Unit 12 Test Review - @cooluser
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Magnetism
The force of attraction or repulsion between poles
Repel
Like poles _______.
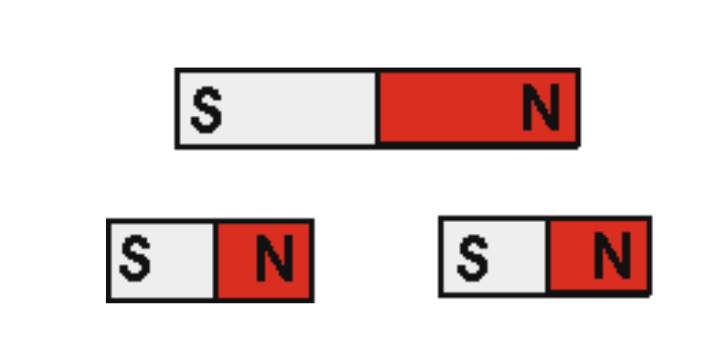
Two new magnets are formed, each with its own north and south poles.
What happens when you break a magnet?
Attract
Opposite poles ______.
Magnetic Field
Area around magnets where magnetic forces act
the magnetic field of the magnet
Field lines around a magnet show _____.
North to South
What direction do magnetic field lines travel in? (North → South / South → North)
Magnetic Domain
An area within magnetic material where all the atoms are lined up in the same direction.
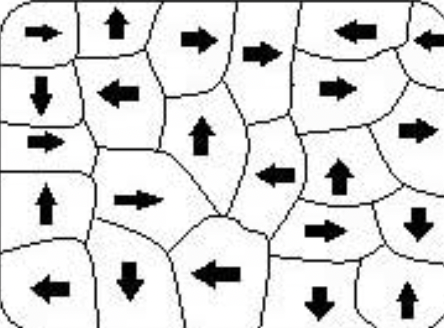
No
Is this an example of magnetized material?
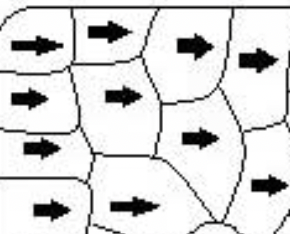
Yes
Is this an example of magnetized material?
Permanent Magents
Materials whose magnetic domains are naturally aligned in the same direction.
Examples:
Bar Magnet
Earth
Temporary Magnets
Materials that are not magnetic but can be temporarily magnetic by forcing its atoms into alignment.
Electromagnet
A strong, temporary magnet formed when a current passes through wire coiled around an iron core.
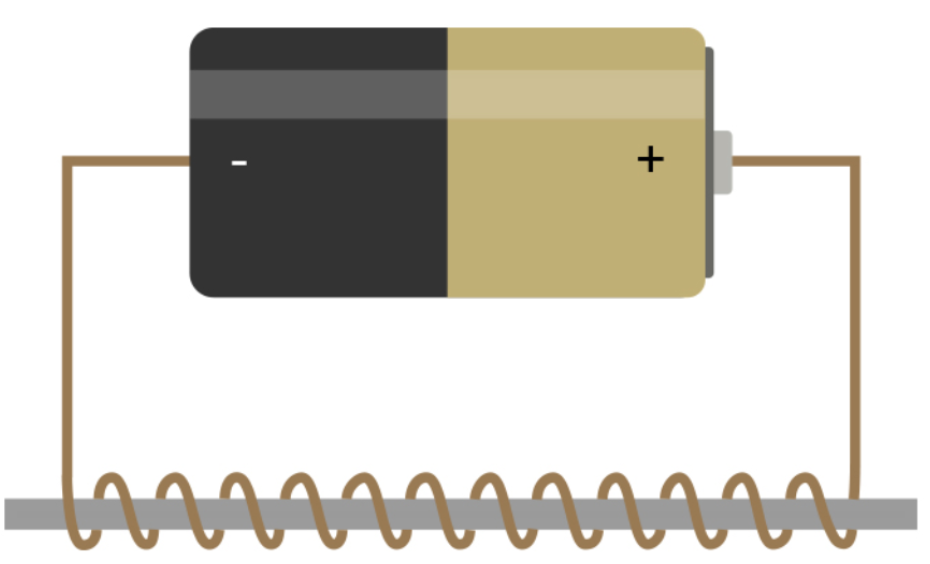
Electromagnet
What type of electromagnet is this?
