Econ 101
1/309
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
310 Terms
marginal product of labor
the extra output you produce from hiring an extra worker
marginal revenue product
marginal product of labor * price
marginal revenue product
the extra revenue produced by hiring an additional worked
rational rule for employers
hire an additional worker if the marginal revenue product is greater than or = wage, this maximizes the business profit
labor demand curve
shows the relationship between the quantity of labor demanded by firms and the wage rate, illustrating how many workers firms are willing to hire at different wage levels. It is the same as marginal revenue product of labor, downwards sloping because of diminishing marginal product
labor demand shifters
changes in demand for your product
changes in the price of capital
scale effect
substitution effect
better management and productivity gains
Nonwage benefit, subsidies, and taxes
scale effect
when the price of capital goods declines so you can produce output at a lower cost so you will sell a larger quantity or produce at a larger scale. Leads to increases labor demand
substitution effect
when the price of capital goods declines so the demand for workers to do tasks that can be done by machines decreases
scale effect
when it dominates labor and capital are complements and demand curve shifts right
substitution effect
when it dominates labor and capital are substitutes and demand curve shifts left
rational rule for workers
work one more hour as long as the wage is at least as large as the marginal benefit of another hour of leisure.
substitution effect (workers)
says higher wages make work relatively more attractive
income effect
higher income makes leisure more attractive
price elasticity of labor supply
measures worker’s responsiveness to wages
why the market labor supply curve is upwards sloping
new people induced to enter workforce
existing workers may put in more hours
some people may switch occupations
labor supply curve shifters
changing wages in other occupations
changing the number of potential workers
changing benefits of not working
nonwage benefits, subsidies, and taxes
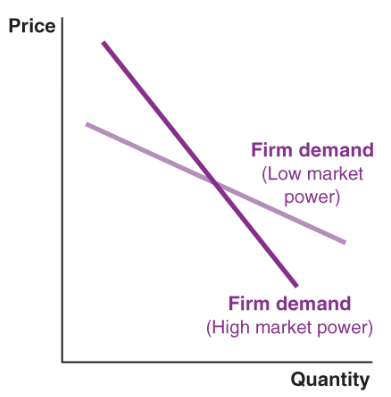
market power
the ability to raise your price without losing many sales to competing businesses
monopoly
only one seller in the market, lots of market power
oligopoly
a market dominated by a handful of large sellers , a strategic battle for market share
Monopolistic competition
product differentiation, having more competitors leads to less market power
product differentiation
making products differ from those offered by their competitors, sellers hope to make each the varieties attractive to a specific group of customers. Can be the product, shipping, or brand image. Ex: Jeans
imperfect competition facts
having more competitors leads to less market power
market power allows you to pursue independent pricing strategies
successful product differentiation gives you market power
imperfect competition among buyers gives them bargaining power
best choice depends on the actions that other businesses take
firm demand curve
how the quantity that buyers demand from your individual firm varies as you change your price
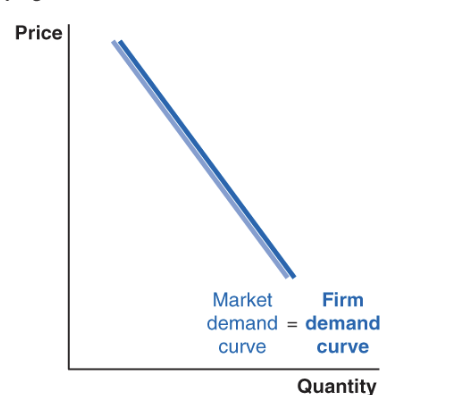
perfect competition demand curve
.
