Immunology and Serology Unit 1 (Chapters 1-4)
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
96 Terms
Immunology
the scientific study of the immune response; the study of molecules, cells, organs, and systems responsible for the recognition and disposal of nonself materials and how they work, or can be manipulated. All aspects of body defense, such as antigens and antibodies, allergy, and hypersensitivity are included.
Primary function of the immune system
DIFFERENTIATE between SELF and NON-SELF (foreign); DESTROY that which is non-self
Lymphatic system
site of most immune activity

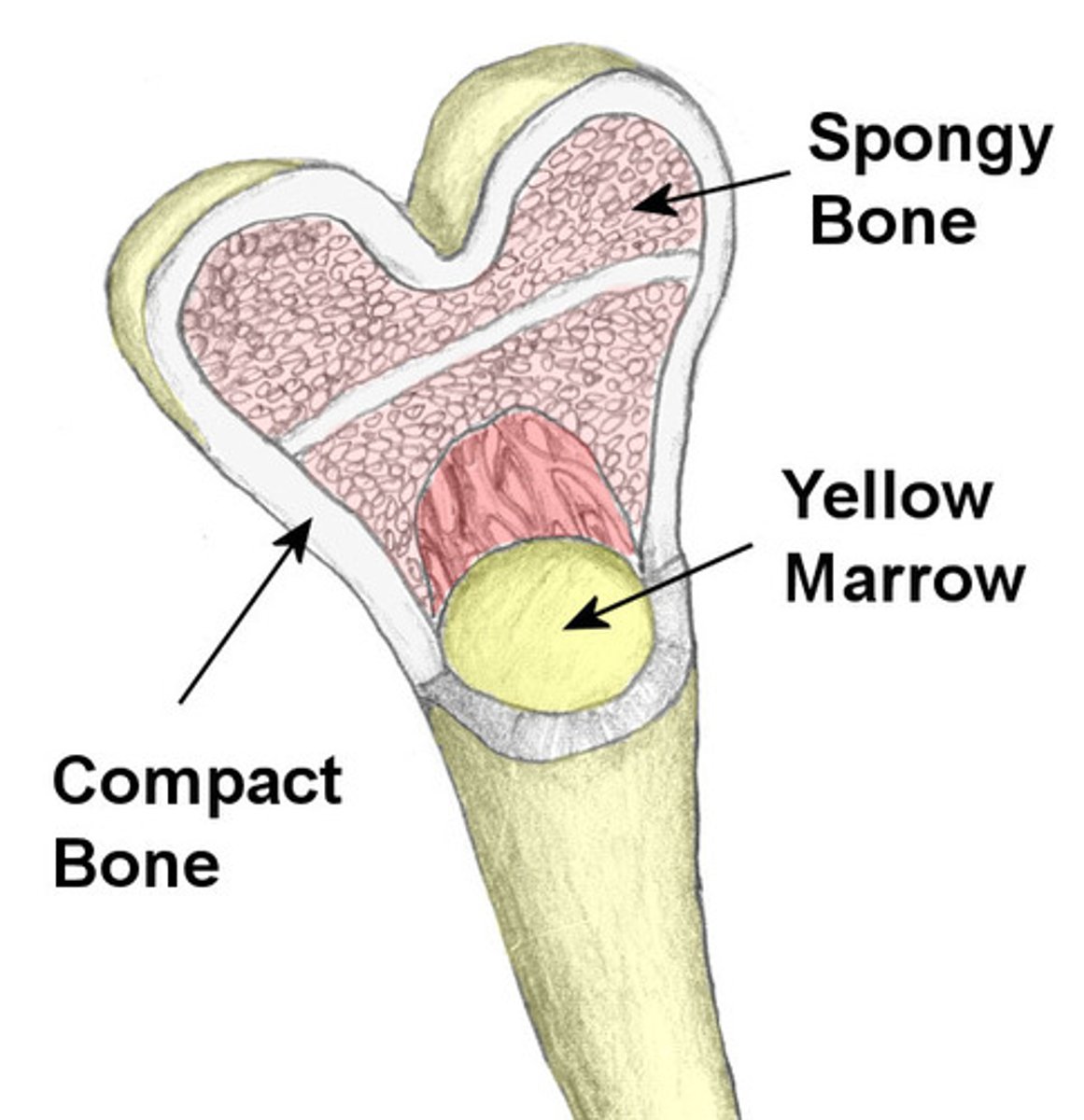
Bone marrow
cells originate here; they may mature and differentiate in other organs (lymphatic system, liver and thymus)
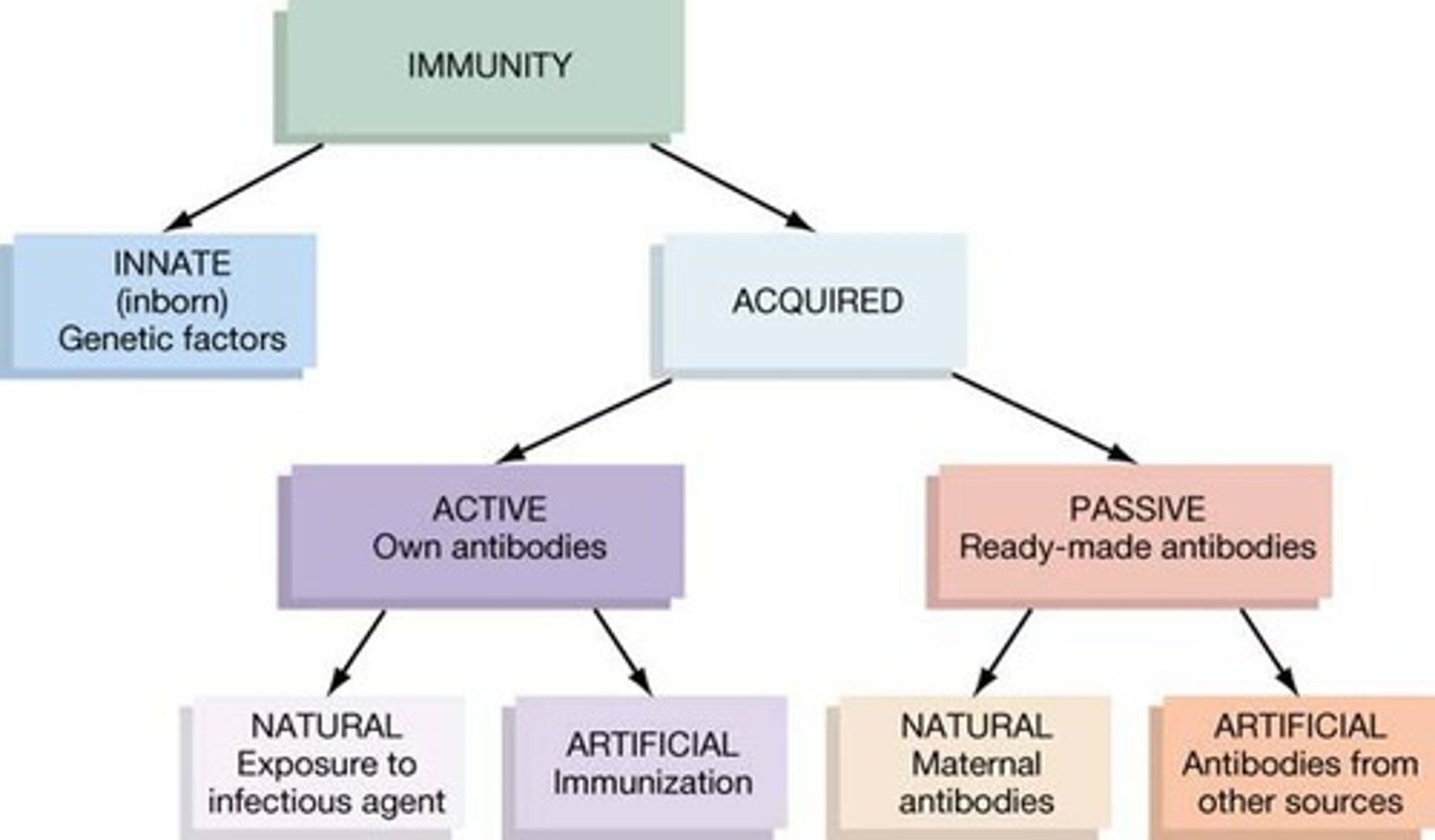
Immune system can be classified as...
non-specific vs. specific
natural vs. acquired
active vs. passive
cellular vs. humoral
innate vs. adaptive
Immune response includes the body's response to...
invading organisms, chemical irritants, malignant cells, and senescent cells
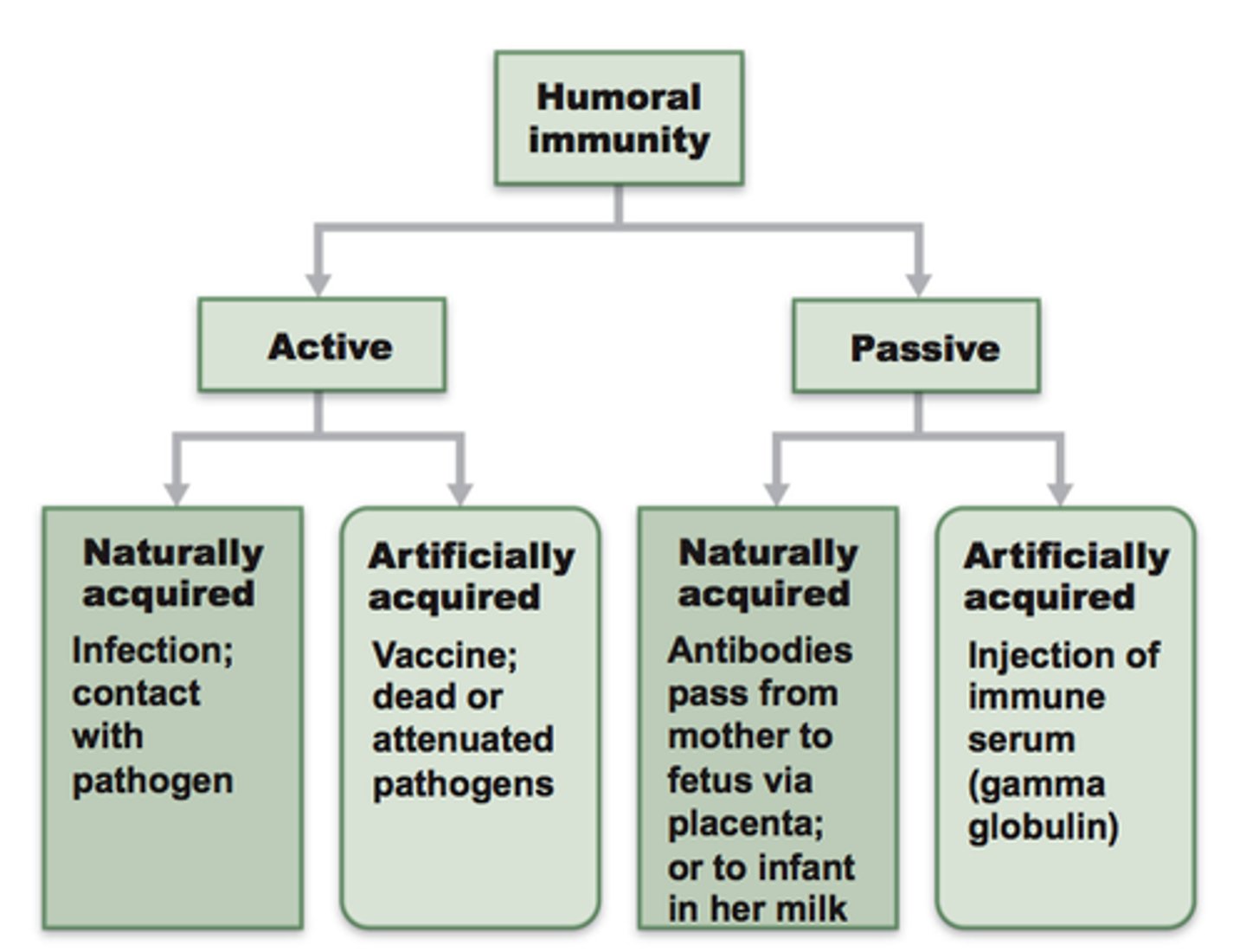
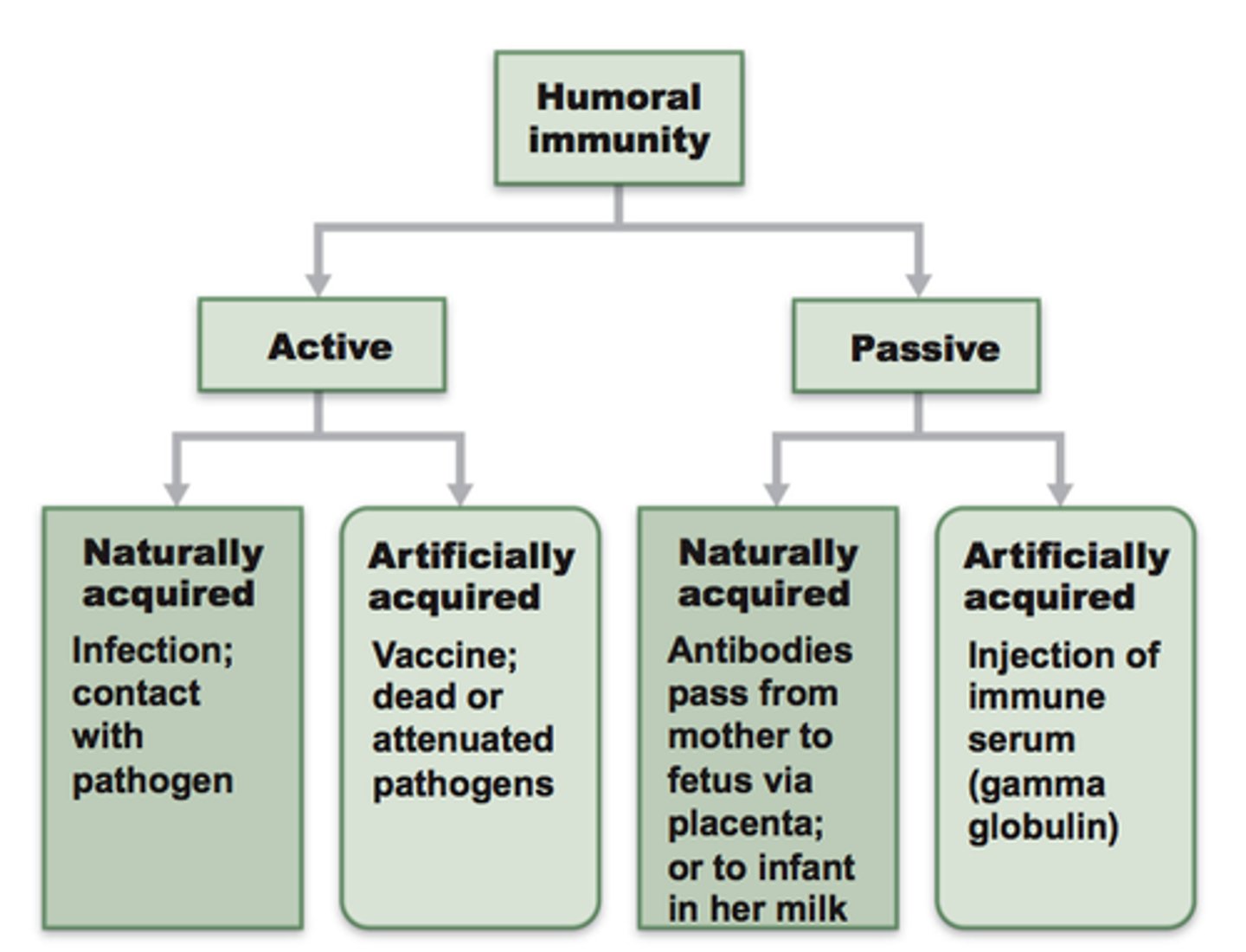
passive immunity
