Mechanisms of Evolutionary Change - Topic 4
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What is the evolutionary process triangle - Where does drift fit in
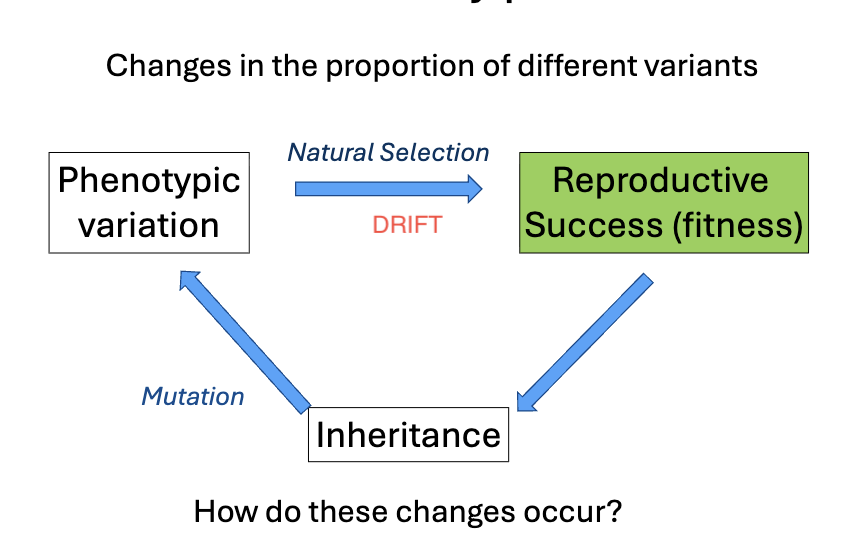
Evolution by random change = WHAT
Evolution by random change = GENETIC DRIFT
Evolution by random change = GENETIC DRIFT
Individual organisms can get WHAT or WHAT
Good luck and bad luck are unrelated to the individual’s WHAT
The net result is random changes in WHAT, just due to chance that is WHAT
Evolution by random change = GENETIC DRIFT
Individual organisms can get LUCKY or UNLUCKY
Good luck and bad luck are unrelated to the individual’s PHENOTYPES
The net result is random changes in ALLELE FREQUENCIES, just due to chance that is GENETIC DRIFT
Genetic drift is WHAT, not WHAT
Genetic drift is STATISTICS, not BIOLOGY
Genetic drift results from WHAT
Genetic drift results from RANDOM SAMPLING ERROR
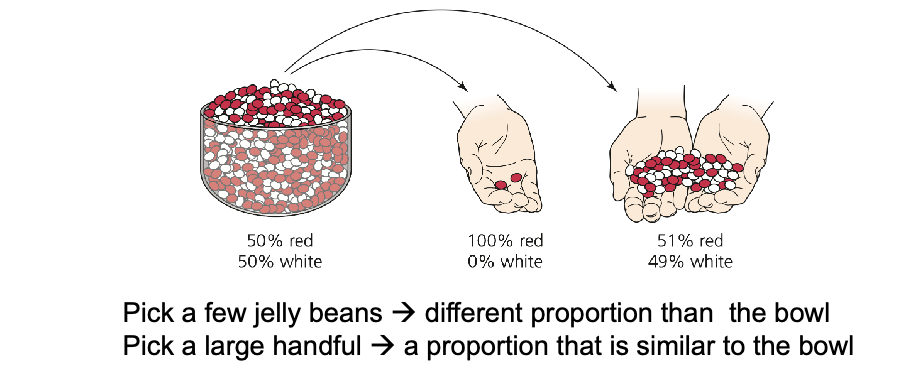
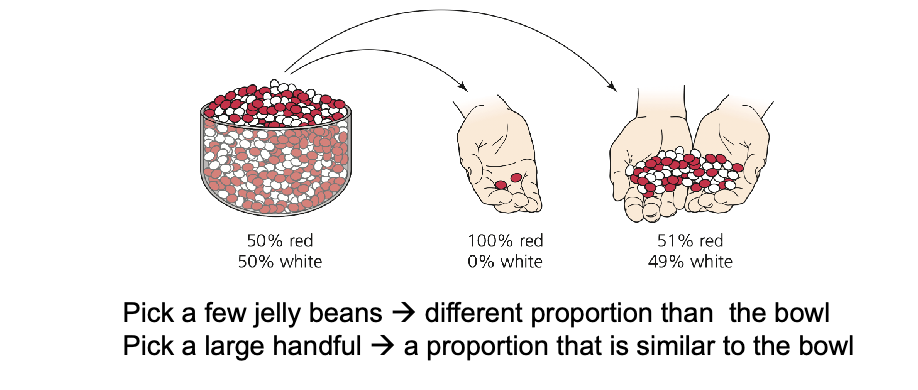
More sampling error in WHAT samples
Analogously: more genetic drift in WHAT populations
More sampling error in SMALLER samples
Analogously: more genetic drift in SMALLER populations
Drift tends to WHAT genetic variation WHAT populations
Drift tends to WHAT genetic variation WHAT populations
Drift is stronger in WHAT populations
Drift tends to REDUCE genetic variation WITHIN populations
Drift tends to INCREASES genetic variation BETWEEN populations
