PHYL 141 LAB Exam Practical #3
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Autonomic (visceral) reflexes
Mediated through the autonomic nervous system (ANS) (it is involuntary)
Somatic Reflexes
Stimulate skeletal muscles by the somatic division (it is voluntary)
What are the 5 basic components of the reflex arc
Receptor
Sensory neuron
Integration center
Motor Neuron
Effector
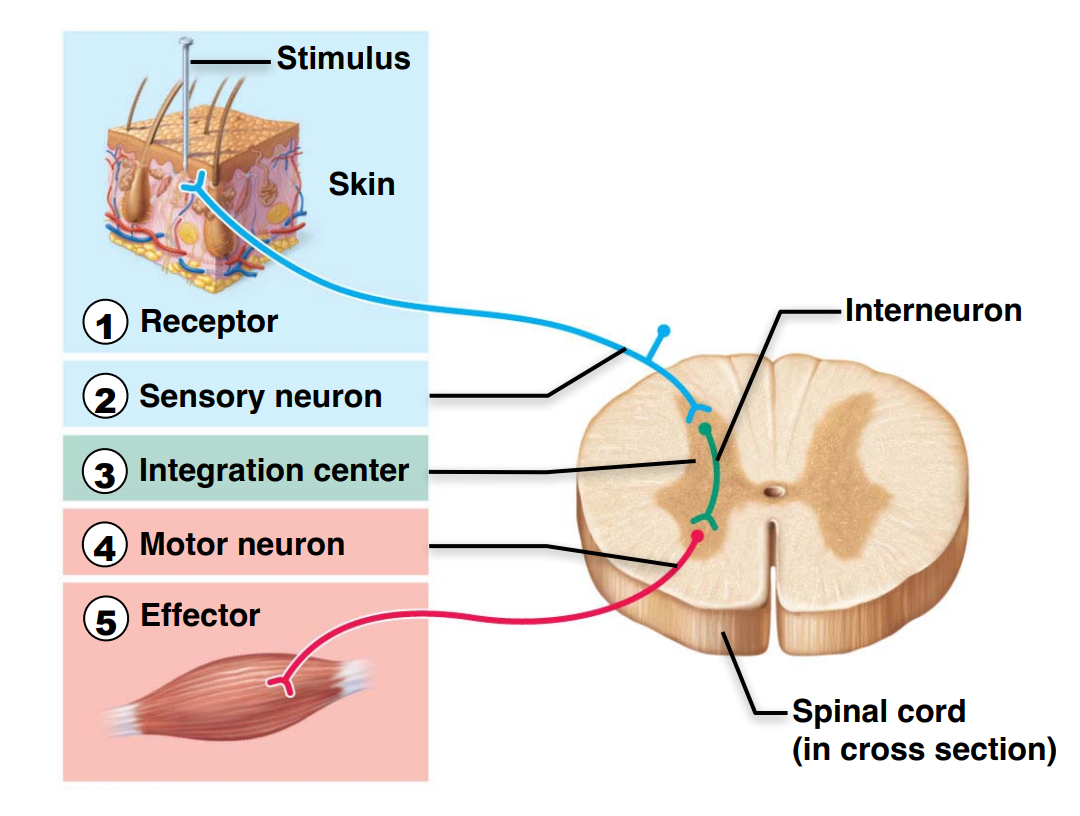
What does this picture show?
The 5 components of the Reflex Arc
What are the 2 different types of reflexes?
Simple and Complex
Simple
Monosynaptic (no more than one interneuron), fast acting
Complex
Polysynaptic (more than one interneuron) slower acting
What kind of reflex is the patellar knee jerk reflex considered as?
It is considered a Monosynaptic reflex
Somatic Reflexes (for posture, balance, and locomotion)
Stretch (deep tendon)
Crossed-extensor (withdrawal reflex ex. automatic response to pull away from painful stimuli)
Superficial (reflex resulting from pain and temp change)
Corneal (light reflected off cornea of eye, Nerve V)
Gag (contraction of back of throat, Nerve IX & Nerve X)
Reciprocal Inhibition (reflexive antagonism)
Interneurons help to control or inhibit the action of antagonist muscles to allow agonist muscles to work more efficiently
Autonomic Reflexes (automatic)
Pupillary — light input is the stimulus (contralateral response: opposite stimulation site to response site) & (Ipsilateral response: same stimulation and response site)
Ciliospinal (sensation input)
Salivary (only reflex which glands are the effectors)
What are the 2 main divisions of the Nervous system?