the short-term immunity that results from the introduction of antibodies from another person or animal (transfer in vivo or colostrum; inclusion of serum/plasma)
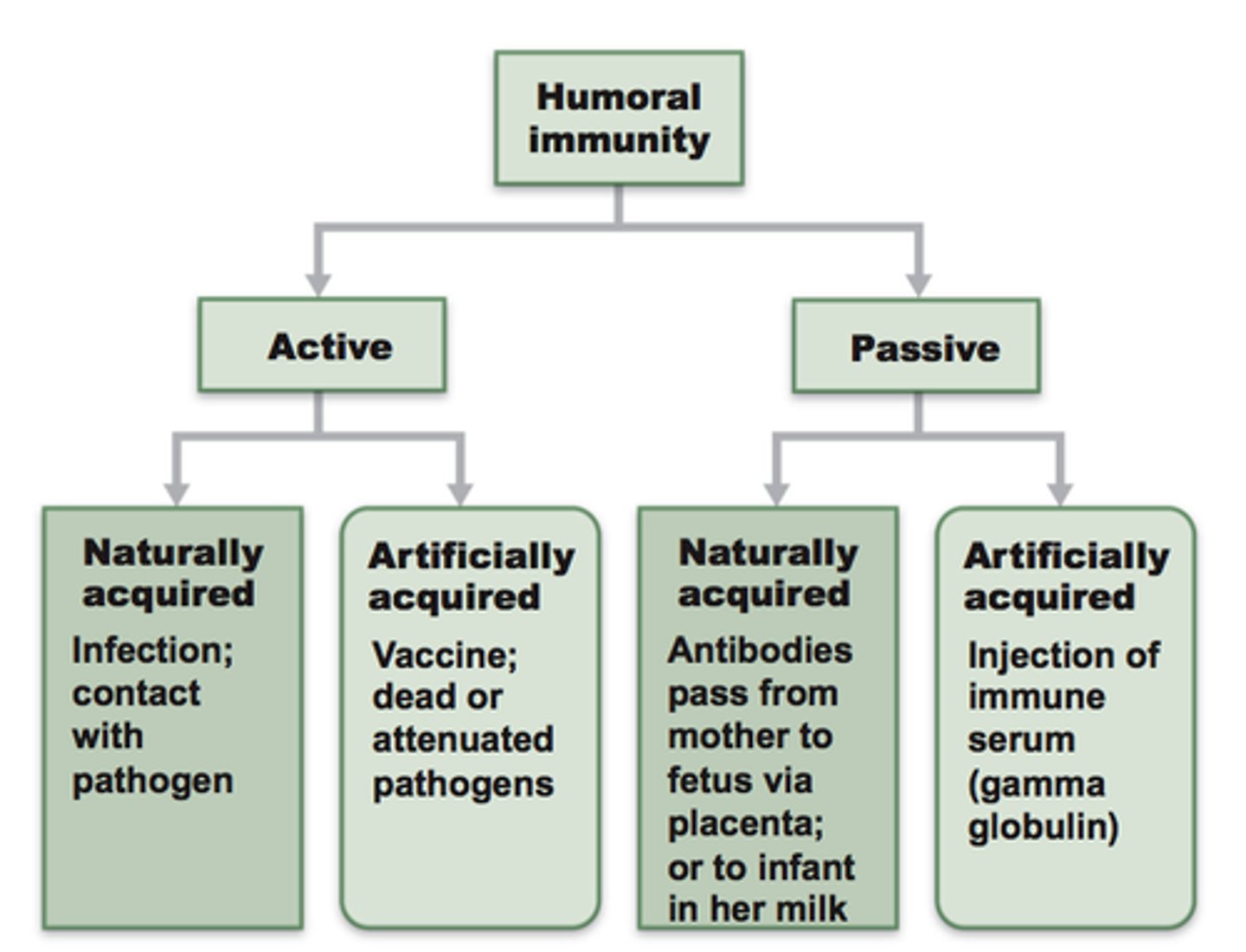
active immunity
the immunity that results from the production of antibodies by the immune system in response to the presence of an antigen (infection; vaccination)
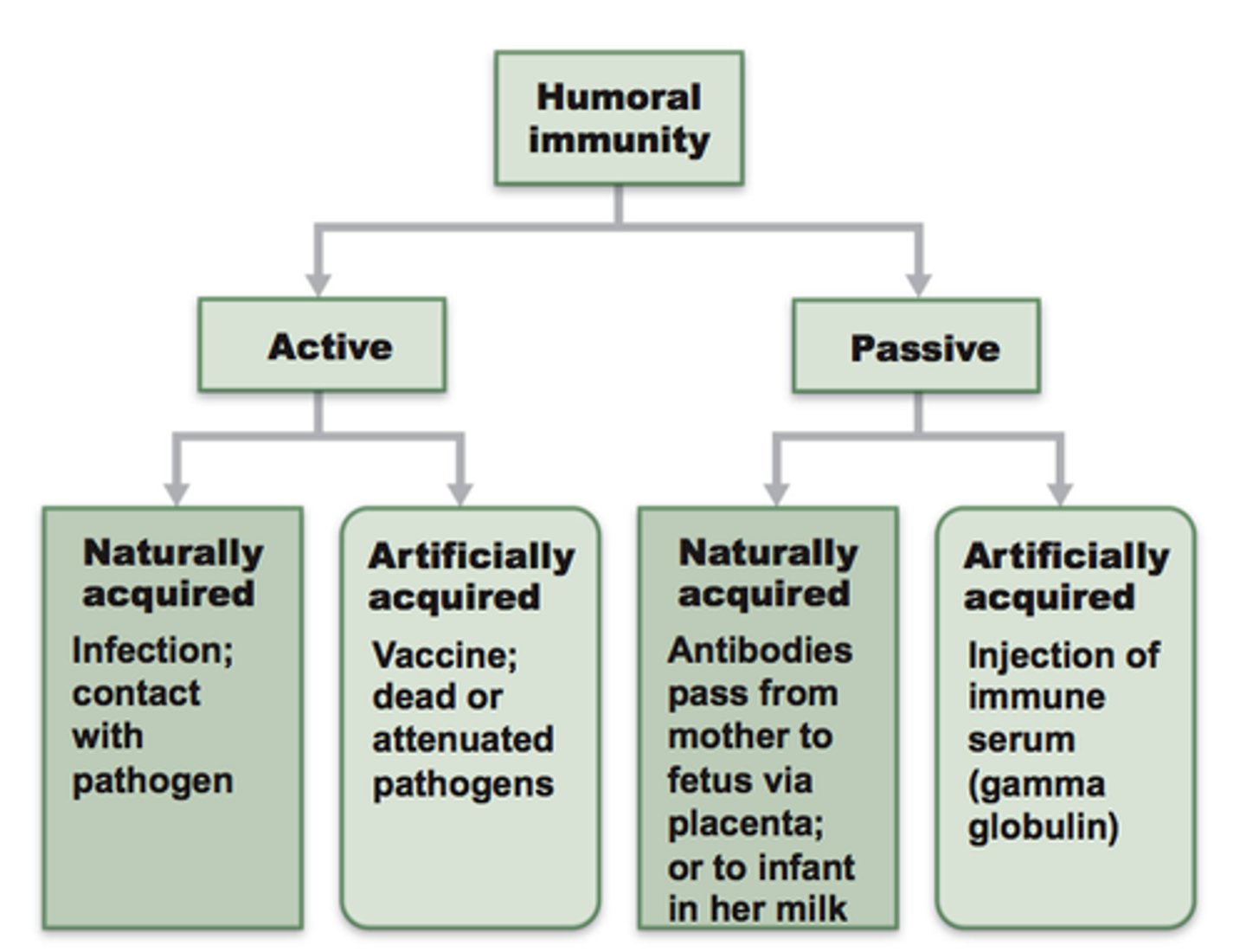
artificial immunity
acquired through a medical procedure such as a vaccine (or infusion of serum/plasma)
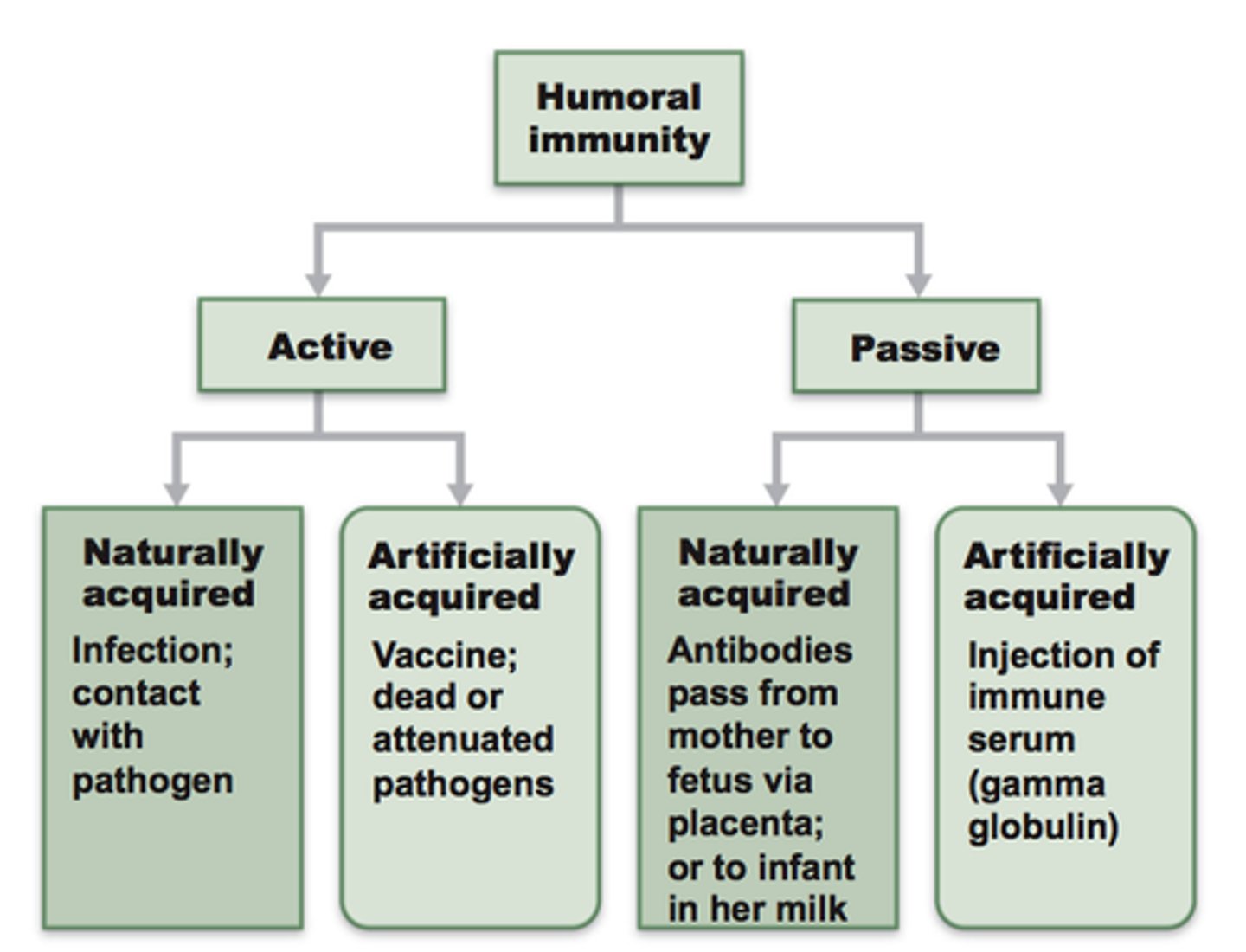
natural immunity
any immunity that is acquired through the normal biological experiences of an individual (e.g. infection; mother's milk)
homeostasis
process by which organisms maintain a relatively stable internal environment
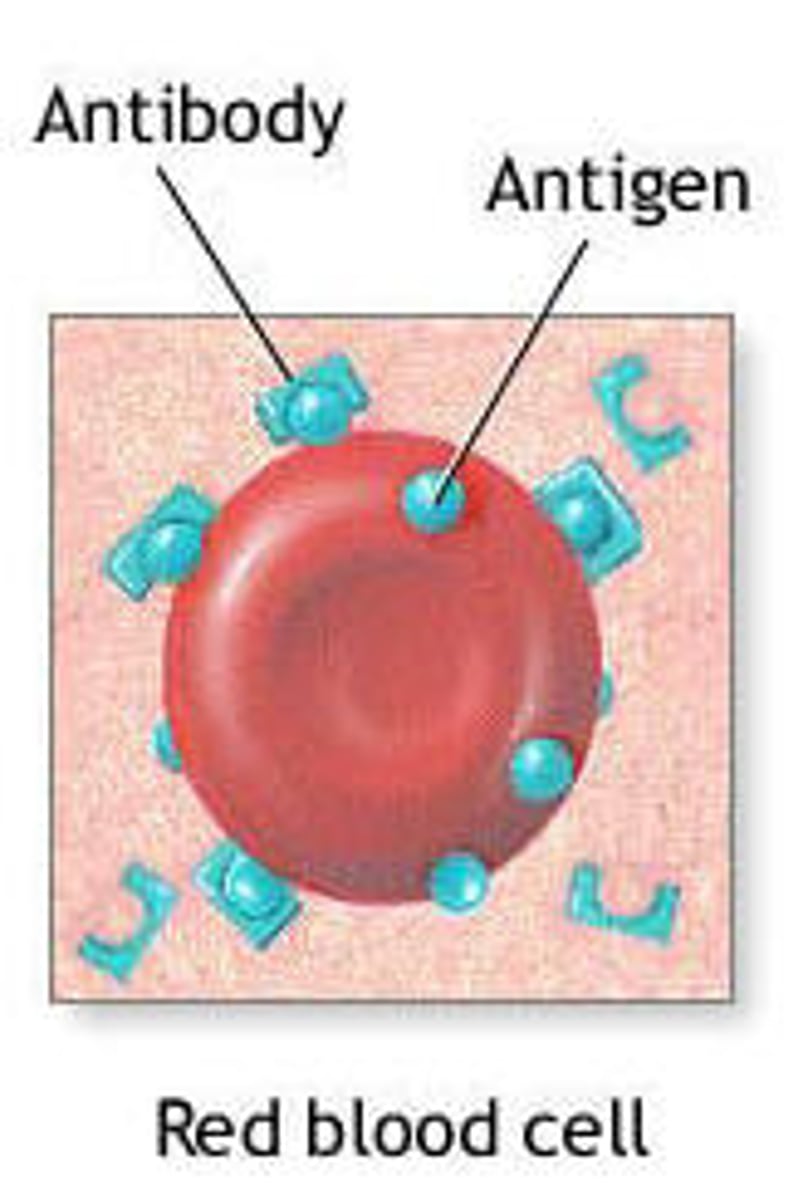
antigen (immunogen)
foreign/organic substance (protein, RNA, DNA, glycoprotein, nucleoprotein) that is large enough to stimulate an immune response (antibodies)
exogenous
Produced outside the body

endogenous
Produced within the body
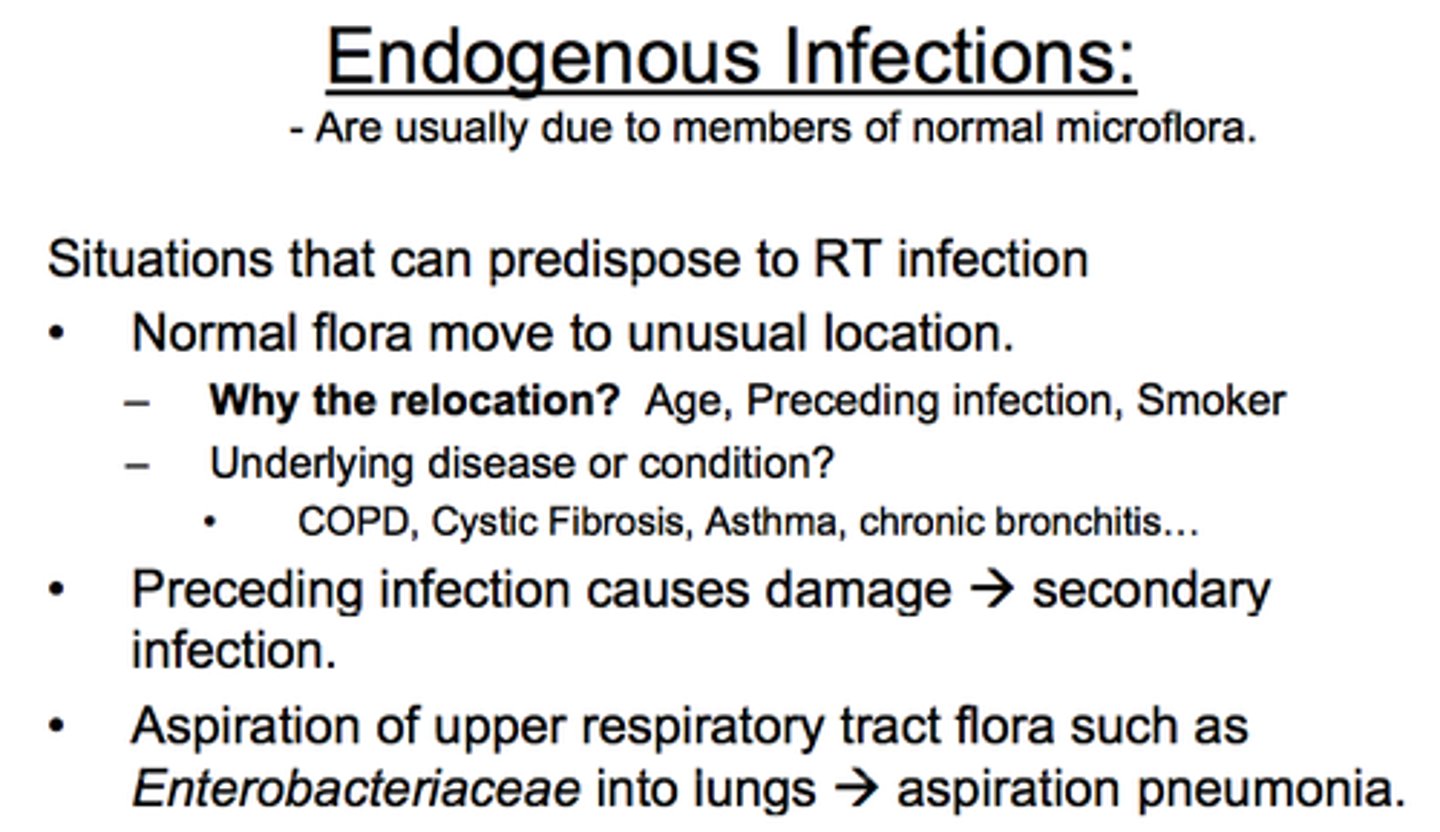
antibody
immunoglobin produced by B lymphocytes in response to a specific antigen. Found in plasma and body fluids (tears, saliva, milk).
