GCE O Level Biology: Definitions of Keywords from Nutrition in Plants, Transport in Plants and Humans
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Photosynthesis
Process in which light energy absorbed by chlorophyll is transformed into chemical energy. This chemical energy is used to synthesize carbohydrates from water and carbon dioxide, with oxygen being released during the process.
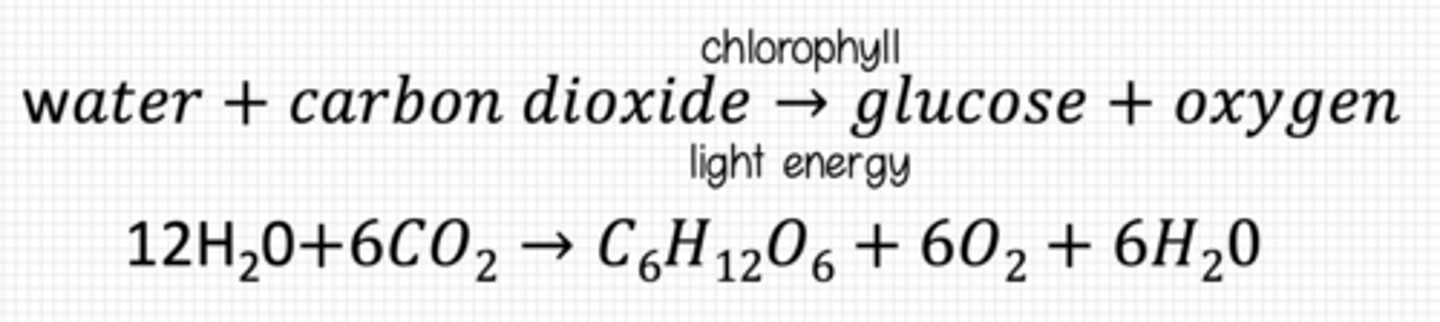
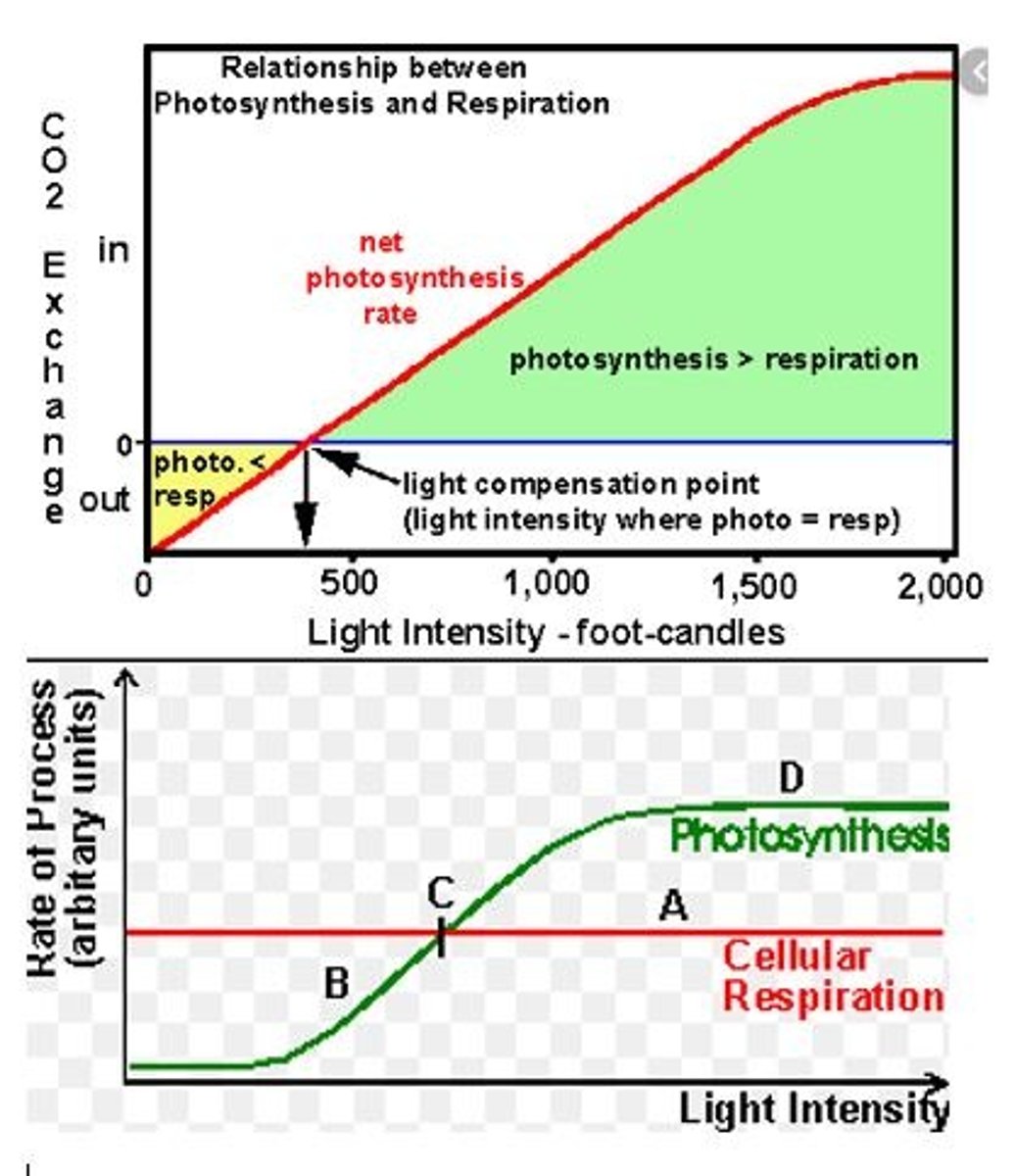
Compensation point
Point when rate of photosynthesis is the same as rate of respiration
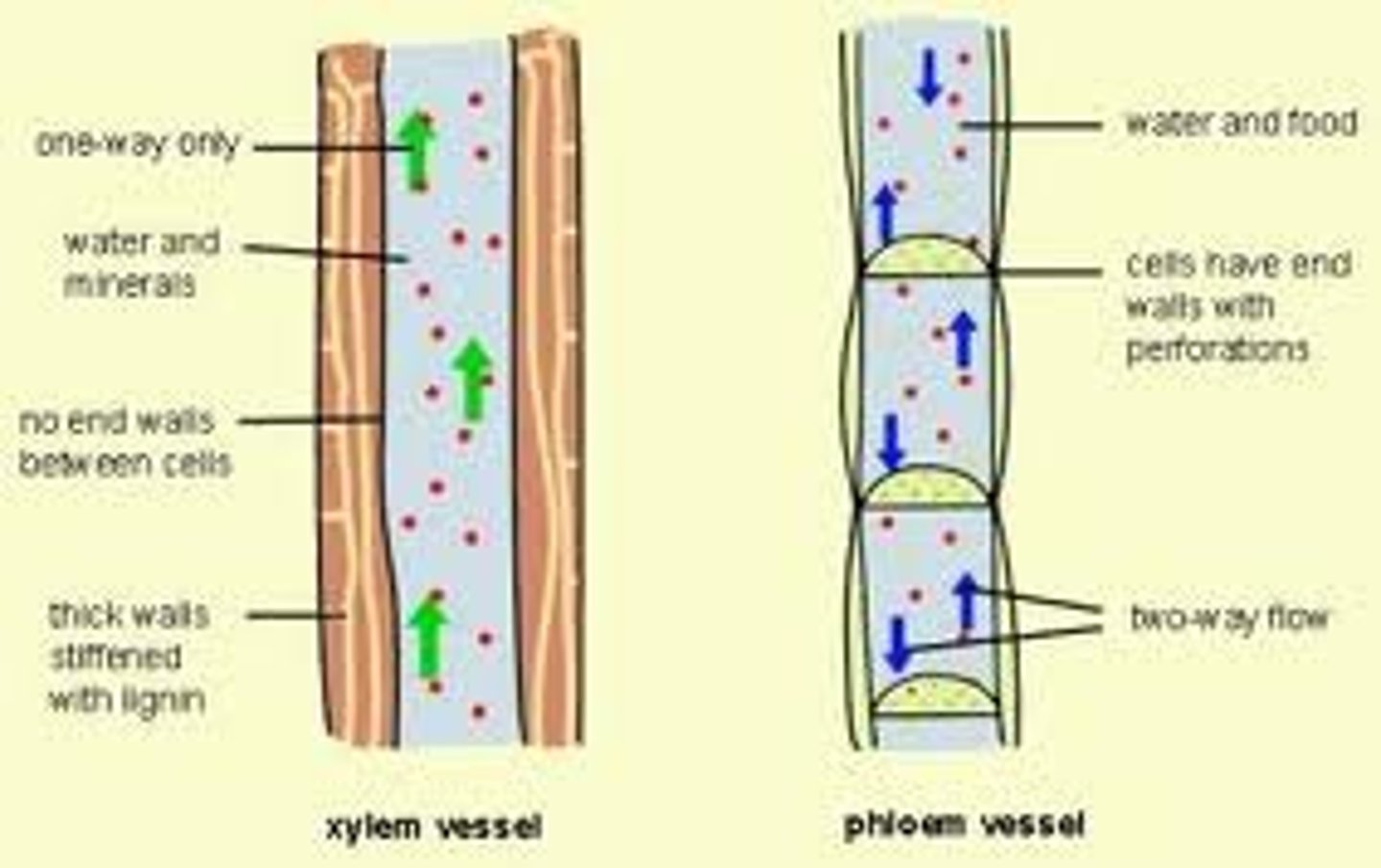
Translocation
Transport of manufactured food substances such as sugars and amino acids in the phloem of plants
Root pressure