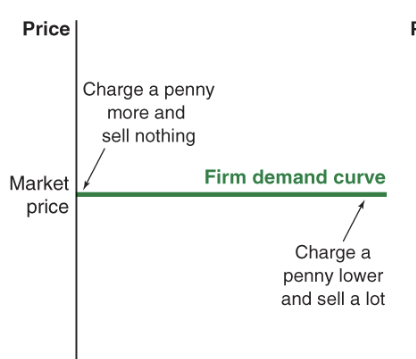
monopolistic competition and oligopoly demand curves
.
monopoly demand curve
also market demand curve
marginal revenue
change in total revenue from selling one more unit, reflect output effect -discount effect
output effect
an extra unit of output will boost revenue by an amount equal to the price of an extra item sold
discount effect
equal to the discount they need to give to sell one more item multiplied by the quantity sold that gets that price count
rational rule for sellers
sell one more unit if the marginal revenue is at least as large as the marginal cost
problems with high market power
sellers exploit mp
higher prices
inefficient smaller quantity
larger economic profits
businesses surviving inefficiently high costs
policies that ensure competition
anticollusion laws
merger laws
monopolizing is illegal
encouraging international trade
human capital
what employers look for. determines wages, accumulated knowledge and skills, education makes you more productive
education as a signal
of ability, the cost of completing a degree for those who are not hardworking is too high, degree is a signal
