Weightlifting Final Exam
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
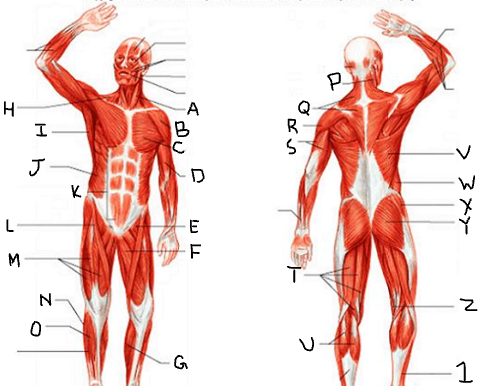
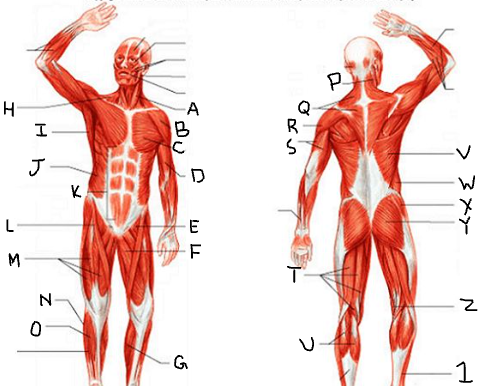
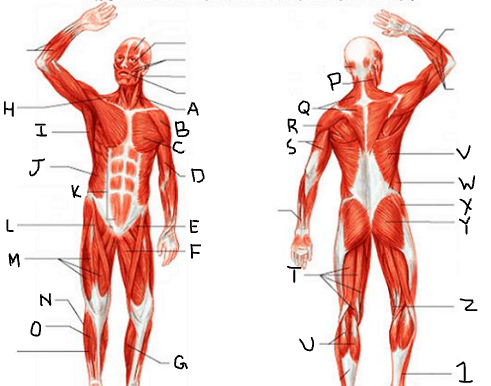
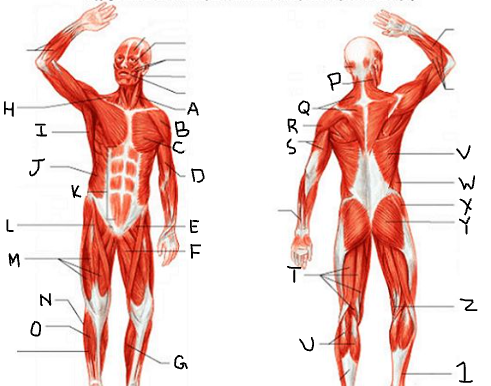
sternocleido-mastoid
What is A?
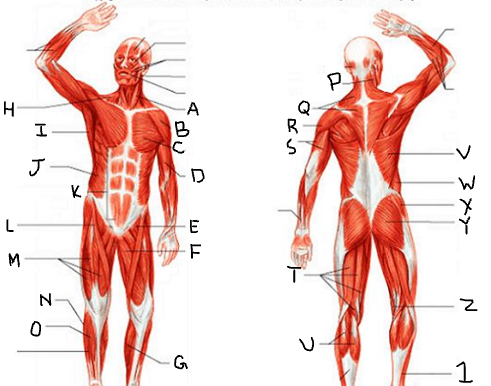
deltoid
What is B?
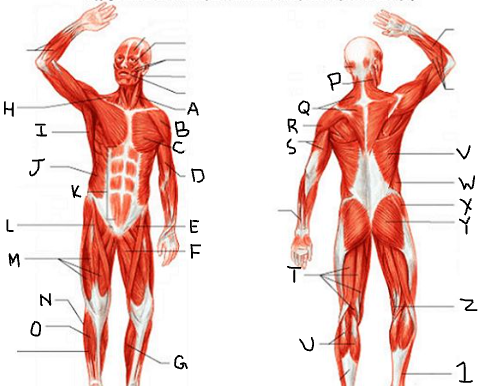
pectoralis major
What is C?