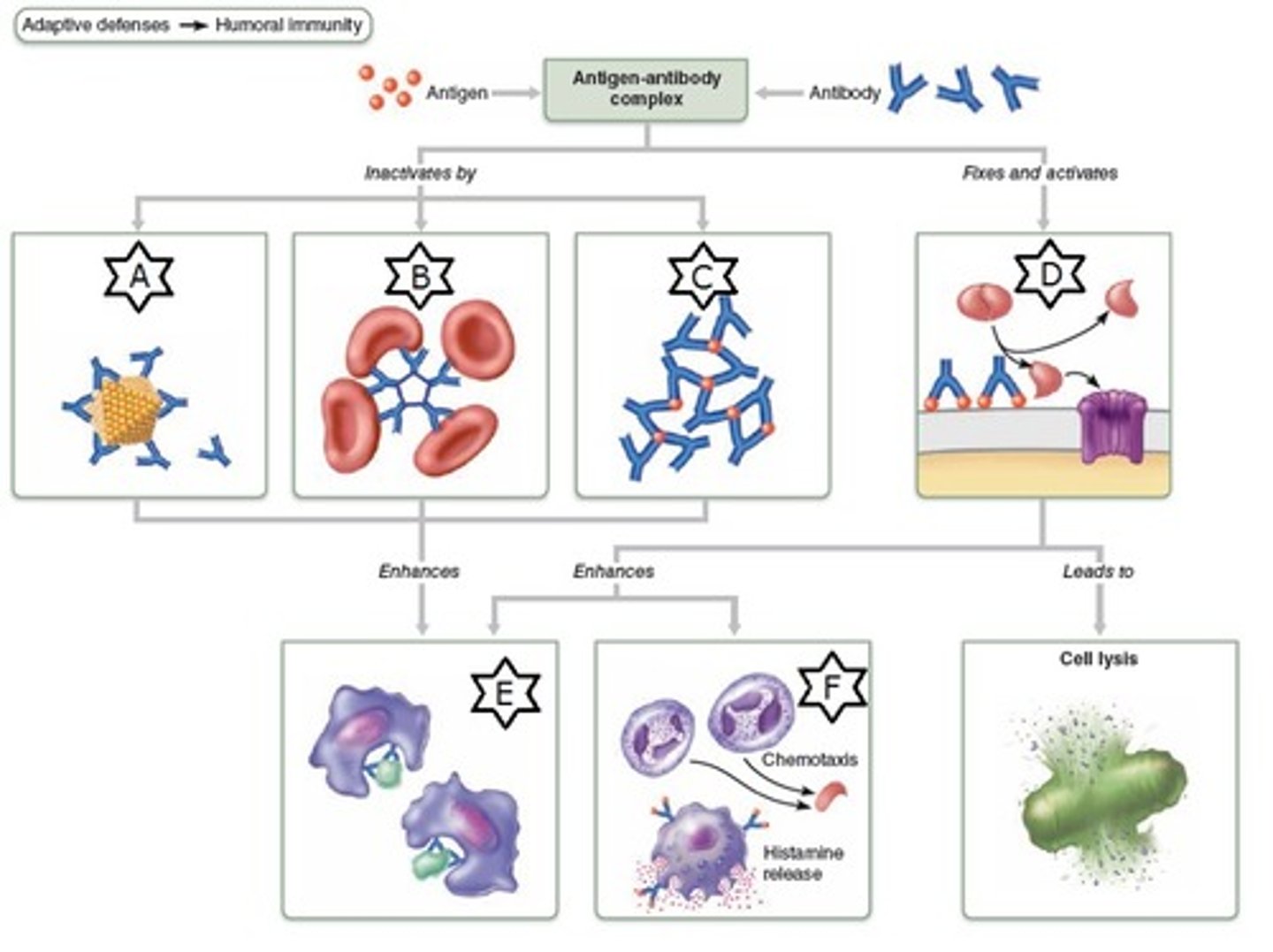
What can antibodies do?
Can 1) bind to toxins 2) the surfaces of bacteria, viruses, etc.. 3) promote the destruction of those cells by activating complement 4) facilitate phagocytosis
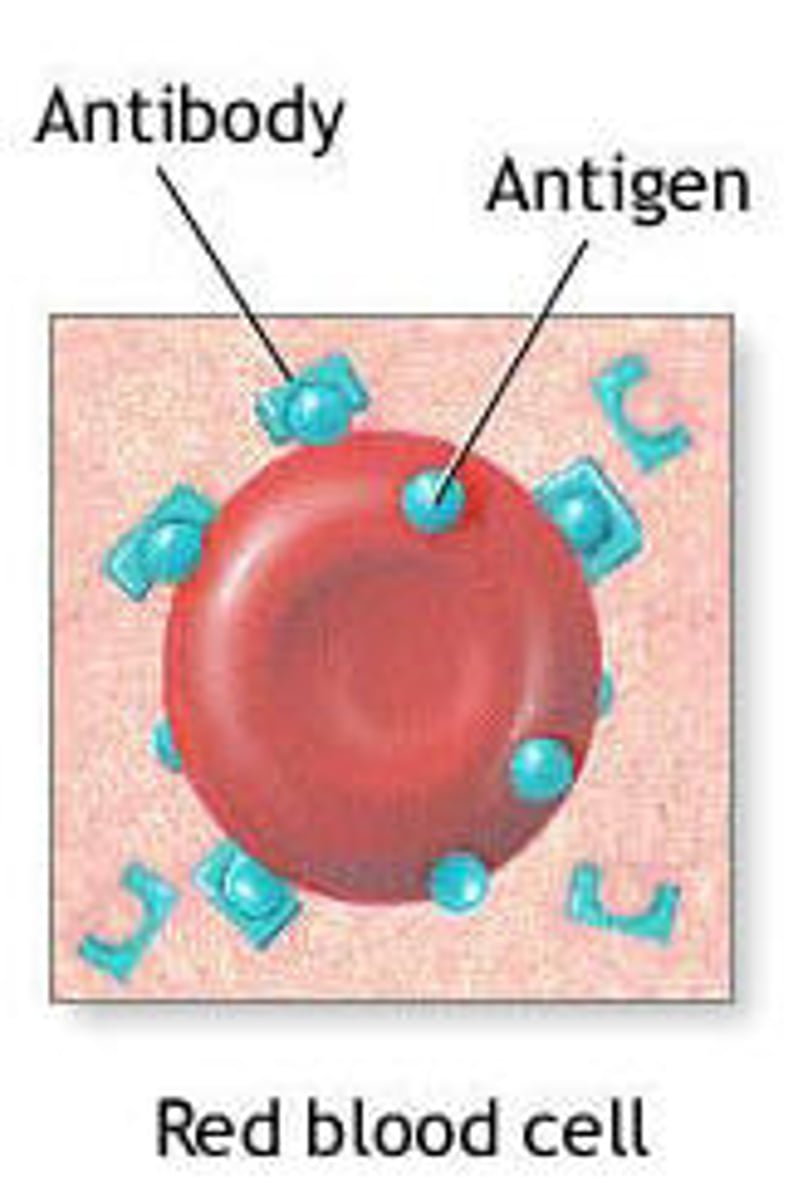
immunoglobulin
ANTIBODIES! Specific protein evoked by an antigen; all antibodies are immunoglobulins
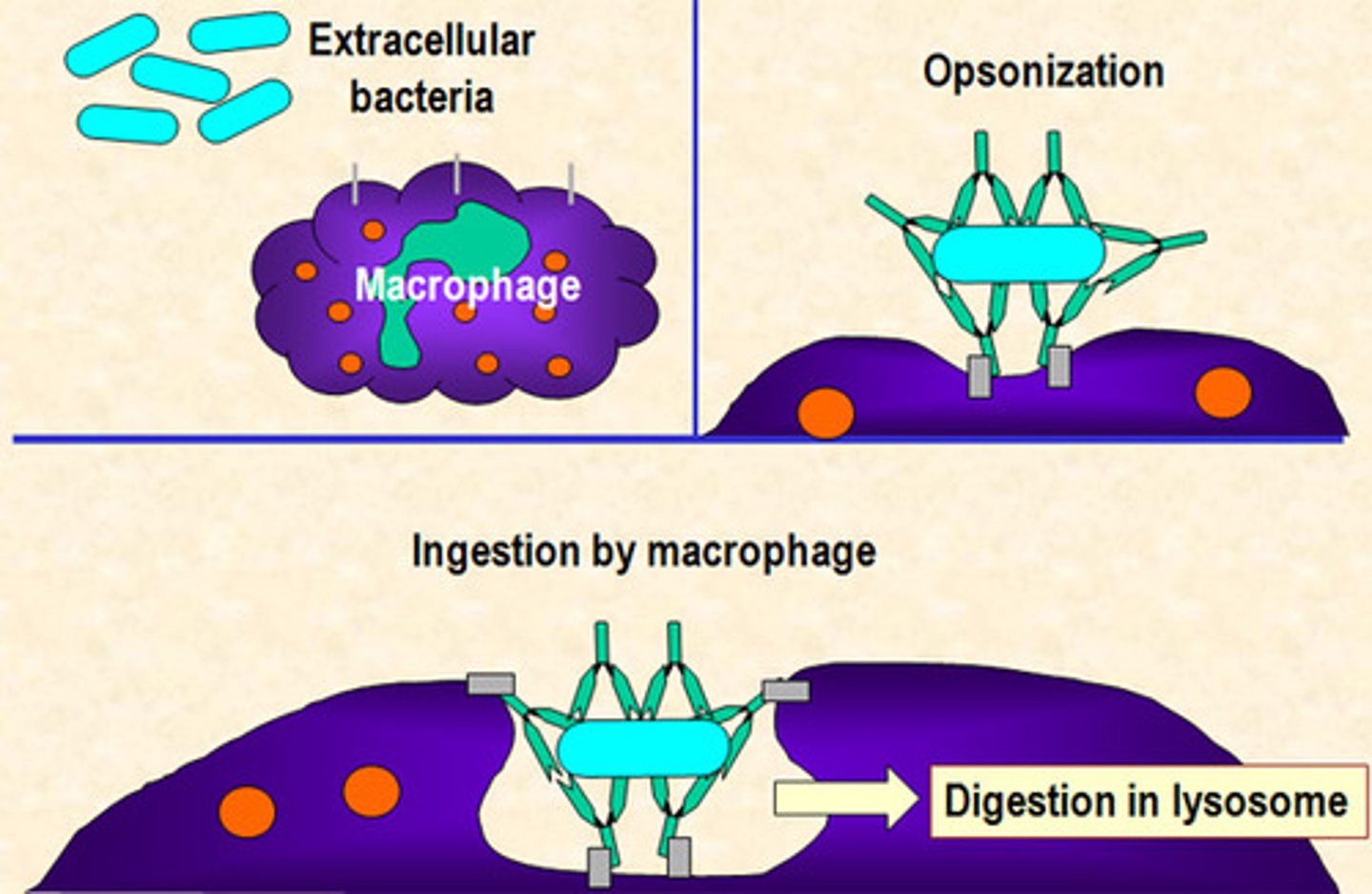
opsonin(s)
substances that enhance phagocytosis; antibodies and complement can act as opsonins
MHC
major histocompatibility complex; a genetic region in human beings and other mammals responsible for signaling between lymphocytes and antigen-bearing cells. It is also the major determinant of transplant compatibility (or rejection).
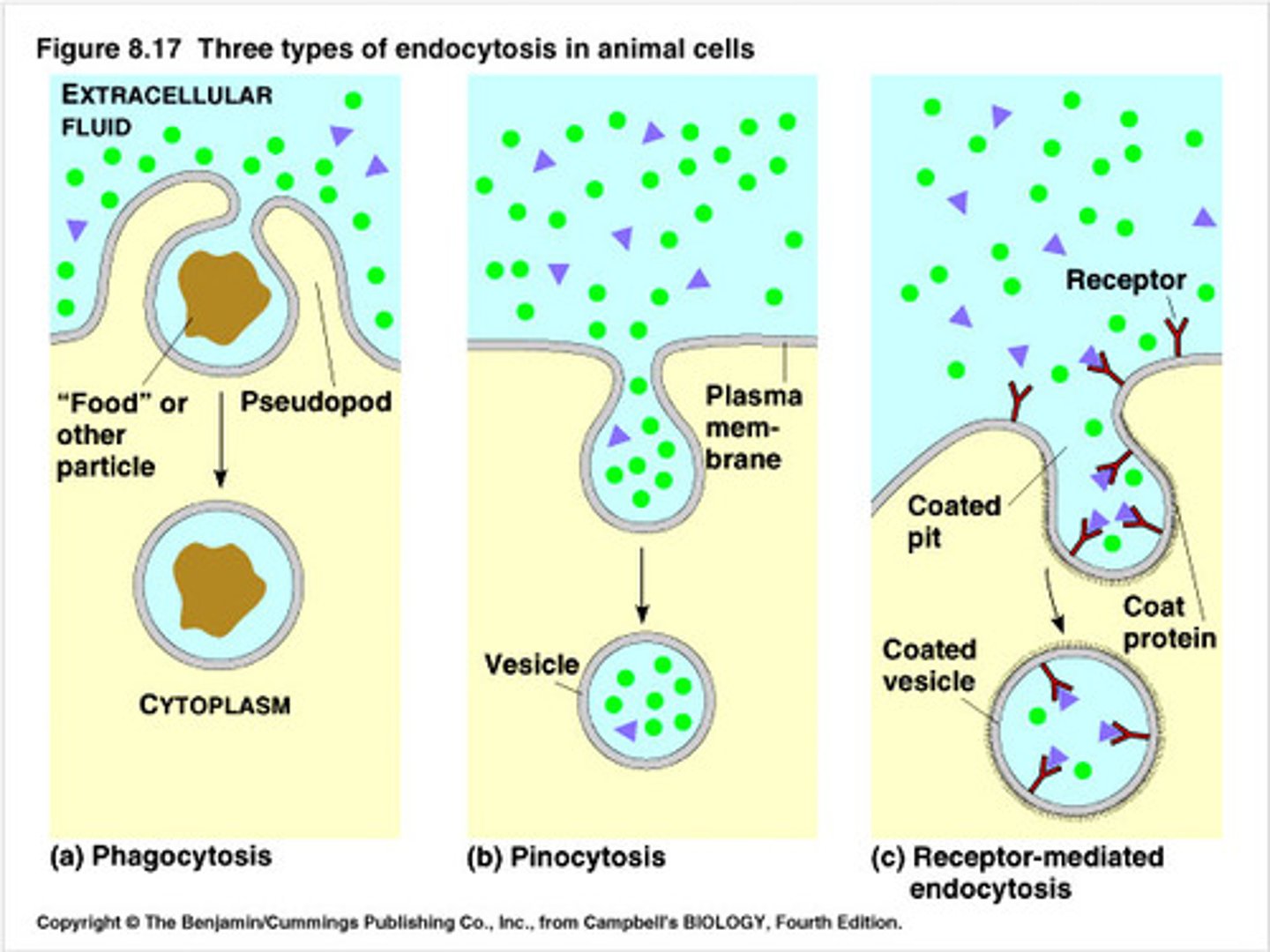
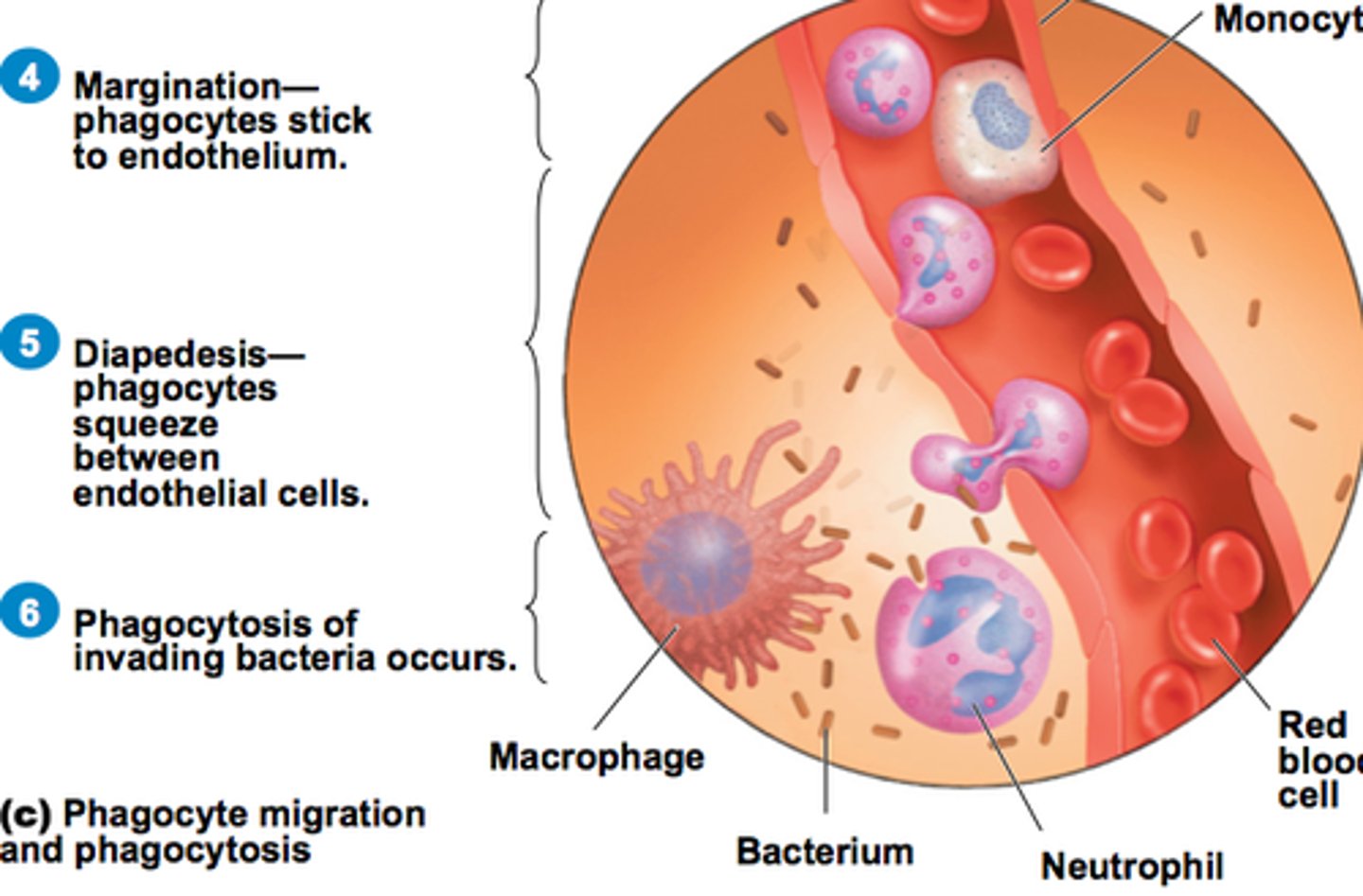
phagocytosis
the important body defense mechanism is the process whereby specialized cells engulf and destroy foreign particles, such as microorganisms or damaged cells. Macrophages and segmented neutrophils (PMNs) are the most important phagocytic cells
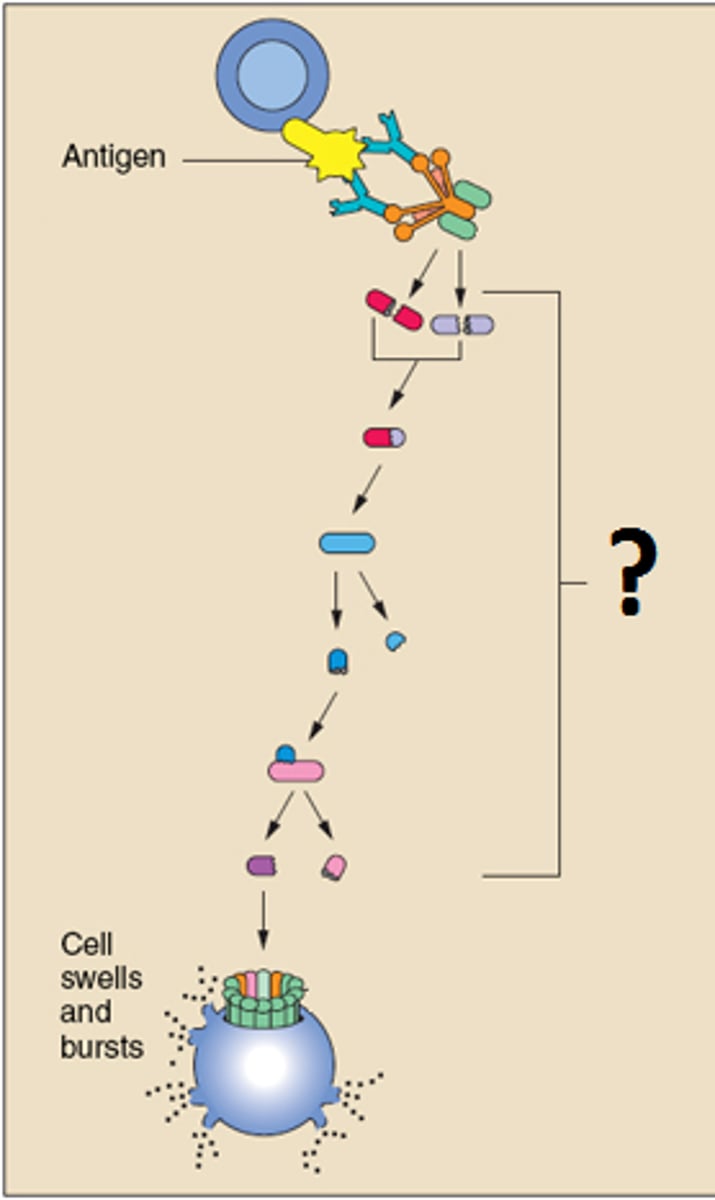
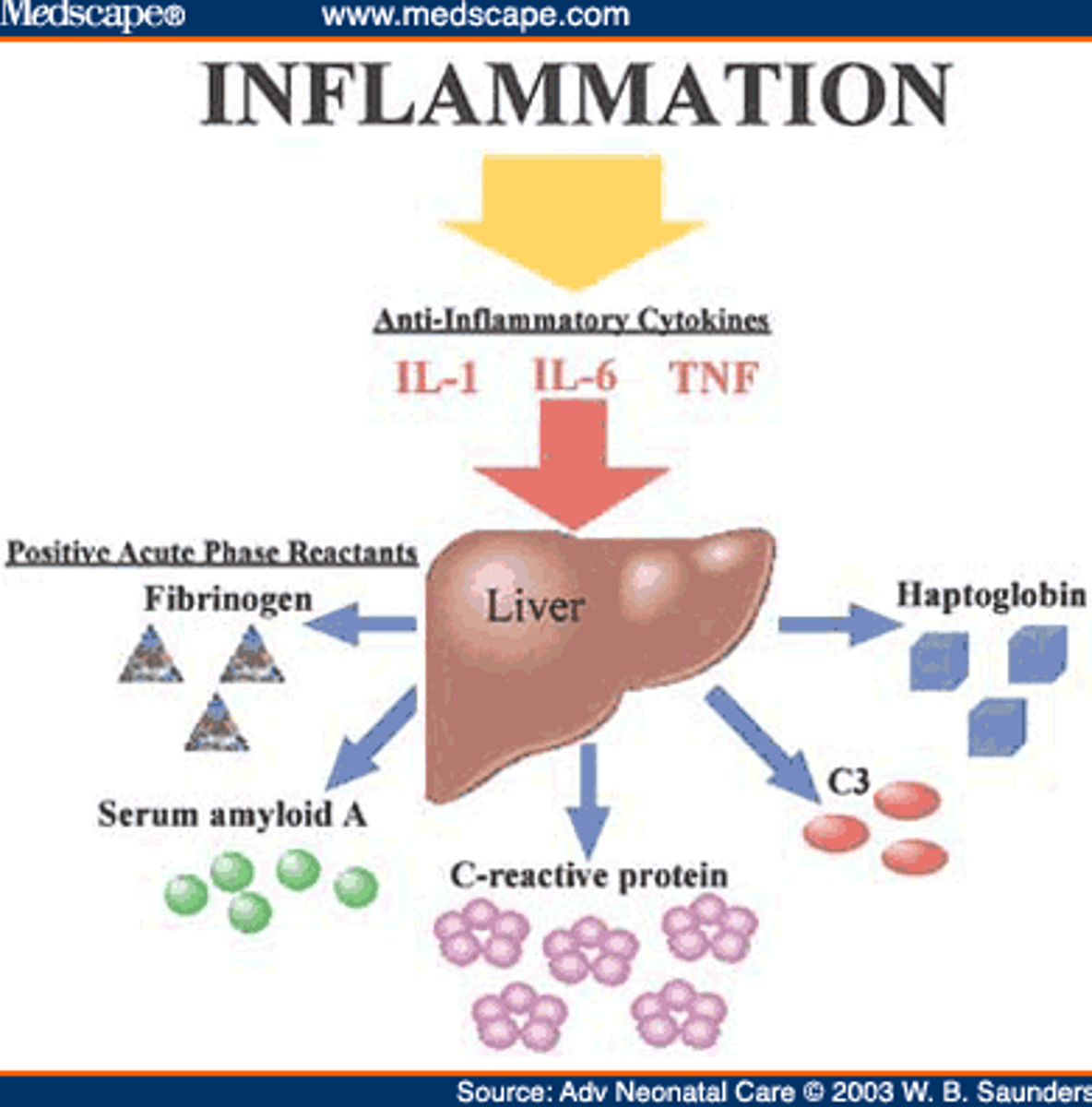
complement
18 blood proteins produced mainly by the liver; a group of soluble blood proteins (enzymes) consisting of C1 to C9. It is present in the blood and can produce inflammatory effects, opsonization, and lysis of cells when activated.