The CNS (central nervous system) and he PNS (Peripheral Nervous system)
What is Nervous tissue made up of?
Neurons (transmits signals) and neuroglia (not capable of generating and transmitting nerve impulses)
Neuroglia (glial cells)
Neuroglia are supporter cells and serves as protectors of the nervous system
What are the 4 types of Neuroglia cells in the CNS
Astrocytes
Microglial cells
Oligodendrocytes
Ependymal Cells
For the PNS, what glial cells would be there?
Schwann cells (forms myelin) and satellite cells
What cell is most abundant in the CNS neuroglia?
Astrocytes
What do Ependymal Cells do?
Ependymal cells line cerebrospinal fluid-filled cavities they also have cilia
Neurons have 2 types of processes
1) Dendrites- receptive regions with neurotransmitter receptors
2) Axons- form impulse generating and conducting region
Myelin sheaths around CNS are generated by
Oligodendrocytes
What are the classifications of Neurons by structure ?
Unipolar, Pseudounipolar, Bipolar, multipolar
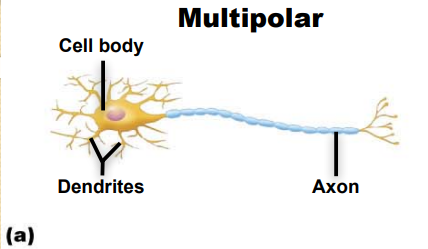
Identify this neuron according to structure
Multipolar
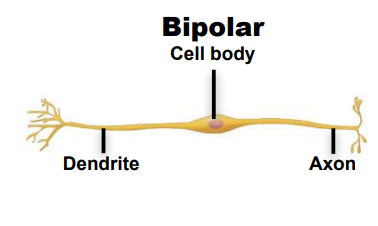
Identify this neuron according to structure
Bipolar
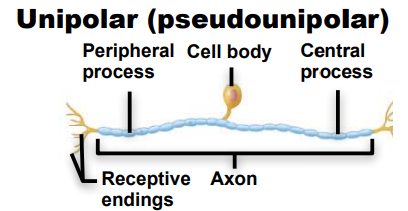
Identify this neuron according to structure
Unipolar
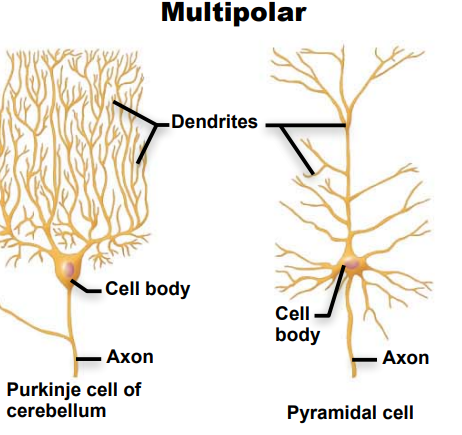
Identify this neuron according to structure
Multipolar
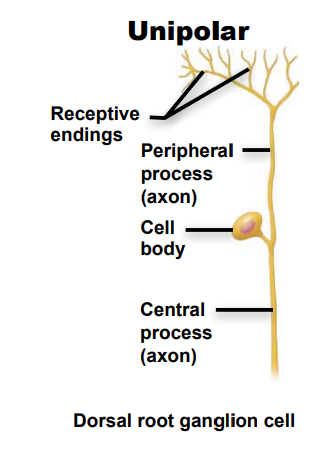
Identify this neuron according to structure
unipolar
Afferent (sensory) neurons:
Neurons carrying impulses from sensory receptors in viscera to the CNS (towards the brain)
Efferent (motor) neurons
neurons carrying impulses from the CNS to the viscera and/or body muscles and glands (away from brain)
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain and spinal CORD
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
cranial enerves, spinal nerves, ganglia, and sensory receptors
Sensory
contains nerve fibers that conduct impulses from sensory receptors TOWARDS CNS
Motor
contains nerve fibers that conduct impulses AWAY FROM CNS
Meninges of the brain
3 connective tissue that protects the brain and spinal cord
Can you list the 3 connective tissues that protect the brain and spinal cord
Dura mater (outermost), Arachnoid Mater, and Pia Mater
Cerebrospinal fluid
watery cushion that protects the brain against trauma
Can you name all the cranial nerves from I - XII
I. Olfactory (OH)
II. Optic (OH)
III. Oculomotor (OH)
IV. Trochlear (TO)
V. Trigeminal (TOUCH)
VI. Abducens (AND)
VII. Facial (FEEL)
VIII. Vestibulocochlear (VERY)
IX. Glossopharyngeal (GOOD)
X. Vagus (VELVET)
XI. Accessory (AH)
XII. Hypoglossal (Heaven)
What is Wernicke’s area in the brain known for
speech processing
Vagus Nerve function
Controls involuntary functions of the body (carries somatic moor impulses)
ex. heart rate, digestion, BP
Vestibulocochlear Nerve Function