Drift is stronger in SMALLER populations
Genetic drift example: Northern elephant seals
underwent a WHAT in the late 1800’s due to commercial hunting
Numbers reduced to WHAT in 1892, all at one breeding ground in mexico
Genetic drift example: Northern elephant seals
underwent a BOTTLENECK in the late 1800’s due to commercial hunting
Numbers reduced to 20-100 in 1892, all at one breeding ground in mexico
Bottleneck effect
Temporary reduction in population size, leading to genetic drift
Genetic drift example: Northern elephant seals
Potential conservation implications, because drift isn’t the only evolutionary force at work
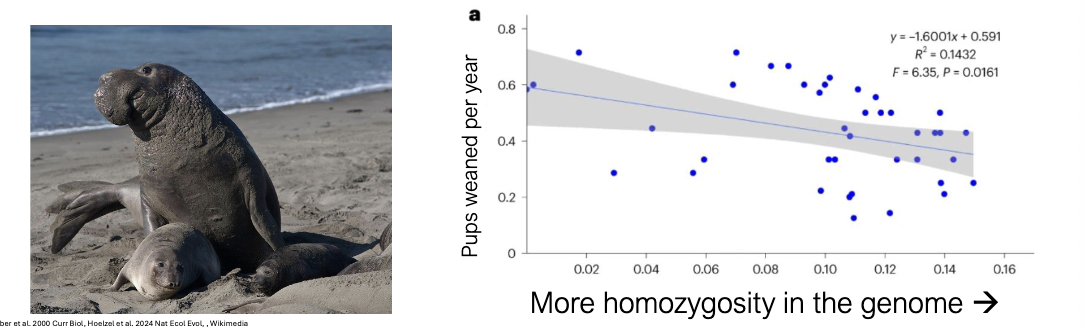
Post-bottleneck seals are more likely to be WHAT at any given locus (drift: we know this from sequencing DNA from thousand-year-old seal bones)
More homozygous seals have WHAT (inbreeding depression, a form of natural selection;)
Genetic drift example: Northern elephant seals
Potential conservation implications, because drift isn’t the only evolutionary force at work
Post-bottleneck seals are more likely to be HOMOZYGOUS at any given locus (drift: we know this from sequencing DNA from thousand-year-old seal bones)
More homozygous seals have LOWER FITNESS (inbreeding depression, a form of natural selection;)
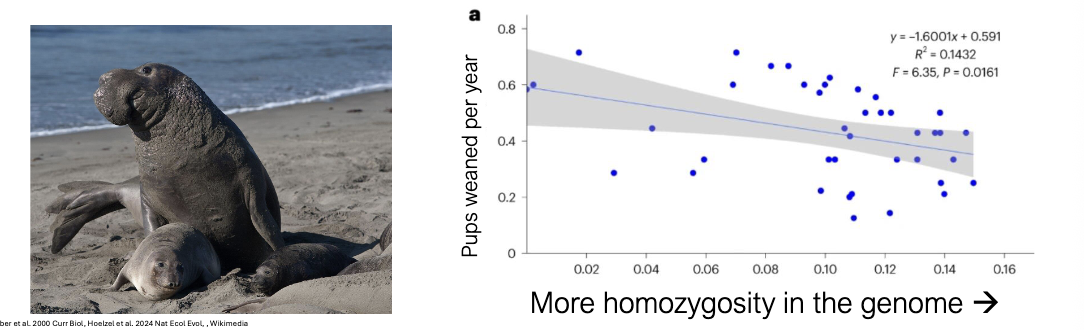
Northern elephant seal recovery:
Commercial hunting WHAT in the late 1800’s (too few seals)
Seal abundance recovered to >WHAT today