lysozyme
a type of bactericidal compound secreted by macrophages; found in saliva, tears, and nasal secretions; humoral mediated

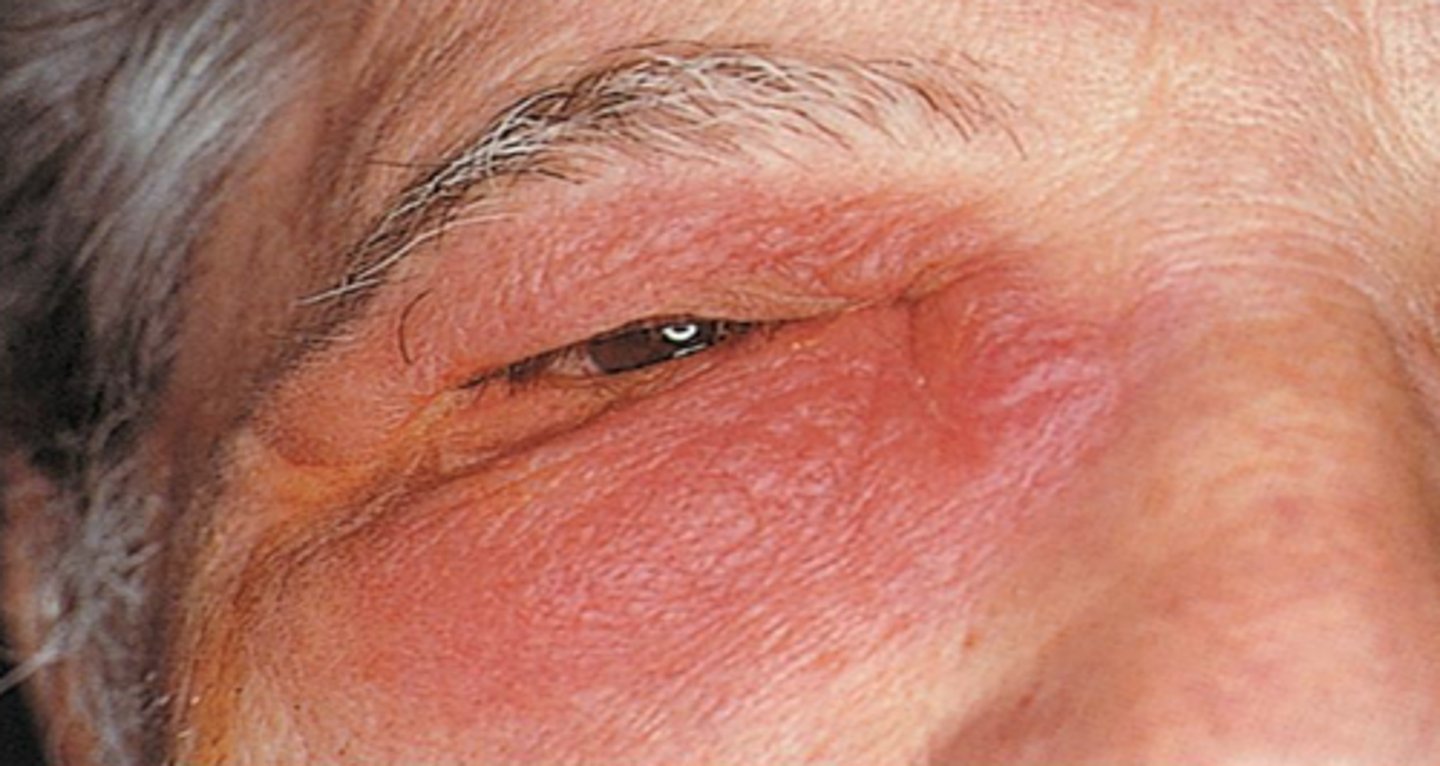
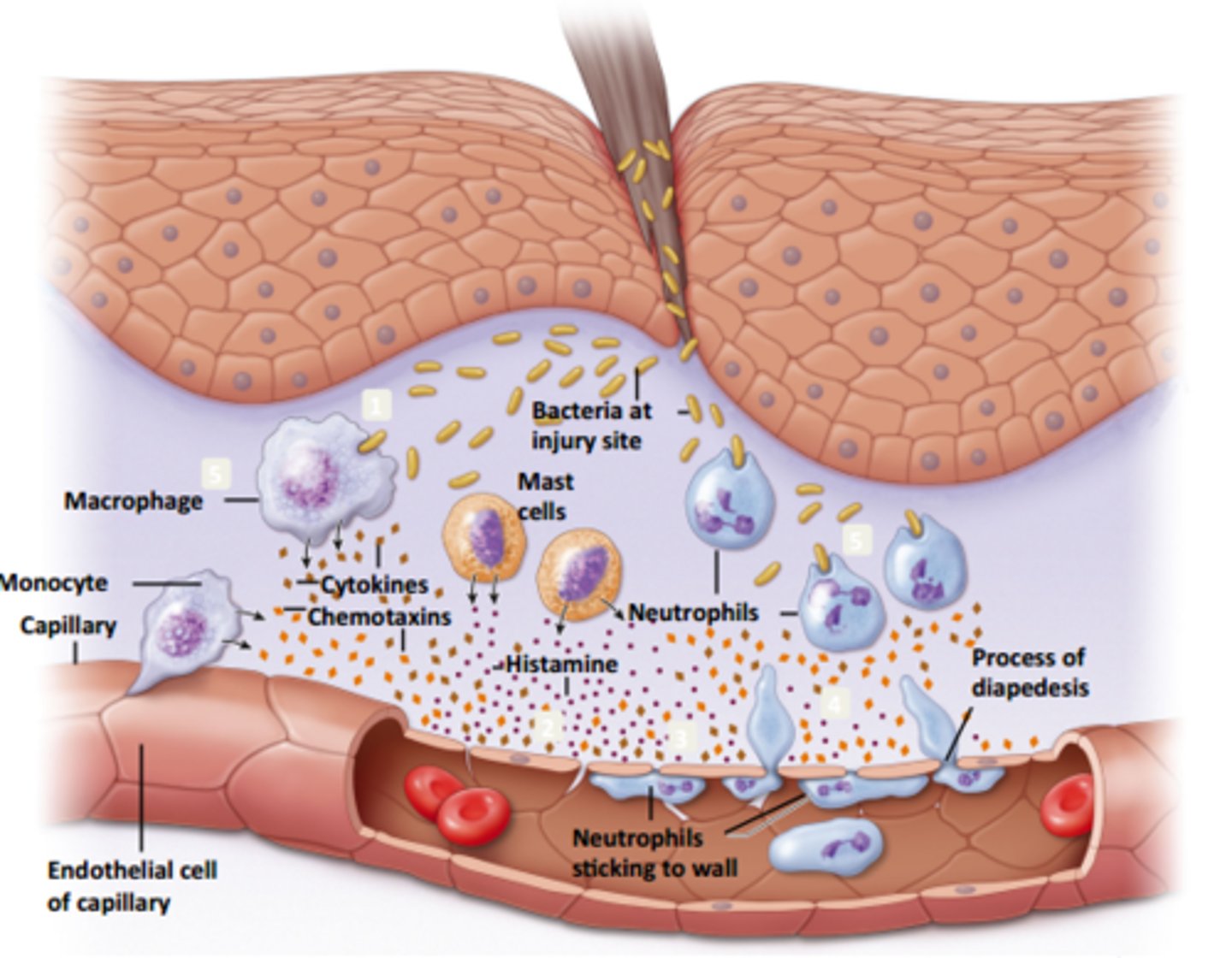
inflammation
Tissue reaction to injury caused by physical or chemical agents, including microorganisms. The classical signs of inflammation are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function. This is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immunity (as compared to adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen)
acute phase proteins (reactants)
group of glycoproteins associated with nonspecific inflammation of body tissues
diapedesis
Passage of white blood cells through intact vessel walls into tissue; ameboid movement of cells such as monocytes and neutrophils to a site of inflammation in phagocytosis
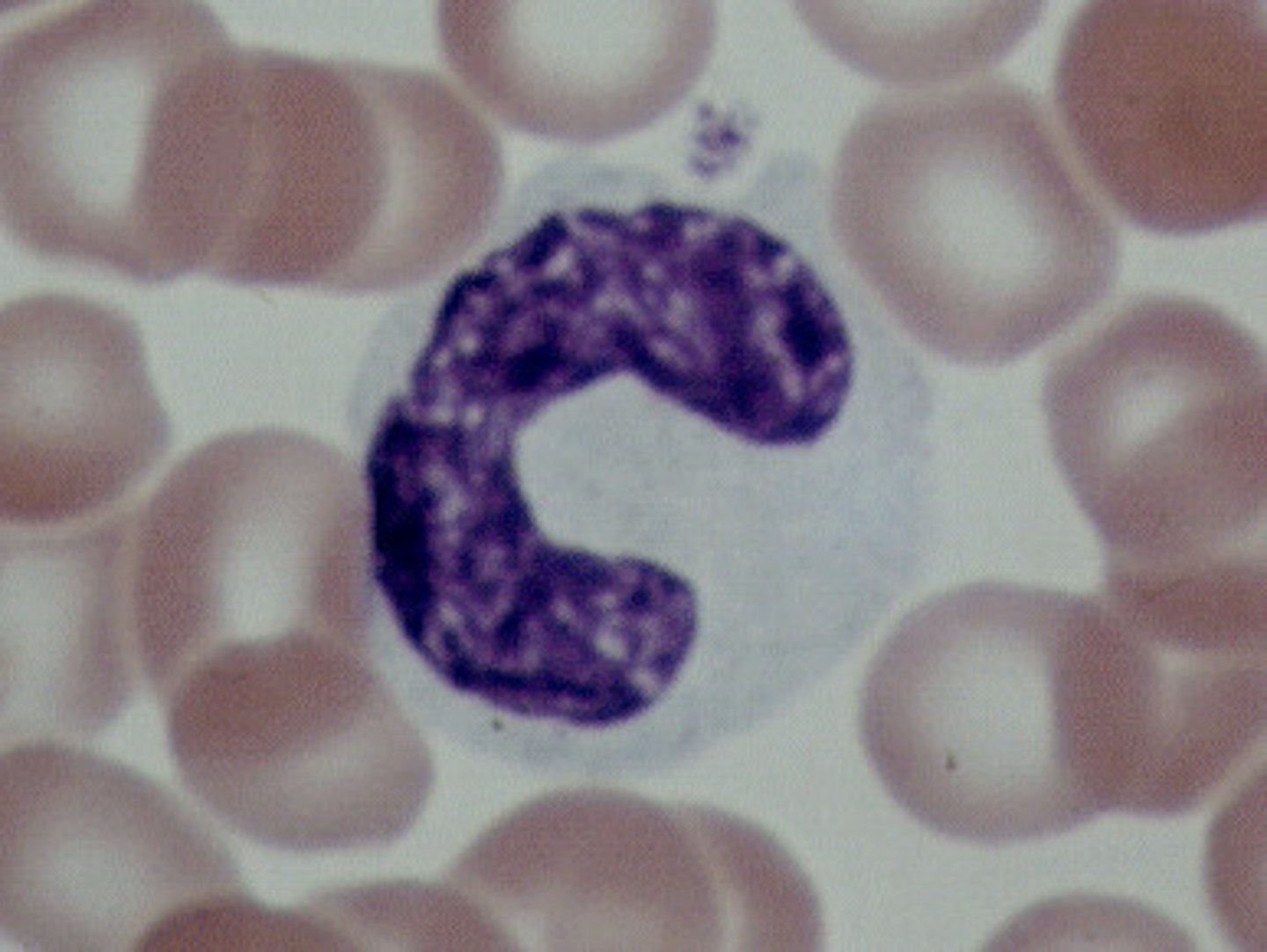
monocytes
a type of white blood cell, or leukocyte. They are the LARGEST type of leukocyte and can differentiate into macrophages and dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate INNATE immune system monocytes also influence the process of adaptive immunity. These become macrophages once they move into the tissues.
