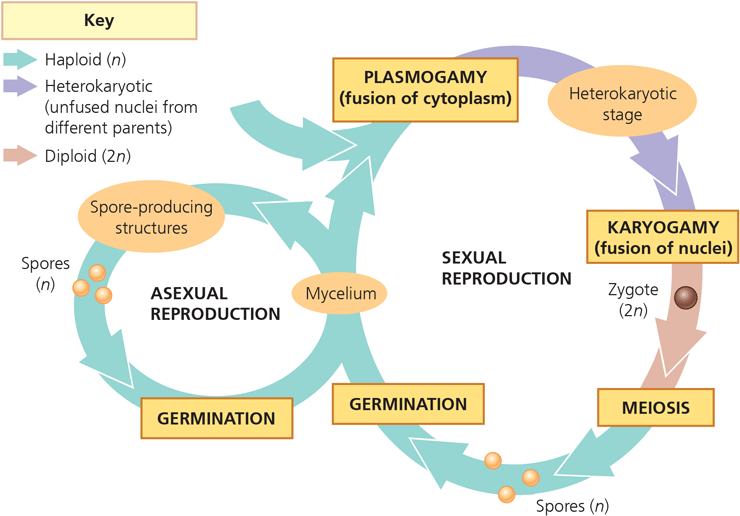
9
New cards
plasmogamy
fusion of cytoplasm in sexual reproduction of fungi
10
New cards
Karyogamy
fusion of nuclei in sexual reproduction of fungi
11
New cards
zygote
fertilized egg; a diploid produced by union of haploids during fertilization
12
New cards
fertilization
union of haploid gametes to form diploid zygote
13
New cards
meiosis
cell division of sex cells
14
New cards
spore
a haploid cell that produces mycelium after germination (can be sexual or asexual)
15
New cards
Why do fungi have “mating types”
asexual for division and spore production, sexual for plasogamy, karyogamy, and mushroom reproduction
16
New cards
heterokaryotic
every cell has two haploid nuclei that are not the same
17
New cards
What are the five groups of fungi?
Chytrids, Zygomycetes, Glomeromycetes, Ascomycetes, Basiodiomycetes
18
New cards
Chytrids Lifestyle & Example
water mold, frogs and other aquatic amphibians are impacted
19
New cards
Zygomycetes Lifestyle & Example
bread mold, gain penicillin from this type of fungi (drugs)
20
New cards
Glomeromycetes Lifestyle & Example
can withstand harsh conditions, soil born symbiotic bacteria
21
New cards
Ascomycetes Lifestyle & Example
multicellular, morel fungi
22
New cards
Basidiomycetes Lifestyle & Example
club fungi, mushrooms, plant fungi
23
New cards
Why are fungi good for life?
eat them, drugs creation
24
New cards
fungal mutualism example
one example is coral and algae
25
New cards
What are the Ancestors of Plants
ancestral green algae, land plants, vascular plants, extant seed plants
26
New cards
what are three traits ancestors of plants share with plants?
being autotrophs, having cellulose cell walls, similar photosynthetic processes (two photosystems), and other molecular and cellular similarities
27
New cards
What Are the Shared Derived Characters that plants share? (five)
alternation of generations, sporangia, gametangia, apical meristem, multicellular embryo that is dependent on parent plant
28
New cards
The Evolution of plants is a story of increasing adaptation to life on _____________.
a terrestrial environment
29
New cards
Bryophytes are defined by what they lack…. what is this?
lack true vascular tissues (depend on water) for reproduction, so they have a small size
30
New cards
Three major groups of bryophytes are?
liverworts, mosses, hornworts
31
New cards
Describe the life cycles of bryophytes, with special attention to the terms Sporophyte and Gametophyte, what does this demonstrate?
begins haploid, gametophyte produces gametes, fertilization produces diploid zygote, then sporophyte takes place to produce spores - demonstrates alternation of two stages (generations). gametophyte dominant
32
New cards
What is the role of water in reproduction for bryophytes
sexual reproduction; allows sperm to swim to egg
33
New cards
gametophyte description (4)
produced by meiosis, both male and female, green part of moss, produces gametes
34
New cards
sporophyte description (3)
produced at fertilization, hair-like part of moss, produces spores
35
New cards
alternation of generations meaning
plants alternate between two different life cycles: gametophyte and sporophyte
36
New cards
Liverwort “war of the sexes”
male and female liverworts sometimes lived in seperate areas, some mixed. Males were faster, females were tougher - proved that liverworts could asexually reproduce
37
New cards
What are the four groups of Fern like plants?
