anatomy midterm review
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
How are anatomy and physiology related? How are they different?
anatomy is the study o the body structures while physiology is how the body works, but they both allow for the understanding of the body
What are the levels of structural organization in the body in order?
atom, molecule, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism
Give multiple examples of which organs are in each body system. Why are they in that system? (ie how do you know that ovaries are part of the reproductive system and the endocrine system?)
integumentary- skin, hair, nails
skeletal- bones, cartilage, ligaments
lymphatic- lymph nodes, lymphatic vessels, thymus, spleen, tonsils
respiratory- nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs
urinary- kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
endocrine- pituitary gland, adrenals, pancreas, thyroid, parathyroids
What are the differences between negative and positive feedback systems? Give examples of both.
negative feedback opposes the stimulus while positive feedback reinforces the stimulus (ex feeling pain when u touch smth hot vs blood clotting)
Know the body regions.
picture + back side: otic (ear), occipital, scapular, vertebral column, lumbar, gluteal, perineal, popliteal, calcaneal, plantar
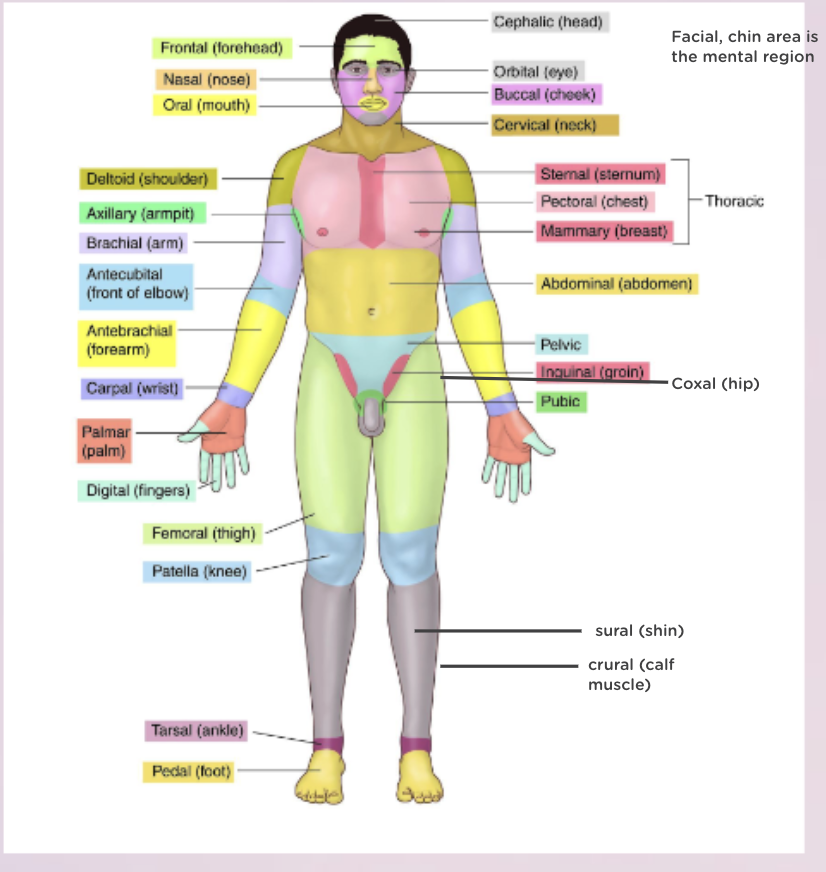
Know the anatomical terms.
medial, lateral,proximal, distal, superior, inferior, superficial, deep, anterior (ventral), posterior (dorsal)
What is anatomical position?
standing, forward facing, palms forward
Know the location of each body cavity.