senescent cells
dead and useless cells in body

malignant cells
e.g. cancer, neoplastic or tumor cells
APC
antigen processing/presenting cells; engulf and breakdown foreign antigens into small parts and present them to T cells; usually MACROPHAGES or DENDRITIC cells
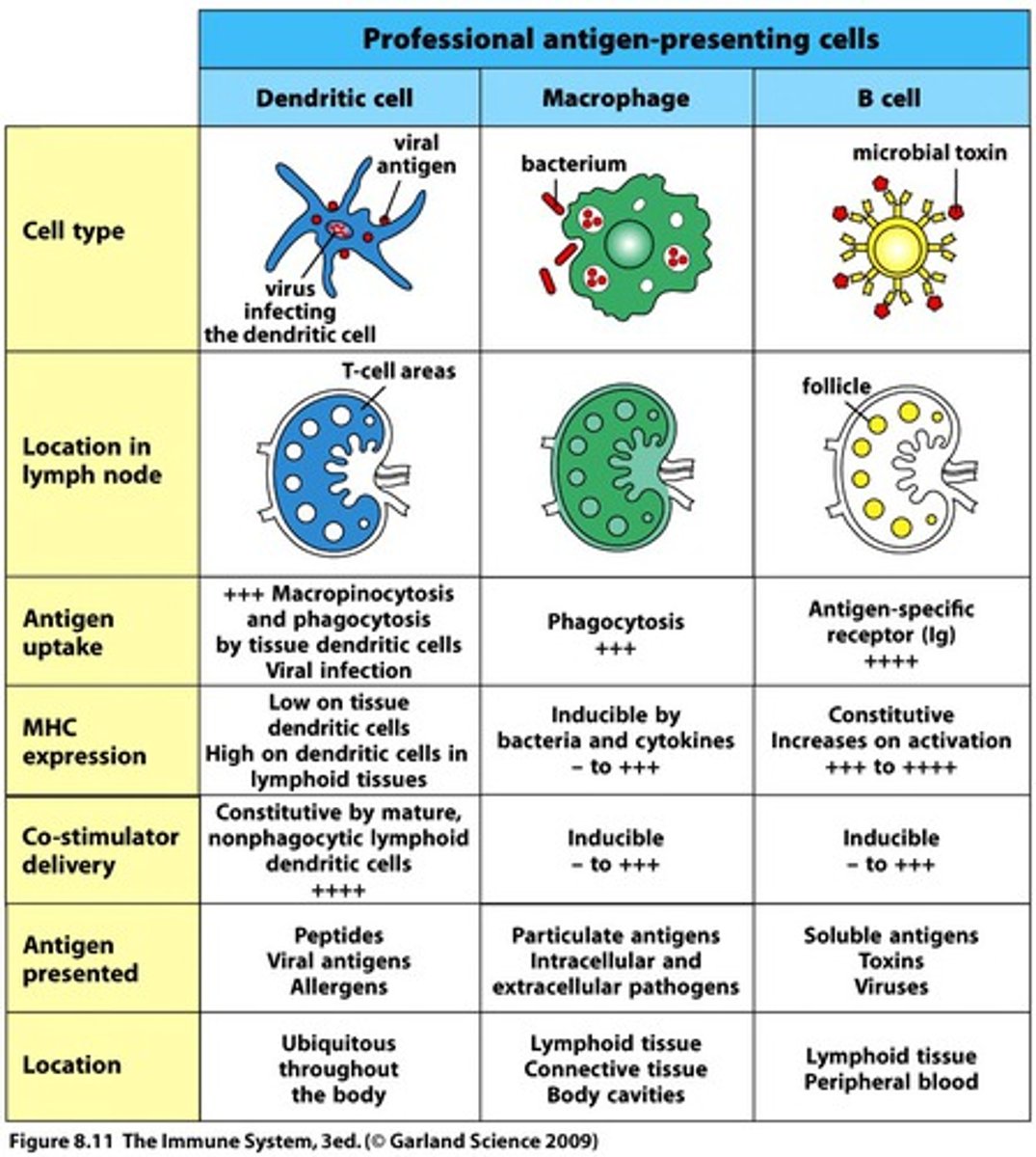
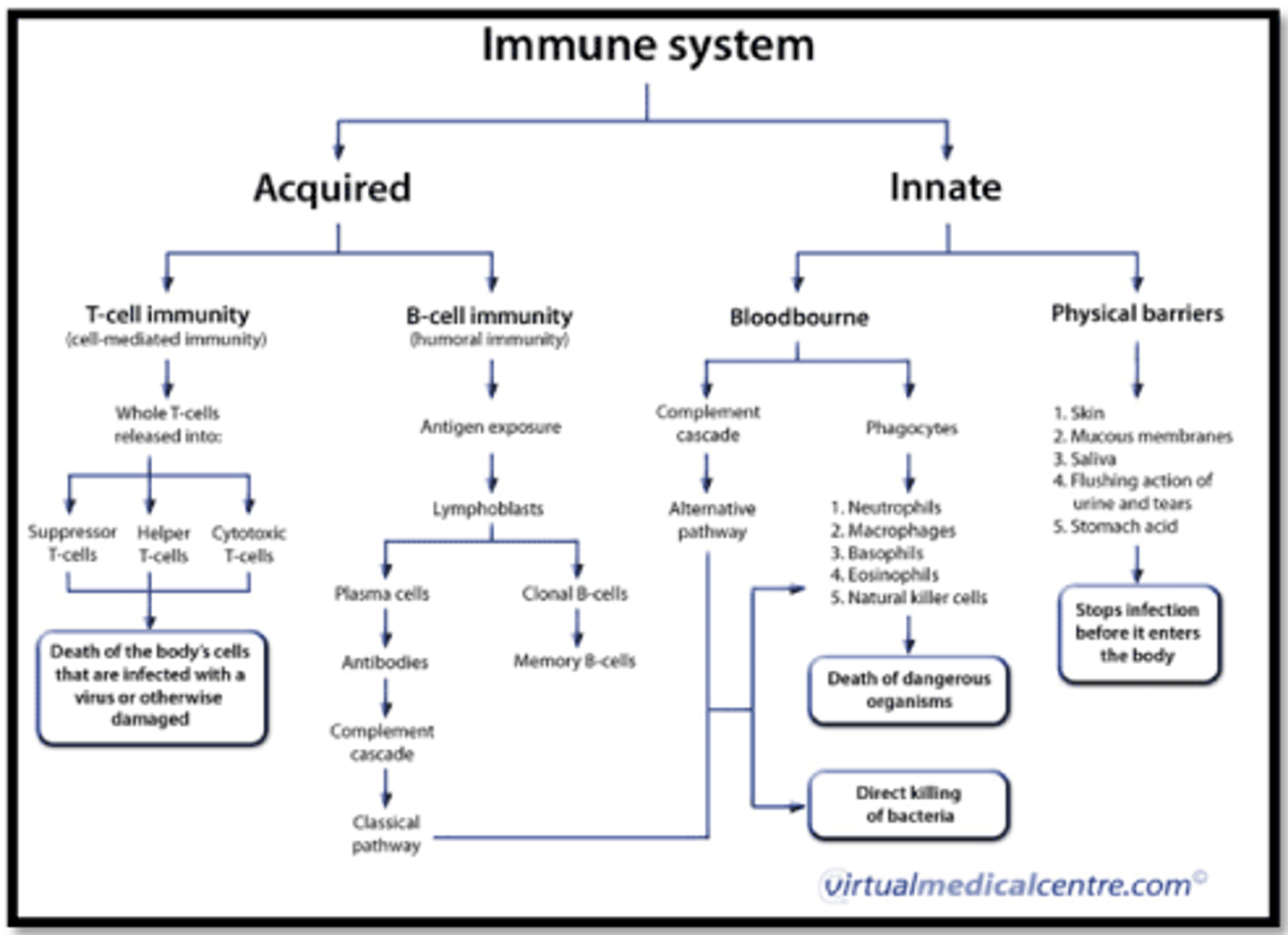
innate (non-specific) vs. adaptive (specific) immunity
innate is fast; adaptive is slow; innate includes 1st and second lines of defense; innate includes complement and inflammation
characteristics of the five classes of immunoglobulins
Describe how skin and mucous membranes provide a defense against infectious disease
skin: secretions, perspiration, fatty acids (lysozyme in saliva, tears, etc.) and ; cilia and mucous found in the mucous membranes trap and remove infectious particles;
Explain the process of phagocytosis
Neutrophils are attracted to a site by chemotactic agents; surround and engulf foreign particles and attempt to destroy them with enzymes from their granules; kills bacteria and WBC/damages tissues, some diseases result from malfunction
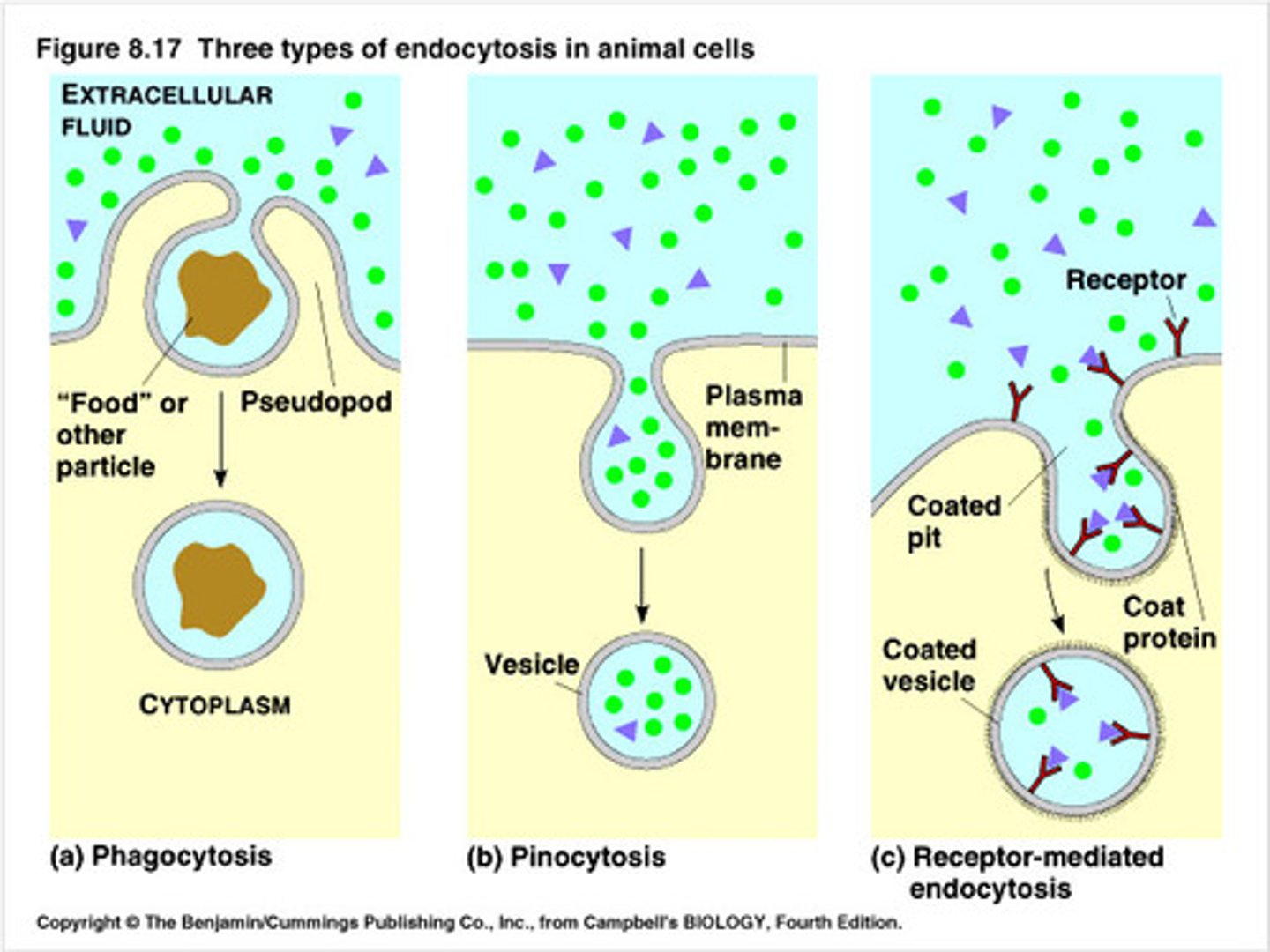
Four steps in phagocytosis
1) chemotaxis 2) attachment 3) ingestion 4) digestion
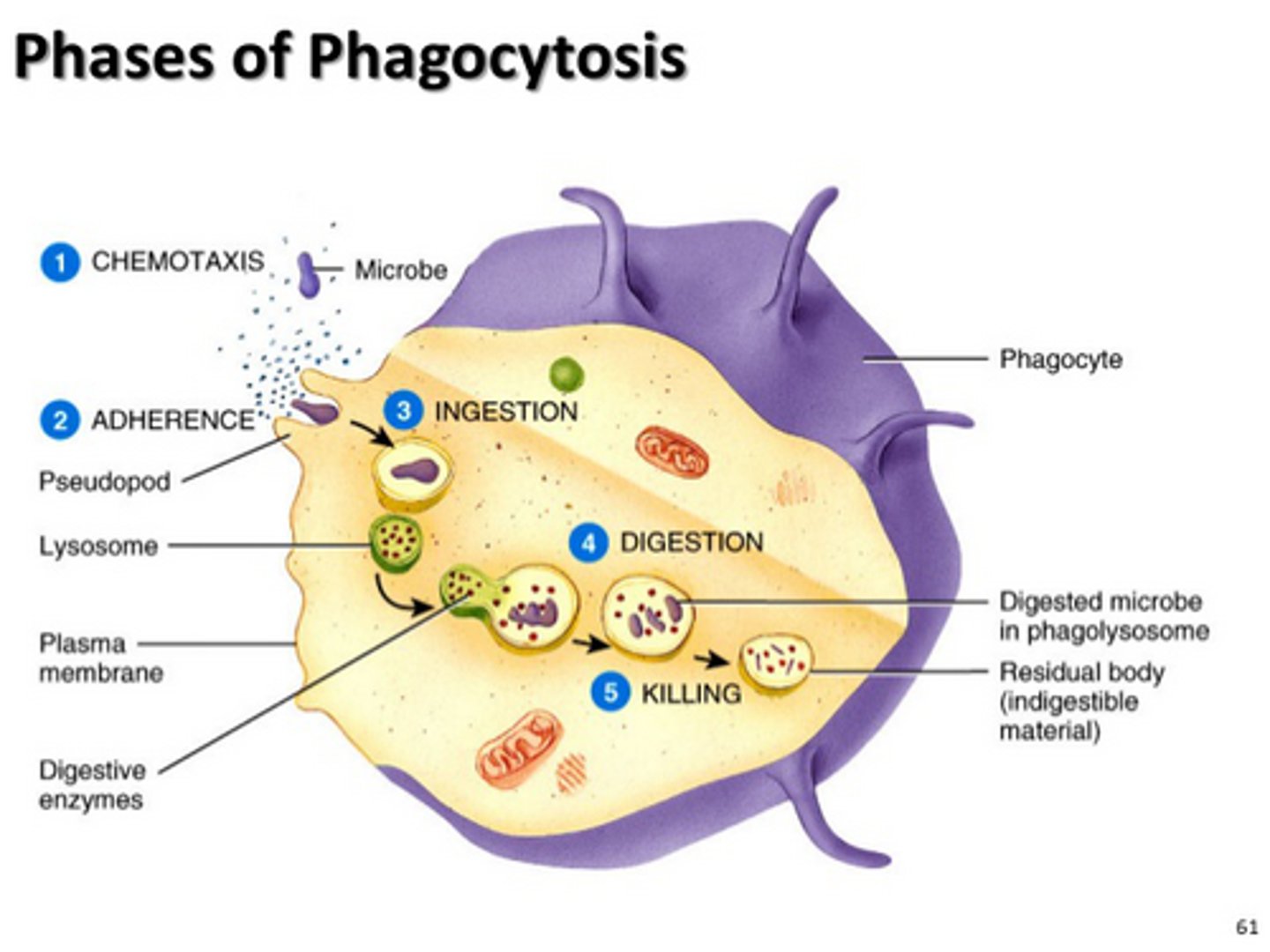
MPS
Mononuclear Phagocyte System; made up of phagocytic cells in the body including macrophages and monocytes; engulf and destroy damaged/old tissues and foreign particles; don't die but activate and stimulate cytokines
Cytokines
-proteins (such as interferons and interleukins) primarily released by macrophages that function as chemical messengers, allowing cells to communicate
-macrophages that destroy foreign material are stimulated to produce these
-often these will attract B and T cells

acute phase reactants
form of natural immunity in which the levels of soluble proteins and other cells increase rapidly in response to the presence of an infectious agent
signs and symptoms of inflammation
tissue reaction to injury caused by physical or chemical agents, including microorganisms. Symptoms include redness, tenderness, pain, and swelling.
