Principles and Techniques of Light Microscopy
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
137 Terms
Compound light microscope
Uses visible light to illuminate specimens.
Bright-field microscopy
Visualizes specimens based on contrast differences.
Phase-contrast microscopy
Enhances contrast without staining live samples.
Dark-field microscopy
Illuminates specimen from the sides, creating contrast.
Fluorescence microscopy
Visualizes specimens that emit light when illuminated.
Total magnification
Objective magnification multiplied by ocular magnification.
Maximum magnification
Light microscope can achieve ~2,000x magnification.
Resolution
Ability to distinguish two adjacent objects clearly.
Limit of resolution
Approximately 0.2 µm for light microscopes.
Contrast
Difference in light intensity between image and background.
Staining
Improves contrast by binding dyes to cellular materials.
Common stains
Examples include methylene blue, safranin, crystal violet.
Differential stains
Separate bacteria into groups based on staining properties.
Gram stain
Widely used differential stain in microbiology.
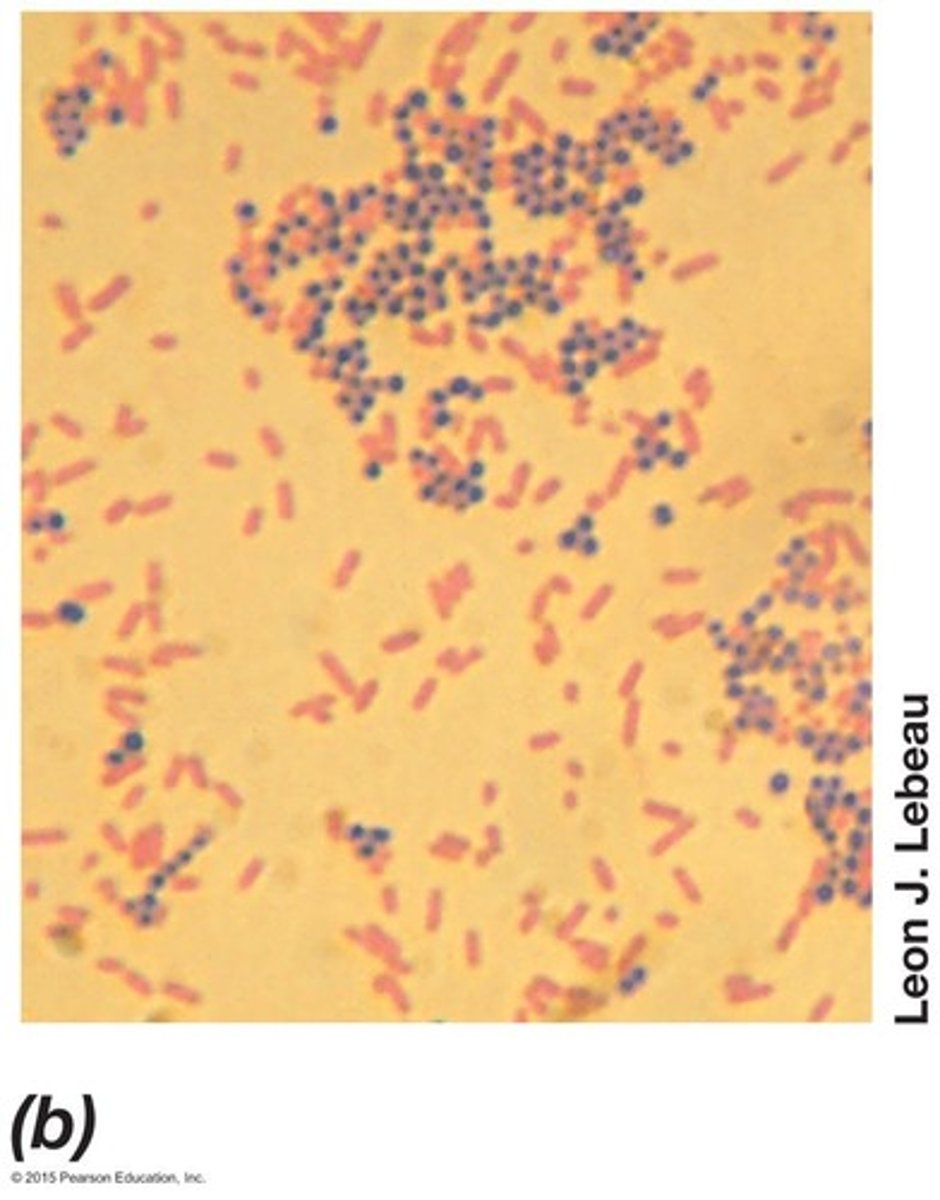
Gram-positive bacteria
Appear purple after Gram staining procedure.