Pressure that forces water, absorbed from soil, to move through the roots and up the stem of a plant. This is normally due to the lower water potential in root cells
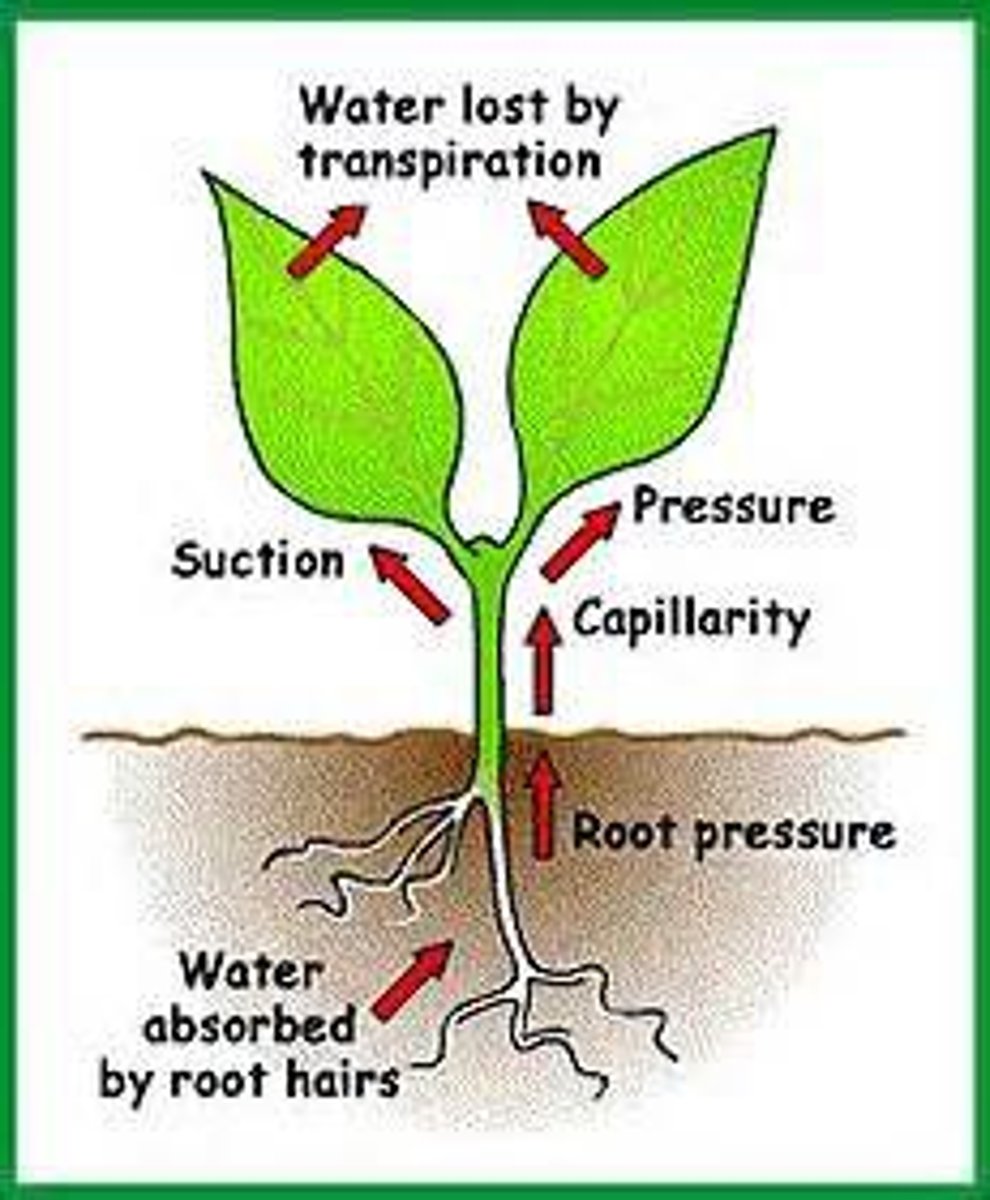
Transpiration
Loss of water vapour from aerial parts of a plant, especially through the stomata of leaves
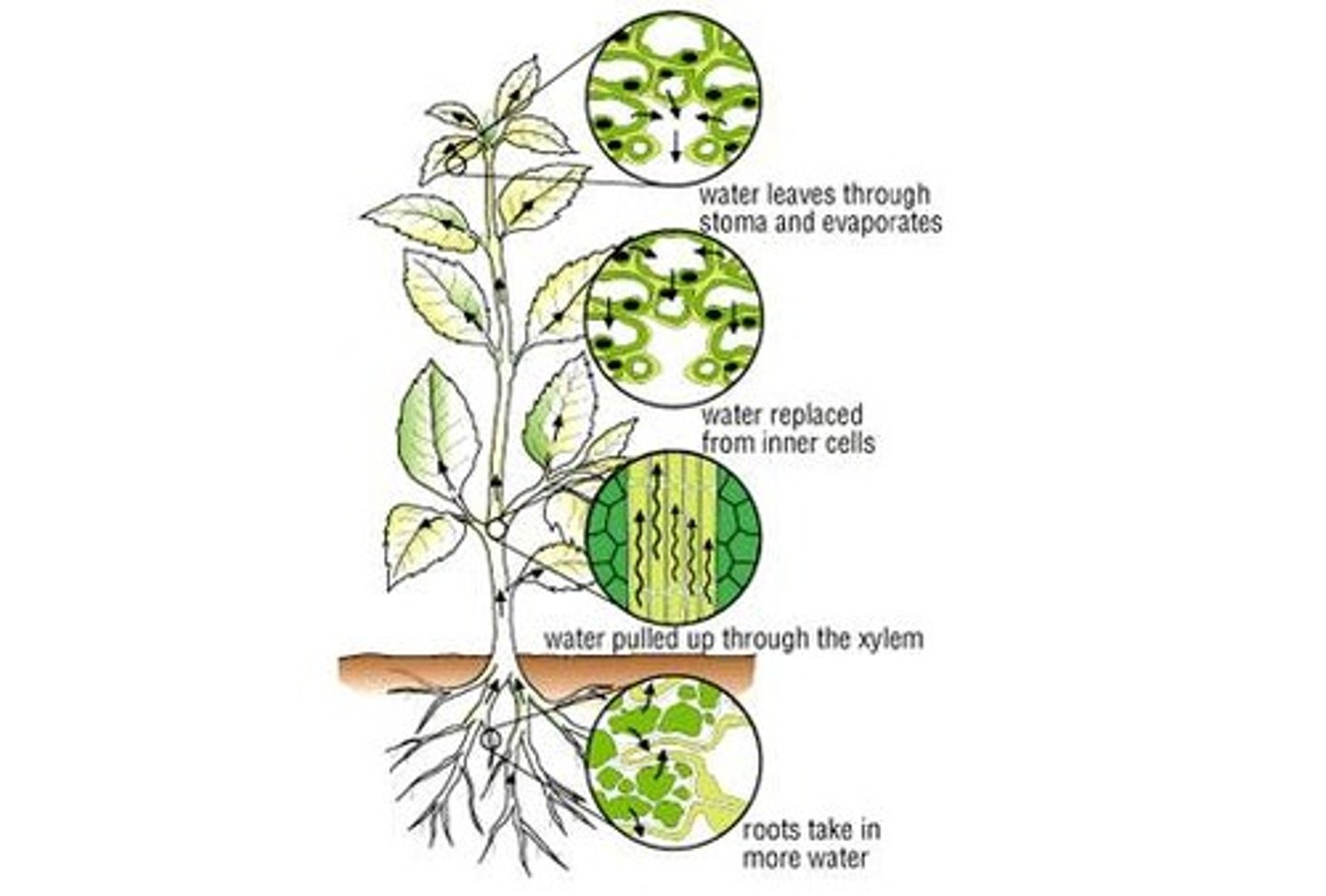