asymmetric information
workers signal, employers screen
an effective signal is one that is easier for the skilled worker
efficiency wage
employers pay workers more to make them more productive
compensating differential
the difference in wages required to offset the desirable or undesirable aspects of a job.
encourages people to take unpleasant jobs
depends of preferences of other workers
ex: makeup on real people vs dead people
firm
a web of contracts between input suppliers and the owners/managers of the firm
production
the process by which inputs are combined, transformed, and turned into outputs
accounting profit
total revenue - explicit financial costs
economic profit
total revenue - explicit financial costs -implicit opportunity costs
average revenue
price or revenue per unit, with more quantity fixed costs decrease but variable costs increase
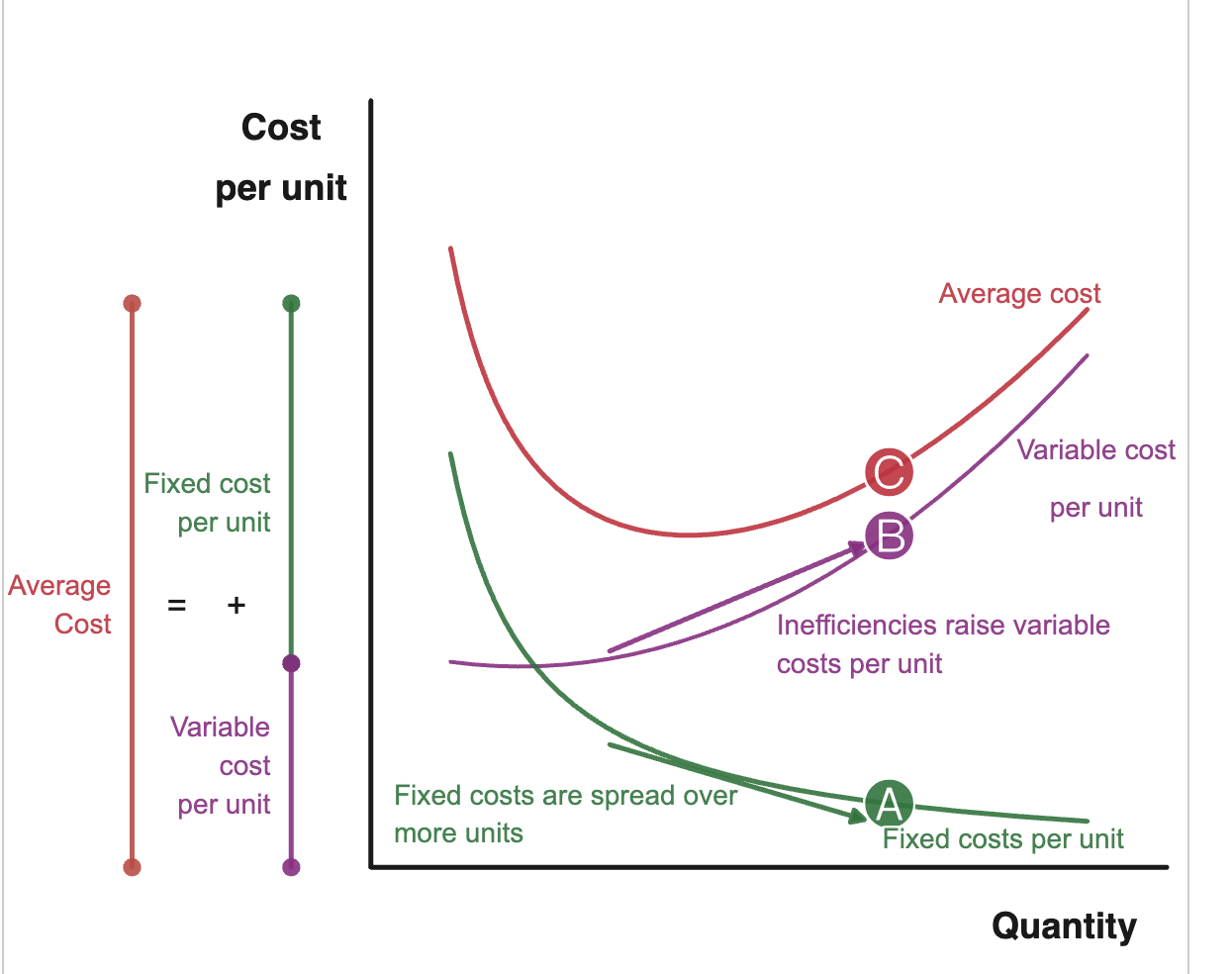
average revenue
total revenue
quantity
average revenue
fixed costs + variable costs
quantity + quantity
profit margin
price - average cost