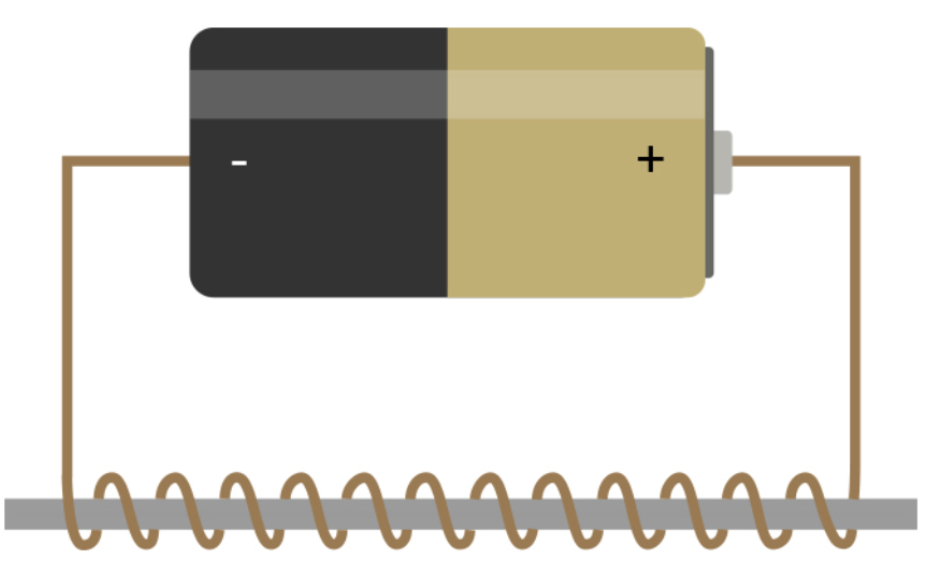
Solenoid
What type of electromagnet is this?
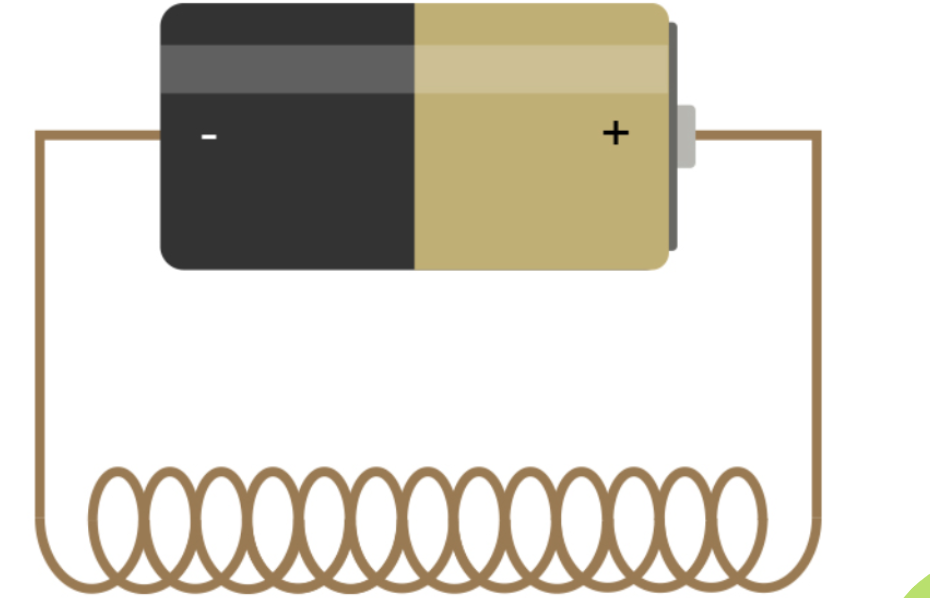
Solenoid
A temporary magnet formed when current is passed through wire that is NOT coiled around an iron core. (1000 times weaker than an electromagnet)
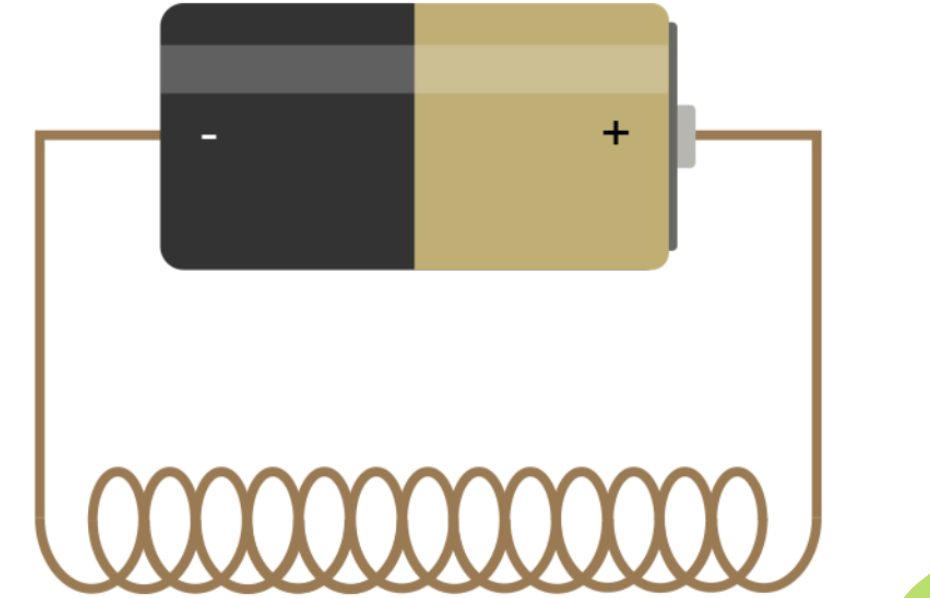
Ferromagnets
1000 times stronger than electromagnets. (Electromagnets on steroids as Mr. Siberski calls them.)
Increase the number of coils
Increase the voltage source
What are two ways to increase the strength of the electromagnet?
Swap the wires on the battery ends
How do you swap the poles of an electromagnet?