Transpiration stream
Stream of water up a plant caused by transpiration pull
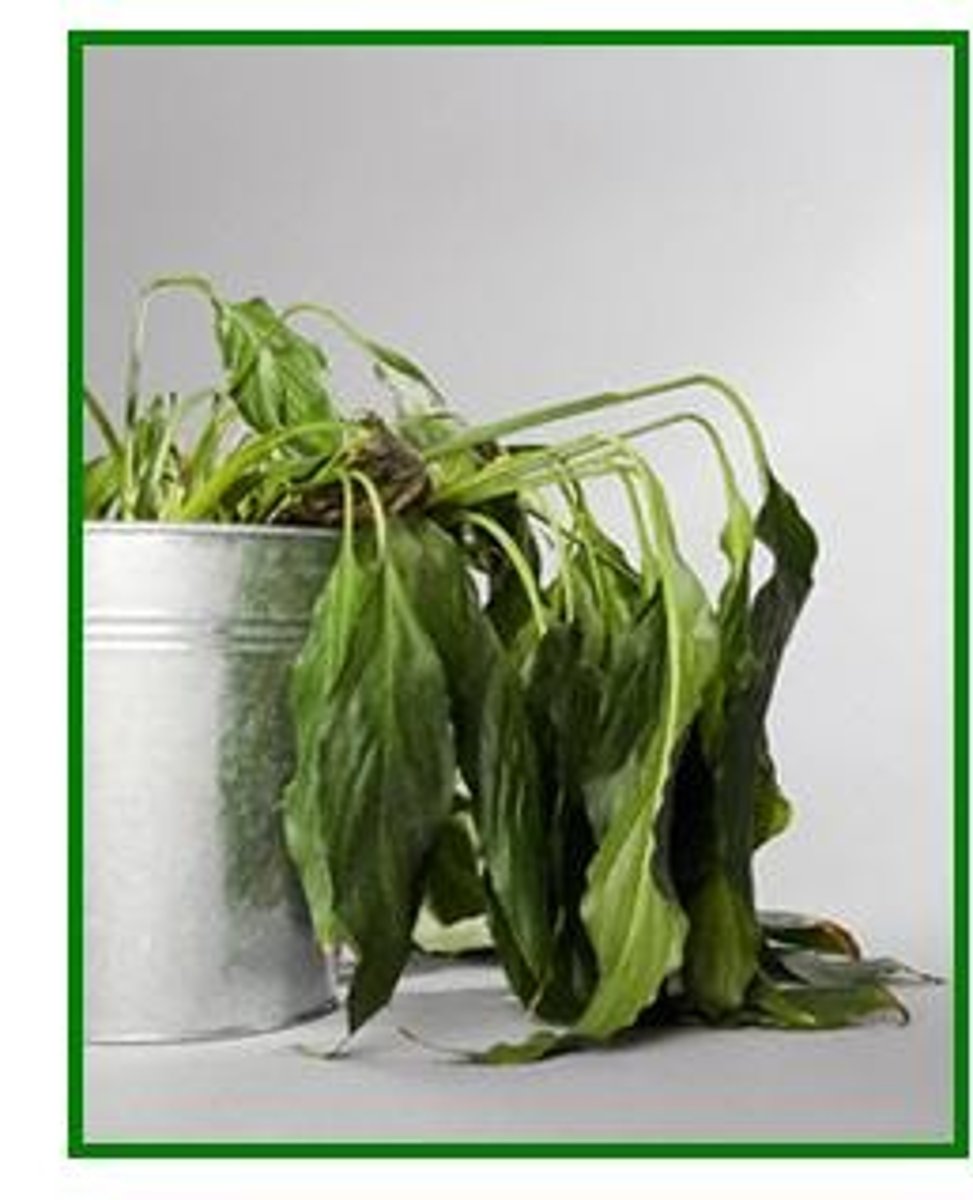
Wilting
Condition which results when plants lose more water through transpiration than is absorbed from roots

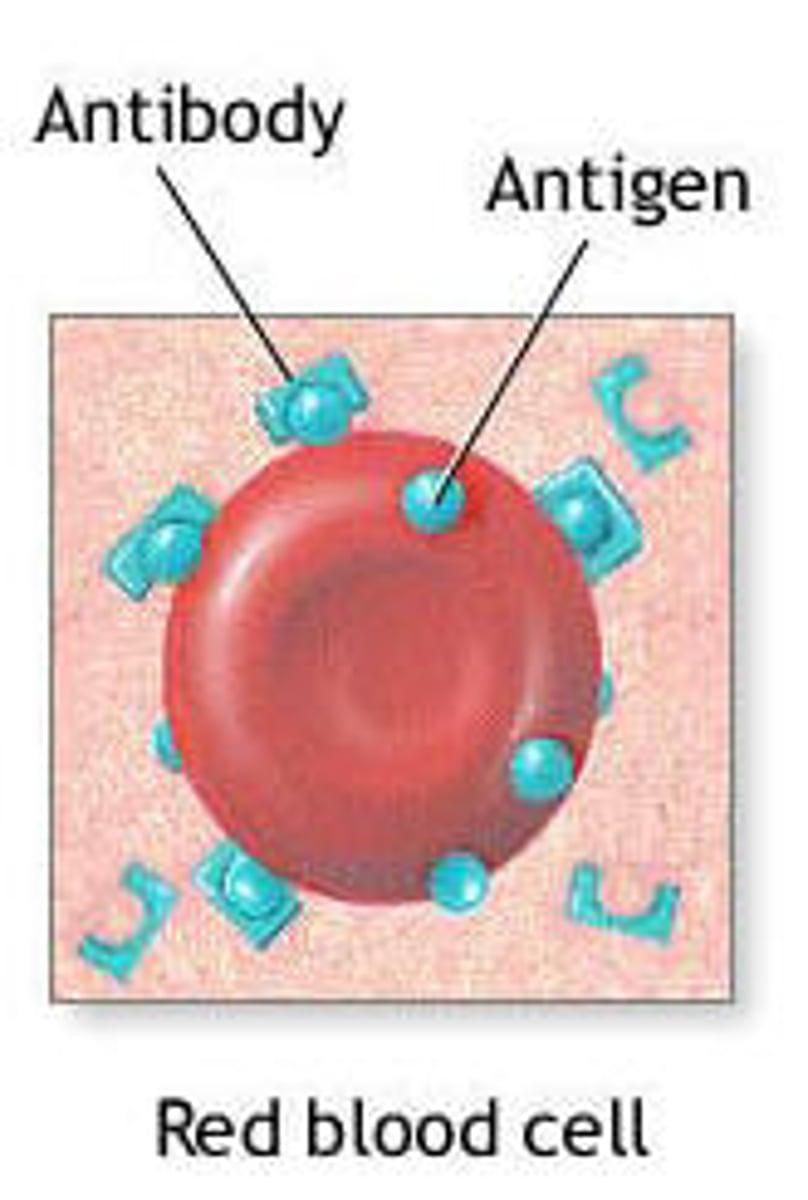
Antigen
Protein found on the surface of red blood cells which can be recognised by the immune system