Know the body planes.
sagittal- divides into left and right
transverse- divides into top and bottom
frontal (coronal)- divides into front and back
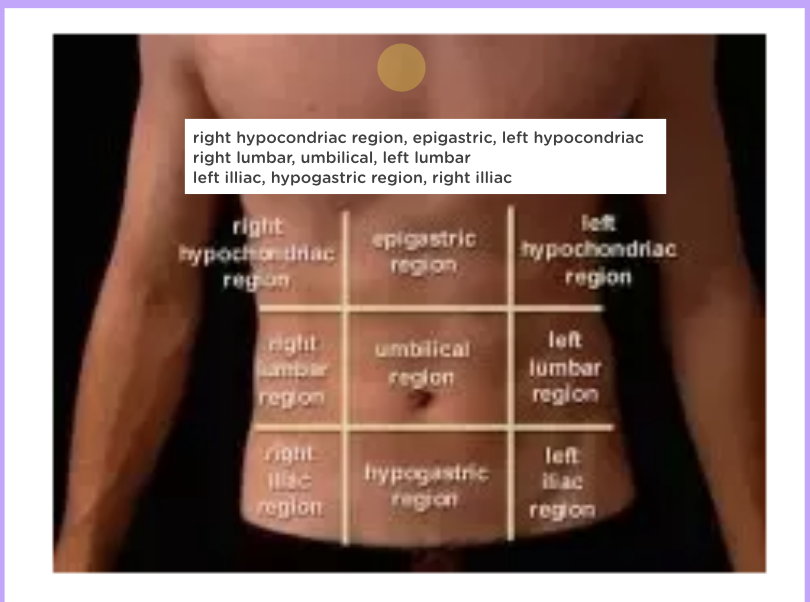
Where is each abdominal region located?
right hypochondriac | epigastric | left hypochondriac
right lumbar | umbilical | left lumbar
right iliac | hypogastric | left iliac
Review each of the types of organic compounds and how they differ from each other.
carbohydrates- C, H, O, glucose, saccharides
lipids- C, H, meats, oils, daries, butter, phospholipids, steroids
protein- C, H, O, N, amino acids
nucleic acid- DNA, RNA
Review cell organelles, their structure and functions.

What is apoptosis?
programmed cell death
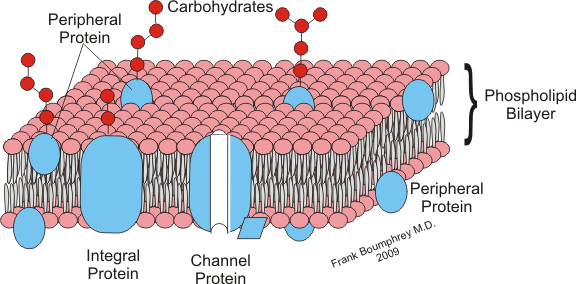
How are integral proteins in cell membranes different from peripheral proteins?
Integral proteins are embedded in the cell membrane's lipid bilayer, spanning all or part of it, while peripheral proteins are loosely attached to the surface, interacting via weak bonds and easily removed.
Differentiate between hypertonic and hypotonic solutions.
hypotonic- cells will gain water (solution has high solute)
hypertonic- cells will lose water (solution has low solute)
Describe lysosomes and peroxisomes.
lysosome- enzyme for excess/waste
peroxisome- enzyme for poisons
Explain how acids and bases are rated on the pH scale.
0-7 acidic, 7- neutral, 7+ basic
What units are used to measure cells?
micrometers (µ)
Know the steps of mitosis in order and what occurs in each step.
prophase- chromatin condenses to form chromosomes, nucleolus disappears
metaphase- chromosomes attach to spindle fibers and go to middle
anaphase- chromosomes separate and go to centrioles
telophase- chromosomes return to chromatin structure, nuclear envelope forms

Identify each of the following organelles and explain their function: nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, cilia, flagella.
cell membrane; phospholipid bilayer, cholesterol keeps it impermeable
cytoplasm- cytosol + organelles containing cytoskeleton
nucleus- control center, contains DNA
ribosomes- site of protein synthesis
mitochondria- powerhouse of the cell
ER- (rough) contains ribosomes for protein synthesis (smooth) lipid synthesis
cilia- microtubules that move back and forth to remove mucus, etc.
