OCS 3103: Global Environmental Cycles
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Biogeochemical Cycle
describe the flow of essential elements from the environment through the living organisms and back into the environment.
Big Bang Theory
~13.7 billion years ago
Extremely Hot (10^8K)
Atomic Nuclei were created about 3 minutes
relative abundance of hydrogen (76% and helium 24%)
Nuclear Fusion in stars; currently abundances
Hydrogen (73%)
Helium (26%)
Everything Else (1%)
Supernova
explosion of a star
Next Three Elements from Big Bang Theory and stars
Lithium (Li)
Beryllium (Be)
Boron (B)
The general trends in the remaining stellar-produced elements
(1) an alternation of abundance in elements as they have even or odd atomic numbers
(2) a general decrease in abundance, as elements become heavier
Atom
an atom is a fundamental piece of matter
three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons
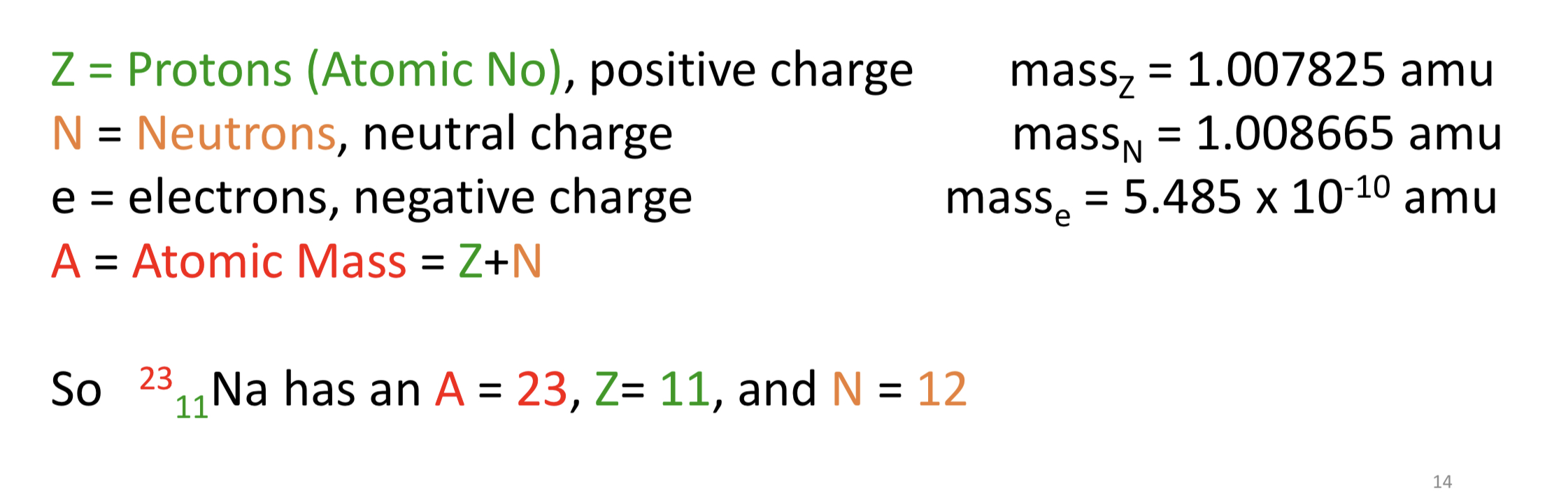
Three Subparticles
Z = protons (atomic no.), post charge
N = neutrons, neutral charge
e = electrons, negative charge
A = atomic mass = Z+N
Stability of Nucleus
Spin Pairing
Shell Binding(Orbitals)
Surface Tension
Column Repulsion
Binding Energy
reflects four processes and is the energy that would be required to dissemble the nucleus of an atom into its components parts
mass defect = change in M
Highest Binding Energy
Iron (Fe)
is STABLE, boding of nuclei is dominated by two forces - strong nuclear force and electromagnetic force.
adding or removing would result in higher-energy configuration
VERY STABLE
small nuclei, they are more likely to stick due to attraction of the strong force
NOT VERY STABLE
larger nuclei, the size of nuclei does not feel much strong force attraction form particles on the other side but they feel the elctromagnric repulsion
Elemental Isotopes
same elect has the same number of protons (Z) but different number of neutrons
Two types of isotopes
Radioisotopes
Stable Isotopes (N/Z = 1 and 1.6)
Radiation
energy in the form of high-speed particles (or electromagnetic waves or photons) can be ionizing and non-ionizing
Mode of Decay
alpha particles:most densely ionizing, but least penetrating
beta particles: use less energetic , but more penetrating
gamma rays: high energy electromagnetic energy waves and the most penetrating types of radiation
Fission vs Fusion
Fission: breakdown into smaller
Fusion: combing
Composition of the Earth Crust
O, Si, Al, Fe, Ca, Na, K, Mg
Composition of the Earth’s core
Fe,S,Ni
Composition of the Mantle
O,Si,Mg,Fe, Al (MgSiO3 and FeMgSiO4)
composition of the human body
O,C,H,N,Ca,P,K,S,Na,Cl,Mg, I, Fe