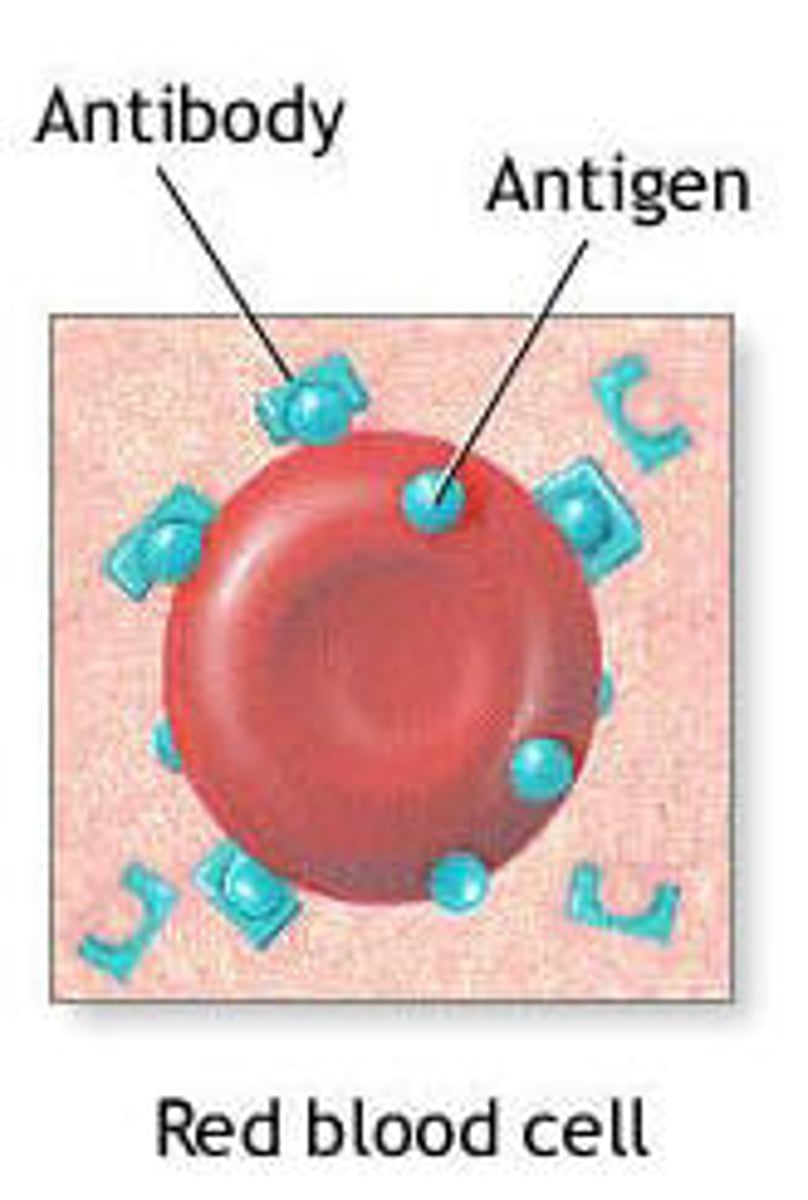
Antibody
A protein produced by lymphocytes in response to the entry of foreign substances in order to render them harmless
Pathogen
Disease-causing micro-organism
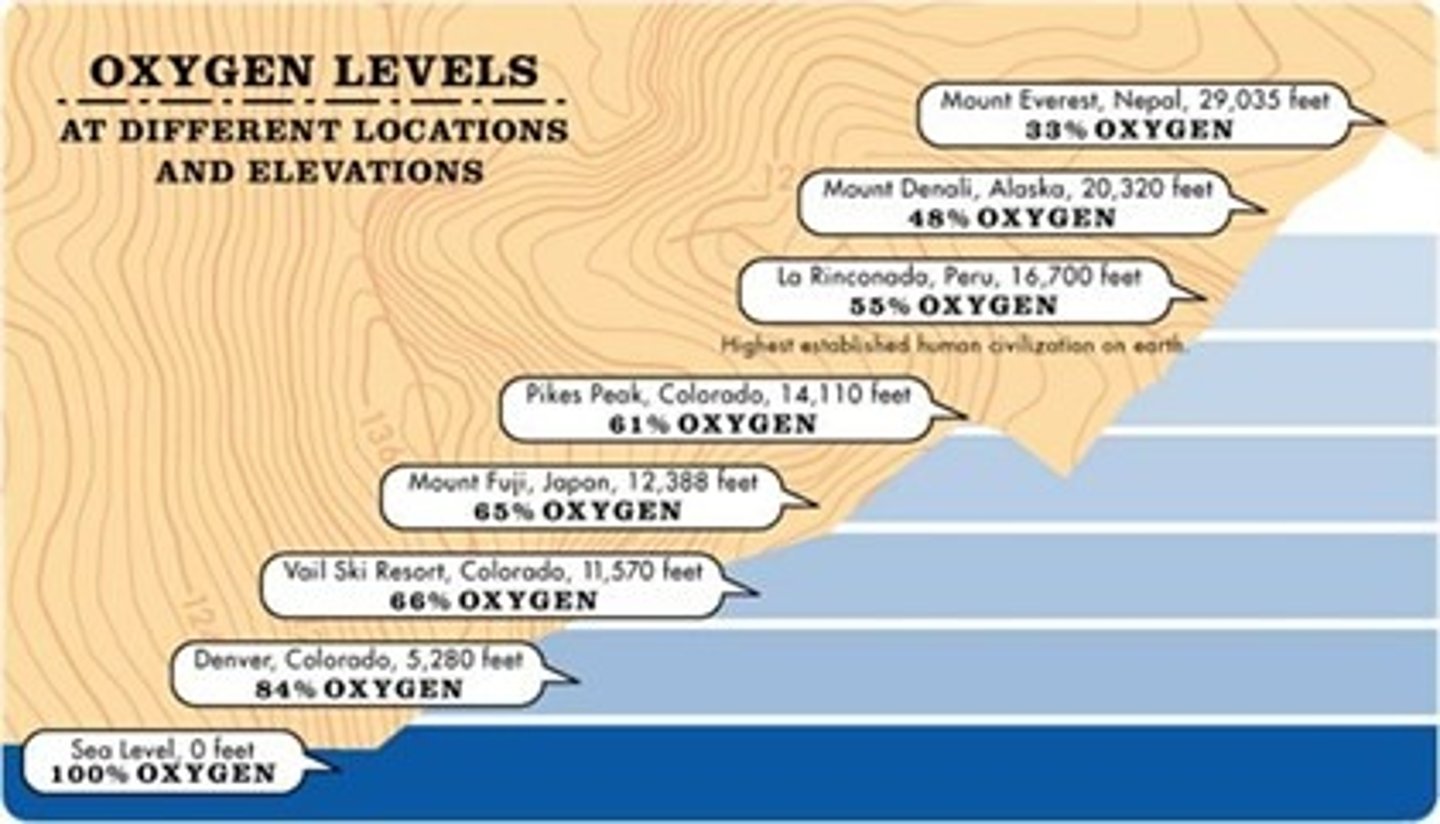
Acclimatisation
Occurs when body produces more red blood cells to compensate for a lower concentration of oxygen in the atmosphere