flagella- longer than cilia, moves the entire cell
Define the following: active transport, diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion.
diffusion- high to low concentration
facilitated- across cell membrane through ion channels, passive
osmosis- passive transport of water
active- low to high concentration, requires ATP (ex: Na+K+ pump)
Define the following terms: stem cell, progenitor cell, totipotent, pluripotent, germ cell, haploid cell, diploid cell.
stem cell- can differentiate into any cell type
progenitor- partially specialized cell
totipotent- daughter cells that specialize to become any cell type
pluripotent- daughter cells that can become limited # of cells
haploid- have 1 set of chromosomes
diploid- 2 sets of chromosomes
germ cell- ½ # of chromosomes of a somatic cell (gamete)
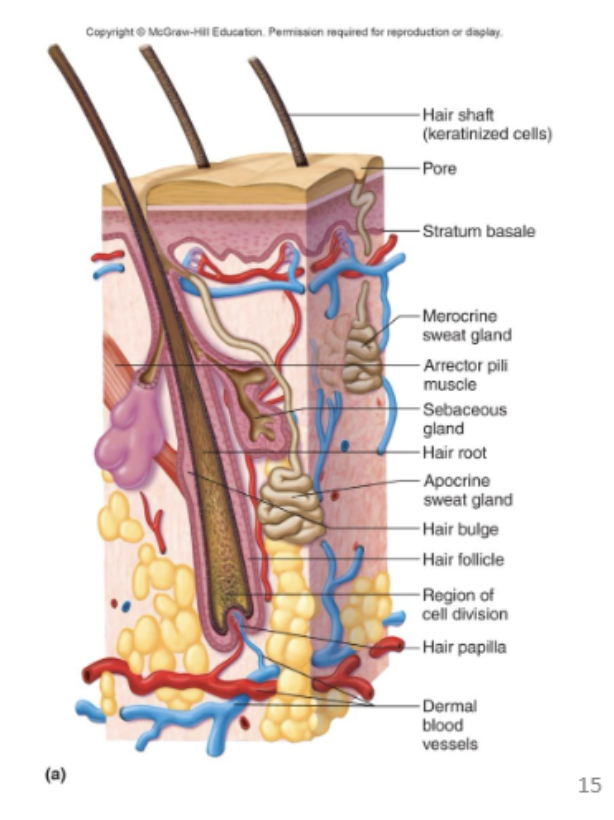
What is the arrector pili muscle, what does it do and where is it attached?
attaches to hair shaft that causes hair to stand up
What happens to the skin during heat production and heat loss?
heat production- vasodialation of blood vessels
heat loss- vasoconstriction of blood vessels
Describe the types of epithelial tissue and where they are found in the body.
simple:
squamos- single layer, rapid diffusion, blood vessels and lung tissue
cuboidal- single layer, secretion and absorption, kidney tissue
columnar- tall, single layer, secretion of mucus, lining of digestive tract
stratified:
squamous- thick protection of epidermis
cuboidal- one or more layers, rare, salivary and mammary glands
stratified- columnar, rare, larynx and male urethra
Name the 4 types of tissue in the body.
connective, epithelial, muscle, nervous
Describe how the Rule of 9s works for burn victims.
divides body into regions of 9 to evaluate extent of burns (ex: anterior trunk= 18%)
How does skin respond to aging?
cell cycle slows, epidermis and dermis thin, dry skin, lowered vitamin D
Besides the skin, what are the other components of the integumentary system?
