IPS1 -Medicinal Biochemistry p2
1/111
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Proverbs 16:3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Metabolism
All reactions in body balance between energy requiring (anabolism) and energy-releasing (catabolism) reactions
anabolism
catabolism
Energy requiring = _____ [anabolism / catabolism]
Energy releasing= _____ [anabolism / catabolism]
Anabolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism]
_____-
Reactions that combine smaller, simpler molecules into larger molecules using energy from energy molecules
Requires energy to make bonds
Monosaccharide → Polysaccharide + H₂O
Amino acid + Amino acid → Protein + H₂O
Glycerol + Fatty acids → Triglyceride lipid + H₂O
Nucleotides + Nucleotides → Nucleic acid
Example of Anabolism [4]
Energy-requiring reactions
Anabolism is aka ____ reactions?
Catabolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Breaks down absorbed nutrients into smaller molecules
Anabolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Synthesis of complex molecules.
Amphibolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Dual function:
both breakdown and synthesis.
Catabolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Releases energy (exergonic)
Anabolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Requires energy (endergonic)
Amphibolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Both releases and requires energy
Catabolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Destructive, "breaking down" a molecule.
Anabolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Constructive, "building up" a molecule.
Amphibolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Can proceed in either direction.
Catabolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Breaks down macromolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins) into simpler ones (monosaccharides , fatty acids, amino acids)
Anabolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Builds macromolecules (e.g., proteins, nucleic acids) from simpler building blocks.
Amphibolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Utilizes intermediates from one process as building blocks for another
Glycolysis
Krebs Cycle
for energy production
Cellular Respiration
Example of Catabolism [3]
Photosynthesis
Protein synthesis
DNA replication
Example of Anabolism [3]
Krebs cycle
→ due to its role in both breaking down glucose and providing precursors for synthesis
Example of Amphibolism [1]
Catabolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Function: To release energy and provide building blocks for anabolic reactions
Anabolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Function: To build and repair tissues, grow, and store energy.
Amphibolism
[Anabolism / Catabolism / Amphibolism]
Function: To link catabolic and anabolic pathways, ensuring a balanced metabolism
Biomolecules
____- are molecules that naturally occur in living organisms
Biomolecules
____-
Large or giant molecules (macromolecules)
Composed of polymers
polymers
Biomolecules are composed of ____ ?
Macromolecules
Large or giant molecules is aka _____ ?
Proteins (amino acids)
Carbohydrates (monosaccharides)
Nucleic acids (nucleotides)
Lipids (fatty acids +glycerol)
FOUR MAJOR BIOMOLECULES
Monomer
Building Blocks
glucose
fructose
Example of Monosaccharides [2]
starch
glycogen
cellulose
Example of Polysaccharides [3]
Glucose
starch
glycogen
cellulose
Example of Carbohydrates [4]
Enzymes
antibodies
hemoglobin
keratin
Example of Proteins [4]
Fats
Oils
waxes
phospholipids
steroids
Example of Lipids [5]
DNA
RNA
Example of Nucleic Acids [2]
Monosaccharides (e.g., glucose, fructose)
What is the monomer of carbohydrates?
A. Amino acids
B. Fatty acids and glycerol
C. Monosaccharides
D. Nucleotides
Amino acids (20 types)
What is the monomer of proteins?
A. Monosaccharides
B. Amino acids
C. Nucleotides
D. Fatty acids and glycerol
20 types
10 essential -diet
10 Non- essential - body
Amino Acids have ______ [how many] different TYPES
Fatty acids + Glycerol
What is the monomer of lipids?
A. Amino acids
B. Fatty acids and glycerol
C. Nucleotides
D. Monosaccharides
Nucleotides
What is the monomer of nucleic acids?
A. Amino acids
B. Monosaccharides
C. Nucleotides
D. Fatty acids
Nucleic Acids
[BIOMOLECULE]
____-Composed of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
Sugar
Phosphate group
Nitrogenous base
Nucleic Acid is composed of ____[3]
Carbohydrates
Which biomolecule has polysaccharides (starch, glycogen, cellulose) as polymers?