Balance and hearing, semicircular canals and cochlear branch
What are the 3 major neuron populations in the eye?
photoreceptors, bipolar cells, and ganglion cells
Rods
Specialized photoreceptors for dim light
Cones
color photoreceptors
the Fovea centralis only contains what?
Only contains cones
The Retina periphery contains more what?
Rods
Ganglion cells receive what?
Ganglion cells receieve signals
Normal eye
emmetropic eye
Astigmatism
Irregularities in the curvatures of lens/cornea, presented in younger populations
Presbyopia
Difficulties focusing for near or close vision (blurry vision) due to aging and loss of lens elasticity
Myopic Eye
Nearsighted-ness concave lens
Hyperopic eye
farsighted, convex lens
Name your special senses
vision, hearing, equilibrium, smell and taste
What are some general sensory receptors?
Exteroceptors, Interoceptors, Proprioceptors
Exteroceptors
React to stimuli in the external environment
(ex: cutaneous receptors in skin, receptors in eye)
Interoceptors (visceroceptors)
Responds to stimuli arising in the body
ex. stretch receptors-internal organs, chemoreceptors
Proprioceptors
Respond to internal stimuli from skeletal muscles, joints, and ligaments/ tissues covering bones and muscles (similar to interoceptros)
What are the 4 qualities of cutaneous sensation
tactile, heat, cold, and pain
What receptors are most abundant?
Pain receptors
Adaptation
When a stimulus remains constant without our reaction, the CNS recognizes it and the receptor discharge slows
(ex: clothing on our skin)
WHat are the 3 major areas of the ear
Externa, Middle, Internal Ear
The external and middle ear are responsible for what sense?
hearing
The Internal Ear is responsible for what sense?
sense of balance/ equilibrium
What does the vestibular apparatus contain (equilibrium Apparatus)
contains utricle, saccule, semicircular ducts filled with endolymph
Semicircular canals
Monitor head rotational acceleration (dynamic equilibrium)
The receptors for olfaction (smell) and taste are?
chemoreceptors
What is the organ of smell called?
Olfactory epithelium (found in rook of nasal cavity)
What 3 cell types does the olfactory epithelium have?
1) Olfactory Sensory neurons (bipolar neurons)
2) Supporting cells
3) olfactory stem cells
Taste buds
Receptors for taste that are widely but not uniformly distributed in the oral cavity
Most taste buds are in ?
Papillae (mostly found on dorsal surface of the tongue)
Where can taste buds also be?
soft palate, epiglottis, pharynx, inner cheeks
Each taste bud has two types of modified epithelium?
Gustatory epithelial cells, basal epithelial cells
sensory (afferent) neurons associated with olfaction in the taste buds are?
1) Facial Nerve (VII)
2) Glossopharyngeal (IX)
3) Vagus (X)
Taste can be categorized in 5 basic qualities, which are ?
Bitter, sweet, salty, sour, and umami (savory)