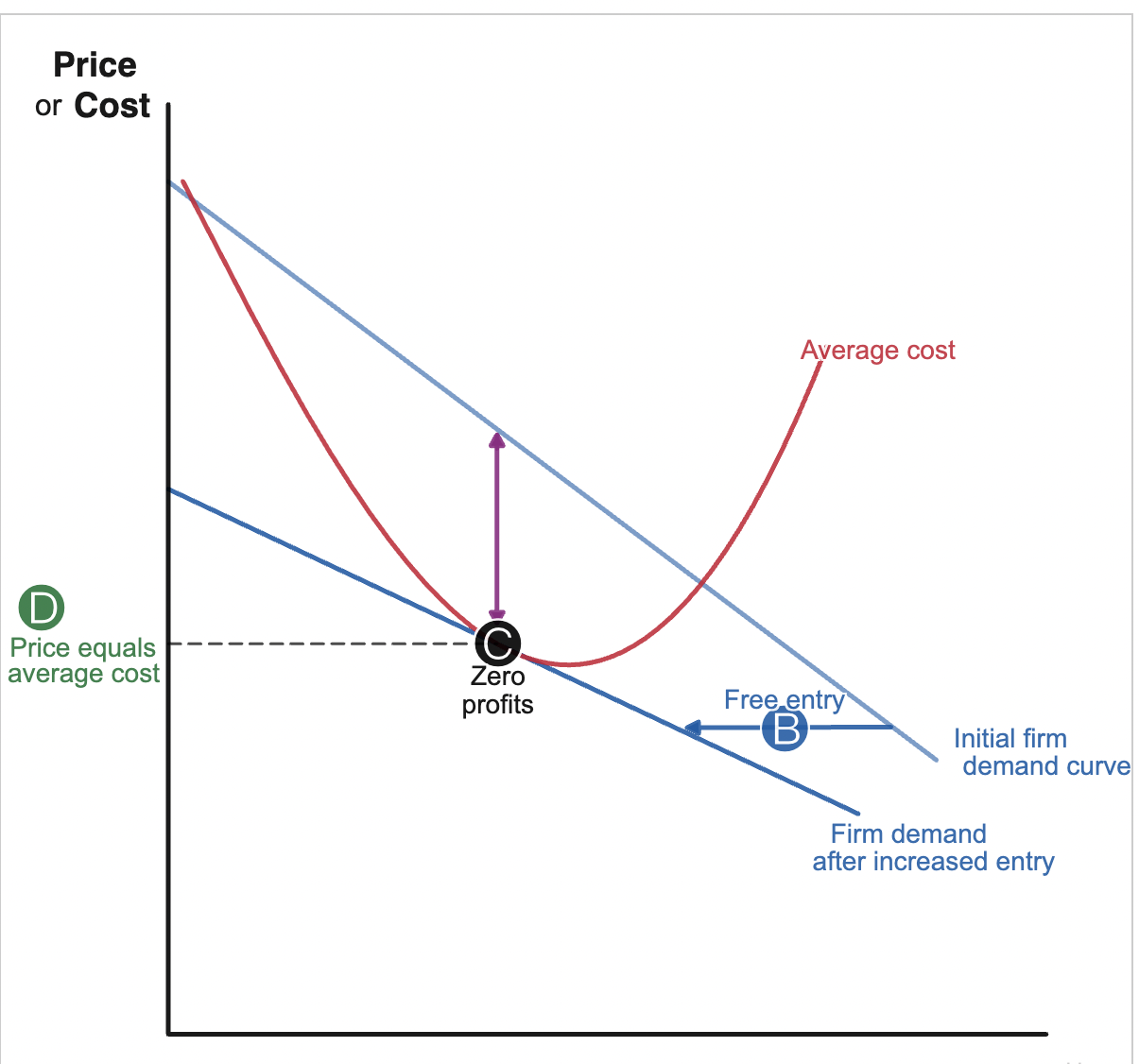
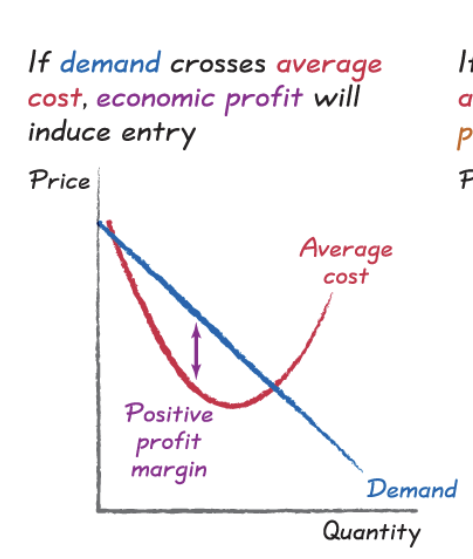
rational rule for entry
enter a new market if you expect to earn a positive economic profit, when price > average cost
new competition enters market
makes the market less profitable, leads to decreased market power, shifts demand curve for firm left, and demand curve becomes more elastic so flatter curve
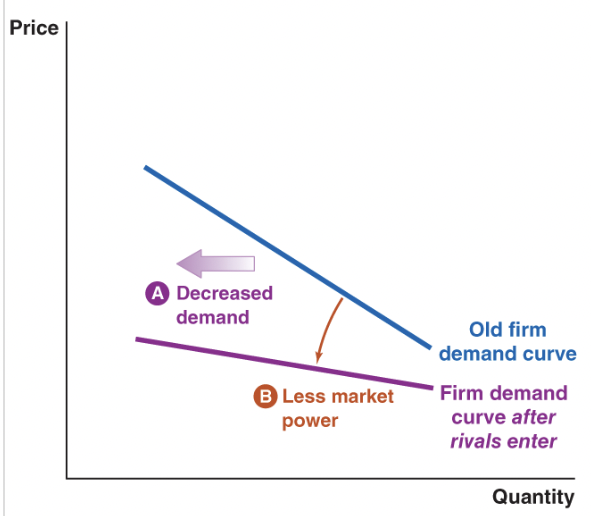
competition exits market
makes the market more profitable, increases demand, more inelastic , increased market power
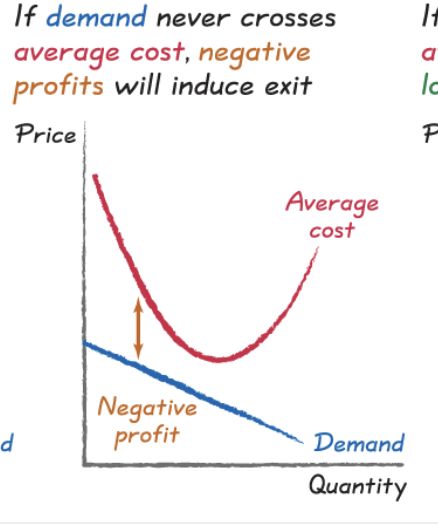
rational rule for exit
exit a market if you expect to earn a negative economic profit, when price < average cost
free entry
no factors making it particularly difficult or costly for a new business to enter the market, pushes economic profits down to zero in the long run, pushes price down toward average cost
free exit
no factors making it particularly difficult or costly for a new business to exit the market, ensure the market won’t remain unprofitable in the long run, pushes price up towards average cost
zero profits
.
