6.1.1 Aromatic compounds
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
arenes
aromatic compounds that contain a benzene ring as part of their structure
Benzene
simplest arene with a planar ring structure
ring of six carbon atoms each bonded to one hydrogen atom
molecular formula of benzene
C6H6
2 primary models for benzenes structure
Kekulé model
delocalised model
Kekulé model
ring of C atoms with alternating single and double bonds betwwen them
later adapted model to say benzene molecule was constantly flipping between 2 forms(isomers) by switching over the double and single bonds

delocalised model
ring of electrons that are delocalised
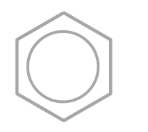
how is the delocailed model formed
each carbon atom uses 3 of its 4 electrons to bond with other 2 carbon atoms and a hydrogen atom
Each carbon contributes one electron from its 2p orbital to a π-bonding system.
The p-orbitals overlap side-by-side around the ring, forming a delocalised system of 6 π-electrons.
This creates an electron density above and below the plane of carbon atoms.
The electrons are not fixed between specific atom pairs, but rather delocalised over the whole ring.
This delocalisation leads to equal C-C bond lengths between the carbon atoms and enhanced stability of the aromatic ring.
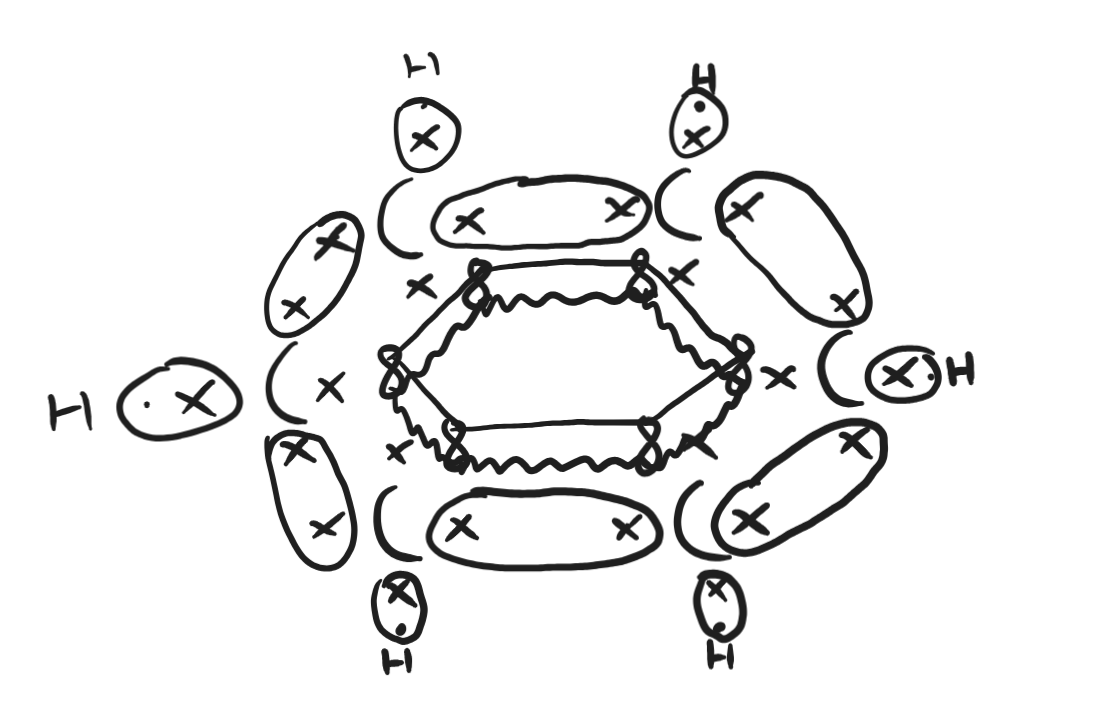
how many π and sigma bonds in benzene
12 sigma bonds
3π bonds delocalised
phyical properties of benzene
colourless liquid at room temperature
Bp comparable with that of hexanes as its flat hexagonal molecules pack together very well in the solid state therefore harder to seperaye and melt
non polar compound and dissolves with other hydrocarbons and non polar solvents
evidence of delocalised model
equal c-c bond lengths
enthalpy of hydrogenation was less negative than expectedmore stable
resistant to electrophilic addition reactions - doesnt decoulirise bromine water
similarities and differences between bonding in kekule model and delocalised model of benzene
Similarities: overlap of p orbitals, π bond above and below atoms
Difference:kekule has localised π electrons but deocalised has π ring system
how to name substituted benzene
the names of the substituents precede the word "benzene". Examples include chlorobenzene, nitrobenzene, and methylbenzene.
how to name phenyl derivatives
These compounds are named as derivatives of the phenyl group (C6H5-). Examples include phenol and phenylamine.
how to name when multiple substituents on benzene ring
the numbering begins from the substituent that gives the molecule its suffix (for example, -OH in phenol).