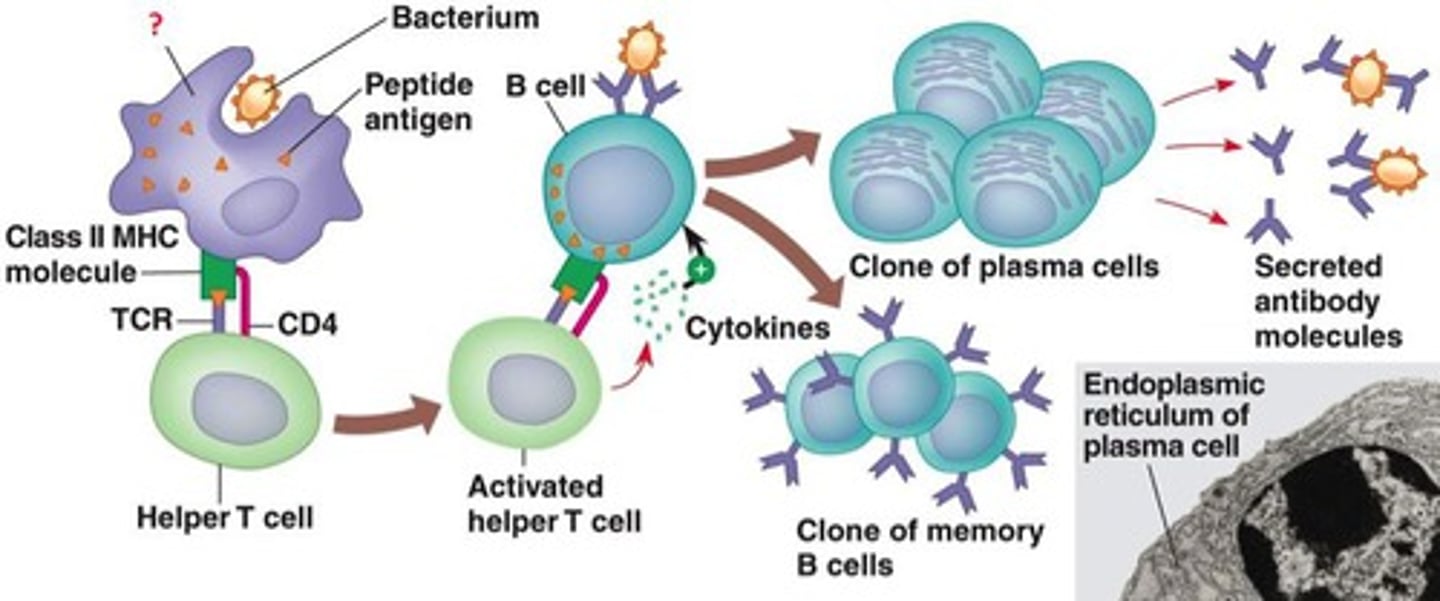
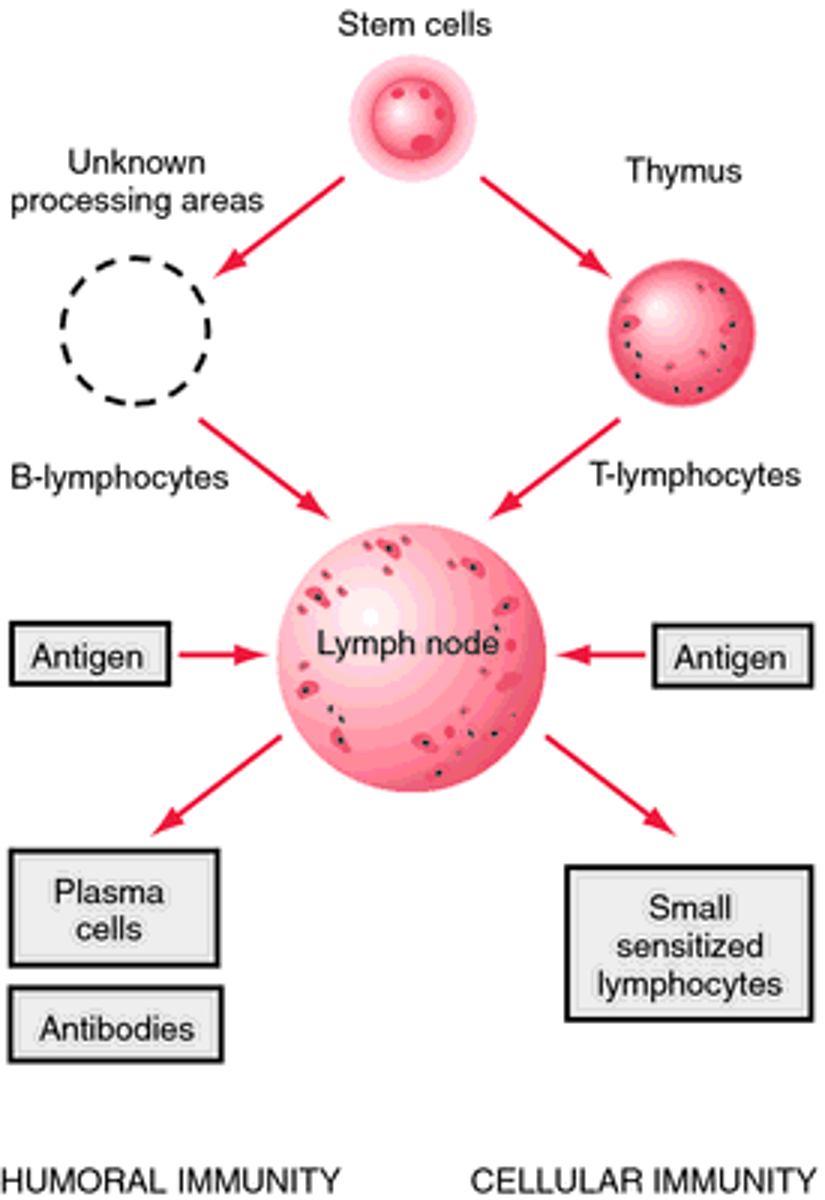
humoral immunity
a form of body defense against foreign substances represented by antibodies and other soluble extracellular factors in the blood plasma (liquid portion of the blood) and lymphatic fluid
Other details about lymphocytes during humoral immunity
B cells activated by DIRECT RECOGNITION of antigen or by T cells that are activated to turn on B cells; activated B cells produce a clone of cells programmed to produce antibody against the antigen that activated the original cell--> differentiate into PLASMA or MEMORY cells.
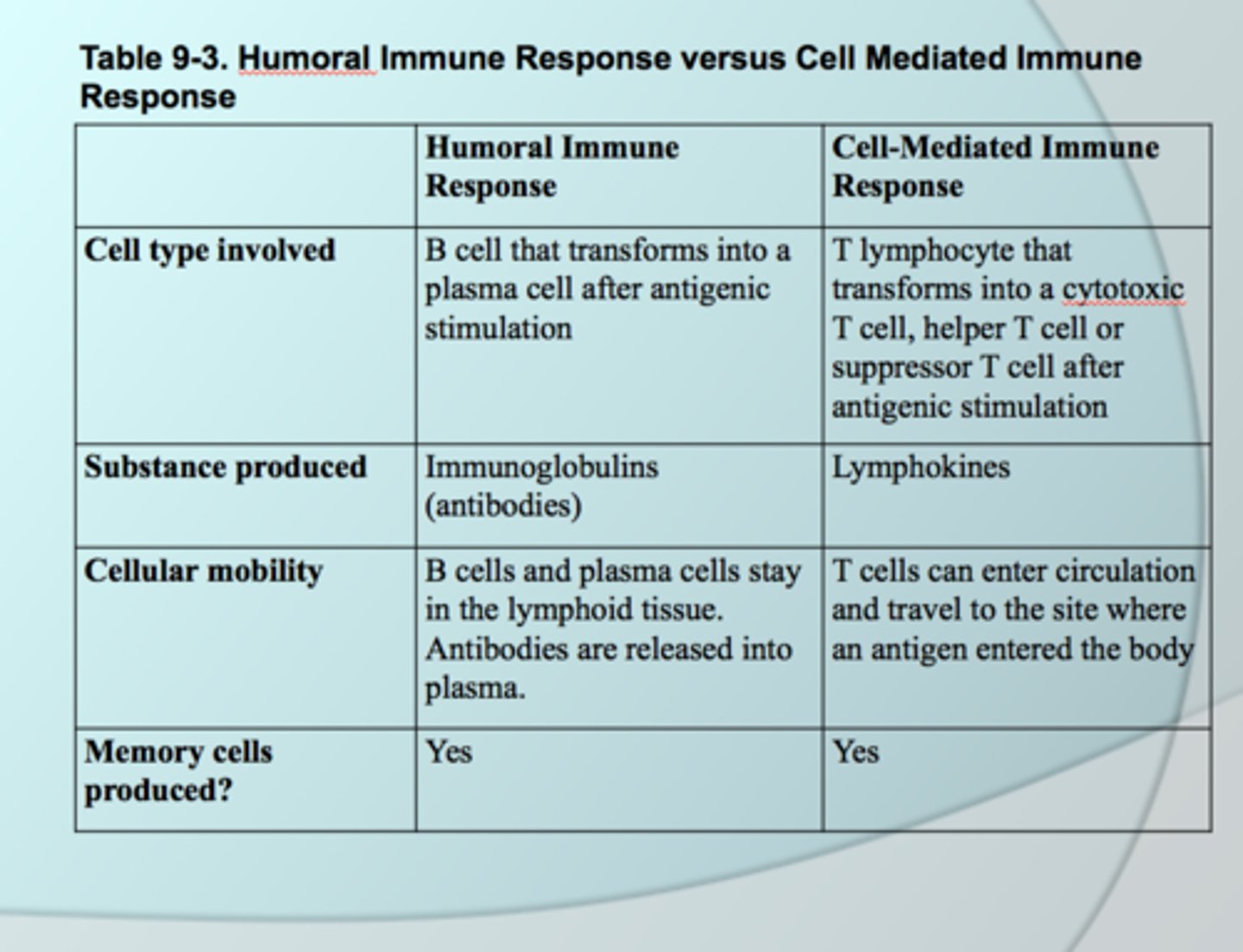
cell mediated immunity
type of immunity dependent on the link between T cells and macrophages
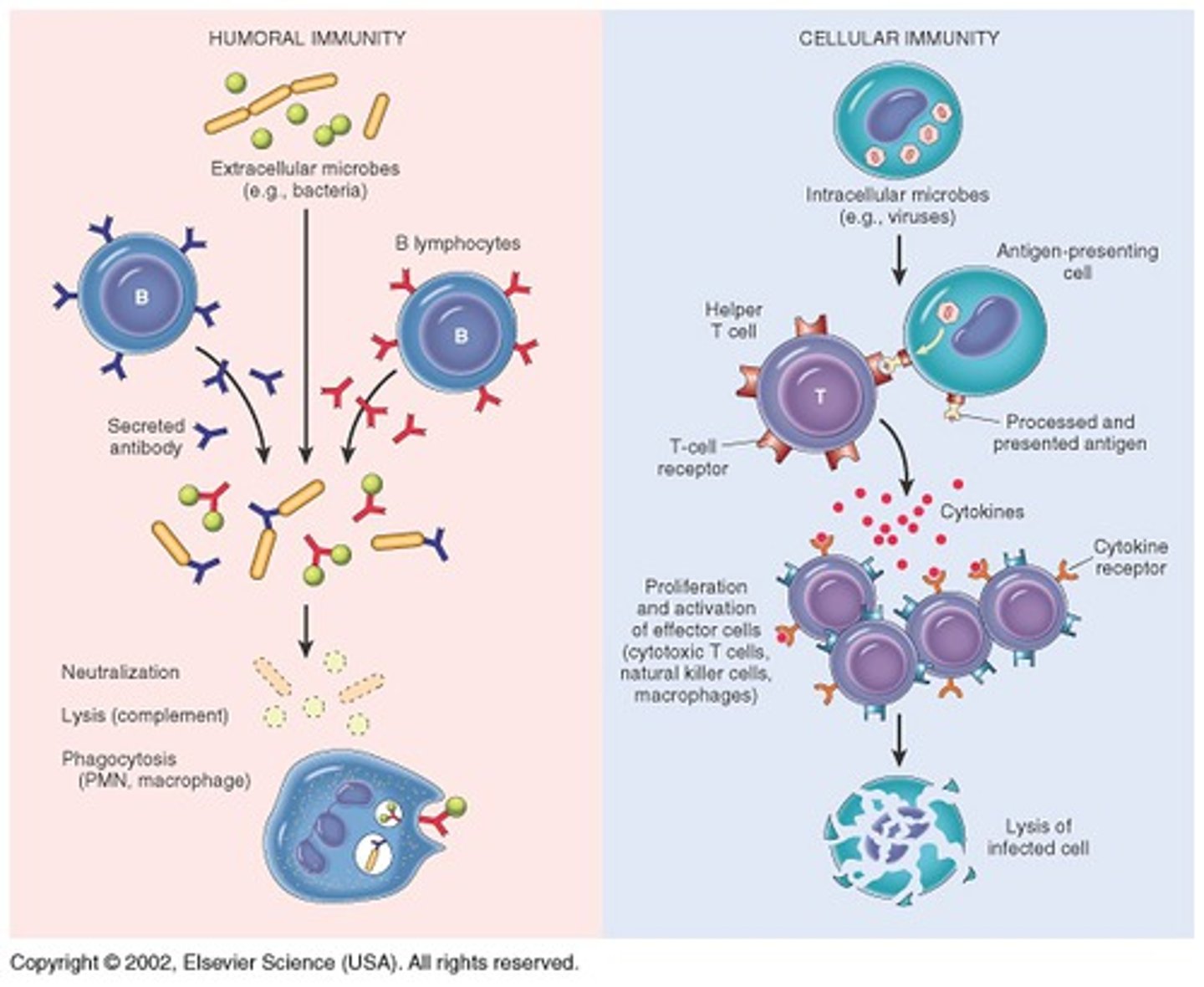
cell mediated vs. humoral immunity
Types of acquired (adaptive) immunity
Has memory. Lympocyte is the major cellular component; antibodies are the major humoral component.
