GCSE OCR Gateway A Physics Topic 6 - Radioactivity
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Nucleon
Proton/ Neutron
Nucleon Number
amount of protons and neutrons in a nucleus
Proton
symbol: P
relative charge: 1
relative mass: 1
location: nucleus
Neutron
symbol: N
relative charge: 0
relative mass: 1
location: nucleus
Electron
symbol: E
relative charge: -1
relative mass: 1/2000 (0)
location: shells
Alpha Emission
symbol: α
2 protons + 2 neutrons
relative charge +2
relative mass 4
range in air a few mc
stopped by paper
penetrating power: weak
Beta Emission
symbol: β
1 electron
relative charge: -1
relative mass: 1/200-
range in air: 1 meter
stopped by: thin aluminium
penetrating power: medium
Gamma Emission
symbol: γ
EM wave
relative charge: 0
relative mass: 0
range in air: near infinite
stopped by: thick lead
penetrating power: massive
Emissions ranked by ionising power
Alpha (Most momentum)
Beta
Gamma
What is used to measure radiation
Geiger-muller counter
Units of Radiation
Becquerels (BQ)
Sievert (SV)
Half life
the amount of time it takes for the radioactive activity in a substance to halve
how to calculate radioactive activity after x number of half lives
original activity ⋅ (1/2)x
(x is the number of half lives)
Contaminated
Radiated from a source internally
Irradiated
Radiated from an external source
Nuclear fission
The process where a neutron collides with a large unstable heavy nucleus (like Uranium) which causes it to split into two smaller nuclei and release energy
What is Fission used for
To generate electricity in a nuclear power plant by using the energy released from the process to boil water into steam and turn a turbine
Chain reaction
When fission takes place and the neutrons released after the nucleus splits invoke fission on other large unstable nuclei
How is Fission controlled in a power station
Control rods made of Boron absorb Neutrons to control the chain reaction
Nuclear Fusion
The Process where two light atomic nuclei (like hydrogen) combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing energy
Why cant Fusion be reproduced in a reaction
Achieving the conditions required is technologically challening and expensive
Atoms absorbing EM Radiation
In the photon model EM radiation is emmited as particles of energy (photons)
when these photons collide with electrons they cause them to move to higher energy levels (excitation)
when the electrons lose the energy they release the photons (de-excitation)
Continuous Spectra
a diagram showing all the wavelengths of visible light
absorption spectrum
a spectra showing the frequencies of radiation that did not cause an electron to undergo excitation
Emission spectrum
a spectra showing the frequencies of radiation emmited by electrons when they de-excite
Uses of alpha radiation
Smoke detectors
Americium-241 emits alpha radiation
alpha radiation ionises oxygen in the air and causes current to flow
when current doesnt flow the smoke alarm goes off
contamination (of air)
long half life
Uses of beta radiation
testing thickness of paper
alpha not penetrative enough
gamma too penetrative
irradiation
Use of gamma radiation for sterilisation
irradiates medical equipment
kills all living organisms without damaging equipment
short half life
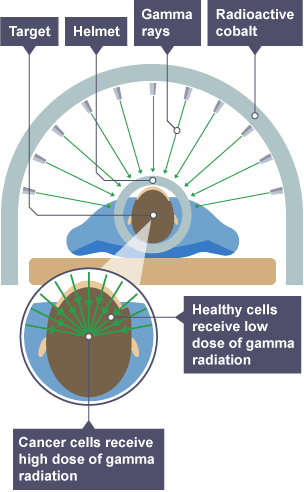
Use of gamma radiation for Treatment
moveable source of gamma radiation aimed at tumor in body
tumor gets lethal dose while other cells do not
irradiation
short half life
Use of gamma radiation for Diagnosing
Doctor injects patient with tracer
radioactive substance absorbed by organs
gamma radiation detected by gamma camera
contamination
short half life