hair, nails, glands
Identify the layers of epithelial tissue. #2
free/apical, basal surface, basement membrane
What are the components of an extracellular matrix? # 11
ground substance; watery gel like substance secreted by cells
fibers/threads- collagen, elastic, reticular
List properties of hair follicles. #6
shaft (above skin), arrector pili muscle, hair root, hair bulge, hair follicle, papillae
Explain the risks of indoor tanning and sun exposure. #4
melanoma and skin cancer from UV radiation
Describe the properties of spongy bone vs compact bone. #7
spongy- cancellous, porous made of trabeculae giving space for red bone marrow
compact- dense, strong outer layer for support made of osteons
Which types of joints and movable? Immovable? #28
fibrous and cartilagenous are immovable while synovial are movable
Differentiate between the functions and locations of osteocytes, osteoblasts, osteoclasts. #11
osteocytes- mature bone cells that make up majority of bone structure
osteoblasts- produce new bone, haversian canal
osteoclasts break down new bone, haversian canal
What is the difference between osteopenia and osteoporosis? #15
osteopenia- bone loss
osteoporosis- severe bone loss leading to spaces and canals tn the bone that weaken them
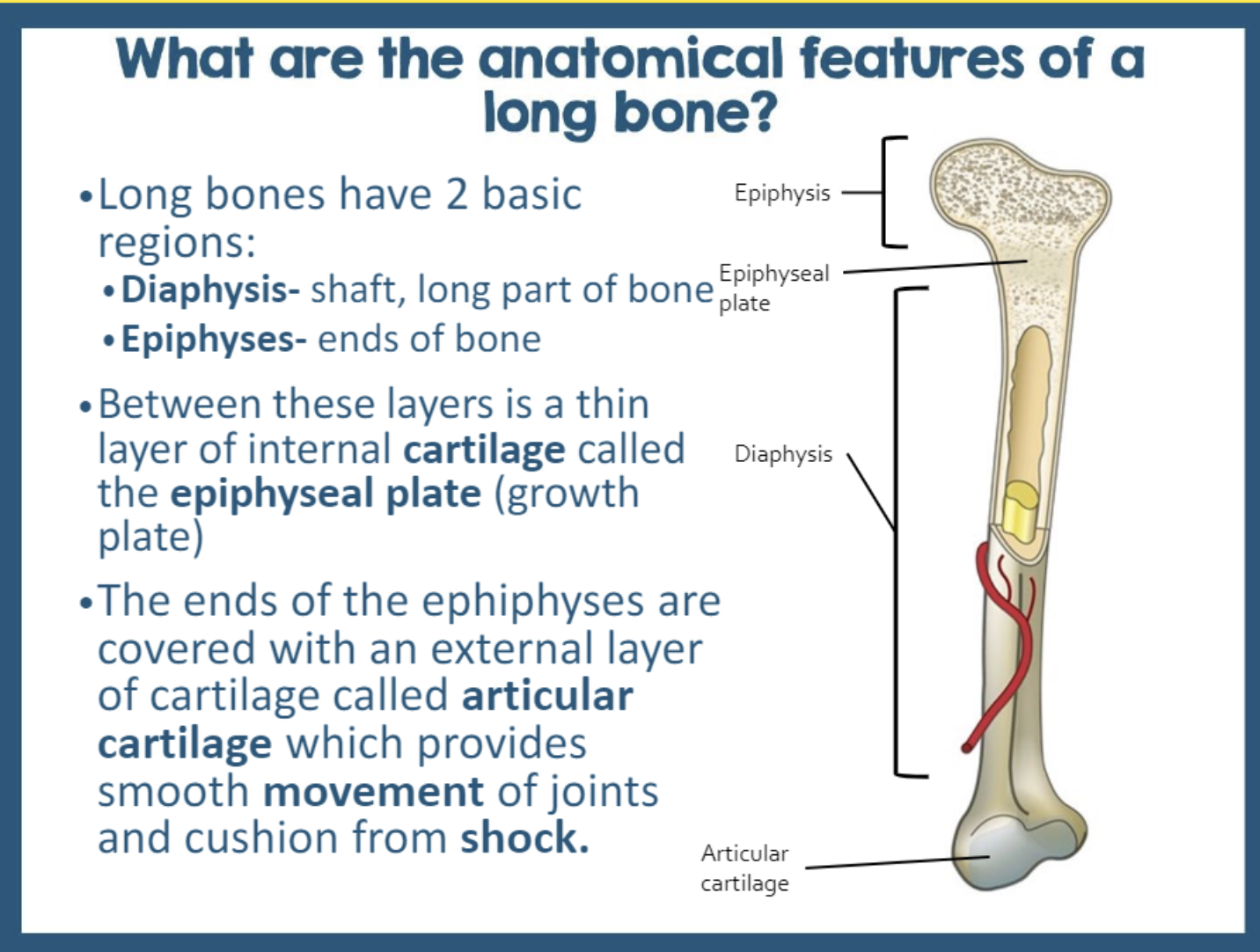
Identify the parts of a long bone. #4
epiphysis, metaphysis, diaphysis, epiphyseal plate, articular cartilage
Differentiate between the axial skeleton and the appendicular skeleton. #21, 26
axial- center line (vertebra, skull, sacrum, etc.)