Gram-negative bacteria
Appear red (pink) after Gram staining procedure.
Crystal violet
First stain used in Gram staining protocol.
Iodine solution
Used to fix crystal violet in Gram staining.
Alcohol decolorization
Differentiates Gram-positive from Gram-negative cells.
Counterstain
Safranin used to visualize Gram-negative cells.
Phase ring
Part of objective lens that amplifies refractive index.
Autofluorescence
Natural fluorescence of cells without additional staining.
DAPI
Fluorescent dye that binds to AT-rich regions.
Differential interference contrast microscopy
Uses polarized light for 3D cell imaging.
Confocal scanning laser microscopy
Generates 3D images using laser and computer.
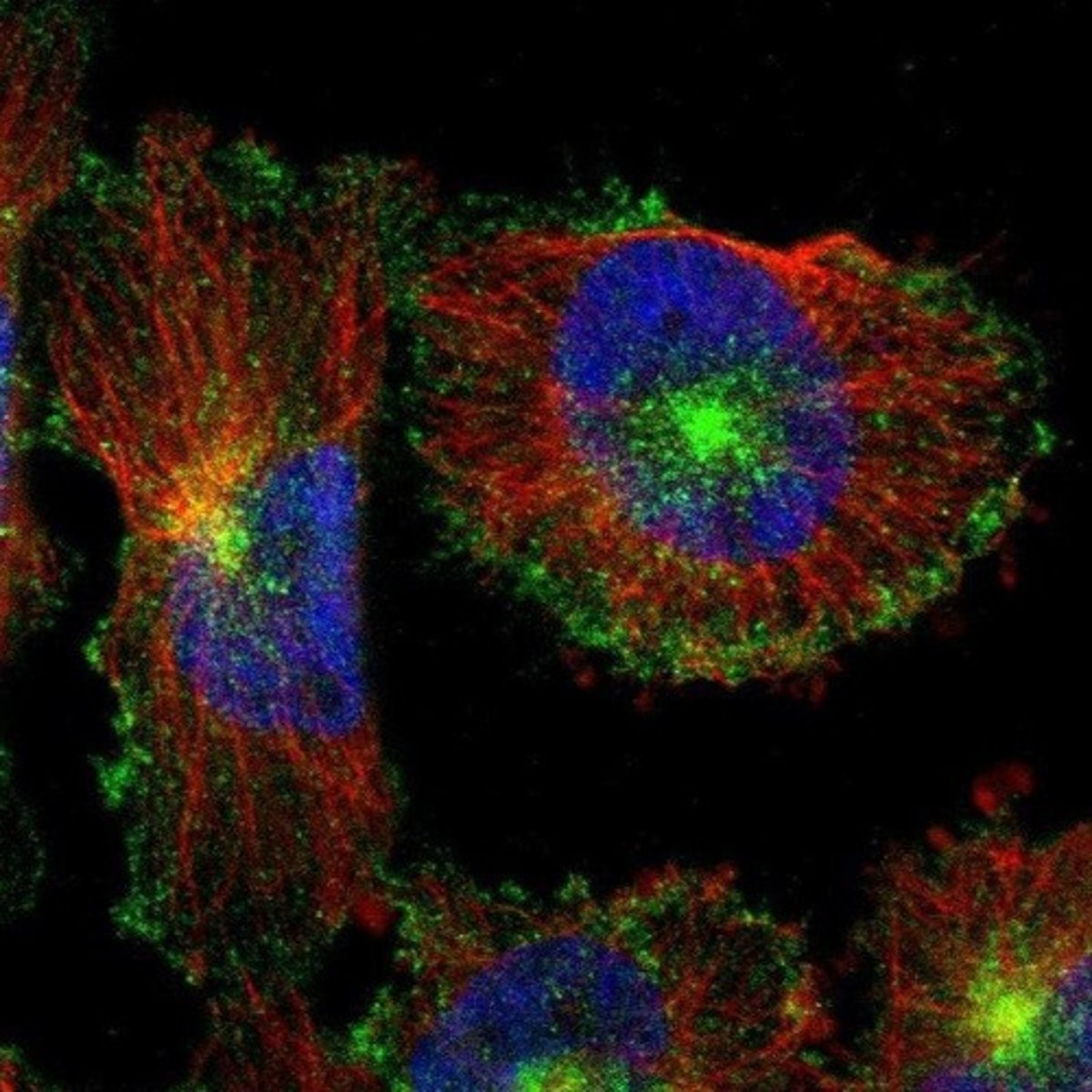
Resolution of CSLM
Achieves a resolution of 0.1 µm.