positive profits
.
negative profits
.
barriers to entry
obstacles that make it more difficult for new suppliers to enter the market
demand side strategies
supply side strategies
regulatory strategies
entry deterrence strategies
demand side strategies
create customer lock in, use switching costs, earn goodwill from customers to keep customers loyal, develop network effects
switching costs
any immediate thing that makes it difficult or costly for your customers to buy from another business instead.
supply side strategies
develop unique cost advantages through experience, mass production, research and development, relationships with input suppliers, limit key inputs
regulatory strategies
enlist government policies to prevent entry, patents, government licenses,
entry deterrence strategies
to scare off potential rivals, convince rivals that if they enter the markets that you will crush them, need to build excess capacity, have financial resources, brand proliferation, have a reputation for fighting
overcoming barriers for entry
demand side strategies to combat customer lock in, supply side strategies to combat cost disadvantages, use regulatory strategies to secure government help, overcome deterrence strategies to fight bad guys
competitive merger
creates more fearsome competition, bad for rivals, could be good for consumers
noncompetitive merger
reduces competition, good for rivals, bad for consumers
natural monopoly
an industry that realizes such large economies of scale in producing its product that single firm production of that good or service is most efficient. Ex: utilities
natural monopoly solutions
government provides goods: set price = marginal cost, tax revenue pays for losses
let private sector supply: price = average cost
price discrimination
the strategy of selling the same product at different prices
reservation price
the maximum price that a customer will pay
perfect price discrimination
when you charge each customer their reservation price. leads to
charging highest possible price
make every possible sale
redistributes economic surplus from buyers to sellers,
efficiency of price discrimination
increase the quantity sold, helps solve underproduction problem, reduces discount effect the more accurate the discrimination is
price discrimination requirements
market power
ways to prevent resale
need to target the right prices to the right customers
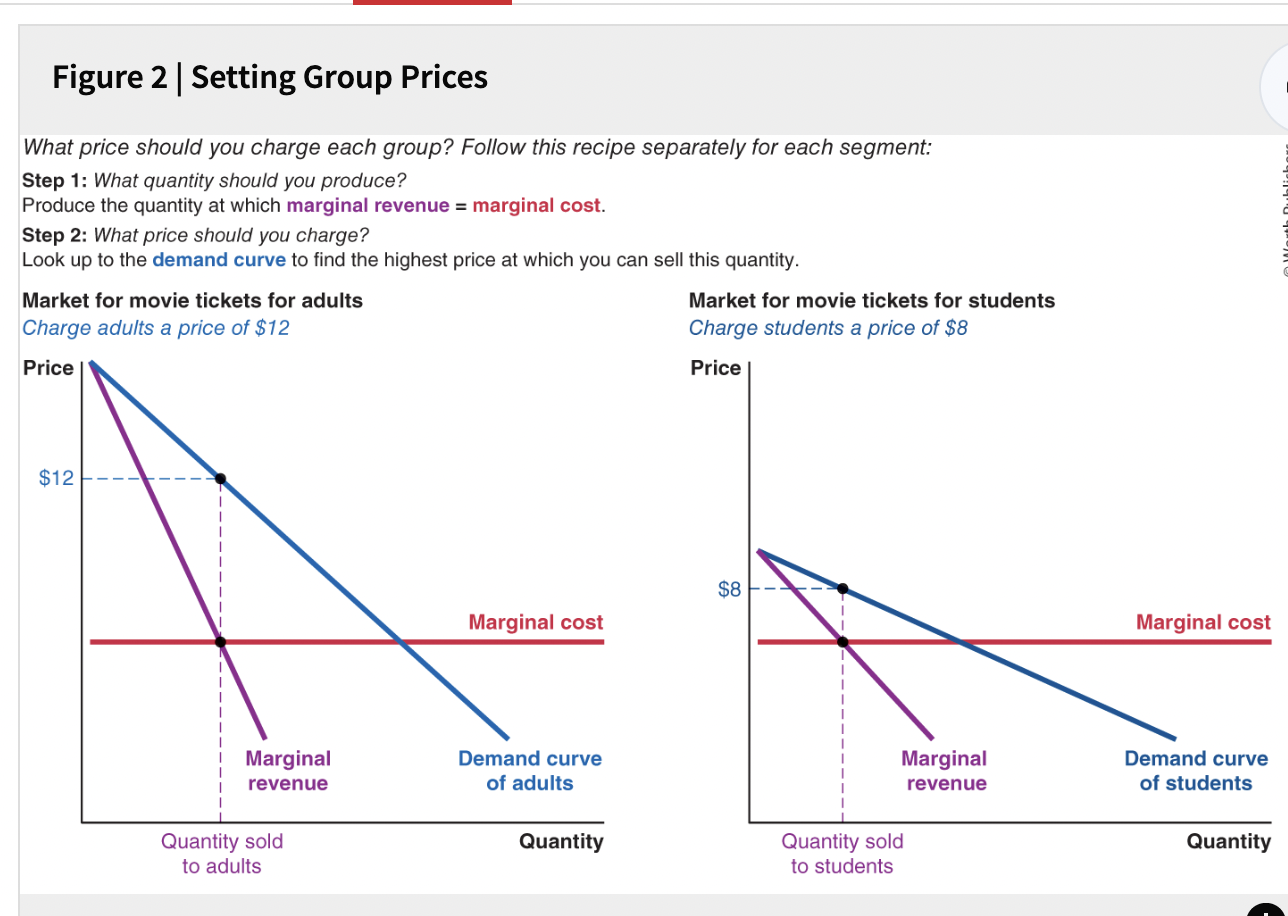
group pricing
charging different prices to different segments of people ex: student discounts
charge a higher price to groups that value your product more
charge a lower price to groups that are price sensitive
segmenting your market
segment your market into groups whose demand differs
target your group discounts based on verifiable characteristics
base group discounts on difficult to change characteristics
hurdle method