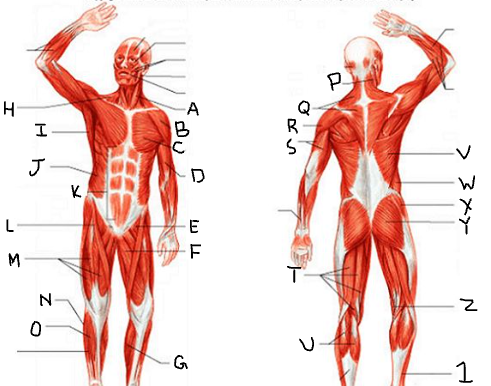
biceps brachii
What is D?
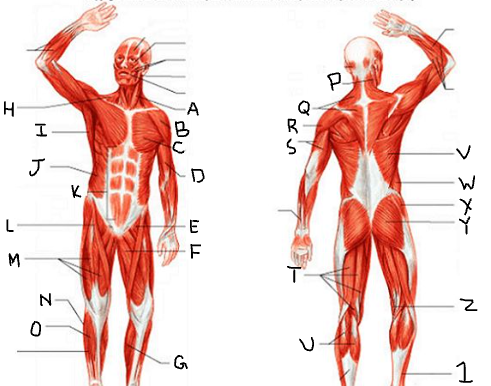
iliopsoas
What is E?
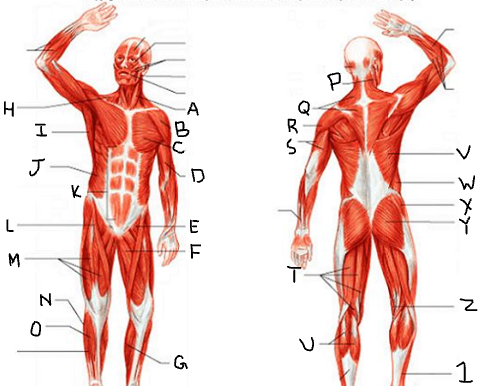
adductor longus
What is F?
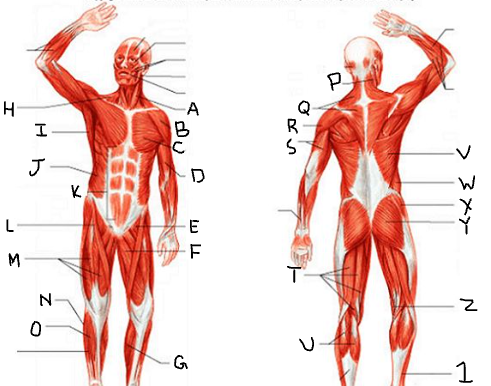
gastrocnemius
What is G?
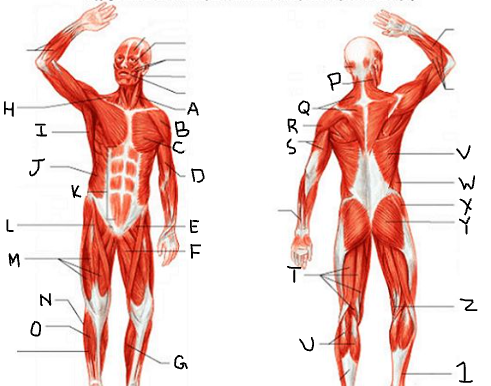
trapezius
What is H?
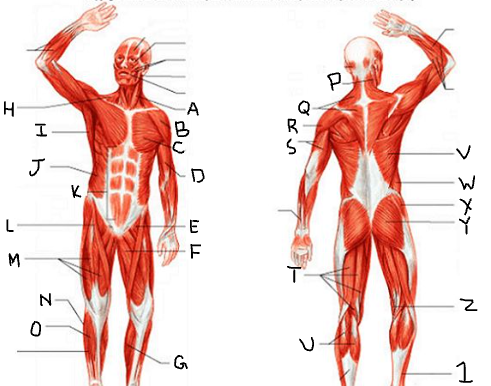
latissimus dorsi
What is I?