If all substituents are identical, numbering starts from any position and proceeds to give the lowest possible numbers.
difference in reactivity between alkenes and benzene
Alkenes are known for their readiness to undergo addition reactions with electrophiles, such as bromine, by breaking the π-bond in the C=C double bond.
Addition reactions in benzene are difficult due to the stability provided by its delocalised π-electron system.
Instead, benzene is more inclined to participate in substitution reactions, which preserve the aromatic ring's integrity.
what is the reason for reactivity difference between benzene and alkene
In benzene, the delocalised π-system across the ring has insufficient electron density to polarise the Br-Br bond, making addition reactions difficult. Heat and a catalyst are required to initiate the substitution reaction.
In ethene, the localised π-system around the C=C double bond has sufficient electron density to polarise the Br-Br bond, allowing addition reactions to occur readily at room temperature without the need for a catalyst
how to number benzene ring
if more than one functional group attached the carbons need to be numberd
if all functional groups are the same make it be the smallest number
if the functional groups are different start from whichever functional group gives the molecule its suffix and continues counting round whichever way gives the smallest numbers
why does benzene not undergo electrophic addition
would involve breaking up stable delocalised ring of electrons
what mechanism does benzene undergo
electrophilic substitution
electrophilic substitution reaction of benzene
involves a hydrogen atom being replaced by an electrophile
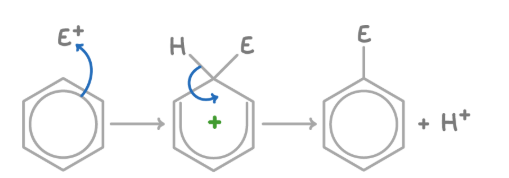
2 stages of electrophilic substitution
addition of electrophile
loss of hydrogen
Halogenation of benzene
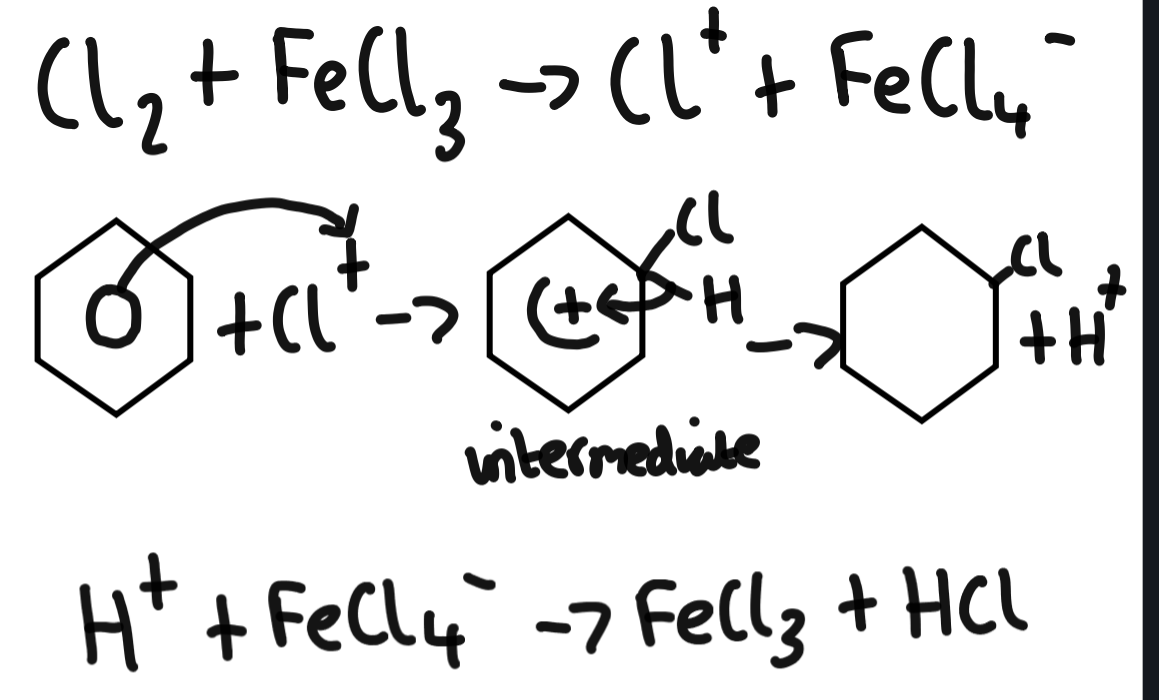
nitration of benzene conditions
50C
nitration of benzene mechanism
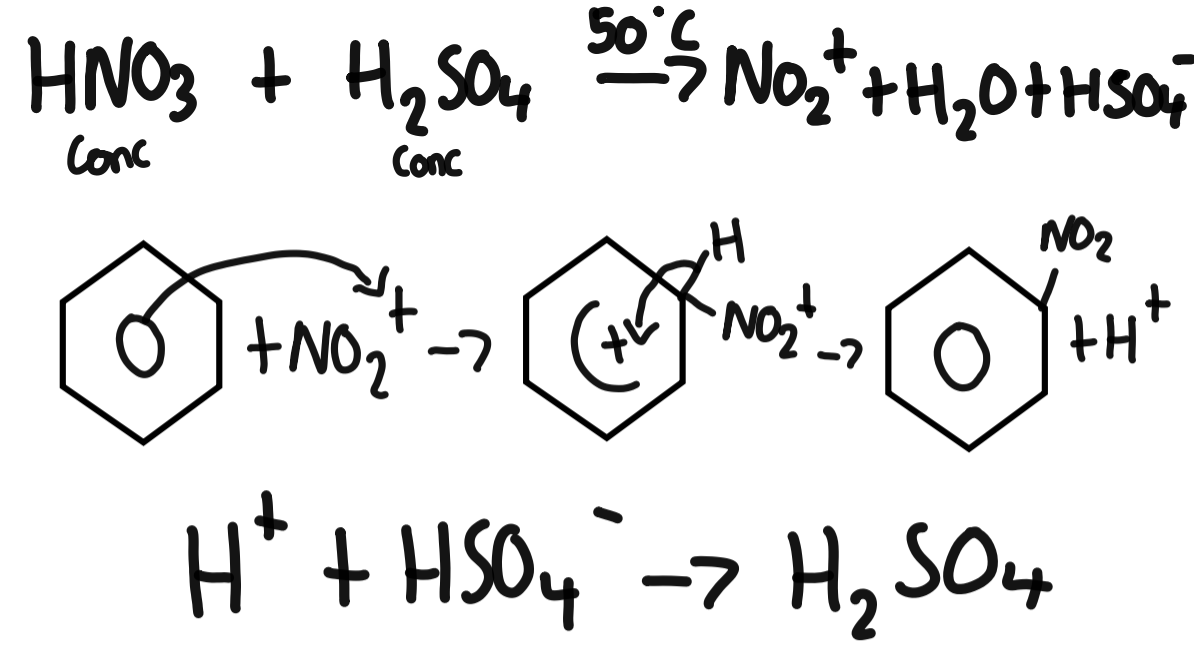
friedel crafts reactions
are really useful for forming C–C bonds in organic synthesis. They are carried out by refluxing benzene with a halogen carrier and either a halogenoalkane or an acyl chloride.
2 types of friedel crafts reactions
Friedel-Crafts alkylation puts any alkyl group onto a benzene ring using a haloalkane and a halogen carrier.