appendicular- appendiges
Be able to identify the following bones: parts of the sternum, patella, bones in the pelvic cradle, skull and facial bones, basic bones in the arms and legs, hands and feet. #21
skull: PESTO (Parietal, Ethmoid, Sphenoid, Temporal, Occipital)
facial bones: My Mom Loves Vibrant Norwegian Zoos (Mandible, Maxilla, Lacrimal, Vomer, Nasal, Zygomatic)

Give examples of the five types of bones. #3
flat (scapula), long (femur), irregular (vertebra), short (wrist), sesamoid (patella)
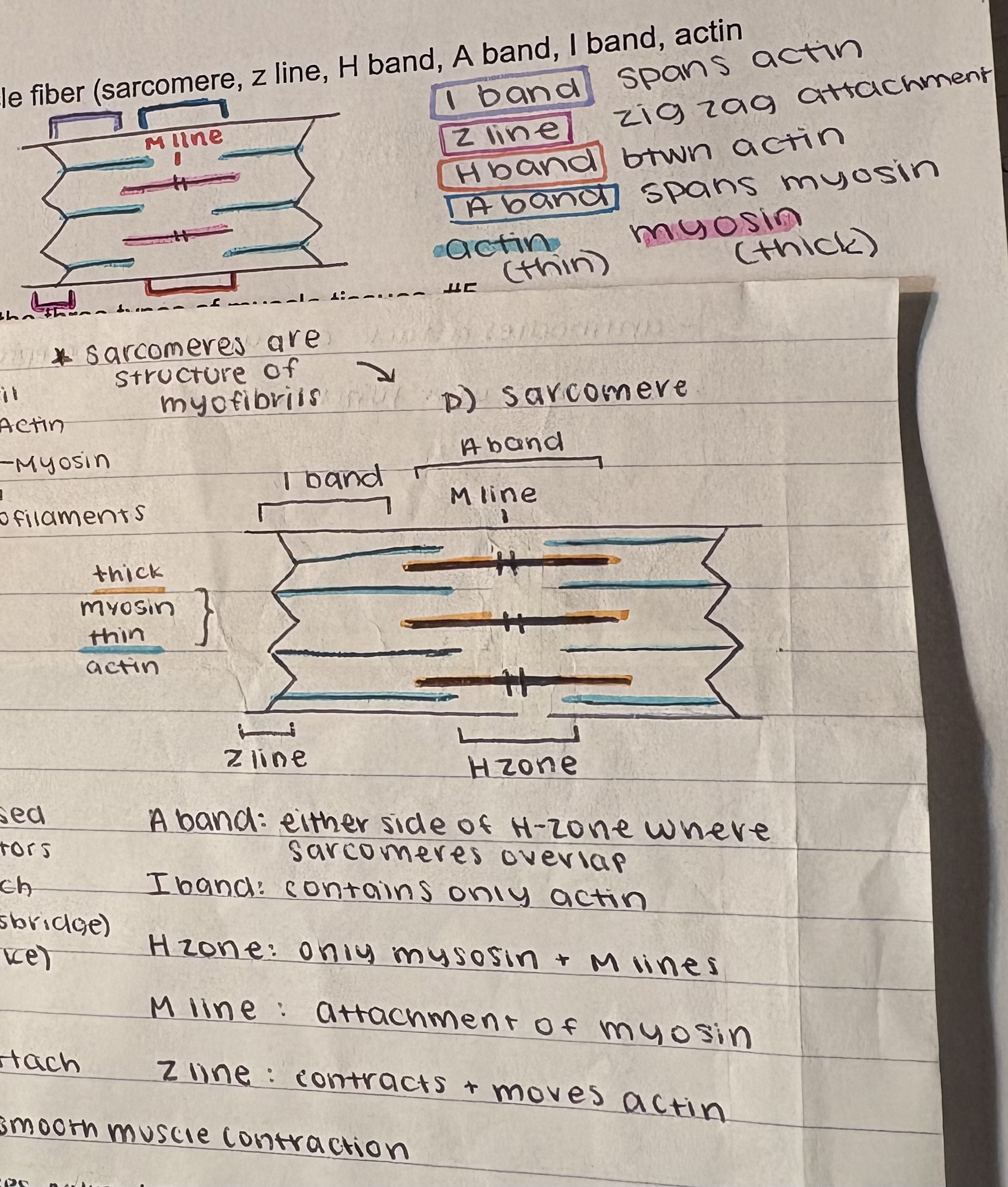
Know the location of the parts of a muscle fiber (sarcomere, z line, H band, A band, I band, actin filaments, myosin filaments). #10, 13
enjoy my beautiful drawing
Compare and contrast the properties of the three types of muscle tissues. #5
skeletal- cylindrical, striated, multinucleated, voluntary, contracts slow or quick
cardiac- branched, striated, uninucleated, involuntary, slow steady contractions
smooth- uniform layers, nonstriated, uninucleated, involuntary, slow sustained contractions
What happens when muscles become fatigued? #17
glucose supply is exhausted and ATP is no longer being used efficiently, oxygen debt is created
Identify the muscles in the facial region and their basic functions. #26

Explain the process of muscle contraction. # 11
nerve impulse sent, acetycholine is released and bind to ACh receptors, ATP is converted to ADPd Phosphate which allows myosin heads attach to actin filaments and pull the z line closer, shortening the sarcomere (sliding filament theory)
tropomyosin blocks the binding sites while Ca2+ allows myosin and actin to attach