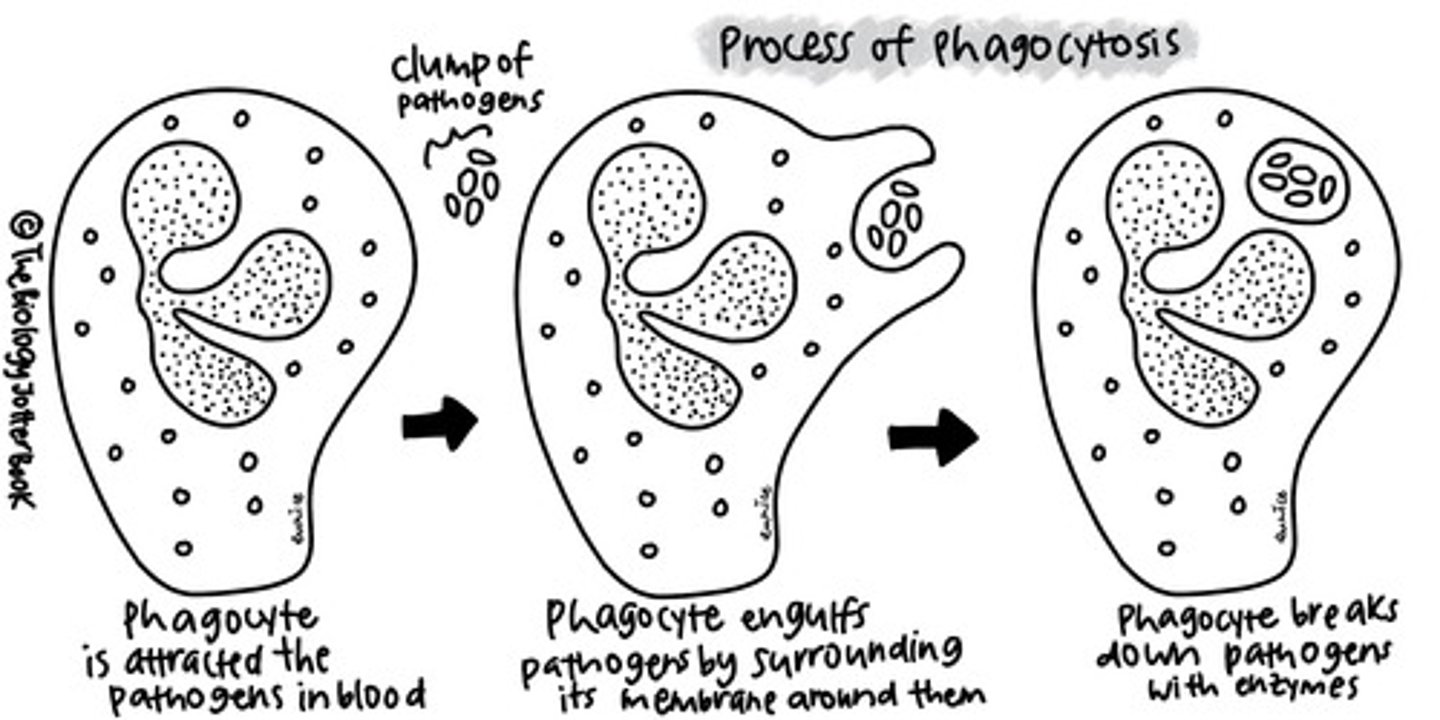
Phagocytosis
Process of engulfing and ingesting foreign particles by white blood cells/phagocytes
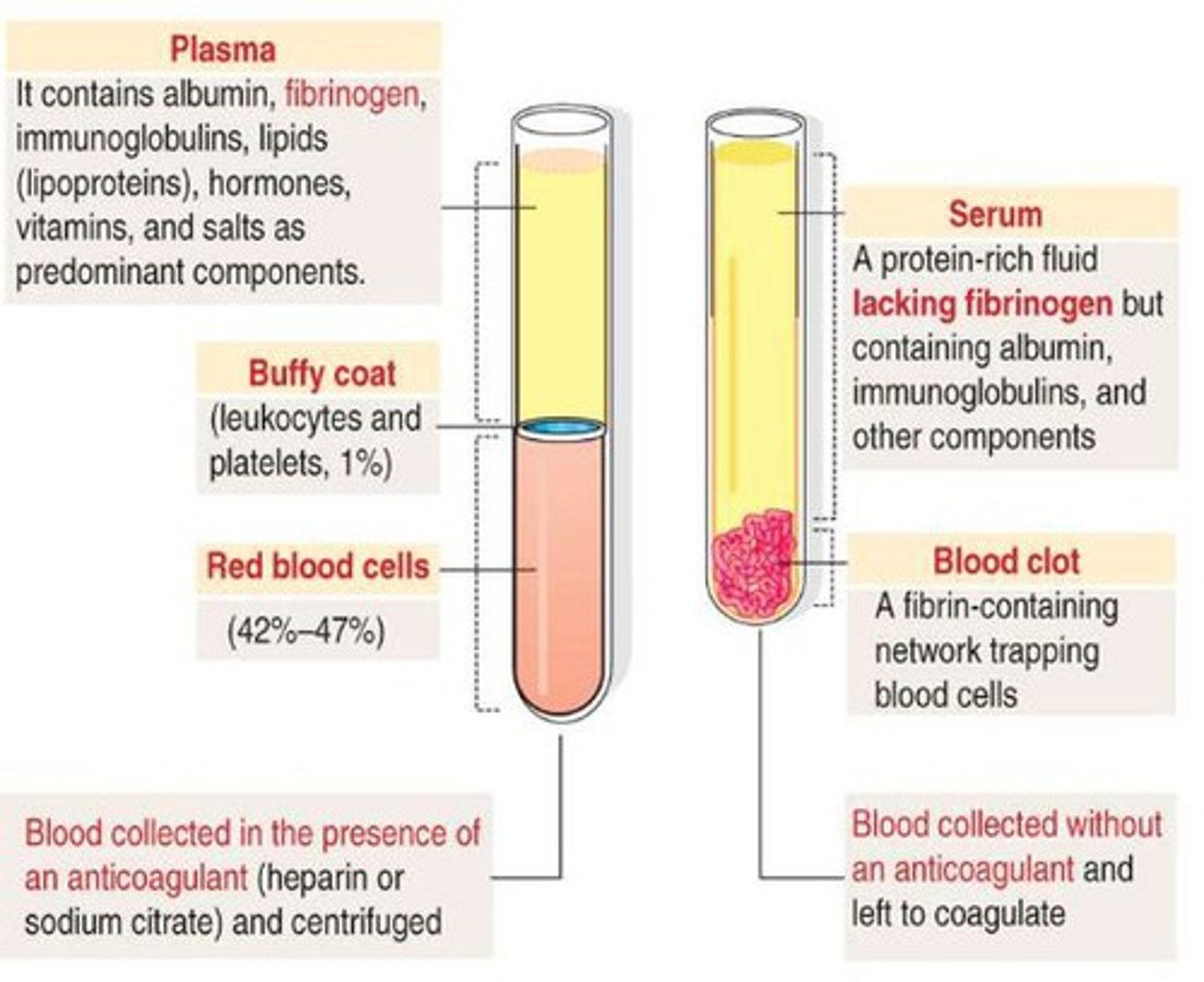
Blood serum
Blood plasma without fibrin and blood clotting factors
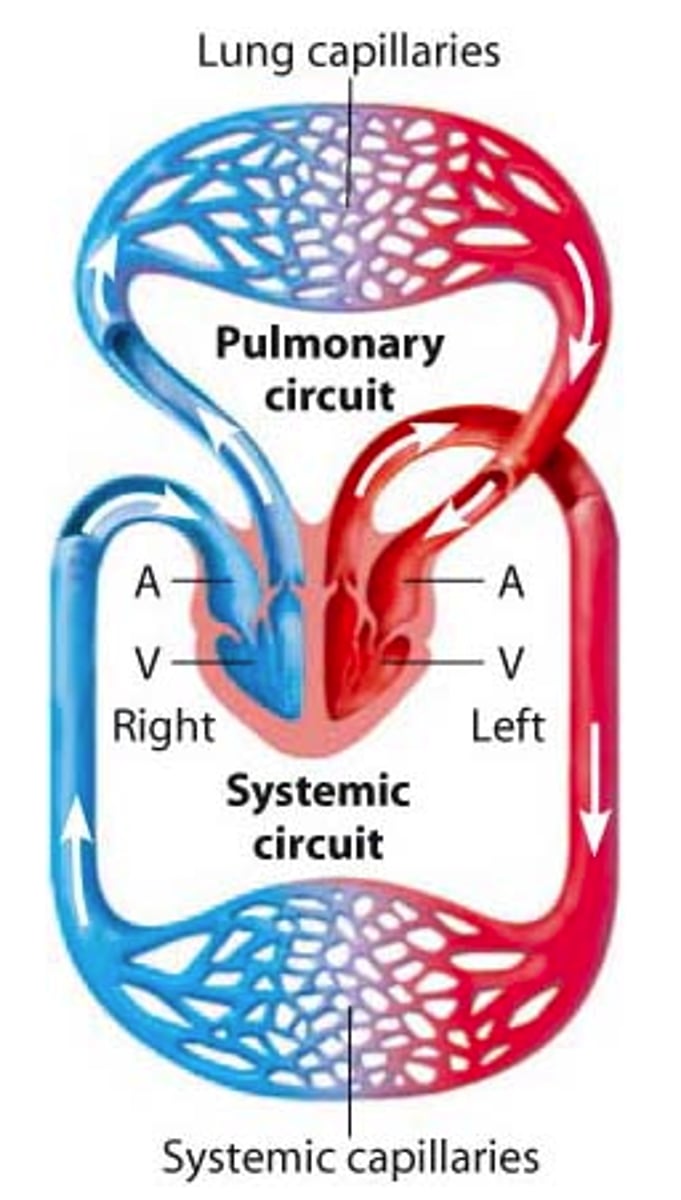
Double circulation