Friedel-Crafts acylation substitutes an acyl group for an H atom on benzene using an acyl chloride and halogen carrier. This produces phenylketones or benzaldehyde
how can something become a stronger electrophile
using a catalyst caled a halogen carrier e.g. AlCl3
alkylation of benzene using chloromethane
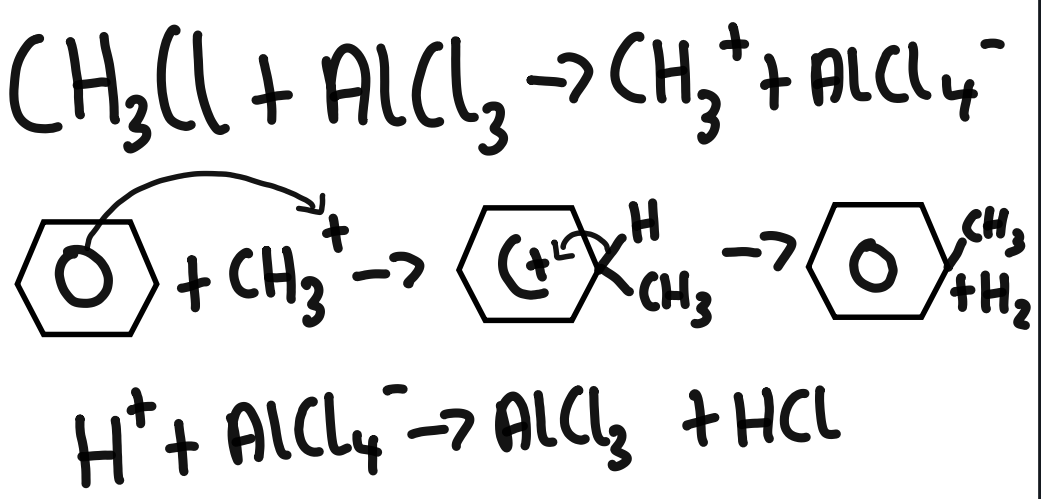
acylation of benzene using ethanoyl chloride and AlCl3
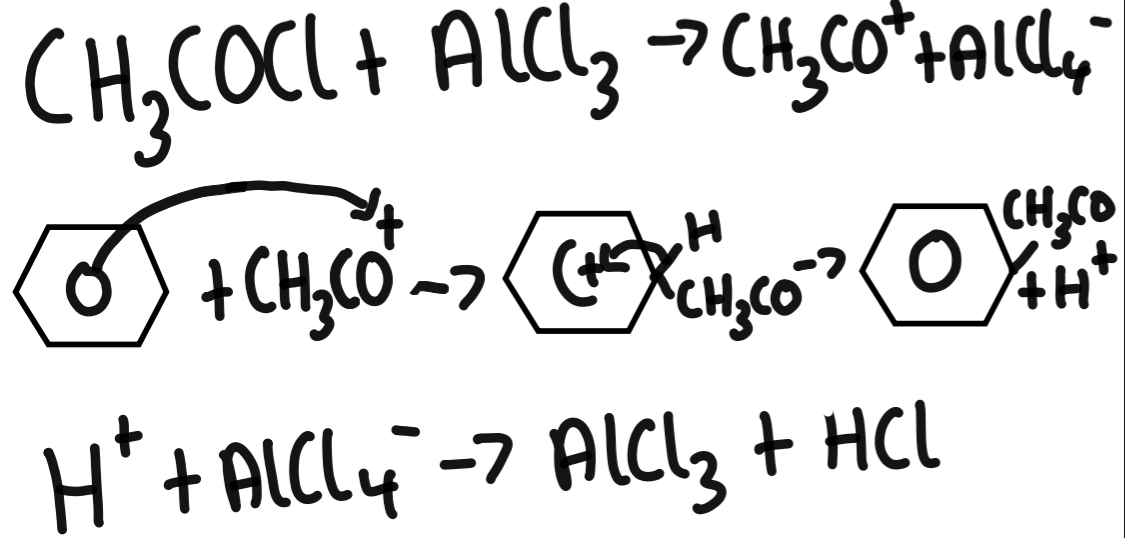
why is benzene resistant to bromination
delocalised electron density of the π system in benzene compared with the localised electron density of the πbond in alkenes
the delocalised model makes benzene relatively stable and the negative charge spread out
phenol
organic compound containing a benzene ring with an OH alcohol group
aromatic alcohol
type of acid phenol
weak
can weak acids react with weak alkalis
no
phenol formula
C6H5OH
phenol skeletal formula
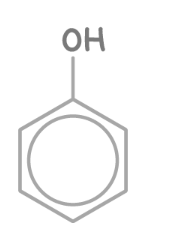
how to name phenol
add suffix -phenol instead of -ol carbon with oh is always carbon 1
phenol reaction with sodium hydroxide solution
neutralisation reaction to form sodium phenoxide and water
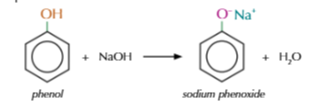
phenol reaction with sodium carbonate
doesnt react as sodium carbonate is not a strong enough base ans so cant remove the hydrogen ion from the oxygen atom
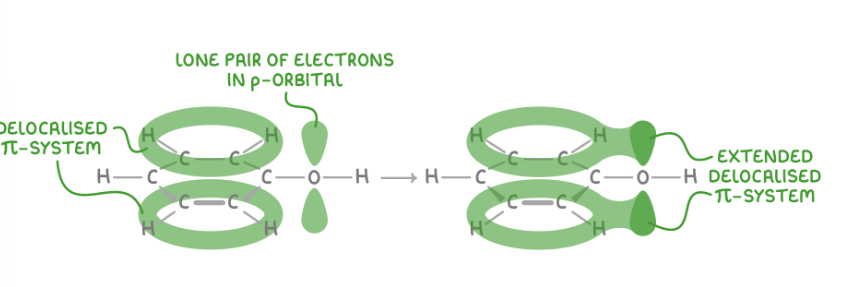
phenol strucute
8π electron
4π bonding regiosn
can phenol react with bromine water
yes
why is phenol more reacitve than benzene
the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen atom is partially delocalised into the π system making henol more susceptible to electrophilic attack