Differentiate between prime mover, antagonist, synergist, origin and insertion. #22
prime mover (agonist)- muscle dong the action
antagonist- opposing muscles
synergist- help contraction (same direction)
origin- nonmoving pt of attachment
insertion- movable pt of attachment
Differentiate between tendons and aponeurosis, #22, 5
tendon- attaches muscle to bone, cord-like
aponeurosis- flat, sheet-like muscle connector for muscles and tissues
What is acetylcholine? Acetylcholinesterase?
acetylcholine is the chief neurotransmitter of the PNS, can stimulate or block a response
acetylcholinesterase is an enzyme in the synapse between the nerve and muscle cells that breaks down the acetylcholine to stop signal
Know the major muscles of the arms and legs. #25
back: glute med and max, gastrocnemius, soleus
front: tensor fasciae latae, ioliopsas, pectieus, adductor longus, gracilis, sartorius, rectus femoris, VLO, VMO, fibularis longus, tibialus anterior, soleus, extensor digitorium longus

What is Myasthenia Gravis?
autoimmune disorder where antibodies attack acetylcholine receptors on skeletal muscle fibers causing muscle weakness and fatigue
Name four ways that mammals are adapted for survival.
inscisors, fur, mammary glands, four chambered heart
Know the locations and functions of the following organs in the rat: heart, lungs, liver, spleen, kidney, large and small intestines, cecum, diaphragm, trachea, esophagus, stomach, uterine horns, testes. # 3 (identify spleen for this question)
spleen- right by stomach, destroys blood cells, helps immune system and stores blood
What personal safety equipment is required during an animal dissection?
googles, apron, gloves