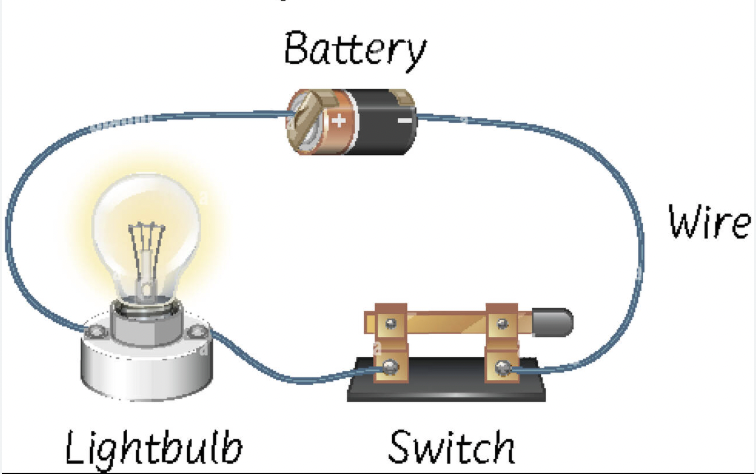
Circuit
The path for the flow of electrons.
(Currents are controlled with these.)
Power Source
Supplies the power for the circuit
(Ex: Battery)

Resistor
Something the resists the flow of electricity.
(Ex: Lightbulb)

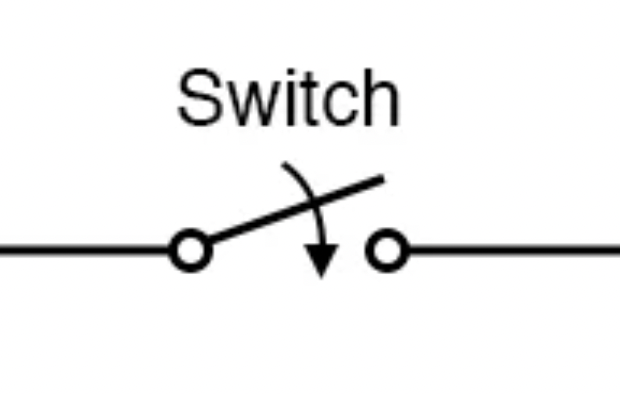
Switch
Opens or closes a circuit.

Wire
Connects all of the components of the circuit.
Voltage (Measured in Volts/V)
The force at which an electric current is pushed through a circuit.
Resistance (Measured in Ohms/Ω)
The opposition to the flow of energy.
The Material, Thickness, Length, and Temperature of the wire.
