Aromatic Compounds- Benzene
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
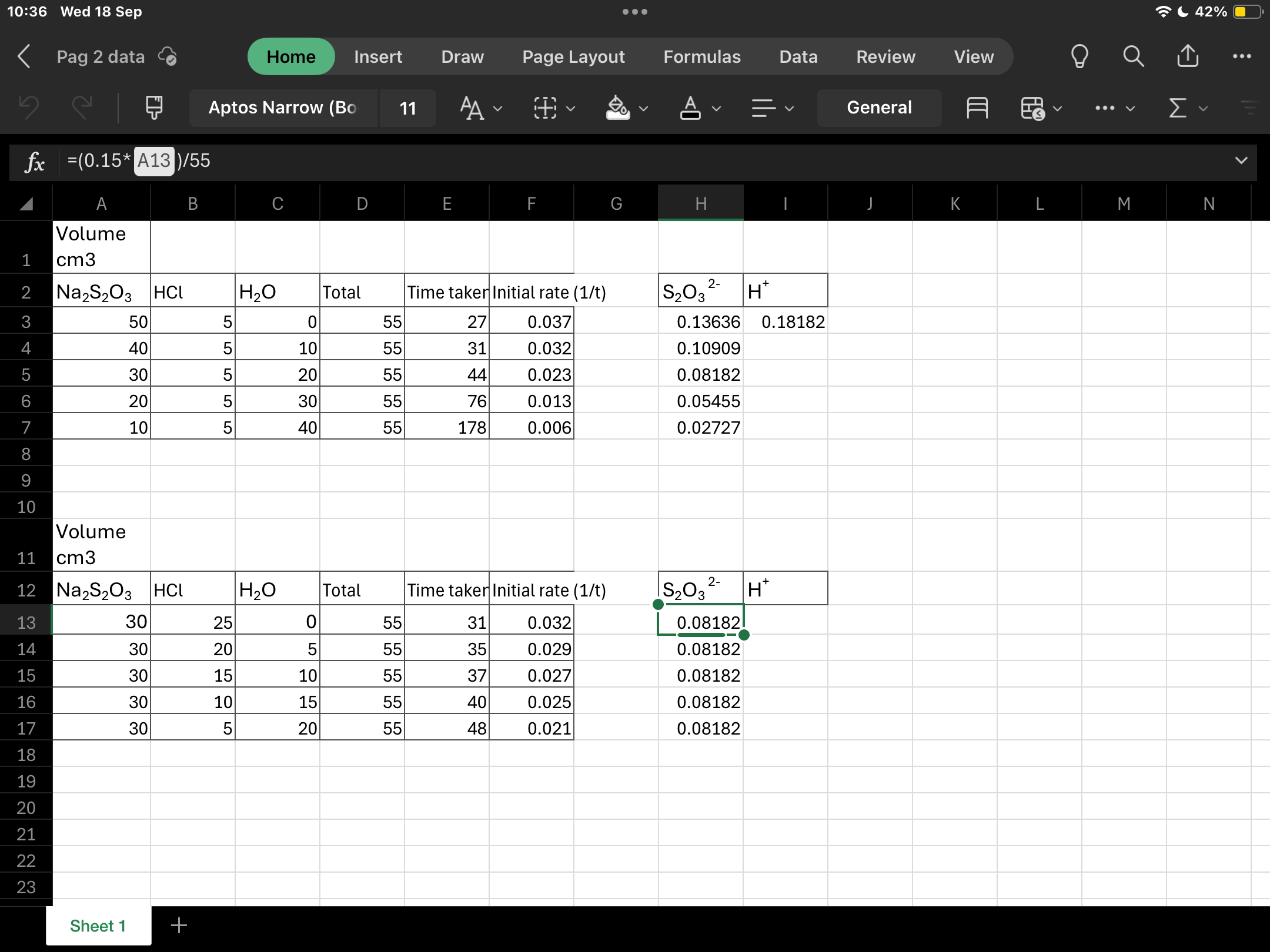
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
3 pieces of evidence to disprove kekules model
lack of reactivity, bond lengths, hydrogenation enthalpies
Lack of reactivity theory
If benzene had c=c bonds it would decolourise bromine in an Electrophilic addition reaction but actually benzene doesn’t tunderogo EA and doesn’t decolourise bromine water under normal conditions
Bond length theory
Used a x ray diffraction to measure bond lengths- found that all were 0.139nm in length= between the lengths of a single and double bond (0.153nm and 0.134 nm)
Hydrogenation enthalpy es theory
Kekules structure is expected to have enthalpy change of hydrogenation that is 3x that of cyclohexene= -360kj mol but actual enthalpy is -208 therefore is 153 less than expected meaning the actually structure is more stable
Replacement for kekules structure
Delocalised model of benzene
Delocalised model of benzene
Benzene is planar, cyclic, hexagonal hydrocarbon with 6 carbon and 6 hydrogen atoms
Bonding in delocalised model
Each carbon atom uses ¾ electrons in bndonign to 2 other carbon atoms and a hydrogen atom- last electron is in a p orbital above and below the plane of the carbon and hydrogen bond
How is the delocalised pi system formed
Adjacent p orbitals overlap sideways above and below the plane to create a ring of electron density, overallping creates a system of pi bonds which spread over the 6 carbons in the ring structure= delocalised pi system
Nitration of benzene word equation
Benzene + nitro acid → nitrobenzene
Conditions and reagents needed for nitration of benzene
Conc HNO3, conc H2SO4, 50deg c
What is nitrobenzene used for
Feedstock for dyes, pharmaceuticals + pesticides
What kind of reaction is nitration of benzene
Electrophilic substitution
Electrophilic in nitration of benzene
NO2+, nitronium ion
How is the electron pile produced