Transmission electron microscopy
Uses electrons for high-resolution imaging.
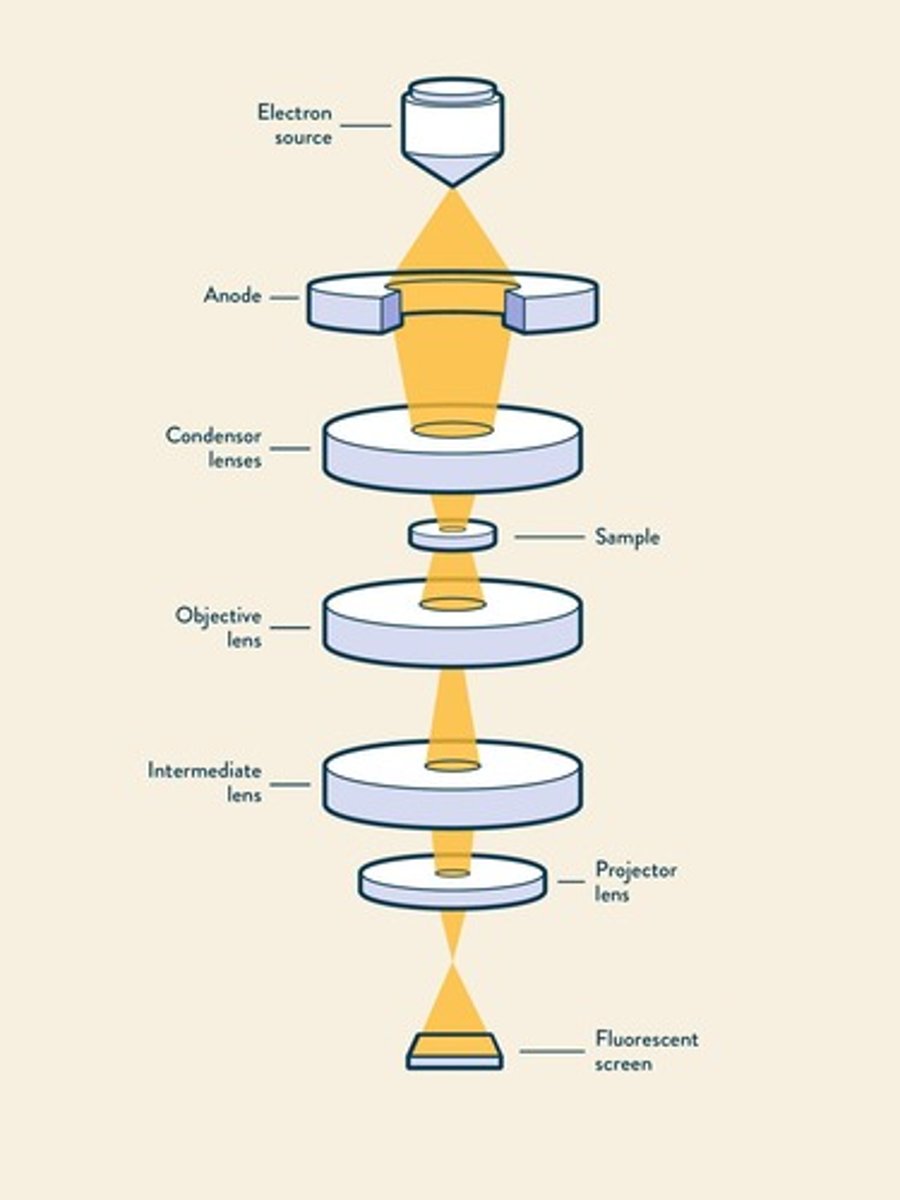
Resolution of TEM
Achieves resolution of 0.2 nm.