Consists of pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation where blood passes through the heart twice in one complete circuit
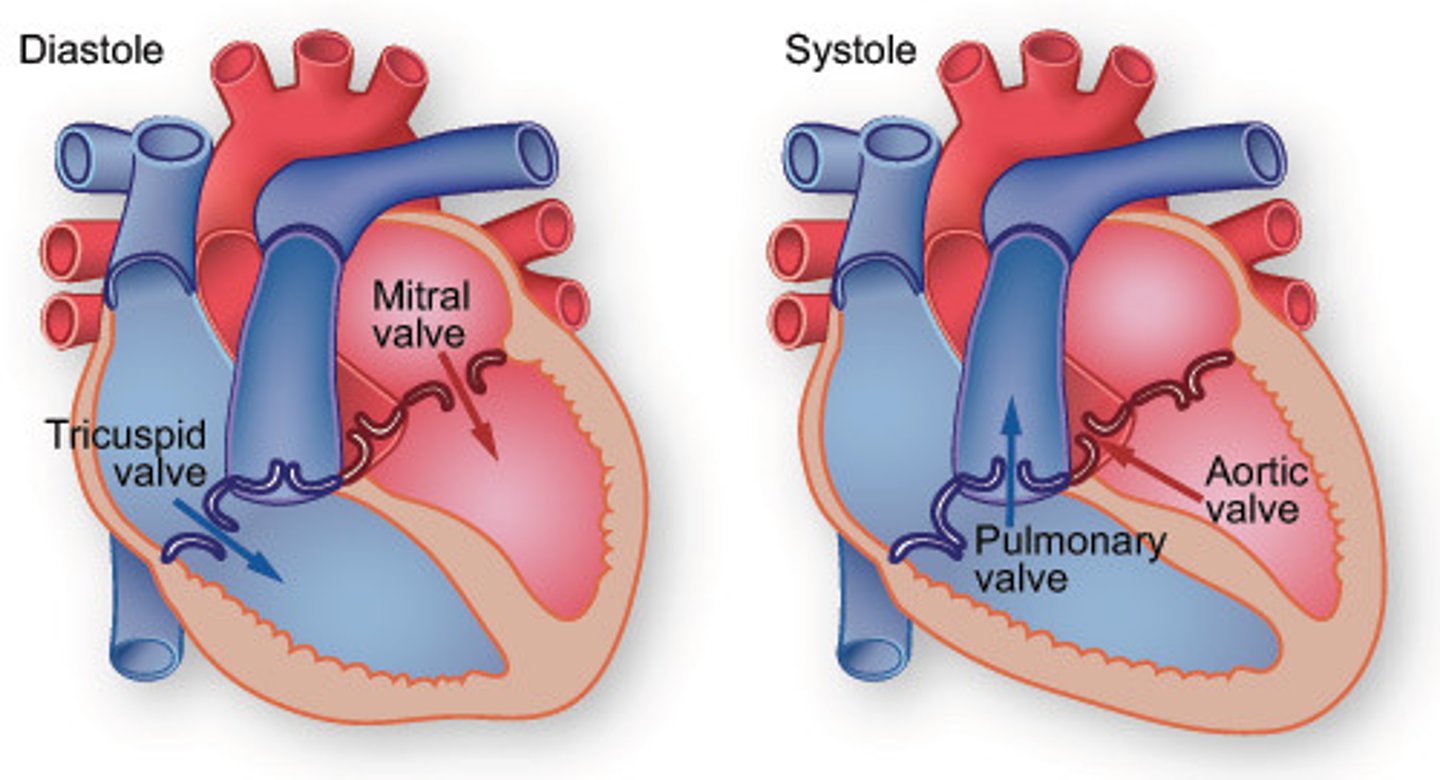
Ventricular systole
Occurs when ventricles contract
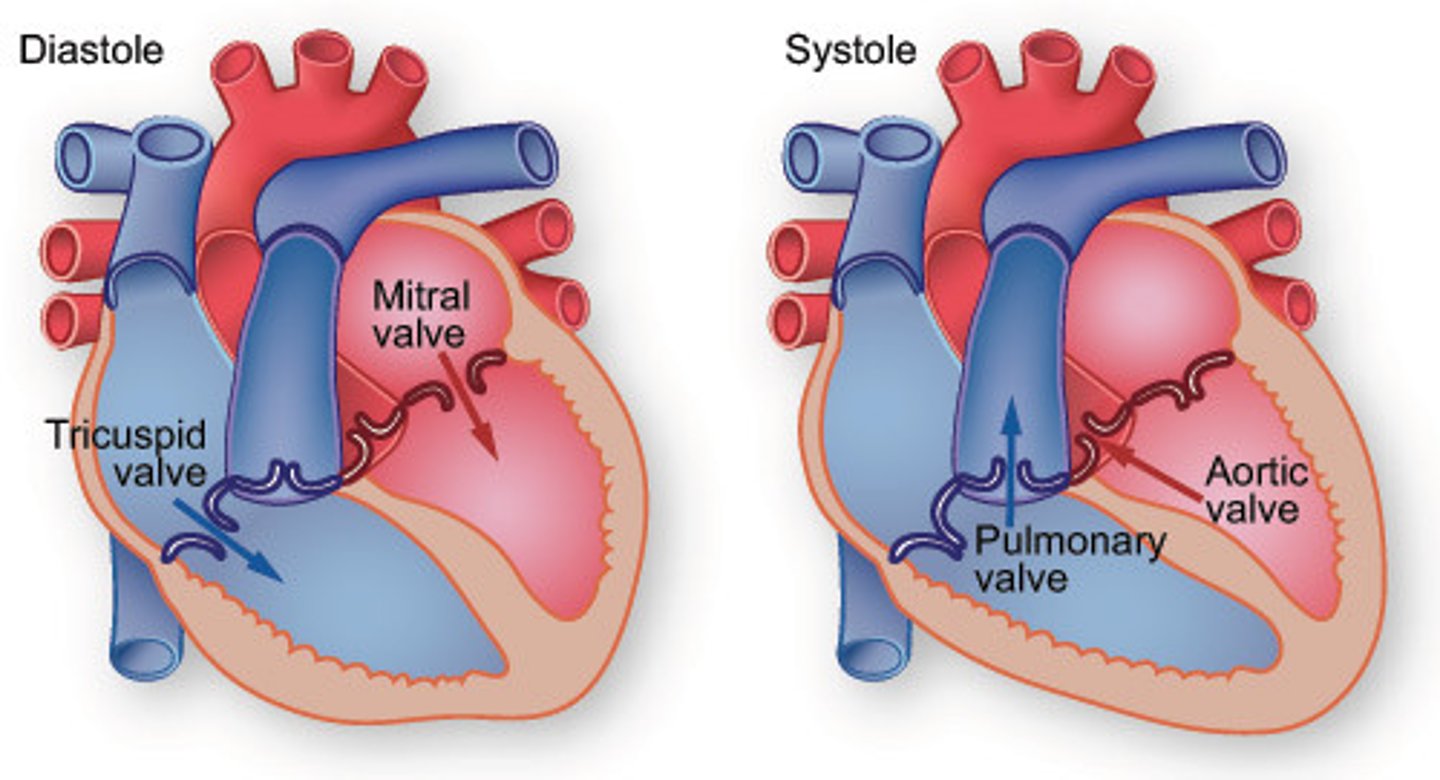
Ventricular diastole
Occurs when ventricles relax
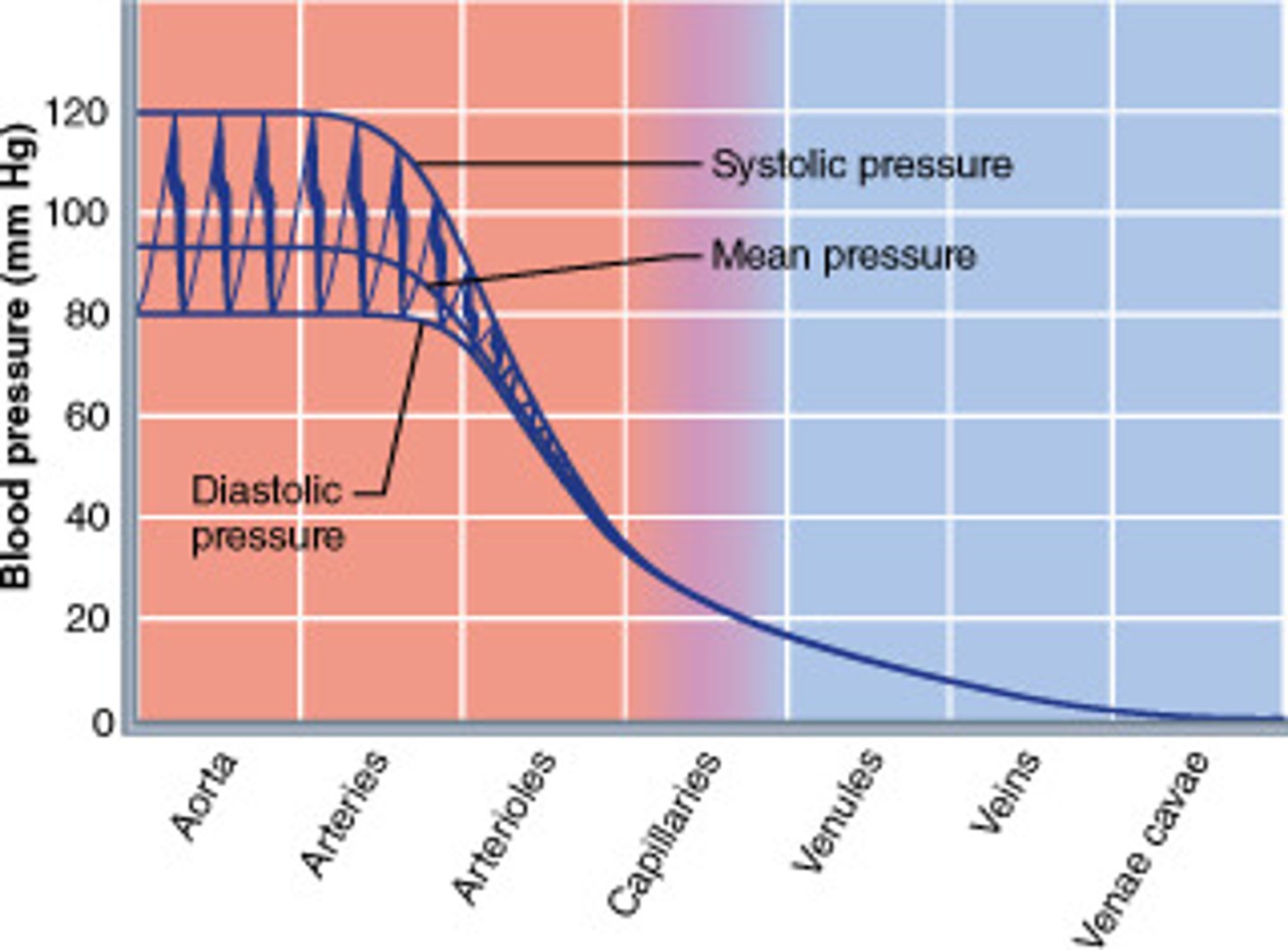
Blood pressure
Force that blood exerts on the walls of blood vessels
