Mouse Genetics part 1 - 4
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
goals: Mendelian inheritance, generation of inbred strains in mice, identify the different methologies to create transgenic animals, tools to regulate transgene expression
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Genotype
an individuals genetic constitution
Phenotype
what is observed physically or clinically
Gene
a section of DNA that encodes for a certain trait
Autosomal gene
a gene located on one of the non-sex chromosomes
Allele
a varient form of a gene
each autosomal gene has two alleles
Homozygous
the two alleles for a gene are the same
Heterozygous
the two alleles for a gene are different
Hemizygous
an allele for a gene is present in only a single copy in an otherwise diploid organism
Dominant allele
an allele that always appears phenotypically
Recessive allele
must carry two recessive alleles in order for phenotype to show
Mendelian Genetics
in 1866, Gregor Mendel deduced several important genetic principles from his well-designed experiments with garden peas, that would lay the foundation for the discipline of genetics
Punnett square
parental genotype on the outside of the box, potential genotypes of offspring inside the box
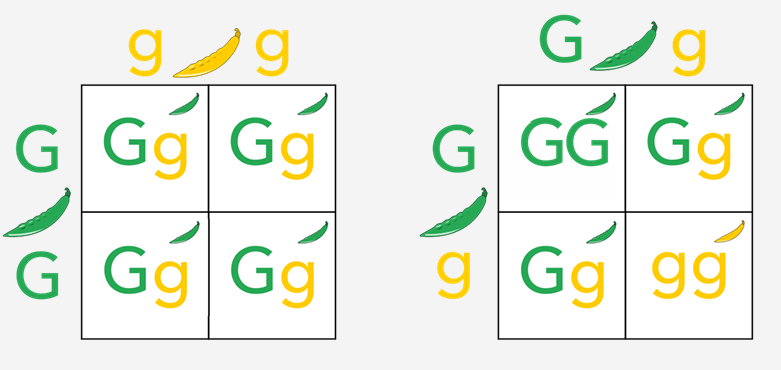
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
a way a trait or genetic condition is passed down from one generation to the next, where only one copy of a mutated gene from either parent is enough to cause the condition in the offspring
if one parent carries a dominant gene mutation, each child has a 50% chance of inheriting the condition
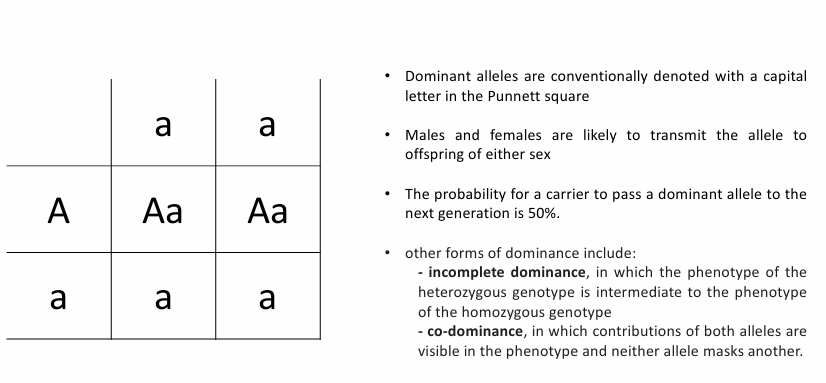
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
the risk for two carrier parents to produce offspring with two aa alleles is 25%
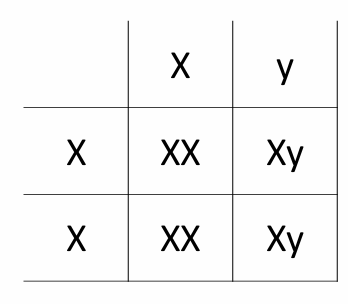
Sex linked inheritance
X-linked inheritance: for alleles located on the X chromosome, males with mutations on the X never transmit to their son, but always to their daughter
Y-linked inheritance: for alleles located only on the Y chromosome. only segregates in males
Abbie Lathrop
created many of the common inbred lines important to mouse geneticists today - including C57BL/6
William Castle
brought the fancy mouse into his laboratory in 1902, and began the development of innbred genetically homogeneous lines of mice
Why are mice ideal for genetic analysis
small, short generation time, breed prolifically, docile, males do not harm their young, vaginal plug, pseudopregnancy
Inbred mating
defined as colonies produced by a minimum of 20 generations of brother-sister mating, traceable to a single founding pair
results in animals that are genetically identical (homozygous across their entire genome) within each inbred strain (free of genetic variants that could increase variation in experimental results)
easily available
results are very consistent across time and the world
Specific inbred mice strains
C57BL/6J has the Nnt mutation, which modulates metabolism and immune response
