Obstructive pulmonary diseases - emphysema
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Types of Obstructive pulmonary diseases (4)
Emphysema
Chronic bronchitis
Asthma
Bronchiectasis
Emphysema Distinct features (4)
Chronic injury (Smoking)
Alveolar wall destruction
Overinflation
Functional obstruction
Chronic bronchitis Distinct features (4)
Chronic injury (Smoking)
Productive cough
Airway inflammation
Physical obstruction
Asthma distinct features (2)
Bronchial hyperresponsiveness triggered by allergens, infections, etc.
Reversible obstruction
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is composed of (2)
Emphysema
Chronic bronchitis
A key feature of obstructive pulmonary diseases is:
Decrease in FEV1/ FVC ratio
A key feature of restrictive pulmonary diseases is:
Near normal FEV1/ FVC ratio
Restrictive summary (4)
Reduced lung expansion
FVC Reduced
FEV1 Reduced
FEV1/ FVC Normal
Obstructive summary
Expiratory obstruction
FVC Normal or slightly reduced
FEV1 Reduced
FEV1/ FVC Reduced
Emphysema is characterized by
Characterized by permanent enlargement of the air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles, accompanied by destruction of their walls without significant fibrosis.
Normal “Maintenance” of Alveolar Wall and ECM (4)
Inhaled particulate material gets into alveoli
Alveolar macrophage phagocytose the particles and secrete cytokines, ROS, and proteases (Elastase)
Proteases can damage the alveolar wall and ECM
Body produces antiproteases like Alpha 1 antitrypsin to keep damage in check
Pathogenesis of emphysema (2)
Smoking, other toxins
Congenital Alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency
Consequences of emphysema
ECM degradation (elastin and collagen!) and alveolar wall destruction
Reduces surface area or gas exchange
Consequences of loss of elastin and collagen with emphysema During inhalation (2)
Relatively easy to breathe in
Airway is open
Consequences of loss of elastin and collagen with emphysema During exhalation (4)
harder to breathe out
Loss of elastin around alveoli → Reduces elastic recoil
The reduced radial traction causes the airways to collapse
Air in alveoli become trapped
The 2 major patterns of emphysema (2)(2)
Centriacinar emphysema
Respiratory bronchiole affected
Panacinar emphysema
Entire acinus affected
Centriacinar emphysema
Acinus involvement
Main cause
Lobe involvement
Typical age of presentation
Main symptom
Prevalence
Acinus involvement - Respiratory bronchiole
Main cause - Cigarette smoking
Lobe involvement - More common upper lobes
Typical age of presentation - 6th and 7th decade
Main symptom - Dyspnea
Prevalence - More
Panacinar emphysema
Acinus involvement
Main cause
Lobe involvement
Typical age of presentation
Main symptom
Prevalence
Acinus involvement - Entire acinus
Main cause - Alpha 1 - antitrypsin deficiency
Lobe involvement - More common lower lobes
Typical age of presentation - 4th and 5th decade
Main symptom - Dyspnea
Prevalence - Less
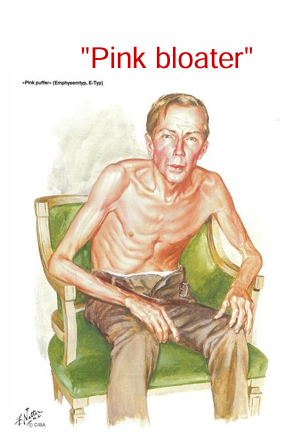
emphysema Dyspnea cause
Decreased gas exchange/obstruction
emphysema Hyperinflation of lung (barrel chest) cause
Destruction of elastin, collagen → Inspiration is easy Expiration is difficult
emphysema Weight loss cause
Decreased gas exchange/obstruction
The clinical features of emphysema (2)
Ventilation perfusion mismatch → Hypoxemia → Increases ventilation rate → Helps maintain blood oxygenation at rest
Until late in the disease when they become hypoxemic and cyanotic
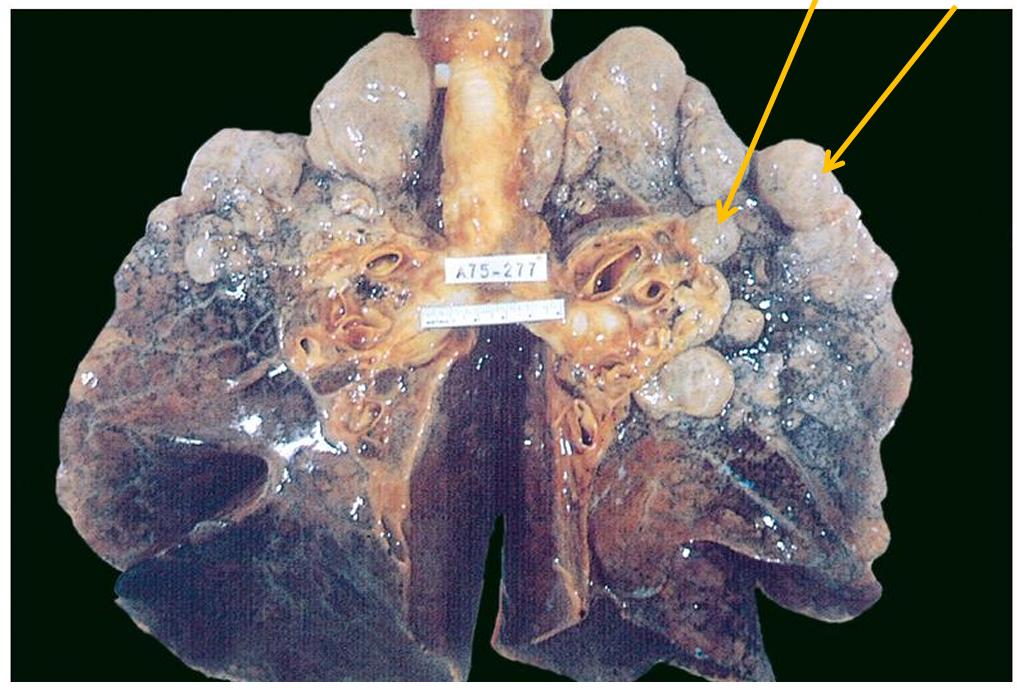
Gross appearance of lungs with Centriacinar emphysema
Dilated airspaces with loss of lung tissue → Voluminous lungs
Name
Bullous emphysema