HNO3 + H2SO4 → NO2+ + HSO4- + H2O
How does nitration of benzene occur
NO2+ accepts pair of electrons from benzen ring to form dative covalent bond. Organic intermediate formed is unstable and breaks down to form nitrobenzene and a H+ ion, stable benzene ring is reformed
How is the H2SO4 catalyst regenerated
H+ ion reacts with HSO4- ion from step 1 to regenerate H2SO4
What is the catalyst needed for halogenation of benzene
Halogen carrier
Examples of halogen carriers
AlCl3, FeCl3, FeBr3
Reactants and conditions for bromination of benzene
Room temperature and pressure, halogen carrier
What kind of reaction is bromiantion of benzene
Electrophilic substitution
Equation for bromination of benzene
Benzene + Bromine → bromobenzene + HBr
What is the Electrophile used in bromination of benzene
Br+
How is Br+ generated
When the halogen carrier reacts with bromine in the first stage of the reaction
Step 1 bromiantion of benzene
Br2+ FeBr → FeBr4- + Br+
Step 2 bromiantion of benzene
bromonium ion accepts pair of electron form the benzen ring to form a dative covalent bond. Organic intermediate is unstable and breaks down to form bromobenze and a H+ ion
How is the FeBr3 catalyst regenerated
H+ + FeBr4- → FeBr3 + HBr
Chlorination of benzene
Sma e as bromine
Reactants and conditions for alkylation
Haloalkane, AlCl3
Reactants and conditions for acylation of benzene
AlCl3
What is formed during acylation reaciotyns
An aromatic ketone
Do alkenes decolourise bromine
Yes though Electrophilic addition reactions
Why doesn’t benzene react with bromine without a halogen carrier catalyst
The delocalised pi electrons spread above and below the plan of the bonds mean the electron density around ay 2 carbon atoms in the benzene ring is less than in a c=c bond in an alkene
Is benzene polar or non polar
Non polar
What is the significance of benzene being non polar
Has insufficient electron density to polarise a bromine molecule preventing a reaction from taking place