Reduced WHAT didn’t prevent recovery, at least in this case → lost WHAT
Northern elephant seal recovery:
Commercial hunting STOPPED in the late 1800’s (too few seals)
Seal abundance recovered to >200,000 today
Reduced GENETIC VARIATION didn’t prevent recovery, at least in this case → lost more GENETIC DIVERSITY
Founder effect
A special case of bottlenecks and genetic drift
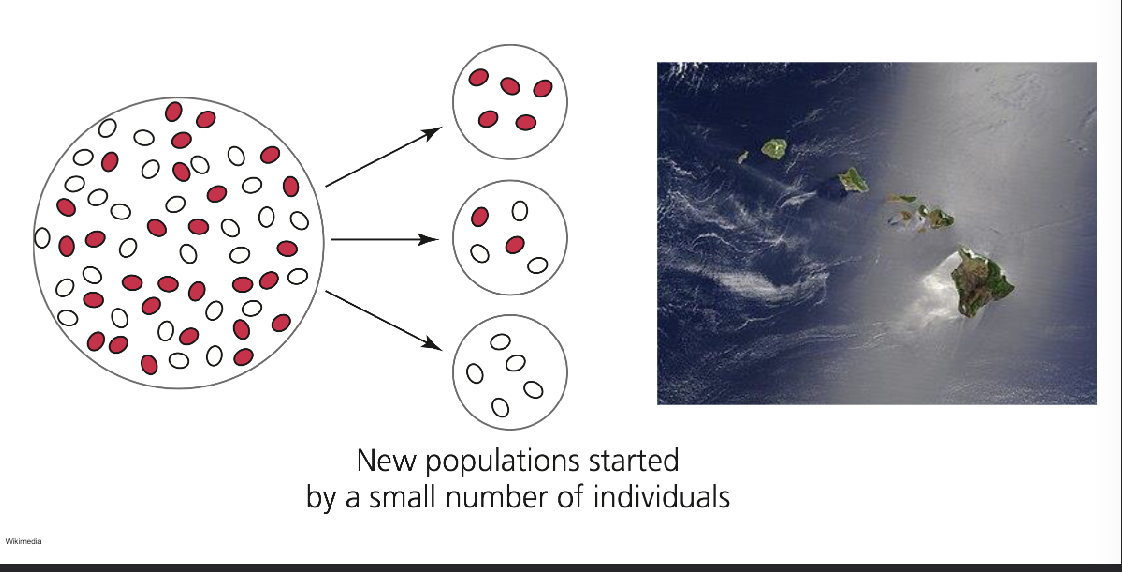
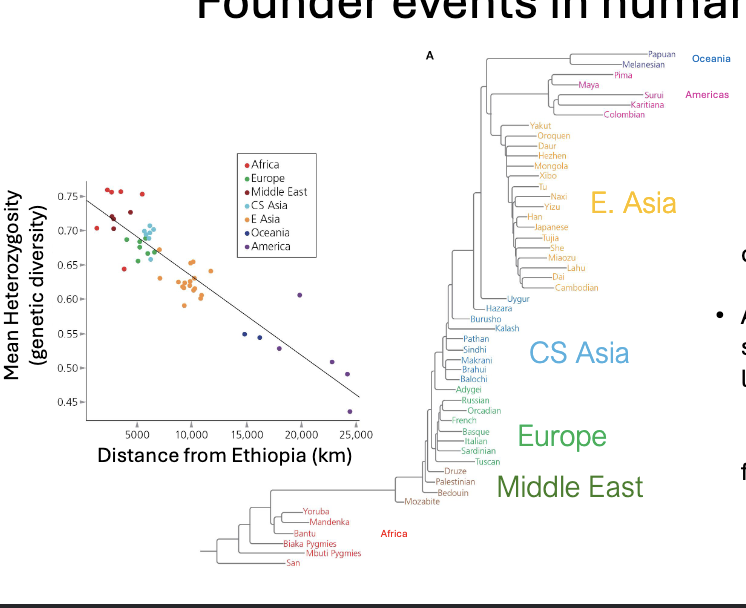
Founder events in human history:
WHAT: human populations closely related to neighbours
All non-African descend from a small population of humans who lived in WHAT
WHAT in genetic diversity reflects the founder effect
Founder events in human history:
PHYLOGENY: human populations closely related to neighbours
All non-African descend from a small population of humans who lived in ETHIOPIA
DECLINE in genetic diversity reflects the founder effect
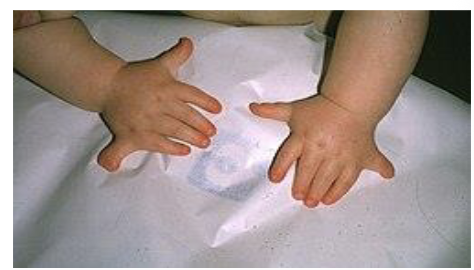
Ellis-van Creveld syndrome in the Old Order Amish in Pennsylvania, USA
Rare WHAT allele, carried by one of the WHAT founders of the community in the 1700’s
Community members mostly married one another
Symptoms can include WHAT, other skeletal anomalies
1/5000 Amish births vs 7/1000000 births in the general population
Ellis-van Creveld syndrome in the Old Order Amish in Pennsylvania, USA
Rare RECESSIVE allele, carried by one of the 200 founders of the community in the 1700’s
Community members mostly married one another