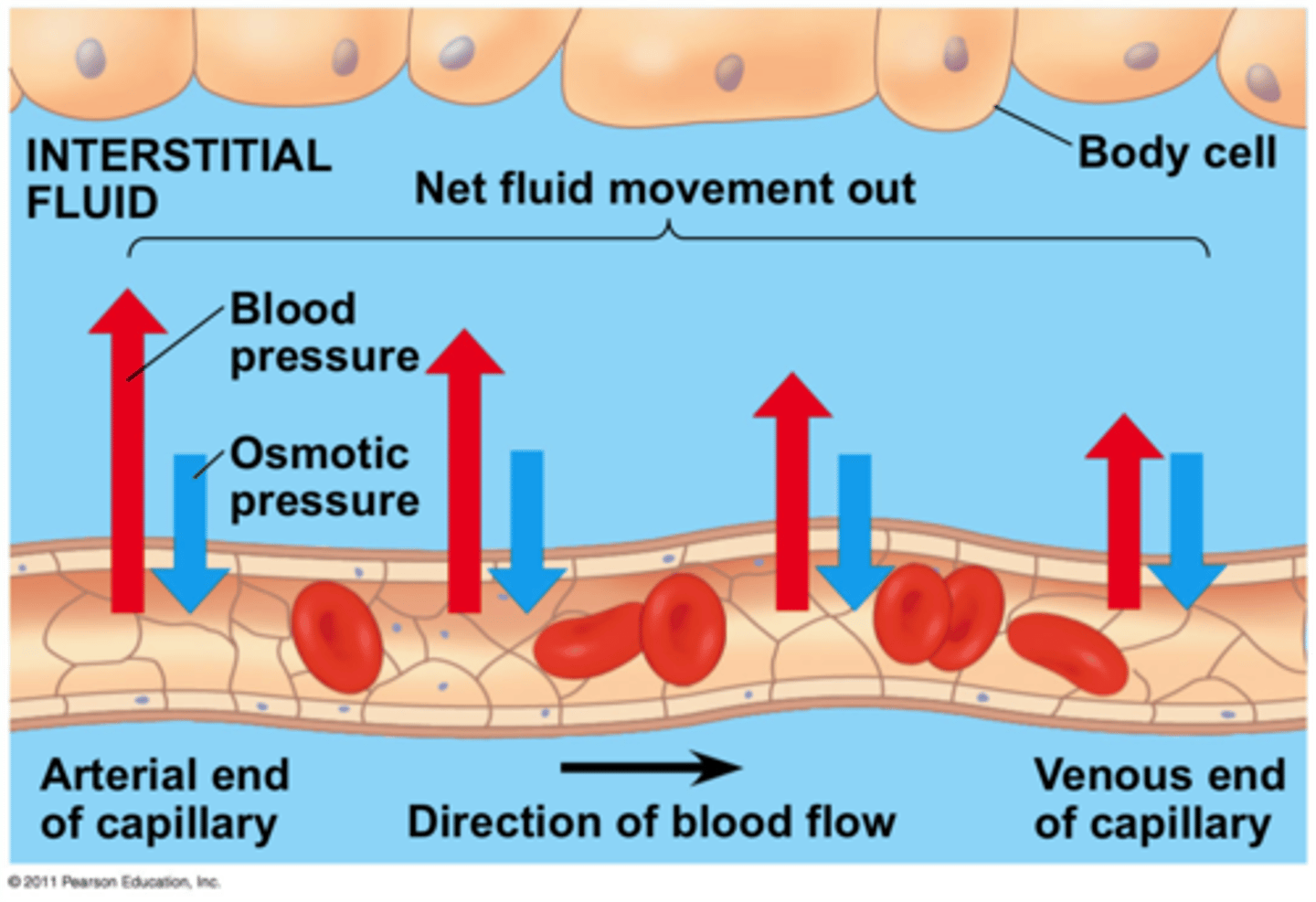
Tissue fluid
Blood plasma that has moved out of blood capillaries to the surrounding tissue cells
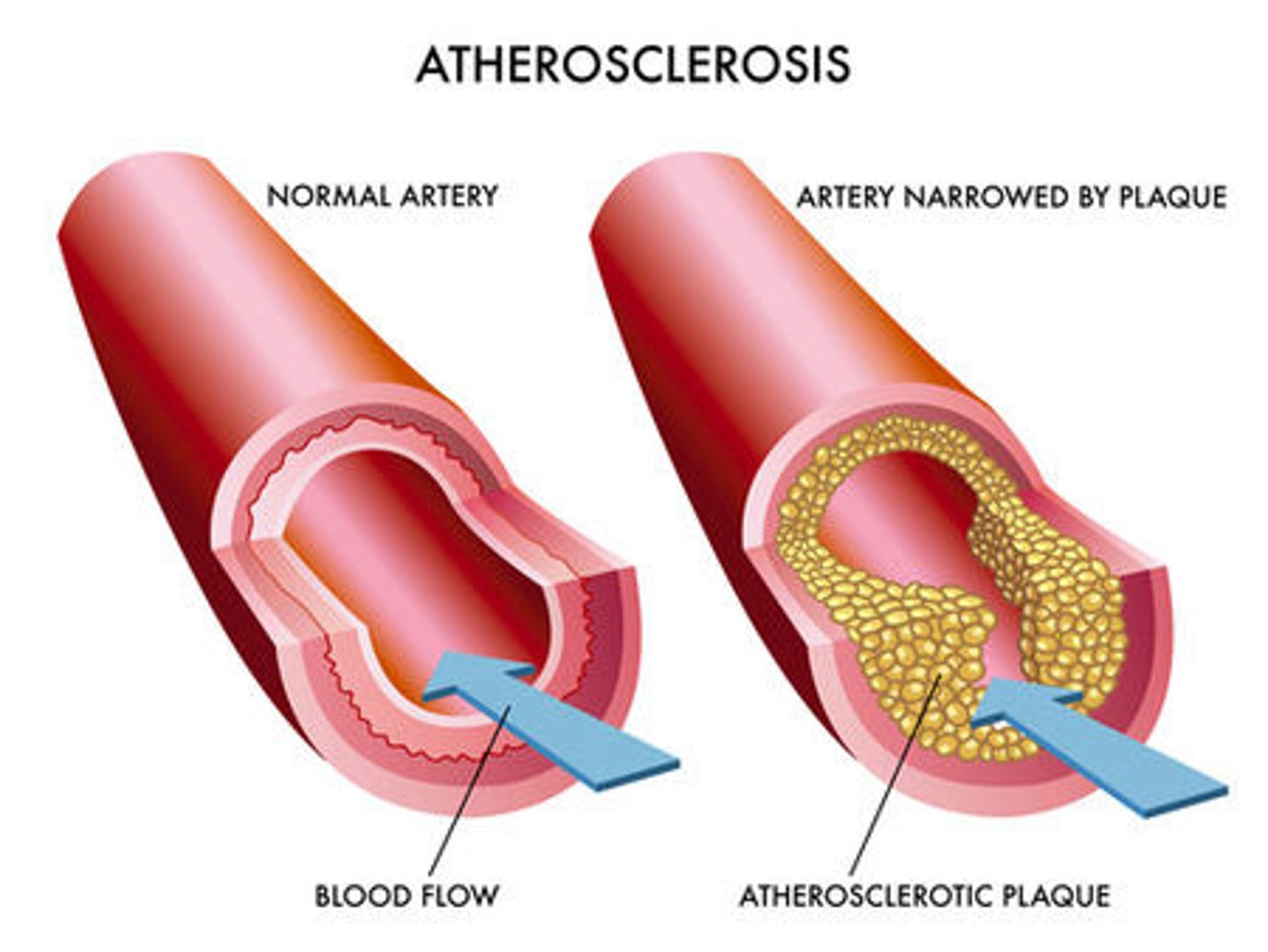
Atherosclerosis
Deposition of fatty substances on the inner surface of an artery
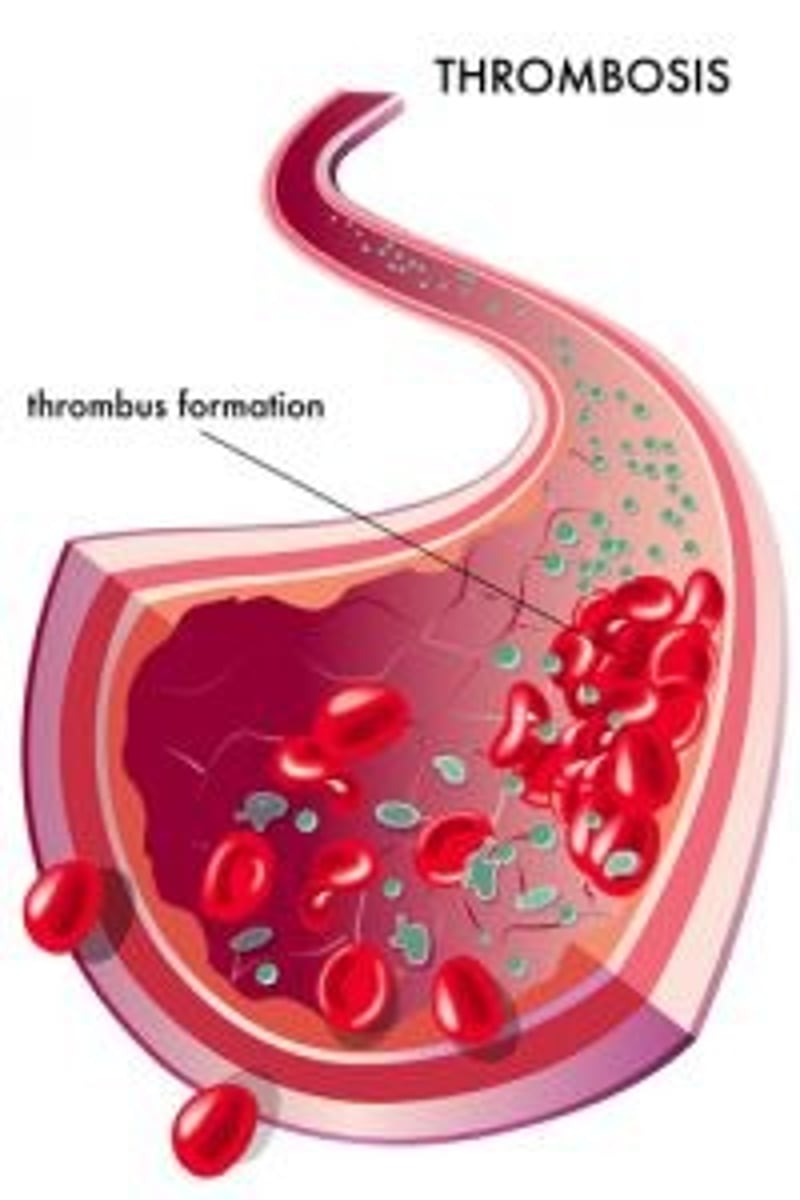
Thrombosis
A blood clot that forms in an artery