Coding, Capacity, Duration - Features of STM and LTM
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is coding?
Format in which information is stored in the memory store. Can be visual, acoustic, or semantic
What was Baddeley 1966 aims?
Investigate coding of STM and LTM
What method did Baddeley 1966 use?
Gave different lists of words to 4 groups of Ps
- Acoustically similar (cat, cab, can)
- Acoustically dissimilar (pit, few, cow)
- Semantically similar (great, large, big)
- Semantically dissimilar (good, huge, hot)
- Asked to recall words in correct order
- Immediately (testing STM)
- After 20 mins (testing LTM)
What were Baddeley 1966’s results
Immediate recall
- Worse performance if acoustically similar
- After 20 minute interval
- Worse performance if semantically similar
What conclusions did Baddeley 1966 come to?
Suggests STM is coded acoustically and LTM is coded semantically
What does capacity mean?
Maximum amount that can be held in a memory store
What was the aim of of Jacobs (1887)
Investigate capacity of short term memory
What was the method of Jacobs (1887)?
- Measured participants digit span = max number of digits they can recall in the correct order.
- Recall a list of 4 digits immediately after hearing them in the correct order.
- Increase one digit until participants answer incorrectly.
What was the results of Jacobs (1887)?
Found mean span for digits across all participants was 9.3 for digits and 7.3 letters.
What was the conclusions of Jacobs (1887)?
Capacity of short-term memory is low around 7-9 items depending on the type of information.
What was the aim of Miller (1956)?
Investigating capacity of short-term memory.
What’s was the method of Miller (1956)?
Observations of everyday practise and short-term memory.
What were the findings of Miller (1956)?
Things come in groups of sevens e.g since, music notes and days of the week.
What were the inclusions of Miller (1956)?
Capacity of short-term memory is 7 plus/minus 2 items (5-9)
Chunk (group) information together into units so 5 words ca be remembered just as easily as 5 letters
What is duration?
Length of time information can be held in memory
What was the aim of Peterson and Peterson (1959)?
Investigate the duration of short-term memory
What was the method of Peterson and Peterson (1959)?
- Ps given a trigram made of consonant syllables e.g. YCG
- Ps count backwards from 3 digit number (to prevent mental rehearsal which might increase duration through practice)
- Ps recall consonant syllable after different retention intervals ranging from 3 to 18 seconds
What were the results of Peterson and Peterson (1959)?
- 80% recall after 3 seconds
- 3% recall after 18 seconds
What were the conclusions made from Peterson and Peterson (1959)?
Suggested short-term memory duration is around 18-30 seconds without rehearsal.
What was the aim of Bahrick et al. (1975)?
Investigate the duration of long-term memory.
What was the method of Bahrick et al. (1975)?
- 392 American Ps aged 17 to 74
- Recall info from school yearbooks
- Photo recognition test of which photos were from their yearbook
- Free recall test were Ps recalled names of their graduating class
What were the results of Bahrick et el. (1975)?
- 90% accurate (photo recognition) within 15 years of graduation
- 70% accurate (photo recognition) after 48 years of graduation
- 60% accurate (free recall) within 15 years of graduation
- 30% accurate (free recall) after 48 years of graduation
What were the conclusions of Bahrick et al. (1975)?
Suggested some long-term memory information might last a lifetime.
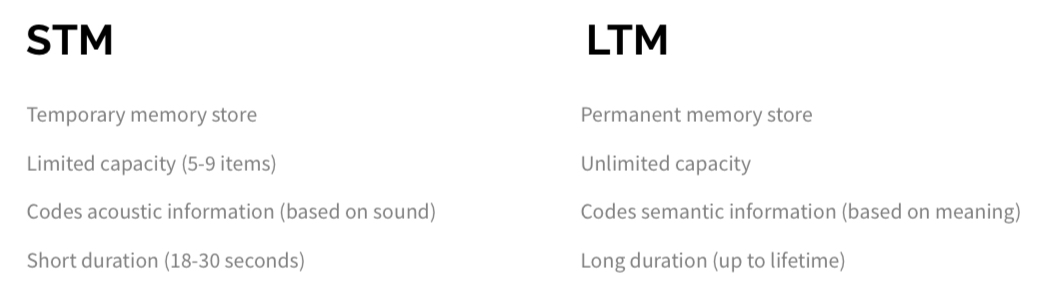
What are the differences between short-term memory and long-term memory?
What is a strength to coding studies ?
Evidence from separate memory stores
What is some evidence to support the strength of coding studies?
Baddeley (1996) demonstrated there is difference between STM and LTM
- Ps had to learn a list of words (acoustically similar / dissimilar or semantically similar / dissimilar)
- Then recall them in the correct order immediately after or 20 minutes after.
- Found recall was worse for acoustically similar words immediately after, and semantically similar words 20 minutes later.
Why is Baddely (1996) a strength to coding studies?
Demonstrates that STM is coded acoustically and LTM is coded semantically. This advanced our understanding of how memory is coded in different stores, which later led to the multi-store model of memory which demonstrates the ways in which STM and LTM are different
What is a limitation of coding studies?
Methodological limitations of research into coding
What is evidence to support that there are methodological limitations of coding research?
Baddeleyʼs study assessed STM and LTM coding by using artificial stimuli in a lab experiment
- Word lists have no personal meaning to Ps and are not representative of memory tasks in everyday life where people remember and process more meaningful information
What is a strength of capacity studies?
Well replicated
What evidence is there to support the strength or capacity studies?
Jacobs 1887 study has been replicated
- Older studies lacked control over confounding variables which can reduce the validity of the conclusions
- Despite this, Jacobsʼ findings have been well replicated by more recent and better controlled studies (Bopp and Verhaeghen 2005)
Why is Jacobs 1887 a strength of research into capacity?
Suggests Jacobsʼ study is a valid test of digit span, therefore STM capacity is likely to be 5-9 items
What is a limitation of capacity studies?
Overestimated short-term memory capacity
What reasearch supports that capacity studies overestimated short-term memory capacity?
Miller may have overestimated STM capacity
- Cowan (2001) reviewed other research and concluded capacity is only 3-5 chunks of info
What are the methodological limitations of duration studies?
Peterson and Petersonʼs study assessed STM duration by using artificial stimuli in a lab experiment
- Recalling consonant syllables have no personal meaning to Ps and are not representative of memory tasks in everyday life where people remember and process more meaningful information
What are the methodological strengths of duration studies?
Bahrick et al. used meaningful stimuli
- Ps were recalling information like peopleʼs names and faces from their graduation year which is a more representative task of everyday life
- When similar studies have been conducted with meaningless stimuli, recall rates appear to be lower (Shepard 1967)