A. Carbohydrates
B. Proteins
C. Lipids
D. Nucleic acids
starch
glycogen
cellulose
Glucose Polymers [3]
Proteins
Which biomolecule has polysaccharides Polypeptides as polymers?
A. Carbohydrates
B. Proteins
C. Lipids
D. Nucleic acids
Lipids
Which biomolecule does not form true polymers?
A. Carbohydrates
B. Proteins
C. Lipids
D. Nucleic acids
Nucleic acids
Which biomolecule has Polynucleotides (DNA, RNA) Polypeptides as polymers?
A. Carbohydrates
B. Proteins
C. Lipids
D. Nucleic acids
DNA
RNA
Example of Polynucleotides [2]
Lipids
Which biomolecule form large structures through non-covalent ineteractions
A. Carbohydrates
B. Proteins
C. Lipids
D. Nucleic acids
C, H, O, N (sometimes S)
Which elements make up proteins?
A. C, H, O only
B. C, H, O, N (sometimes S)
C. C, H, O, P
D. C, H, O, N, P
Cystein & Methionine
Which amino acids are sulfur containing?
A. Valine & Leucine
B. Cystein & Methionine
C. Glycine & Alanine
D. Phenylalanine & Tryptophan
CGUA – ribose
Which bases are present in RNA?
A. CGTA – deoxyribose
B. CGUA – ribose
C. ATCG – ribose
D. CGTA – ribose
fructose polymer
Inulin is a ____[glucose /fructose polymer]
Phenylalanine
Valine
Threonine
Tryptophan
Isoleucine
Methionine
Histidine
Arginine
Leucine
Lysine
Classic mnemonic for the 10 essential amino acids:
MNEMONIC: PVT TIM HALL
C, H, O only
Which elements make up Carbohydrates
A. C, H, O only
B. C, H, O, N (sometimes S)
C. C, H, O, P
D. C, H, O, N, P
C, H, O (less O than carbs)
Which elements make up Lipids
A. C, H, O (less O than carbs)
B. C, H, O, N (sometimes S)
C. C, H, O, P
D. C, H, O, N, P
C, H, O, N, P
Which elements make up Nucleic Acids
A. C, H, O (less O than carbs)
B. C, H, O, N (sometimes S)
C. C, H, O, P
D. C, H, O, N, P
CGTA – deoxyribose
DNA bases and sugar
A. CGUA – ribose
B. CGTA – deoxyribose
C. CGTA – ribose
D. CGUA – deoxyribose
CGUA – ribose
RNA bases and sugar
A. CGUA – ribose
B. CGTA – deoxyribose
C. CGTA – ribose
D. ATGC – ribose
Phosphate
What do both DNA and RNA have in common?
A. Sulfur group
B. Phosphate
C. Fructose
D. Fatty acid chain
Carbohydrates
[BIOMOLECULE]
They are the primary energy source (short-term energy).
Carbohydrates
[BIOMOLECULE]
They provide structural support in plants (the cellulose).
Carbohydrates
[BIOMOLECULE]
They are involved in cell recognition.
Proteins
[BIOMOLECULE]
____-
They catalyze reactions (the enzymes).
They provide structural support (the collagen).
Proteins
[BIOMOLECULE]
_____-
They transport molecules (the hemoglobin).
They play a role in immune function (the antibodies).
Proteins
[BIOMOLECULE]
They act as hormones (the insulin).
Lipids
[BIOMOLECULE]
They are for long-term energy storage
Lipids
[BIOMOLECULE]
They are the main component of cell membranes (the phospholipids).
Lipids
[BIOMOLECULE]
They provide insulation and protection.
They also act as hormones (the steroids).
Nucleic Acids
[BIOMOLECULE]
They store and transfer the genetic information.