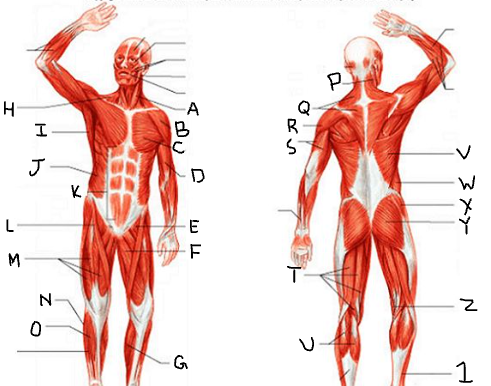
external oblique
What is J?
rectus abdominis
What is K?

sartorius
What is L?
quadriceps femoris group
What is M?
peroneus longus
What is N?

tibialis anterior
What is O?
sternocleido-mastoid
What is P?
trapezius
What is Q?
deltoid
What is R?
triceps brachii
What is S?
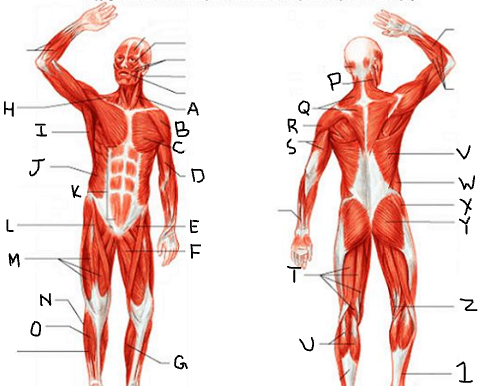
hamstring group
What is T?
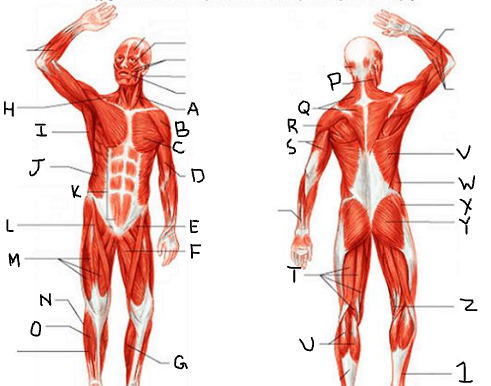
gastrocnemius
What is U?
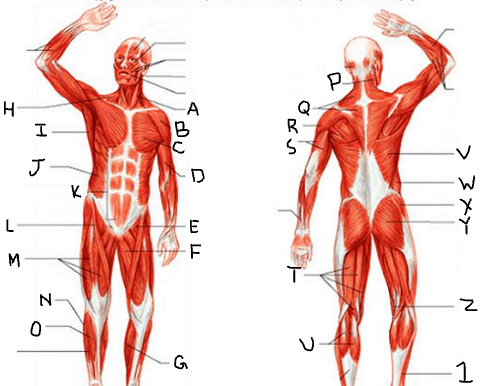
latissimus dorsi
What is V?
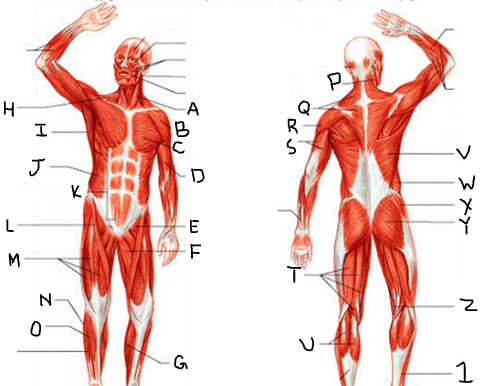
external oblique
What is W?
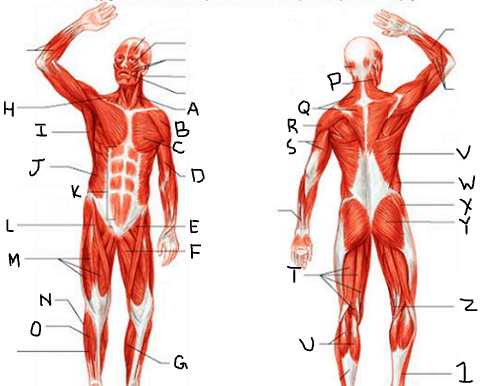
gluteus medius
What is X?