Scanning electron microscopy
Produces images by scanning with electron beam.
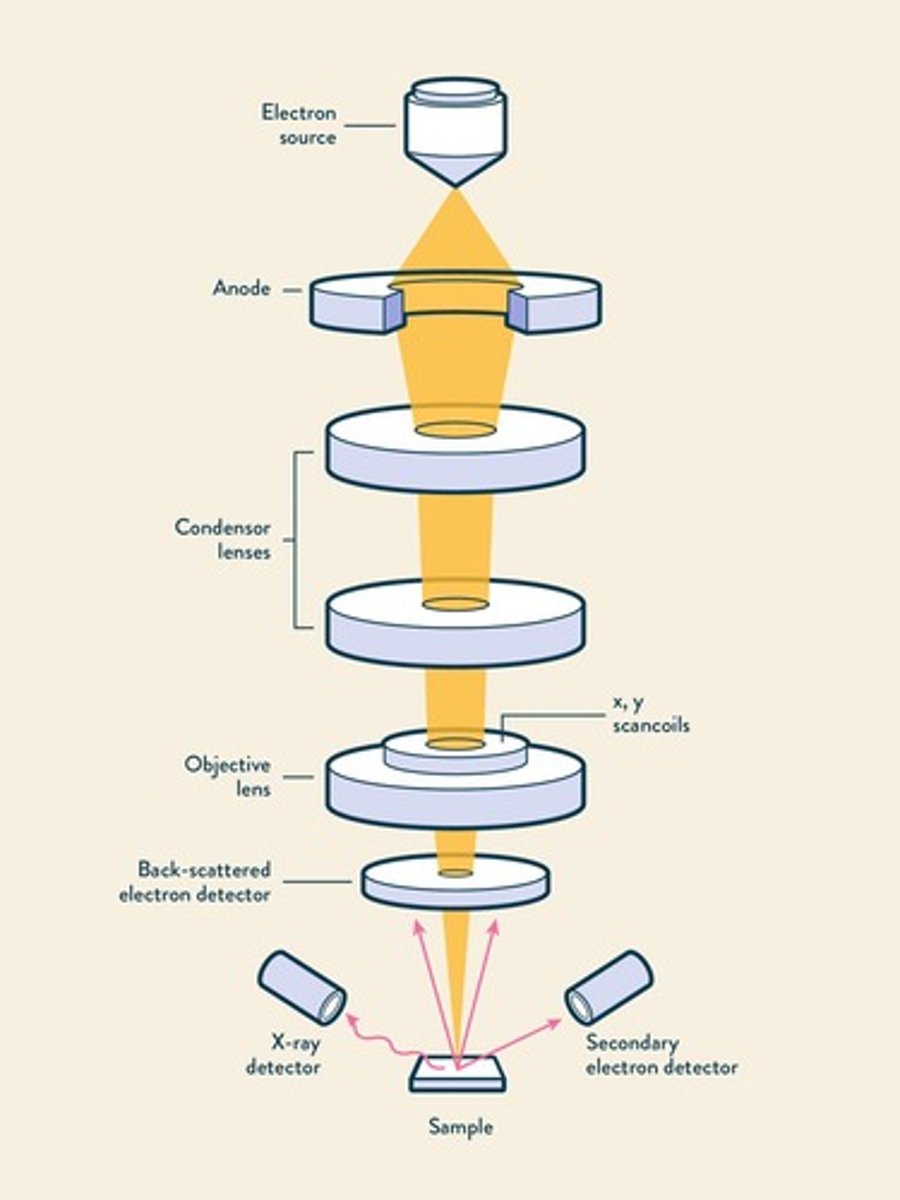
Magnification range of SEM
Magnifies specimens from 15✕ to 100,000✕.
Resolution of SEM
Achieves resolution of approximately 10 nm.
Coccus
Spherical or ovoid cell shape.
Rod (bacillus)
Cylindrical cell shape.
Spirillum
Spiral-shaped cell morphology.
Spirochete
Flexible spiral-shaped bacteria.
Filamentous bacteria
Bacteria with long, thread-like structures.
Budding bacteria
Bacteria that reproduce by budding off.
Gliding motility
Non-flagellated movement along surfaces.