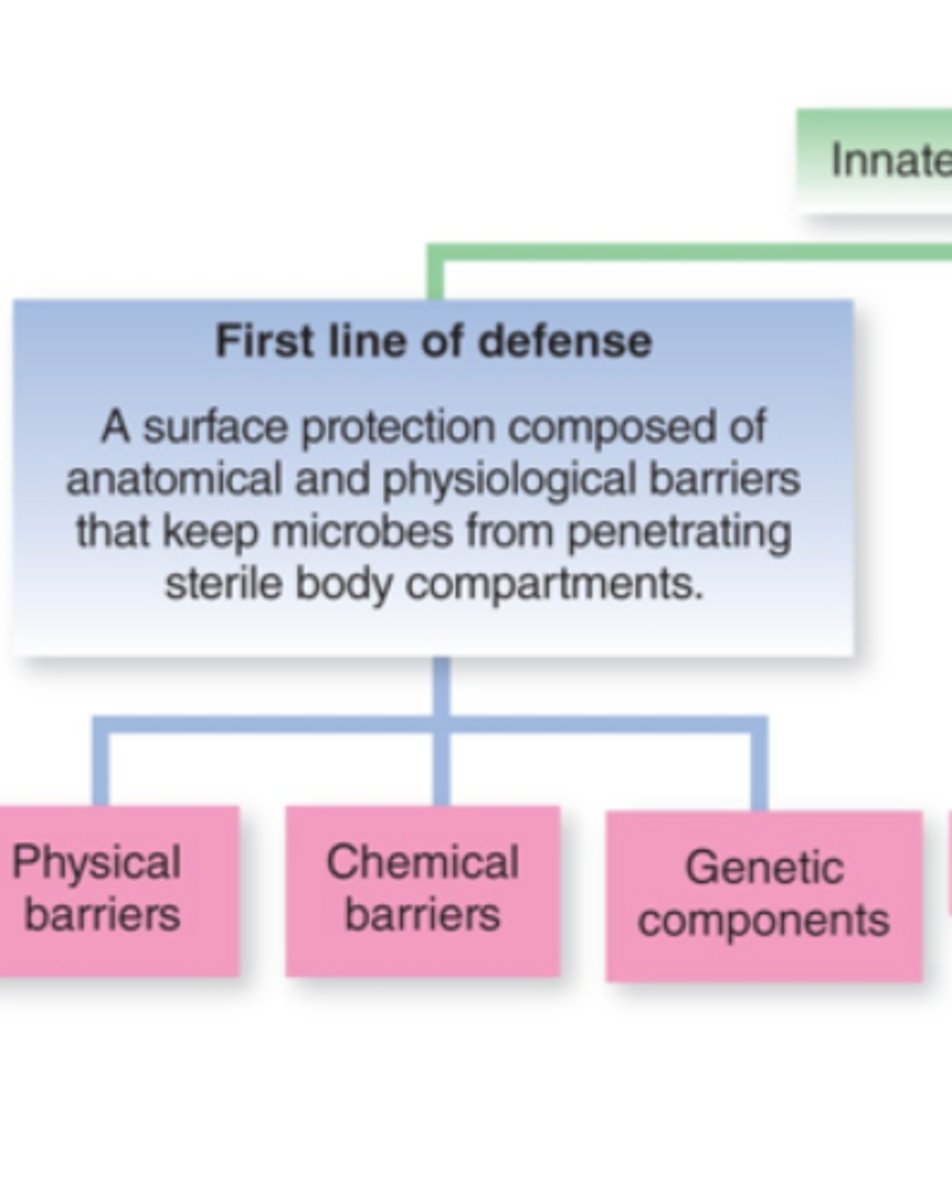
Physical barriers (first line of defense)
includes skin and mucous membranes; NON-SPECIFIC
Three Things Flora Do
1) Take up space 2) Use nutrients 3) Excrete waste
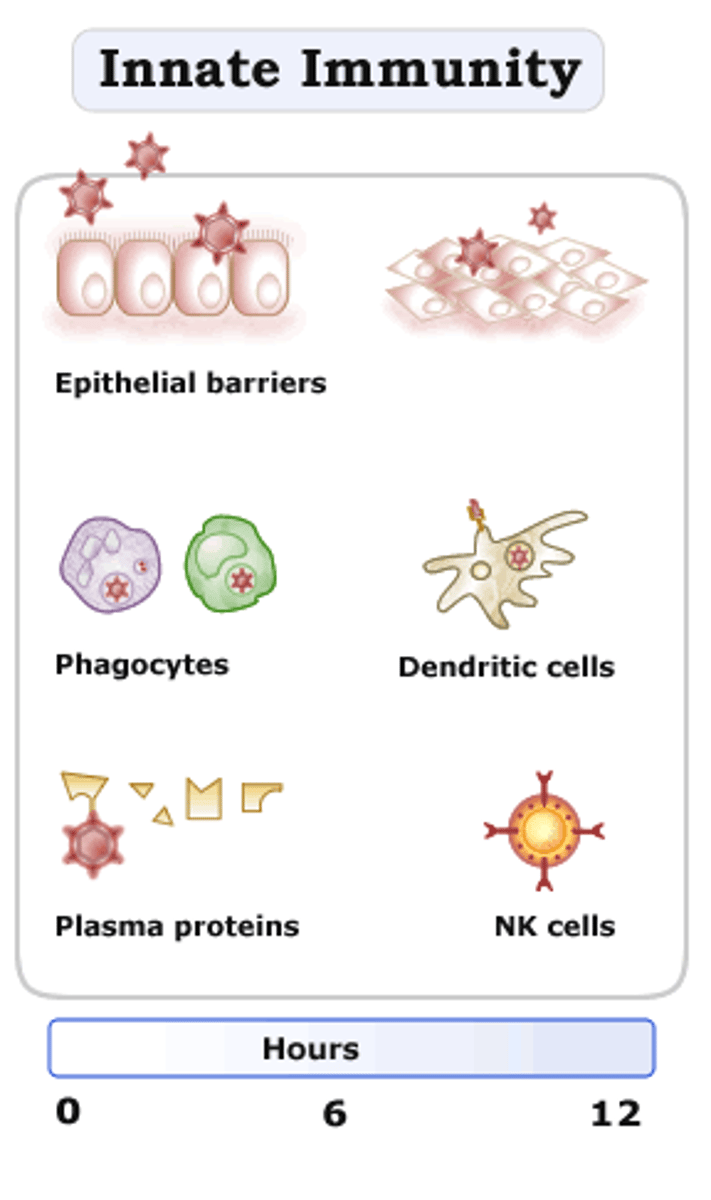
Innate immunity (2nd line of defense)
Natural or inborn ability to resist infection; aka non-specific immune response; always present; not changed by repeated exposure; e.g. inflammatory response, species immunity, s
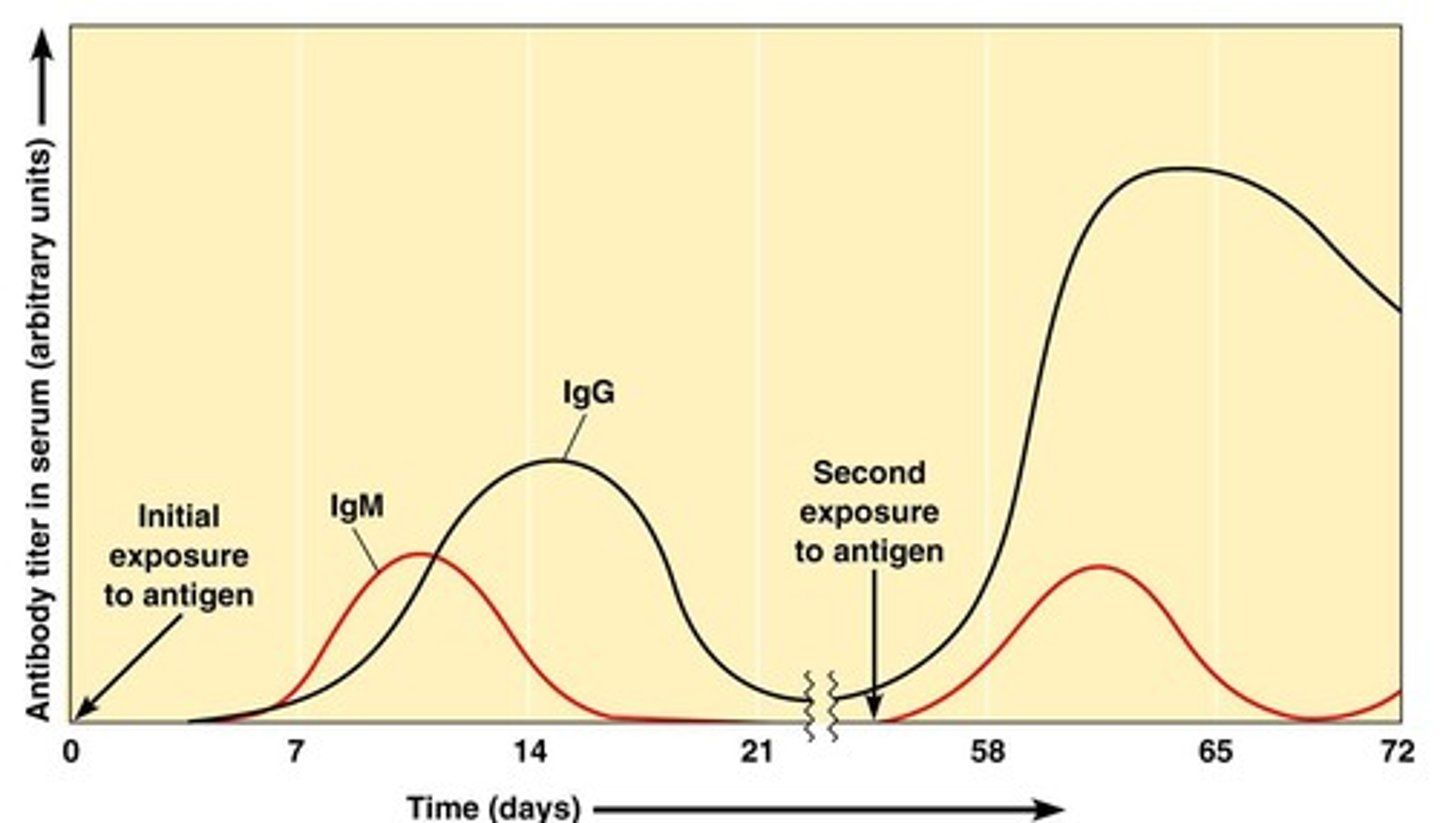
Primary response
Initial immune response to a particular antigen (Part of this is that plasma cells produce large quantities of antibody and then die).
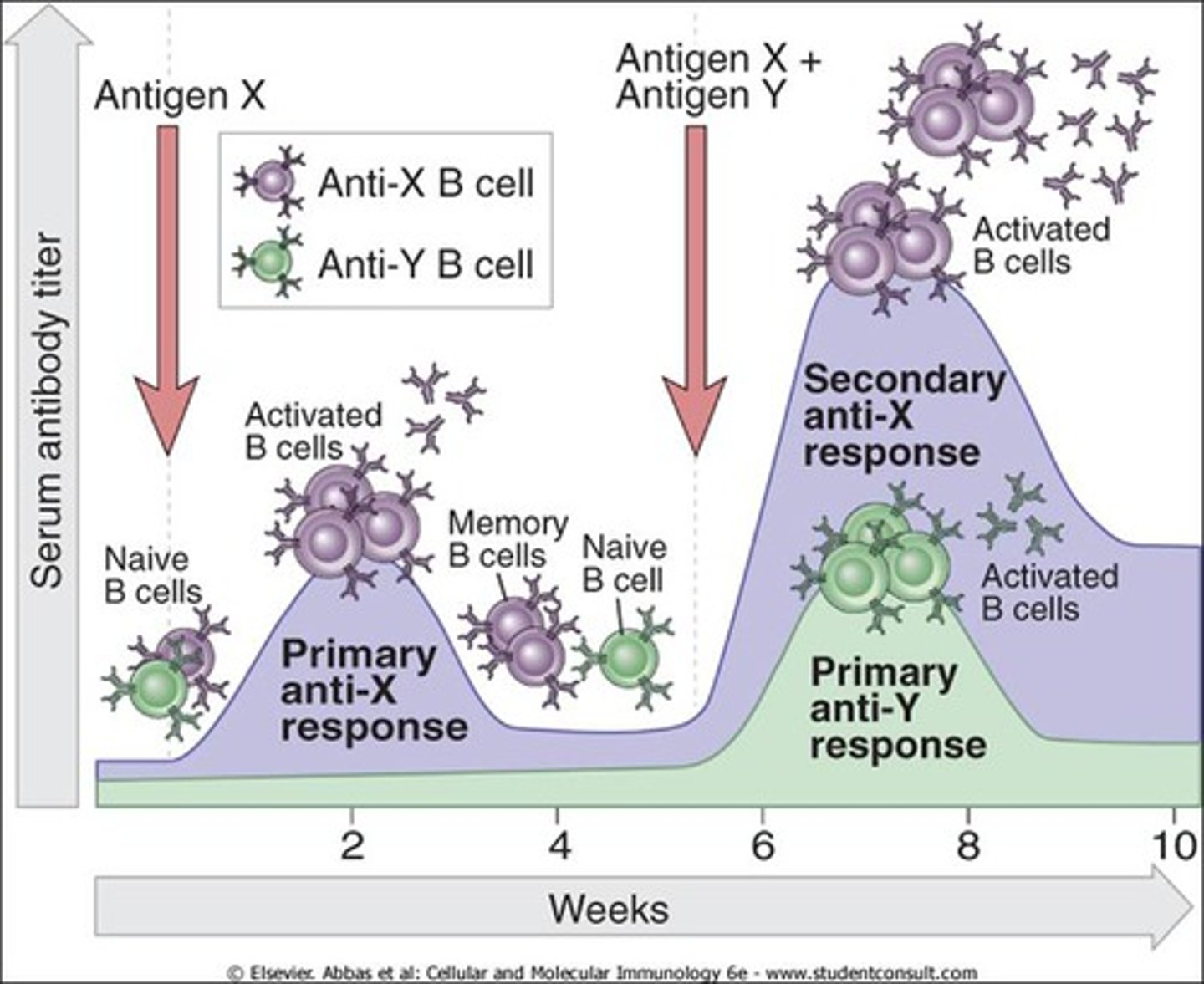
Lag phase
5 to 7 days before antibody titer starts to rise; IgM first to be produced (small quantities/short period of time). Next, IgG is produced.
Adaptive or acquired immunity or adaptive immune response (3rd line of defense)
the augmentation of body defense mechanisms in response to a specific stimulus, which can cause the elimination of microorganisms and recovery from disease. Response leaves host with a specific memory (acquired resistance). Organized around T and B lymphocytes
Antigen recognition
First step in specific immune response
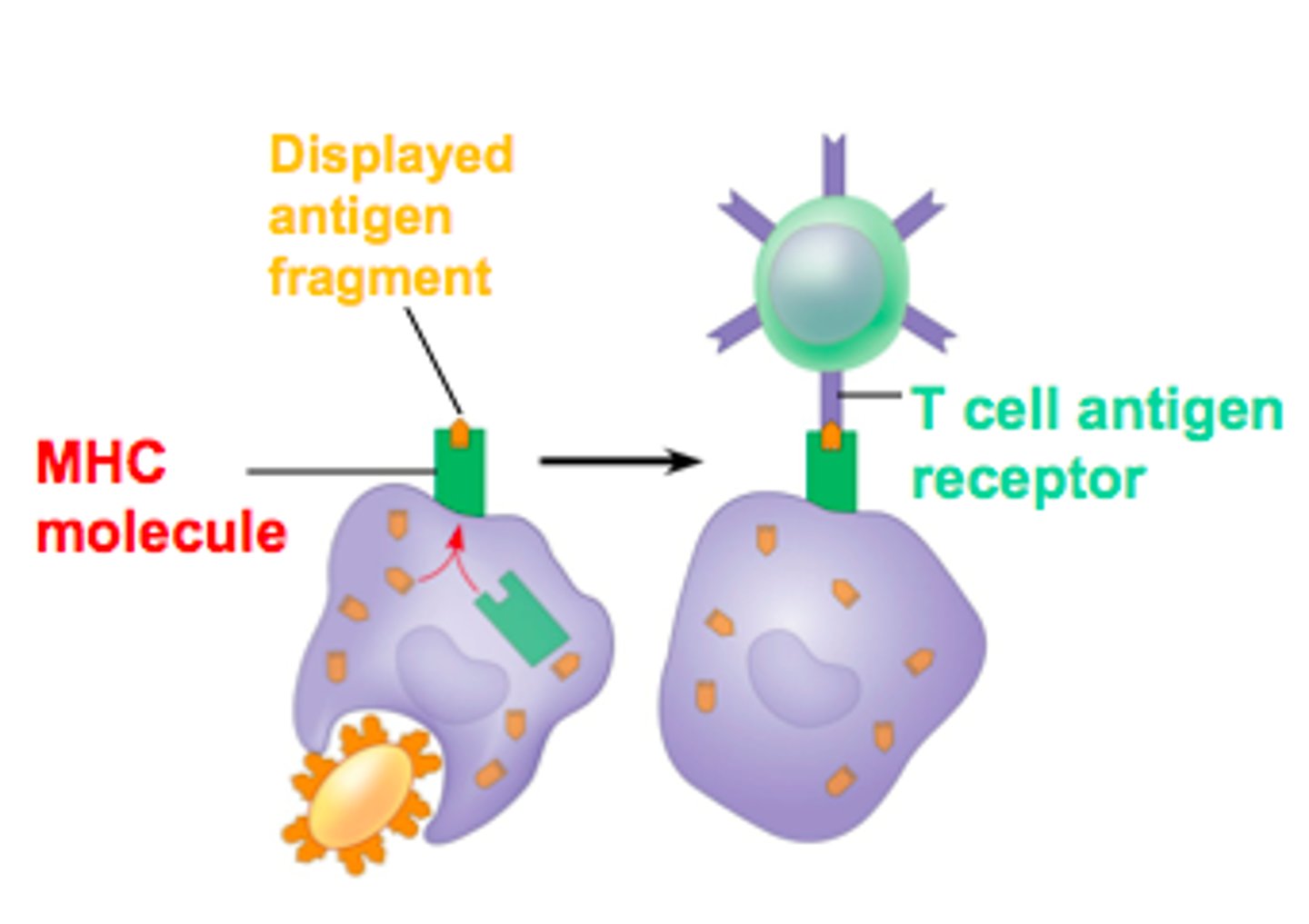
T and B cells
recognize different antigen forms; every B or T is preprogrammed to recognize ONLY ONE antigen
Memory cells
antigen-stimulated B cells; can be stimulated to rapidly produce large quantities of antibodies when later exposed to the same antigens. Perhaps known as memory cells.
Activation
aka blast transformation. Conversion of a B lymphocyte into a plasma cell. Cell enlarges and produces DNA; nucleoli become visible; clone is produced. Effector cells are differentiate into producing antibody (B cells) or cytokines (T cells).
Secondary Response (anamnestic or memory response)
the increased production of antibodies after the second exposure to the antigen (e.g. a booster shot of a vaccine). Rapid, mostly IgG, and has a higher titer. This response persists for a LONG time.