What factors affect resistance?
Low
When the wire is thick, the resistance is _____.
High
When the wire is thin, the resistance is _____.
Low
When the wire is short, the resistance is _____.
High
When the wire is long, the resistance is _____.
High
When the temperature of a wire is high , the resistance is _____.
Low
When the temperature of a wire is low, its resistance is _____.
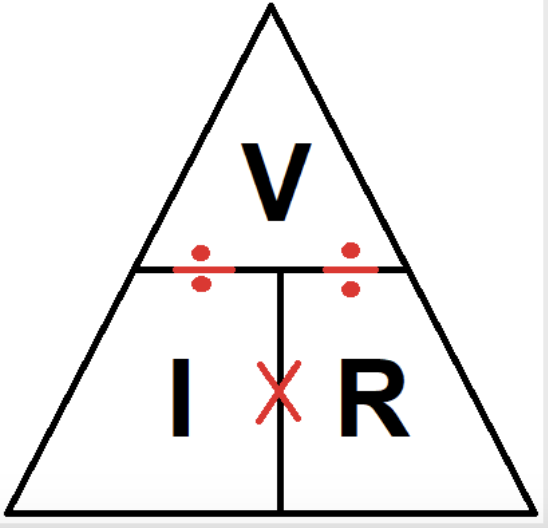
Ohm’s Law
What does the formula, V = IR, refer to?
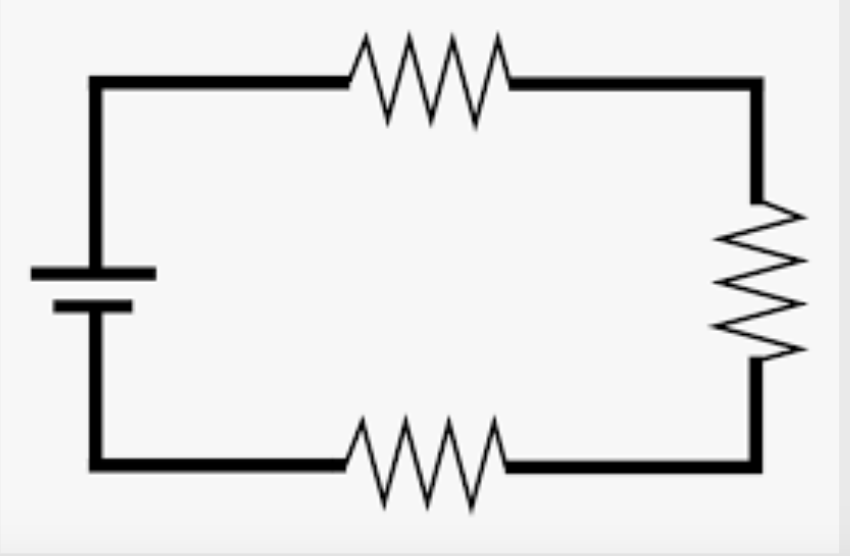
Series Circuit
A circuit where all of the components are lined up on one continuous path
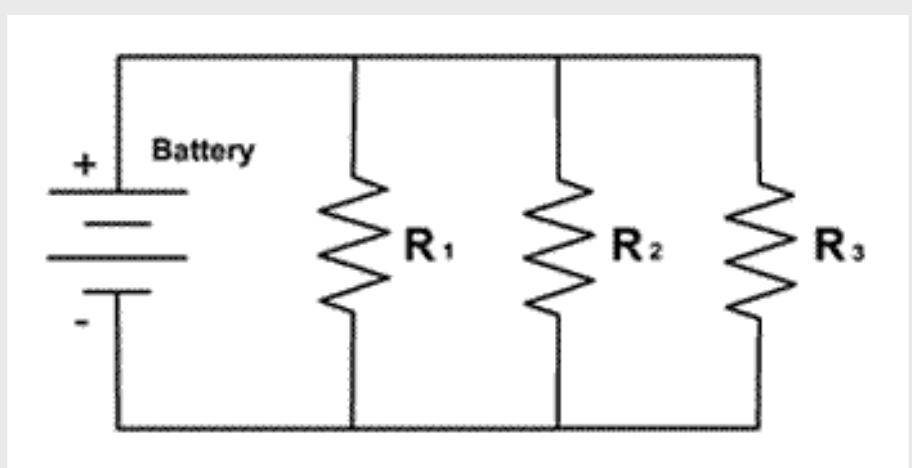
Parallel Circuit
A circuit whose components are NOT lined up on a continuous path. This circuit is similar to a ladder.