offer lower prices only to those buyers who are willing to overcome some obstacle. Induces customers to sort themselves into groups
hurdles
timing, fluctuating prices, haggling and coupons are this
quantity discount
the per unit price is lower when you buy a larger quantity
bundling
selling different goods together as a package also a hurdle
setting group prices
.
types of barriers to entry
government franchising, regulations, licensing
patents
economies of scale or other cost advantages
ownership of a scarce factor of production
network effects and switching costs
game theory
the science of making good decisions in situations involving strategic interactions
strategic interactions
when your best choice may depend on what others choose, and their best choice may depend on what you choose, comes from interdependence principle
thinking strategically
consider all possible outcomes
consider whatifs separately
evaluate your best response
put yourself in someone else’s shoes
best response
the choice that yields the highest payoff given the other players choice
nash equilibrium
occurs when you both choose your best response
correct expectations
each player’ expectation about what the other player chooses is correct
multiple equilibria
when there is more than one equilbrium
coordination game
both of the players are better off if they coordinate their choices
anticoordination game
when your best choice is to take a different action to the other player
solving coordination problems
communication
focal points,culture, and norms
laws and regulations
focal points
a cue from an outside game that helps you coordinate a specific equilibrium
simultaneous games
choosing at same time, you choose without knowing the other persons choice
first mover advantage
the strategic gain from an anticipatory action that can force a rival to respond less aggressively, occurs when you commit to being aggressive
second mover advantage
about the benefits of flexibility, the strategic advantage that can follow from an action that adapts to your rivals choice
collusion
an agreement by rivals to limit competition with each other
one shot game
strategic interaction that occurs only once
repeated game
when you face the same strategic interaction with the same rivals and the same payoffs in successive periods
finitely repeated game
when you face the same strategic interaction a fixed number of times indefinitely
repeated game
when you face the same strategic interaction an unknown number of times
grimm trigger strategy
if the other players have cooperated in all previous rounds, you will also cooperate. If any player has defected in the past you will defect
statutory burden
the burden of being assigned by the government the responsibility of sending a tax payment
economic burden
the burden created by the change in after tax price faced by buyers and sellers as a result of the tax. It doesn’t matter who the tax is levied on it has the same effect.