Nucleic Acids
[BIOMOLECULE]
They direct the protein synthesis.
Lipids (9 kcal/g)
Which biomolecule has the highest energy yield?
A. Carbohydrates
B. Proteins
C. Lipids
D. Nucleic acids
4 kcal/g
How much energy do carbohydrates provide?
4 kcal/g
How much energy do proteins provide?
9 kcal/g (highest)
How much energy do lipids provide?
No (N/A)
Do nucleic acids provide energy?
a. YES
b. NO
Amylase test
An important indicator for pancreatic disease, especially acute pancreatitis.
True
[T/F] DNA is synthesized in our body
lipid
fatty acids +glycerol = _____ ?
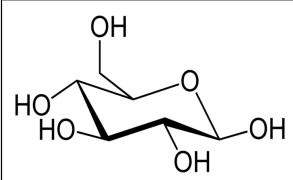
Glucose (carbohydrate)
IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING MONOMERS
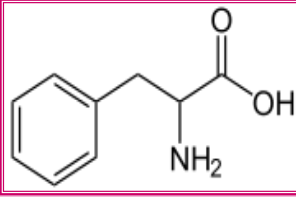
Phenylalanine (protein)
IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING MONOMERS
Adenosine Monophosphate (AMP)
—Nucleic acid
—fat
IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING MONOMERS
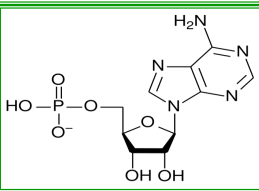
Monomers
The simple subunits or building blocks
Amino acid
Nucleotide
Saccharide
Example of Monomer [3]
Polymer
Larger molecules made by joining monomers
Peptide, Oligopeptide, Polypeptide, Protein
Nucleic acid (DNA, RNA)
Oligosaccharide, Polysaccharide
Example of Polymer
Oligosaccharides
They are carbohydrates made of a few monosaccharides (3–10 units) joined together.
Polysaccharides
They are carbohydrates made of many monosaccharides (more than 10, often hundreds or thousands).
glucose
galactose
fructose
Example of Monosaccharides [3]
sucrose
maltose
lactose
Example of Disaccharides [3]
Mnemonic: Share Mo Lang
raffinose
Example of Oligosaccharide [1]
cellulose
starch
glycogen
Example of Polysaccharides [3]
glycogen
_____-
Also called animal starch.
It is the storage form of carbohydrate in animals.
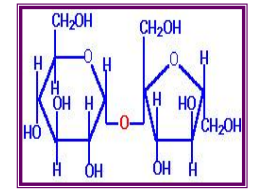
Sucrose
[Carbohydrates – Disaccharides]
____= Glucose + Fructose (G–F)
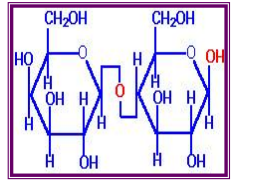
Lactose
Carbohydrates – Disaccharides]
____= Glucose + Galactose (G–Gal)
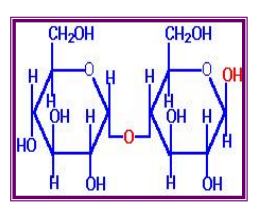
Maltose
Carbohydrates – Disaccharides]
____= Glucose + Glucose (G–G)
Straight chain
Amylose structure
A. Branched chain
B. Straight chain
C. Helical chain with β bonds
D. Random chain
α (1→4) glycosidic linkages
Amylose bond type
A. β (1→4) glycosidic linkages
B. α (1→4) glycosidic linkages
C. α (1→6) glycosidic linkages
D. β (1→6) glycosidic linkages
Starch
Amylose and Amylopectin are found in:
A. Starch
B. Cell walls
C. Glycogen only
D. Chitin
Branched chain
Amylopectin structure
A. Straight chain
B. Branched chain
C. Spiral chain
D. Cross-linked chain