Function of the immune system
1) differentiate between self and non-self
2) destroy that which is non-self
Non-specific immune response
aka the innate response
Innate response qualities
1) always there
2) not changed by repeated exposure
3) the same response to any challenge
4) includes species immunity, the skin and mucous membranes, and inflammation
First line of defense
non-specific; skin and mucous membranes
antigen
aka immunogen; organic substance (usually protein) that is large enough to stimulate an immune response
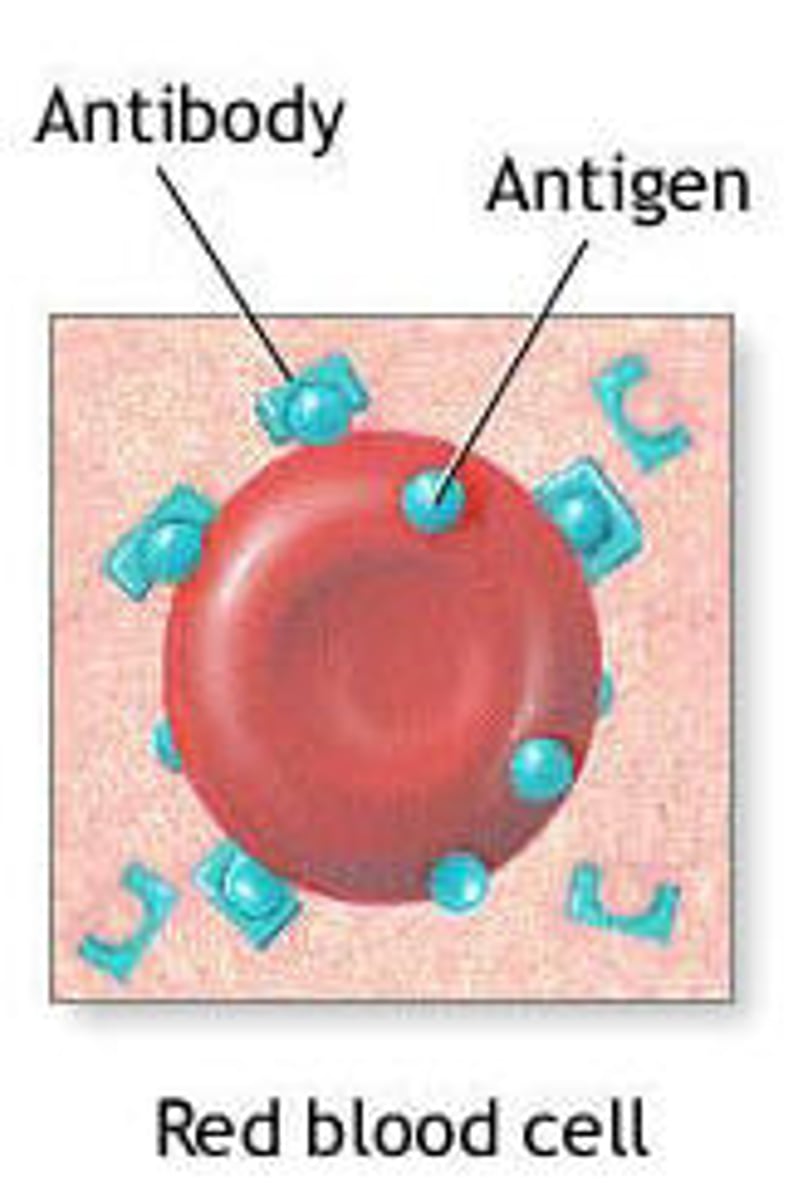
Foreign antigens
Our immune system is programmed to react only to foreign antigens
Antibody production
Produced by B lymphocytes (plasma cells) in response to a foreign antigen
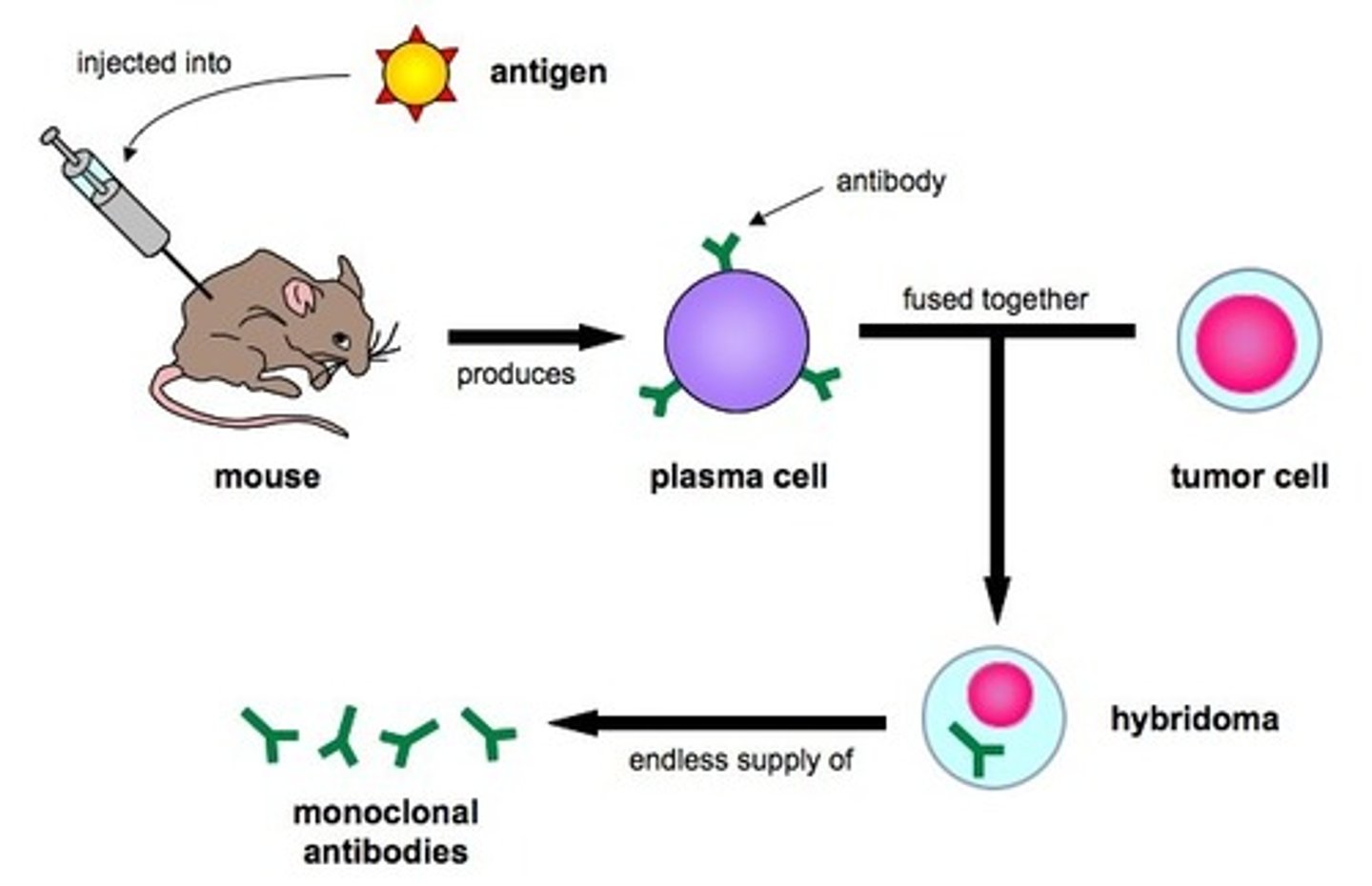
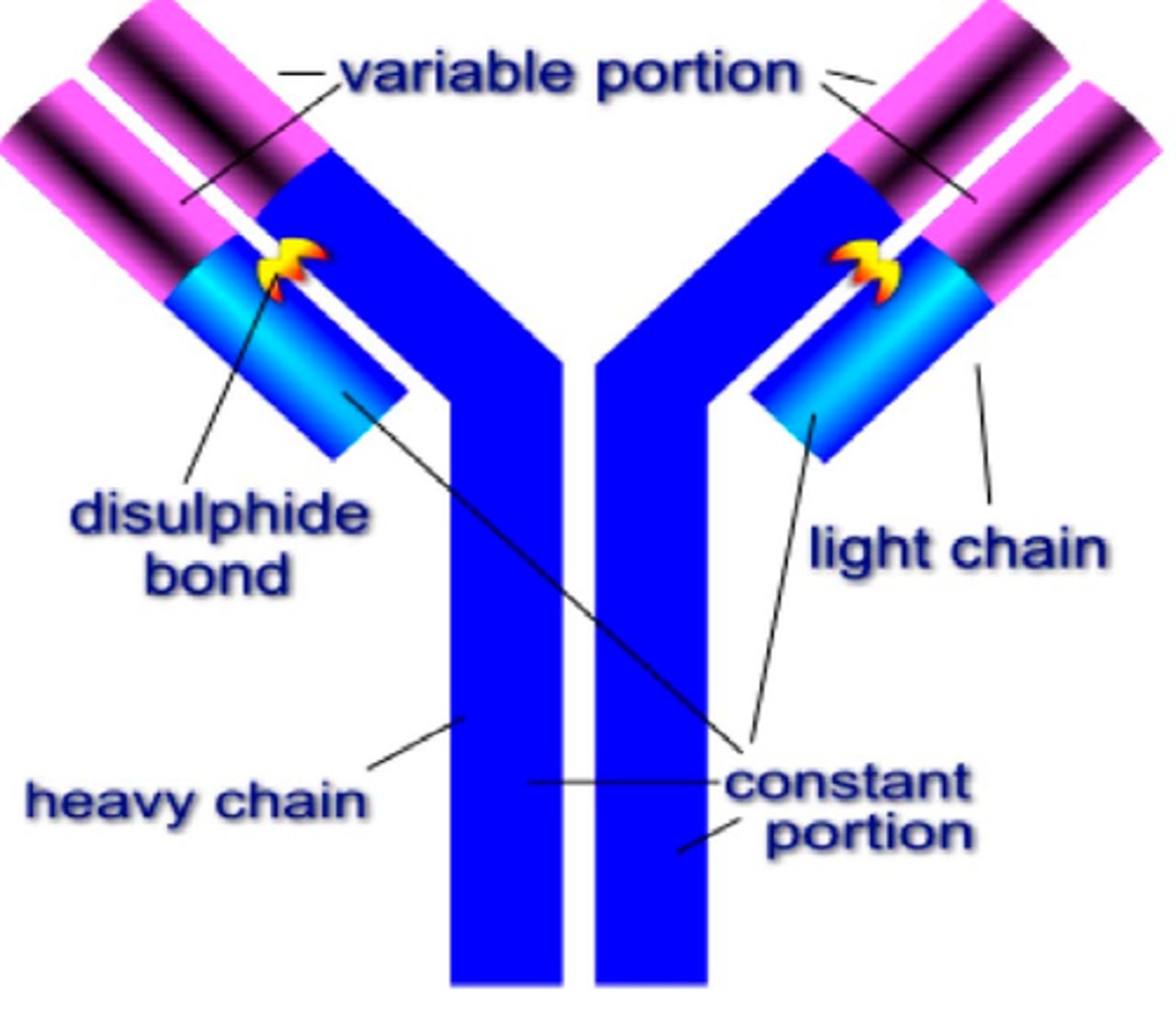
Antibodies
1) specific that they recognize and bind only to the antigen that stimulated their production
2) neutralize toxins
3) kill microbes
4) combine with antigens on cellular surfaces
5) promote the destruction of those cells by activating complement (opsonization)
5) can't go in a cell
***Immunoglobulines are antibodies!!!
Major histocompatibility complex
Group of glycoproteins that identifies cells as a part of the body
Senescent cell
Cell that cannot divide again but may still remain functioning; old or dead cells

Neoplastic cells
aka malignant or cancerous cells
Inflammation
A reaction to injury or infection that is characterized by pain, redness, heat, and swelling
Phagocytosis process step 1
1) chemotaxis 2) attachment 3) ingestion 4) digestion
Mononuclear Phagocyte System
Macrophages differentiate into differently named cells based on their location in the body; made up of phagocytic cells found throughout the body
Neutrophils
aka PMNs
1) aggressive phagocytic cell-most often involved in inflammation
2) usually die in the process of phagocytosis
3) During phagocytosis release substances from their granules that kill pathogen
4) Effective against bacteria and fungi in particular
Immunology is defined as the study of molecules, cells, organs, and systems.
True or False?
True
Immunology is defined as the system responsible for the recognition and disposal of foreign (nonself) material.
True or False?
True
Immunology is defined as the desirable and undesirable consequences of immune interactions.
True or False?
True
Immunology is defined as the relationship among cells during embryonic development.
True or False?
False
The "father" of immunology is generally considered to be:
A. Koch.
B. Pasteur.
C. Gram.
D. Salk.
B. Pasteur
A specific function of the immune system is to:
A. Recognize self from nonself.
B. Defend the body against nonself.
C. Amplify specific functions.
D. Both a and b.
D. Both a & b.
The first line of defense against infection is:
A. Unbroken skin or mucous membranes.
B. Phagocytosis.
C. Antibody production.
D. Antigen recognition.
A. Unbroken skin and mucous membranes
A child who contracts a contagious disease from an older sibling could develop _______________ immunity against the disease.
A. natural active
B. artificial active
C. natural passive
D. artificial passive
A. natural active
Artificial passive immunity is achieved by:
A. Vaccination.
B. Contracting a disease.
C. Infusion/injection of preformed specific antibody.
D. Transfer in vivo.
C. Infusion/injection of performed specific antibody.
The innate immune system is:
A. The most ancient form of host defense.
B. Divided into two components, each with a different function.
C. Mediated by germline-encoded receptors.
D. Both a and c.
D. Both a and c.
An antigen is described as a substance that:
A. Stimulates antibody formation.
B. Has the ability to bind to an antibody.
C. Is capable of stimulating an immune response.
D. All the above.
D. All the above.
Haptens are characterized as being:
A. Able to react directly with an antibody.
B. A large molecule.
C. Antigenic when coupled to a carrier molecule.
D. A member of the lipid class of biochemicals.
C. Antigenic when coupled to a carrier module
The primary function of an antibody in body defenses is to:
A. Combine with antigen.
B. Contribute to secretions.
C. Promote phagocytosis.
D. Either a or b.
A. Combine with antigen.
Which immunoglobulin (Ig) class is the first to be manifested after antigen exposure?
A. IgM
B. IgG
C. IgD
D. IgA
A. IgM
Which immunoglobulin (Ig) class is produced in the highest concentration in a secondary (anamnestic) response?
A. IgM
B. IgG
C. IgD
D. IgE
B. IgG
IgE is an important immunoglobulin because it:
A. Mediates some types of hypersensitivity (allergic) reactions.
B. Is generally responsible for an individual's immunity to invading parasites.
C. Binds strongly to a receptor on mast cells and basophils and, with antigen, mediates the release of histamines and heparin from these cells.
D. All the above.
D. All the above.
Match the following physical characteristics of antigens with the appropriate description (A-D; use each answer only once).
A.__Foreignness
B.__Degradability
C.__Molecular weight
D.__Complexity
1.Contributes to greater effectiveness.
2.The greater the difference, the better.
3.The higher, the better.
4.Avoidance of rapid destruction is essential.
A. 2, B. 4, C. 3, D. 1
If the first line of nonspecific body defense, intact skin, is cut with a piece of glass contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus, which cellular component of the immune system quickly responds?
A. T lymphocytes
B. B lymphocytes
C. Neutrophils
D. Platelets
C. Neutrophils
Place the stages of phagocytosis in the correct sequence of occurrence.
A.Digestion and destruction
B.Chemotaxis
C.Adherence
D.Engulfment
E.Phagosome formation and fusion
B, C, D, E, A
Match the type of blood cell with the appropriate function (an answer may be used more than once).
A. __ Polymorphonuclear neutrophilic (PMN) leukocytes
B. __ Mononuclear monocytes-macrophages
C. __ Lymphocytes
D. __ Plasma cells
1.Primary phagocytic cells
2.Recognition of foreign antigen
3.Antibody-synthesizing cells
A. 1, B. 1, C. 2, D. 3
Match the type of leukocyte with the appropriate function (use each answer only once).
A. __ Neutrophil
B. __ Eosinophil
C. __ Basophil
1.Principal leukocyte associated with phagocytosis
2.High concentrations of heparin and histamine
3.Homeostatic regulator of inflammation
A. 1, B. 3, C. 2
What is the source of undifferentiated T lymphocytes?
A. Bone marrow
B. Lymph nodes
C. Liver and spleen
D. Thymus
A. Bone Marrow
Surface markers on lymphocytes can be used to:
A. Identify and count CD4+ and CD8+ cells.
B. Classify leukemic cells.
C. Monitor patients on immunotherapy.
D. All the above.
D. All the above.
Cluster designation (CD) antigens are involved in various lymphocyte functions, which can include:
A. Promotion of cell-to-cell interactions and adhesion.
B. Transduction of signals that lead to lymphocyte activation.
C. Detection of cytokine secretion.
D. Both a and b.
D. Both a and b.
When mature T lymphocytes leave the thymus, their T-cell receptors are either CD4+ or:
A. CD2+.
B. CD8+.
C. CD19+.
D. CD31+.
B. CD8+
Match the T-cell populations with the appropriate description.
A. __ Helper T type 1 (Th1)
B. __ Helper T type 2 (Th2)
C. __ Regulatory T (Treg)
1.Play a greater role in the regulation of antibody production and the release of cytokines required for B-cell differentiation
2.Responsible for cell-mediated effector mechanisms
3.Are an immunoregulatory type of Th cells
A. 2, B. 3, C. 1
Match the lymphoid organs with the approximate percentage of T lymphocytes.
A. __ Lymph nodes
B. __ Blood
C. __ Bone marrow
1.80%
2.60%
3.20%
4.10%
A. 2, B. 1, C. 4