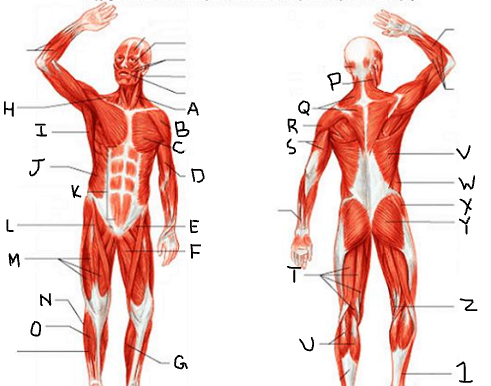
gluteus maximus
What is Y?

sartorius
What is Z?
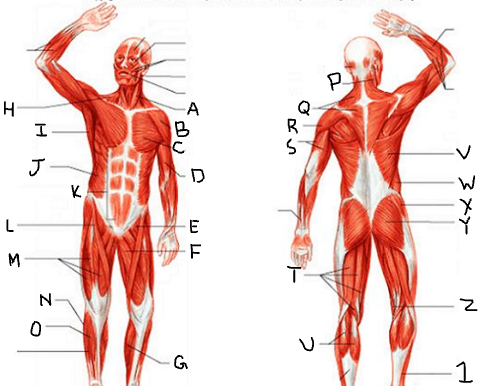
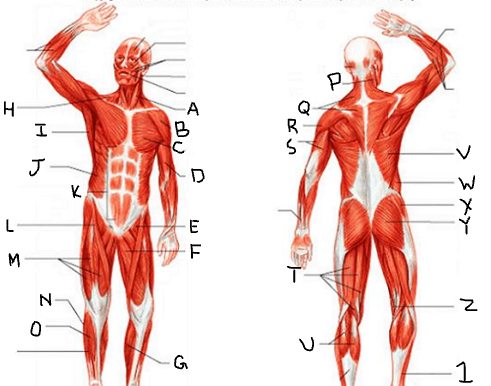
peroneus longus
What is 1?
strength
the ability of a muscular unit, or a combination of muscular units, to apply force
flexibility
the ability to maximize the range of motion at a given joint - dynamically
mobility
the ability of a joint to move freely through a given range of motion (ROM) without restriction from surrounding tissues - passively
power
the ability of a muscular unit, or a combination of muscular units to apply maximum force in a minimum amount of time
speed
the ability to minimize the time cycle of a repeated movement
coordination
the ability to combine several distinct movement patterns into a singular district movement
agility
the ability to minimize transition time from one movement to another
balance
the ability too control the placement of the body’s center of gravity in relation to its support base
muscle strength
the ability of a muscle to produce a maximal force
muscle endurance
the ability of a muscle to execute repeated contraction
agonist
a muscle in a state of contraction, opposed by the antagonist
antagonist
the muscle that can move a joint in opposite of the agonist muscle
isometric contraction
static (not moving) contraction of a muscle
isotonic
contraction of a muscle against a natural resistance; two types - concentric and eccentric
concentric contraction
shortening of the muscles during a contraction
eccentric contraction
lengthening of a muscle during contraction
extension
straightening the joint resulting in an increase of angle
flexion
bending a joint resulting in a decrease of angle
frequency
number of training sessions in a given time period
load
amount of weight lifted
hyperplasia
an increase in the number of muscle fibers
hypertrophy
enlargement of the muscle fibers and building of muscle
atrophy
decrease in the number and size of the muscle fibers, losing of muscle
repetitions
number of times an exercise is preformed in one set
sets
grouping of the number of repetitions followed by a rest period
building strength
sets range from 3-6 with 1:30 - 2:00 of rest
reps range from 5-12
weight range 65-85% of rep max
building endurance
set range from 2-4 with 60-90s of rest
reps range from 12-20
weight range 55-65% of rep max
types of endurance exercises that can replace running
boxing
agility ladders
sprints
rowing
burpees
air bike (arodine)
jump rope
cross country skiing
swimming
battle ropes
and more
over training
doing to much, too fast - leading to extreme soreness or injury
10 percent rule
training intensity or duration of exercise should no be increased more than 10% each week
FITT Principle
F - Frequency
I - Intesnity
T - Time
T - Type
5 Basic Principles of Fitness
The Overload Principle
The FITT Principle
The Specificity Principle
The Rest and Recovery Principle
The Use or Lose Principle