Prokaryotic cell size range
Typically 0.2 µm to >700 µm in diameter.
Cultured bacillus size
0.5-4.0 µm wide and <15 µm long.
Epulopiscium fishelsoni
Large prokaryote, 600 µm long.
Thiomargarita namibiensis
Prokaryote, 400-750 µm wide.
Cell morphology
Shape of cells influencing various functions.
Selective forces on morphology
Factors influencing cell shape and function.
Optimization for nutrient uptake
Small cells enhance surface-to-volume ratio.
Surface-to-volume ratio
Higher in small cells, enhances nutrient exchange.
Nutrient exchange
Greater per unit volume in small cells.
Growth rates
Small cells typically grow faster than larger cells.
Lower limit of cell size
Cells <0.15 µm diameter are rare.
Cytoplasmic membrane
Thin barrier separating cytoplasm from environment.
Selective permeability
Membrane allows specific metabolite concentration.
Phospholipid bilayer
Basic structure of cellular membranes.
Hydrophobic fatty acids
Point inward, forming a hydrophobic environment.
Hydrophilic components
Expose to external environment or cytoplasm.
Integral membrane proteins
Firmly embedded proteins within the membrane.
Peripheral membrane proteins
Anchored proteins interacting with membrane surface.
Membrane stabilization
Mg2+ and Ca2+ stabilize phospholipid interactions.
Transport proteins
Facilitate movement of molecules across membranes.
Proton motive force
Energy source for active transport processes.
Active transport
Moves solutes against concentration gradient.
Carrier-mediated transport
Saturation effect observed in nutrient transport.
Simple diffusion
Passive movement of molecules across membranes.
Simple transport
One of three active transport systems.
Group translocation
Transport system modifying substrate during transport.
ABC system
ATP binding cassette transport requiring energy.
Transport events
Include uniport, symport, and antiport mechanisms.
Uniporters
Transport one molecule in one direction.
Symporters
Co-transport two molecules in the same direction.
Antiporters
Transport one molecule in opposite direction.
Lac permease
E. coli symporter using proton motive force.
Phosphotransferase system
Group translocation system in E. coli.
Group Translocation
Transport method modifying substance during membrane crossing.
Phosphoenolpyruvate
Energy-rich glycolysis intermediate for transport.
ABC Systems
Transport systems utilizing ATP in prokaryotes.
Substrate Specificity
High affinity for specific organic and inorganic compounds.
Periplasmic-binding Proteins
Proteins aiding transport in Gram-negative bacteria.
Substrate-binding Proteins
Proteins anchored to surface in Gram-positive bacteria.
Efflux Systems
Mechanisms for pumping out substances like antibiotics.
Peptidoglycan
Rigid layer providing strength to bacterial cell walls.
N-acetylglucosamine
Component of peptidoglycan structure in bacteria.
N-acetylmuramic Acid
Another component of bacterial peptidoglycan.
Amino Acids in Peptidoglycan
Include L-alanine, D-alanine, D-glutamic acid.
Diaminopimelic Acid
Structural analog of L-lysine in peptidoglycan.
Gram-positive Bacteria
Bacteria with thick peptidoglycan layers (15+ layers).
Gram-negative Bacteria
Bacteria with thin peptidoglycan and outer membrane.
Interbridge
Amino acid connections in peptidoglycan layers.
Teichoic Acids
Acidic substances in Gram-positive cell walls.
Lipoteichoic Acids
Teichoic acids bound to membrane lipids.
Osmotic Protection
Survival mechanism for wall-less prokaryotes.
Mycoplasmas
Pathogenic bacteria lacking cell walls.
Thermoplasma
Archaea with lipoglycans for membrane rigidity.
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Major component of Gram-negative outer membrane.
Endotoxin
Toxic component of LPS, specifically Lipid A.
Porin Proteins
Proteins forming channels in Gram-negative membranes.
Porins
Channels for hydrophilic low-molecular-weight substances.
Periplasm
Space between cytoplasmic and outer membranes, ~15 nm.
Peptidoglycan
Polymer forming bacterial cell wall structure.
Pseudomurein
Polysaccharide similar to peptidoglycan in Archaea.
S-Layers
Outer layer of interlocking protein or glycoprotein.
Capsule
Tight polysaccharide layer excluding small particles.