Electricity
The flow of electrons. Like charges repel and opposite charges attract.
Electrical Force
The attraction or repulsion of electrical charges.
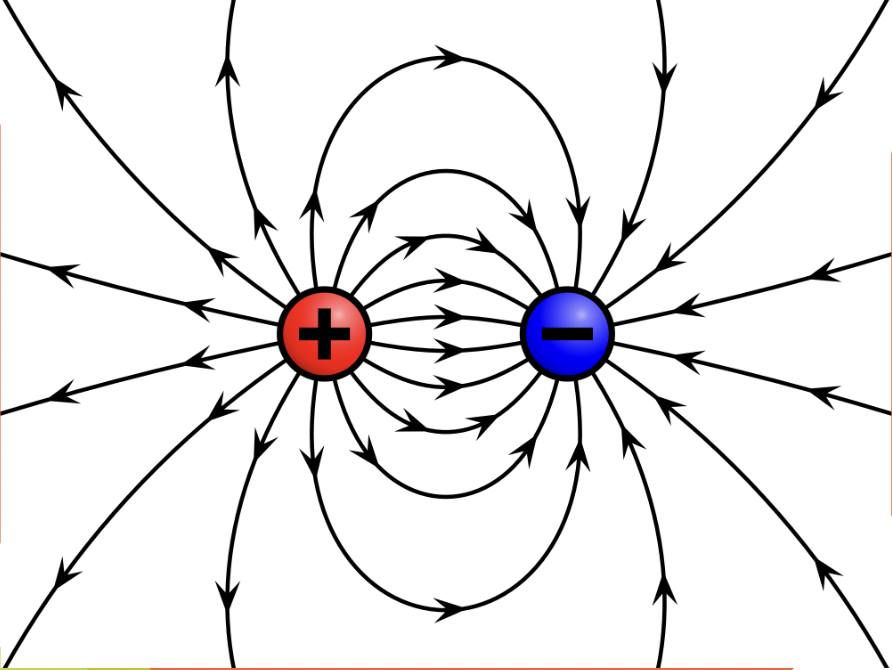
Electric Field
The region around a charged object where an object’s force is exerted on other charged objects.
Static Electricity
Potential Electrical Energy
Electrical Current
Kinetic Electrical Energy
Law of Conservation of Charge
Charges are neither created nor destroyed, they are transferred from one object to another
Current (Measured in Amperes/Amps/a)
Flowing electricity. Measures how much electricity is in a circuit.
Direct Current (DC)
Electrons flow in a single continuous direction in a wire.
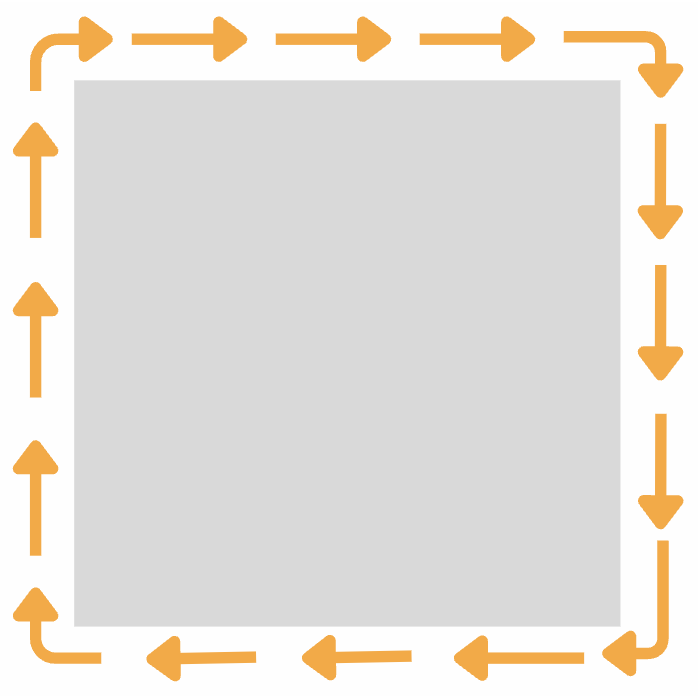
Alternating Current (AC)
Electrons move in short back-and-forth movements in a wire.