Club Mosses, Ferns, Horsetails, Whisk Ferns
38
New cards
Ferns are define by what they have (2)___________ and what they lack ___________ (1)
vascular tissue and roots, seeds (use spores instead)
39
New cards
What is the significance of “vascular tissue”
has xylem and phloem. Xylem - conducts water and mineral nutrients (raw materials), Phloem - transports sugars, amino acids (cell products)
40
New cards
value/significance of bryophytes
colonize sterile soil, absorb water and nutrients, and contribute to new soils for ecosystems to begin on
41
New cards
Describe the life cycle of the fern, with special attention to the terms Sporophyte and Gametophyte.
begins haploid, gametophyte produces gametes, fertilization produces diploid zygote, then sporophyte takes place to produce spores - demonstrates alternation of two stages (generations). sporophyte dominant
42
New cards
What is the role of water in reproduction for ferns?
sexual reproduction, allows sperm to swim to eggs
43
New cards
Heterosporous
producing different kinds of spores (for different sexes)
44
New cards
homosporous
producing same kind of spores
45
New cards
What are the advantages of seed plants and Pollen?
help against drought, UV, and helps them fertilize without water
46
New cards
define mega sporangia
ovules produce *megaspores* that give rise to female gametophytes
47
New cards
define microsporangia
pollen produce *microspores* that give rise to male gametophytes
48
New cards
What are the traits gymnosperms have that previous plant groups lack, what plant characteristics do they lack?
They produce seeds that are naked (no protective ovary wall), and they lack pistils and stamens
49
New cards
what is a seed?
embryonic plant surrounded by protective outer covering with some food
50
New cards
Describe the life cycle of gymnosperms, with attention to sporophyte and gametophyte.
diploid until meiosis, micro/megasporangia produce haploid pollen, mega/micro gametophyte processes lead to fertilization. sporophyte dominant
51
New cards
What are the four Major groups of gymnosperms?
Cycadophyta, Gnetophyta, Ginkgophyta, coniferophyta
52
New cards
Which gymnosperm has the most diversity?
coniferophyta
53
New cards
What is an Angiosperm?
a plant that produces seeds within an enclosure- a fruiting plant
54
New cards
What Shared Derived traits define Angiosperm?
endosperm present within seeds, production of fruit that contains seeds
55
New cards
Describe the angiosperm life cycle, with attention to sporophyte and gametophyte.
diploid until meiosis, micro/megasporangia produce haploid pollen, mega/micro gametophyte processes lead to fertilization. sporophyte dominant
56
New cards
What is double fertilization?
two sperm cells unite with two cells in female gametophyte (embryo) to form the zygote and endosperm
57
New cards
Besides some “primitive groups” what are the two major groups of angiosperms
monocots and dicots
58
New cards
What are the six differences between monocots and dicots?
monocots: one cotyledon, parallel veins, vascular tissue scattered, no main root, pollen grain with one opening, floral organs in multiples of three
Dicots: two cotyledon, netlike veins, vascular tissue in a ring, main root present, pollen grain with three openings, floral organs in multiples of four or five
Dicots: two cotyledon, netlike veins, vascular tissue in a ring, main root present, pollen grain with three openings, floral organs in multiples of four or five
59
New cards
What are some basic plant types that fit in each group (monocots and dicots)?
monocots: bananas, wheat, rice, orchids, corn, palm trees.
Dicots: maple and oak trees, cacti, wild flowers, tomatoes, peppers, potatoes.
Dicots: maple and oak trees, cacti, wild flowers, tomatoes, peppers, potatoes.
60
New cards
Describe the role of Symbiosis with pollinators in angiosperm diversity.
Also provide an example
Also provide an example
mutualistic relationship, as pollinators help spread seeds and spores, while the plant provides the pollinators with a food reward.
Ex: Hummingbirds with wild flowers
Ex: Hummingbirds with wild flowers
61
New cards
Significance of Seed Plants for our lives
economic food supply, can create a variety of drugs
62
New cards
Define what a botanist means by roots, Shoots and Leaves.
