exam 3 - inorganic chemistry
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Labile
Fast ligand substitution
Inert
Slow ligand substitution
If we have strong ligand field stabilization then the complex is kinetically…?
Inert
If configuration places electrons in orbitals that are anti bonding (eg set) or weak bonding, the substitution is…..
Labile
smaller radius —> stronger M-L bonds —> slower substitution meaning….
Inert
larger radius —> weaker bonds so….
Faster (liable) substitution
Ionic radius increases going down a period, meaning the larger, the radius, the…..
Faster the reaction more labile
Stronger ligand filed (stronger bonding) tends to make substitution….
Slower (inert)
Kinetic means what compared to thermodynamics ?
How fast vs how stable
remember a complex can be thermodynamically stable but kinetically Labile (or vice versa)
For an Oh complex, if substitution requires breaking a string M-L bond first this is what type of RXN and how quickly does it happen?
This is Dissociative rxn and this happens SLOW
If there is a ready path for ligand to associate or interchange, this is what type of RXN and how quickly does it happen?
Associative RXN and it happens FAST
Metal high charge/small radius = ?
Strong bonds
Low charge/larger radius = ?
Weaker bonds
Thermodynamics correlates to what equation
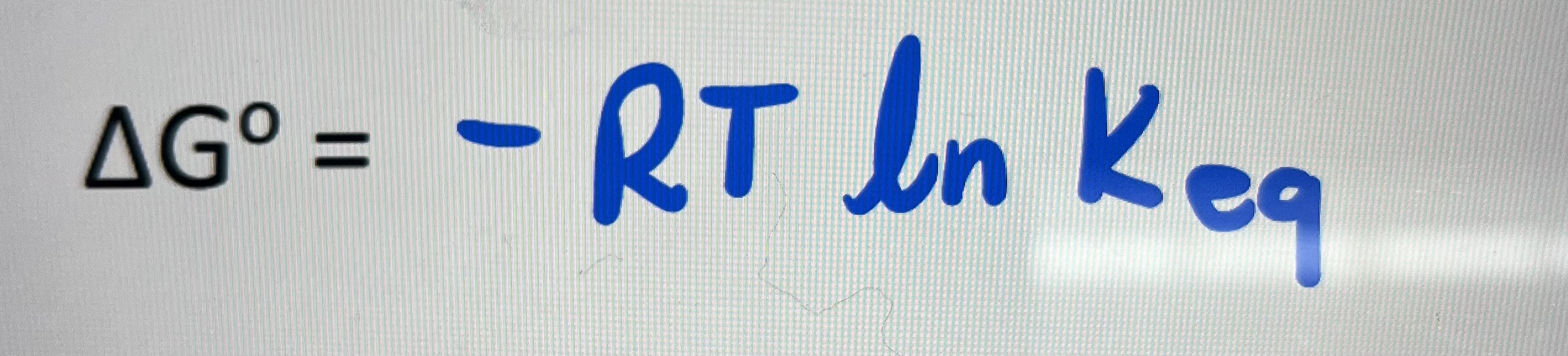
Kinetics relates to what equation
Ea= activation energy
A= frequency factor
R=gas constant
T=tempatute (K)
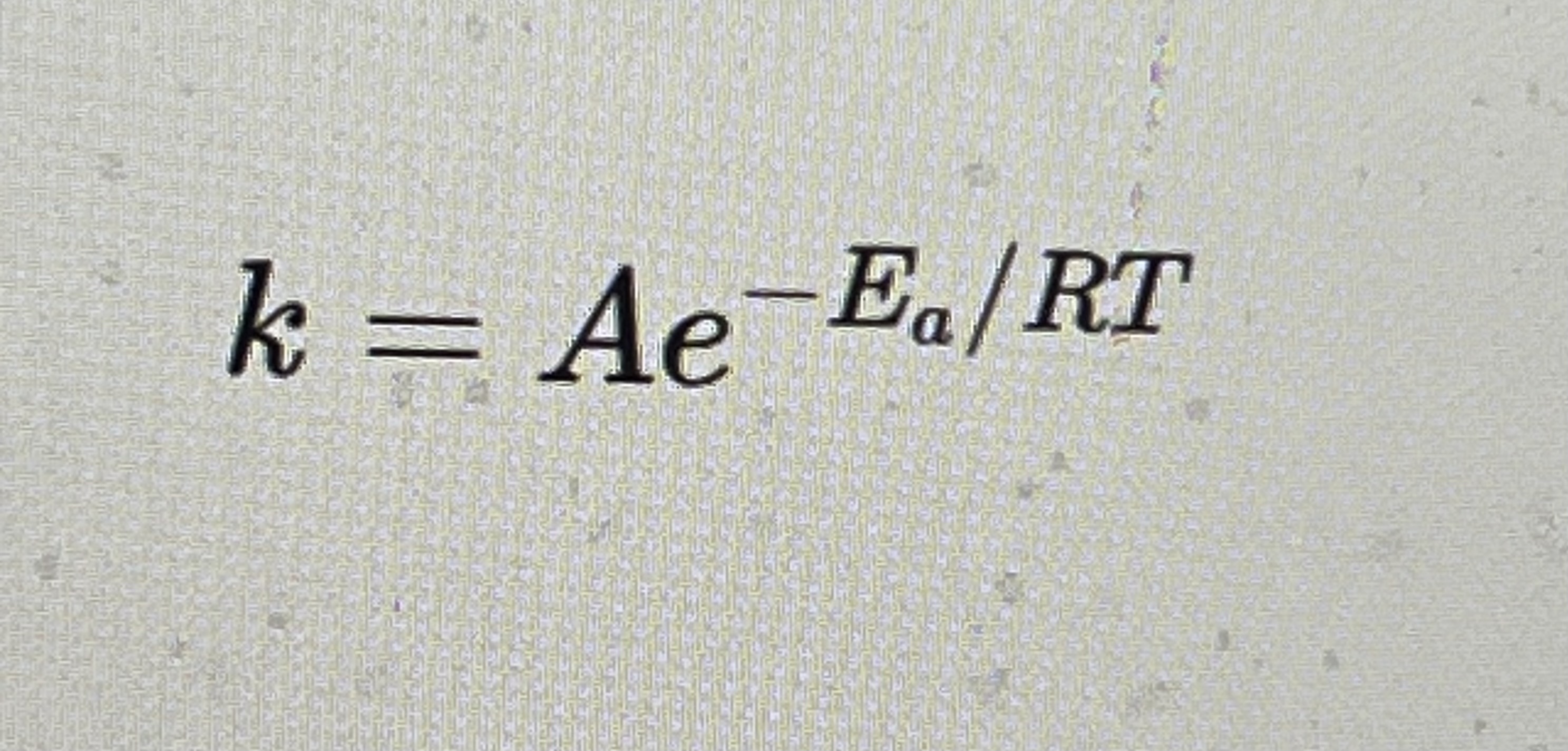
Higher Ea= ?
Slower reaction (smaller k)
Lower Ea=?
Faster reaction (larger k)
Labile complex’s have low or high Ea
Low Ea (their bonds are easier to break)
Inert complex’s have high or low Ea
High Ea, (their M-L bonds are very strong).
Half life = t(1/2)
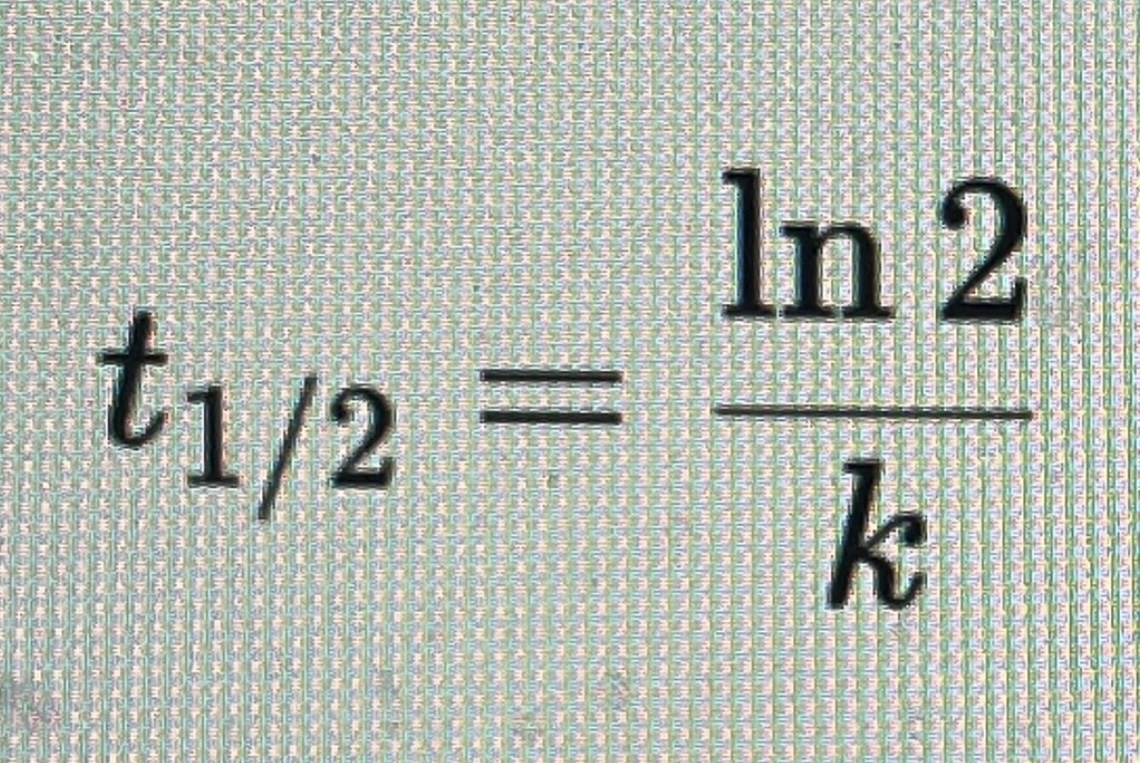
Lifetime - average time before substitution
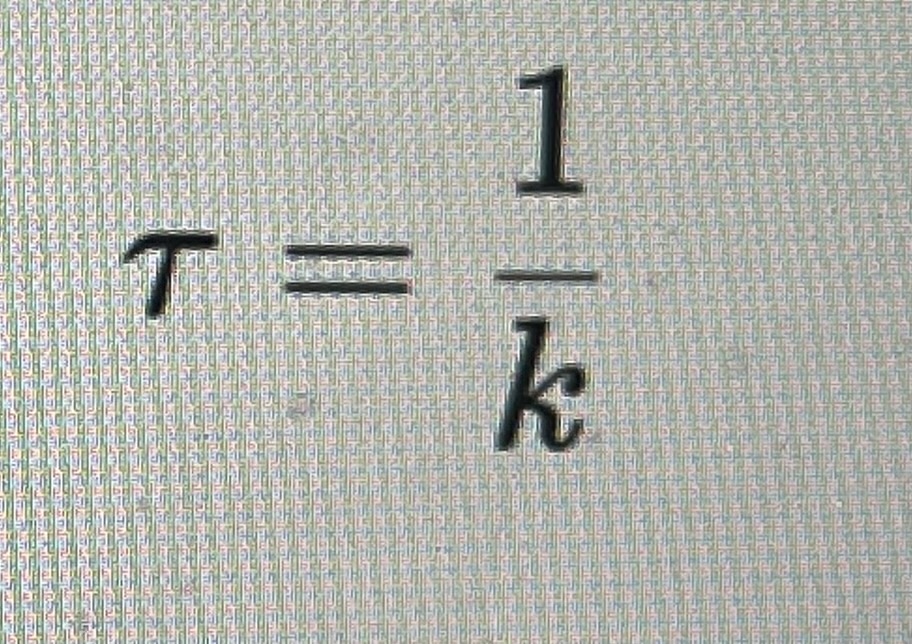
If we have a full lower energy orbital (t2g has all 6 e-) and an empty eg orbital (d6!) what does that mean in terms of reactivity
Indicates inert, and not reactive (or reacts very slowly)!
If we have a half -full lower energy orbital (t2g has all 3 e-) and an empty eg orbital (d3!) what does that mean in terms of reactivity
Inert, and not reactive (or reacts very slowly)
If we have a full lower energy orbital (t2g has all 6 e-) and eg has 1 electron (d7!) what does that mean in terms of reactivity
Think Jahn Teller distortion (d7 and high field). Labile and highly reactive
4d metal are ….
All LOW SPIN
Dissociate mechanism means what about bonds and donor atoms
Bond-breaking, RDS
Weaker donor —> more labile
Stronger donor —> more inert
Associate mechanisms mean what for bonds and donor atoms
Bond-making RDS
stronger donor —> faster (more labile)
Weaker donor —> slower (more inert)
D orbitals are gerade or ungerade with respect to inversion
D orbitals are GERADE
( s and d =gerade)
(p and f =ungerade)
No change in multiplicity and symmetry changed means
Allowed!
Change in multiplicity and no change in symmetry
Forbidden
high oxidation state and pi system mean
LMCT —> high molar absorbtivity