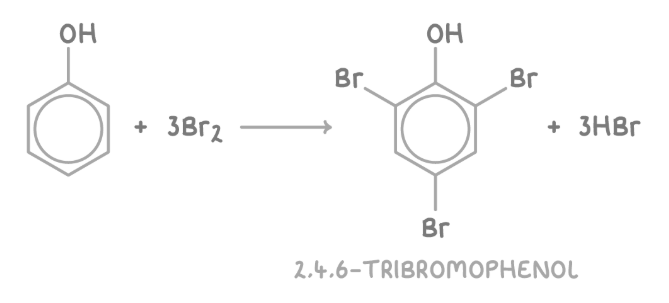
reaction of phenol with bromine water
Phenol causes bromine water to decolourise as substitution occurs at the 2- and 4- positions, producing 2,4,6-tribromophenol as a white precipitate.
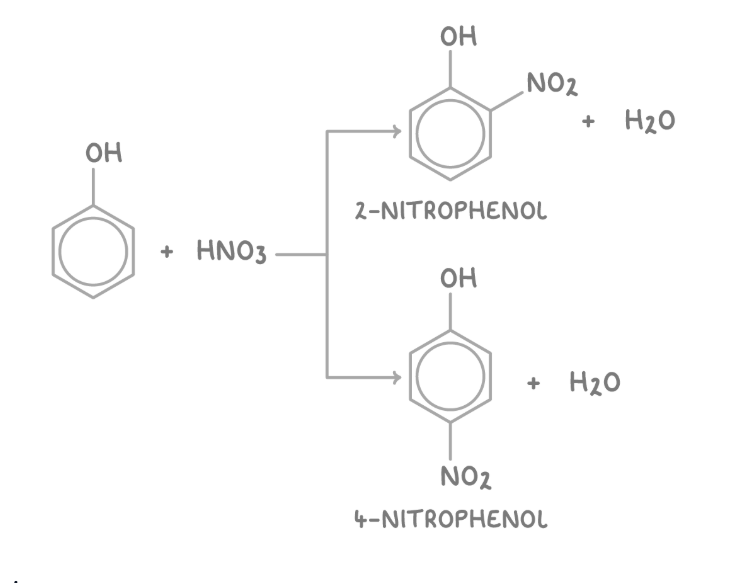
reaction of phenol with dilute nitric acid
Direct nitration of phenol at room temerature yields two main isomers, 2-nitrophenol and 4-nitrophenol, at the 2- and 4- positions respectively.
directing effect
refers to the influence of a functional group on the position where a second substituent is added to a benzene ring during an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction
electron donating groups
contribute electrons into the delocalised π-system of the ring, increasing its electron density.
they enhance the electron density at carbons 2-, 4-, and 6-, making these positions more likely to react with electrophiles.
Thus, electron donating groups activate positions 2-, 4-, and 6- for electrophilic attack.
electron withdrawing groups
do not have orbitals that overlap with the ring's π-system. Instead, due to their electronegativity, they pull electron density away from the ring, particularly from positions 2-, 4-, and 6-.
This action directs electrophilic substitution towards the 3- and 5- positions, which retain relatively more electron density.
Thus the -NO2 group activates positions 3- and 5- for electrophilic attack.
examles of electron withdrawing groups
NO2 Cl
examples of electron donating groups
OH NH2 CH3