NCSU Chem 101 Final - Lalloo
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
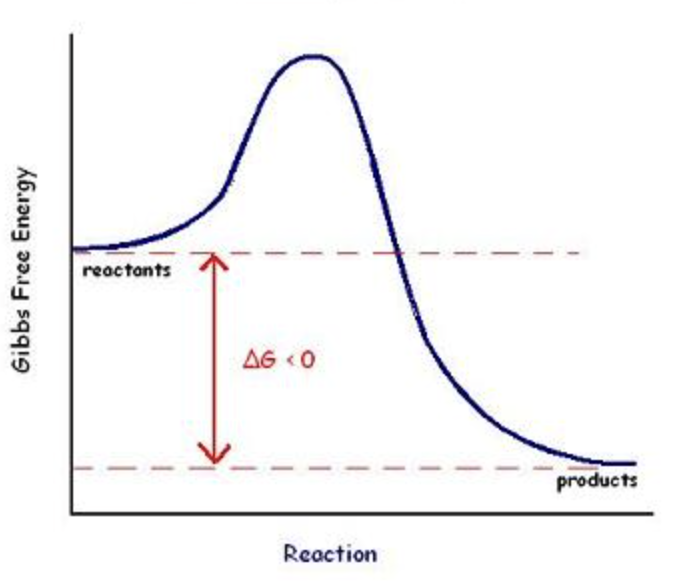
Exergonic
Spontaneous ΔG<O
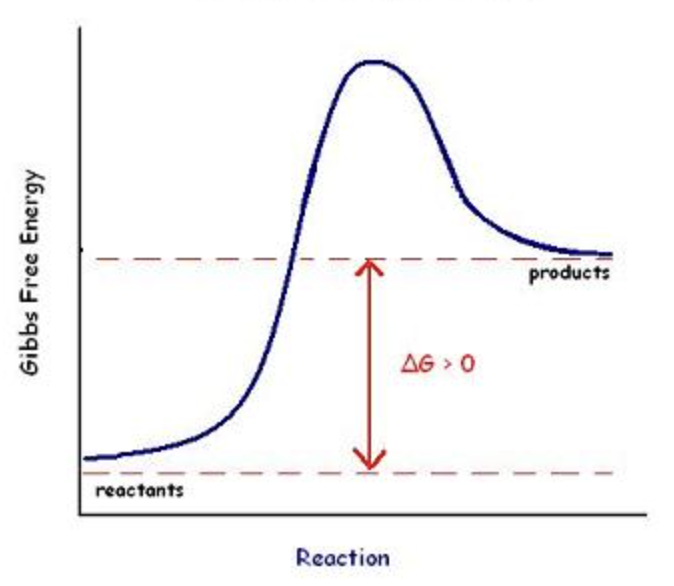
Endergonic
Not Spontaneous ΔG>0
ΔS
Entropy
ΔH
Enthalpy
ΔG>0 —> Keq?
Keq<1
ΔG<0 —> Keq?
Keq>1
ΔG~0 —> Keq?
Keq~1
Endothermic
Solid —> Liquid —> Gas
Exothermic
Solid <— Liquid <— Gas
Solid —> Liquid —> Gas (ENDO)
ΔH>0 and ΔS>0
Solid <— Liquid <— Gas (EXO)
ΔH<0 and ΔS<0
ΣBroken-ΣFormed where do I put heat if ENDO vs EXO?
ENDO - Reactant Side
EXO - Product side
Soluble if
both polar or both are nonpolar
Insoluble if
one is polar and one is nonpolar
Work done ON the system
POSITIVE (+)
Work done BY the system
NEGATIVE (-)
ABSORB heat
POSITIVE (+)
RELEASE heat
NEGATIVE (-)
Select all that are driving forces behind a process (e.g. a chemical reaction):
A. To lower the potential energy of the system
B. To raise the potential energy of the system
C. To minimize the number of ways the system can distribute its energy
D. To maximize the number of ways the system can distribute its energy
A. To lower the potential energy of the system
D. To maximize the number of ways the system can distribute its energy
Half Reactions: for oxidation put e^-
product side (M → Mn+ + ne1-)
Half Reactions: for reduction put e^-
reactant side (M^n+ + ne1- → M )
ΔG favorable?
ΔG<0
ΔH favorable?
ΔH<0
ΔS favorable?
ΔS>O
Increasing pressure shifts with _____ moles of gas
fewer
VESPR 2 LINEAR
180°
VESPR 3 TRIGONAL
120°
VESPR 4 TETRAHEDRAL
No LP: 109.5° 1+ LP: <109.5°