C57BL/6J and C57BL/6N vary in their fear responses and how anesthetics affect their cardiac functions
C57BL/6N mice and embryonic stem cells derived from them harbor the Rd8 mutation of the Crb1 gene, which causes developmental defects in photoreceptor segments
Incrosses
a cross between two animals of the same inbred strain
serves primarily for maintaining strains of animals that are inbred or carry particular alleles of interest
Outcrosses
a cross between two animals from different inbred strains
resulting offspring are called F1
many experiments start with an outcross, in which at least one animal is carrying a mutation of interest
Intercross
a cross between two animals that have the same heterozygous genotype at a designated loci
a cross between sibling F1 hybrids (Aa) that were derived from an outcross
Backcross
a cross of a hybrid animal with one of the two parental strains
number of backcrosses are denoted as N
Wild-Type mice
“Normal” mice of a given strain. often referred as allele “+”
Transgenic mice
genetically modified mice that have a transgene introduced to their genome
Knockout mice
a type of transgenic mice in which a gene is functionally inactivated by deleting or silencing it
help to understand the function of specific genes in an organism by blocking the expression of a gene
issues: large delay due to backcrossing to a pure strain
Knockin mice
a type of transgenic mice in which a gene is inserted into a specific locus in the genome
allows the creation of mutants that mimic exactly human mutation (ex. single nucleotide change) to substitute mouse gene by a human one
Rosa26: locus found on chromosome 6 of the mouse genome that encodes nonessential RNA that replicates in every cell/tissue in the body that expresses it
provides a useful place for making gene insertions and studying how proteins ectopic or overexpression impact cells
ES cells
embryonic stem cells are derived from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst
Locus/Loci
specific physical location of a gene
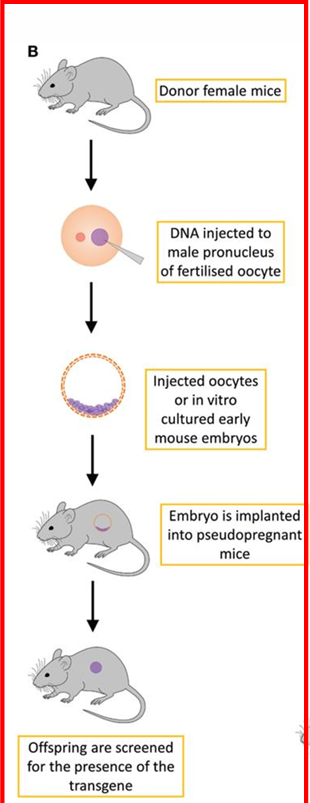
How transgenic mice are made
CRISPR/Cas9
“Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats”
one repair mechanism can lead to knock outs, whereas the second can lead to knock ins
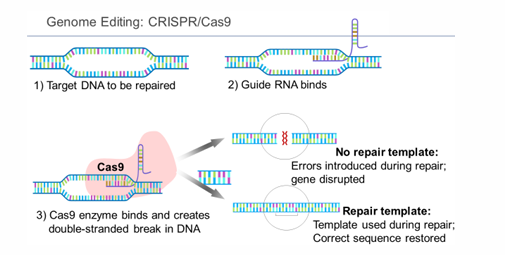
CRISPR-Cas9 vs Embryonic stem (ES) cell
CRISPR-Cas9 is faster (skip stage of breeding chimeric offspring with wild type mice) and has a higher success rate
CRE/Lox system *
used to regulate spatially and temporally the expression or the knockout of a gene (global knockout could be lethal)
system allows generate tissue-specific and inducible knockouts to have control over the location and timing of gene expression
CreER/Tamoxifen system
Tamoxifen is an estrogen analog that binds to estrogen receptors
in order to control WHEN the Cre enzyme will function, the Cre protein can be used with a modified estrogen receptor, that gets activated when bound with tamoxifen, and in turn activates the Cre protein (by moving it to the cell nucleus)