plants can be categorized into being roots or shoots
63
New cards
Three tissue types:
dermal, vascular, ground
64
New cards
Dermal tissue function
outer tissue layer, covers and protects the plant
65
New cards
ground tissue function
middle tissue layer, basic metabolic activities, stores nutrients
66
New cards
parenchyma function
thin walled, metabolism function
67
New cards
collenchyma function
thick, flexibility, support
68
New cards
sclerenchyma function
secondary rigid cell wall (due to lignin), cannot lengthen
69
New cards
vascular tissue function
transport nutrients (water, sugar, etc) to different parts of the plant
70
New cards
xylem (vascular tissue) function
tracheas, long and thin, short/wide vessel
71
New cards
Phloem function
sieve tube, conducting sugar, companion cell to support tube
72
New cards
root hair (dermal tissue) function
absorbs water and nutrients (projection of a single cell)
73
New cards
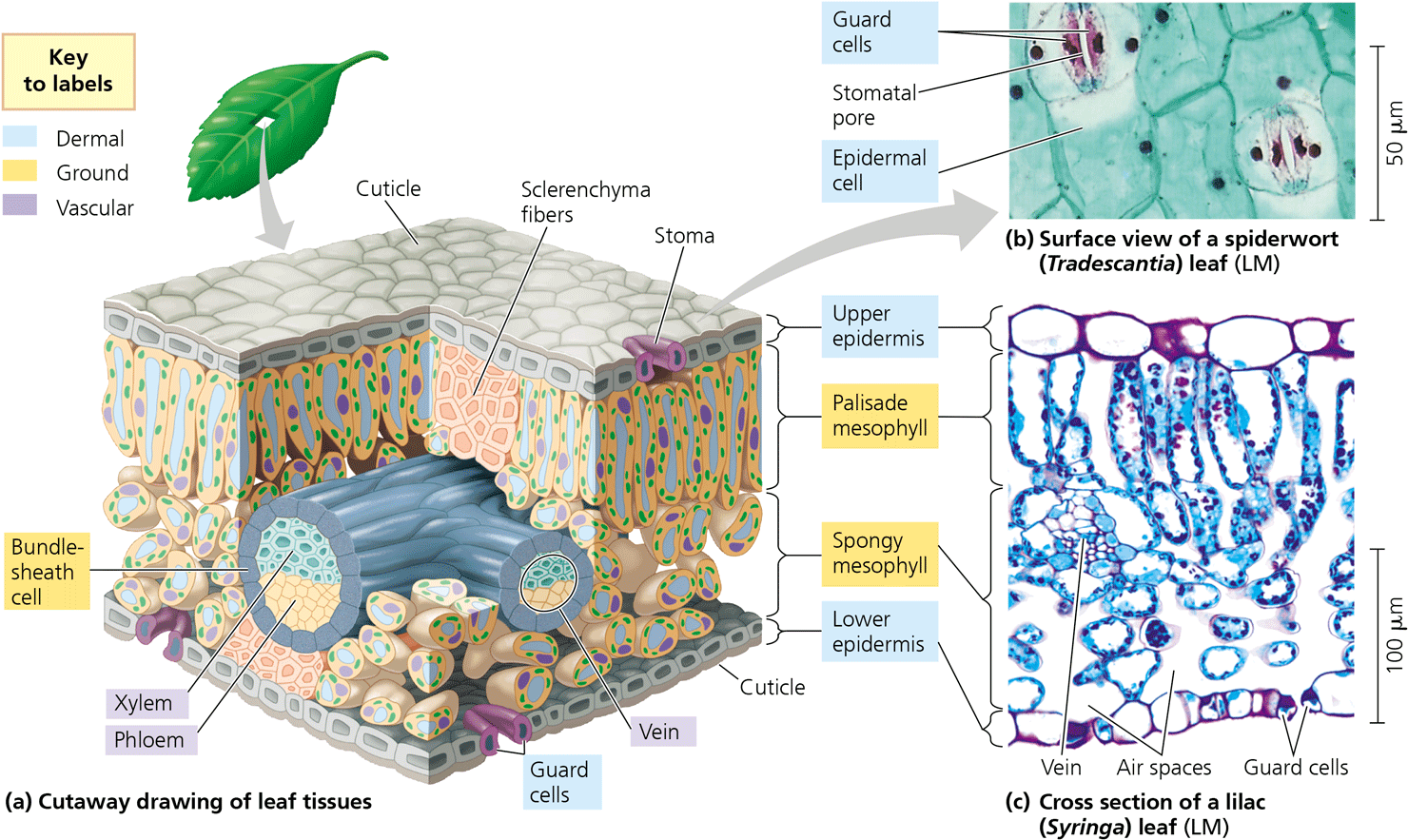
Describe the leaf and how it’s structure facilitates Photosynthesis. (35.18) GOOD ESSAY!
stomata (outside portion) allows exchange of CO2 and O2 in leaves, mesophyll contain chloroplast cells that help capture light, vascular tissue help spread nutrients from photosynthesis throughout plant