W6 - ACTIVE TRANSPORT AND ATP
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
obtaining energy
organic compounds = carbohydrates, lipids, proteins
enzymes speeds up reactions
making energy
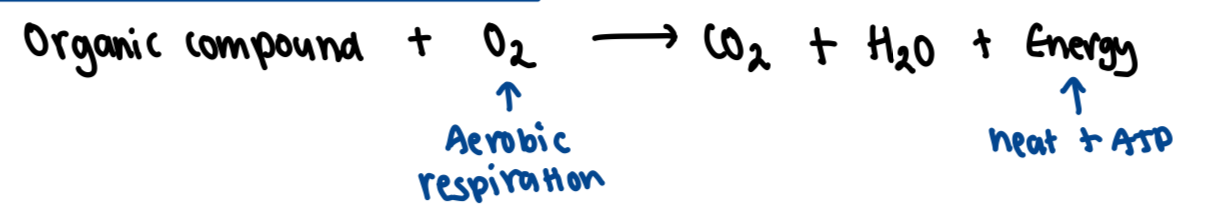
Aerobic respiration
| Anaerobic respiration
|
Steps
glucose is transported into the cell
undergoes reactions to create a substate (2 ATP made)
substate in presence of O2 foes to mitochondria
through the CAC and ATC, creates 30 ATP
CAC = citric acid cycle
ETC = electron transport chain
ATP and energy release
ATP stored in mitochondria
conversion to ADP releases energy
hydrolysis with water
ATP replenished by providing energy
ATP + H2O → ADP + Pi + energy
Active transport
uses energy to “pump: solutes (ion) across plasma membrane
against concentration gradient
carrier proteins
Na+/K+ ATPase pump
primary (direct) and secondary (indirect)
low to high concentration (needs energy)
Steps of active transport
Step 1.
Step 2
Step 3
| Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
|
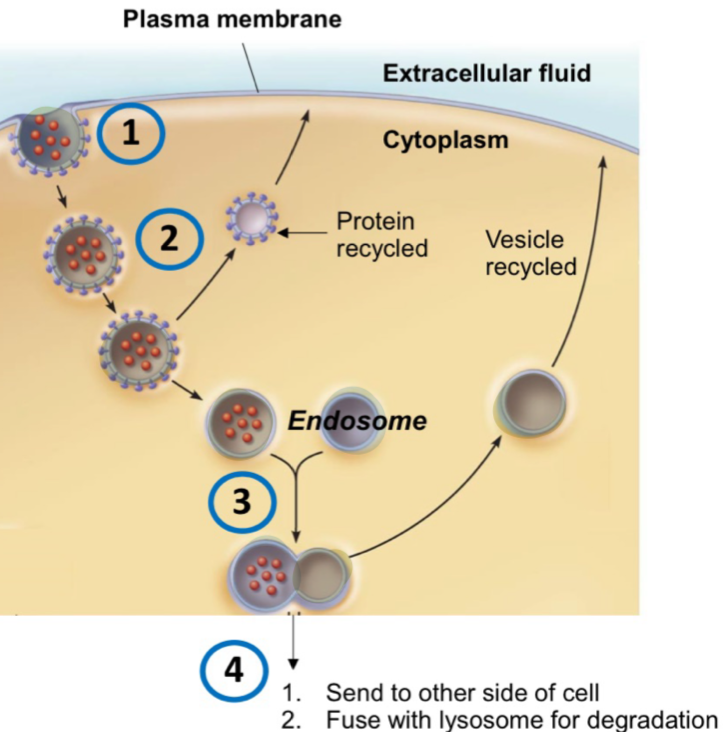
Endocytosis (vesicular transport)
Process of brining bulk fluids and substances into a cell
vesicle from fromphospholipds in plasma membrane and cytoplasmic proteins
vesicle transport engulfed substance within cell (protein recycled)
vesicle fuses with endosome (sorting vesicle) - vesicle recycled
endosome vesicle “sorted” to appropriate destination
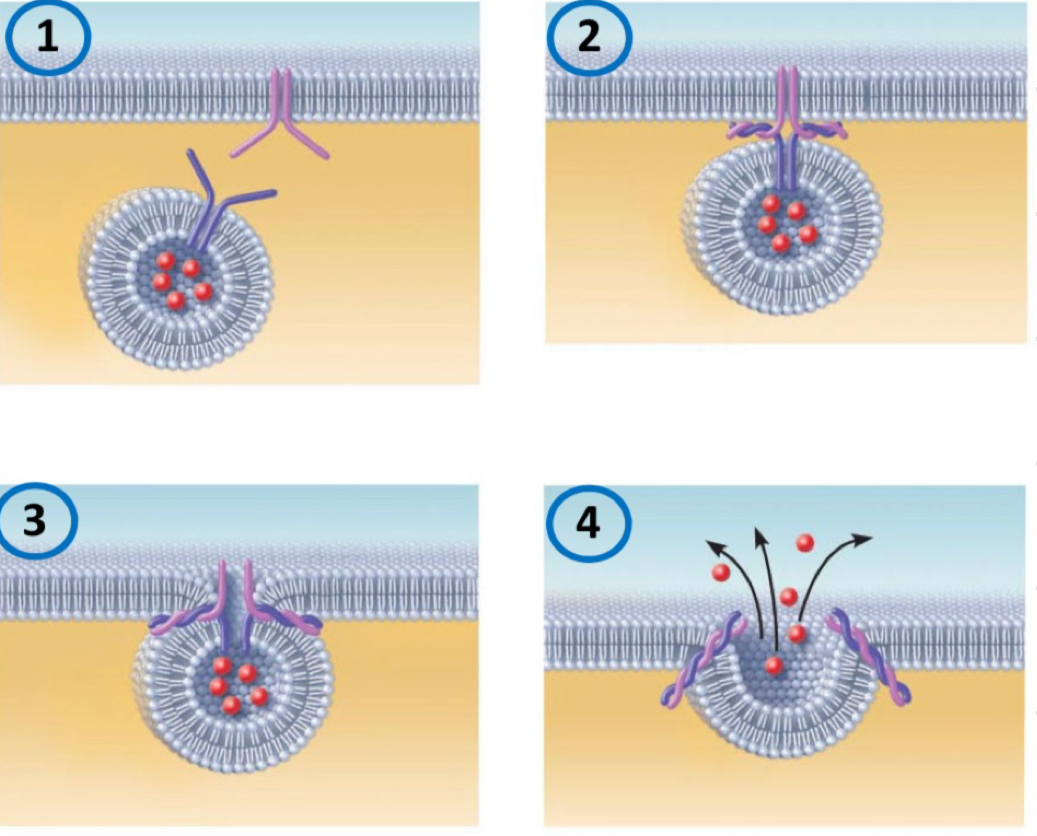
Exocyotisis
The process of ejecting substances from a cell’s interior into the extracellular fluid
the membrane bound vesicle migrates to the plasma membrane
proteins on the vesicle fuse with protein on the plasma membrane
the vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane
pore opens to the ECF
contents of vesicle released