Symptoms can include POLYDACTYLY, other skeletal anomalies
1/5000 Amish births vs 7/1000000 births in the general population
Other historically isolated human populations elsewhere have high incidence of other genetically-based WHAT
Other historically isolated human populations elsewhere have high incidence of other genetically-based PHENOTYPES (eg 10% colour blind on Pingalep Island in Micronesia)
Genetic drift → increases genetic variation WHAT population
Genetic drift → increases genetic variation WHAT population
Genetic drift causes allele frequencies to WHAT in populations - WHAT
Genetic drift causes allele frequencies to WHAT in populations - WHAT
Genetic drift causes a reduction in WHAT within a population - variation is lost most rapidly in small populations (WHAT and WHAT events)
Genetic drift causes a reduction in WHAT within a population - variation is lost most rapidly in small populations (BOTTLENECK and FOUNDER events)
Genetic drift causes WHAT
Genetic drift causes WHAT
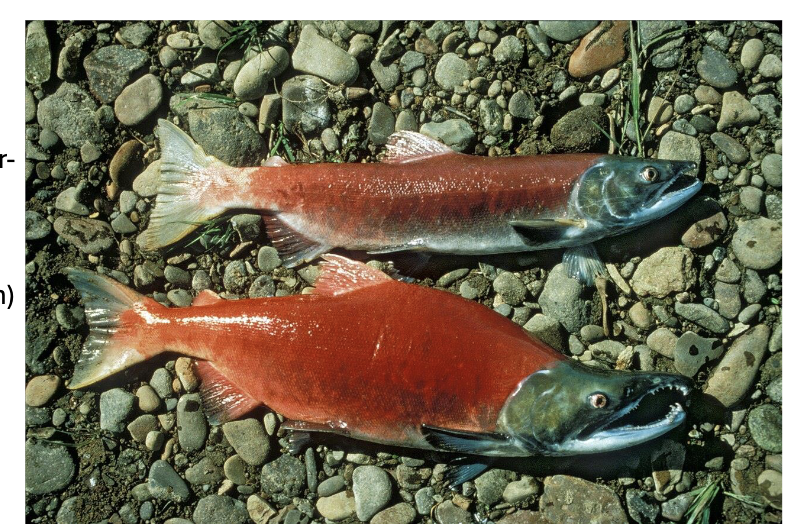
Breeding sockeye salmon in body size and shape
Males are WHAT and WHAT-bodied than females
Variation in WHAT and WHAT within sexes too
Breeding sockeye salmon in body size and shape
Males are LARGER and DEEPER-bodied than females
Variation in WHAT and WHAT within sexes too

Salmon are bigger and deeper-bodied in bigger streams, where there’s less bear WHAT
Salmon are bigger and deeper-bodied in bigger streams, where there’s less bear WHAT
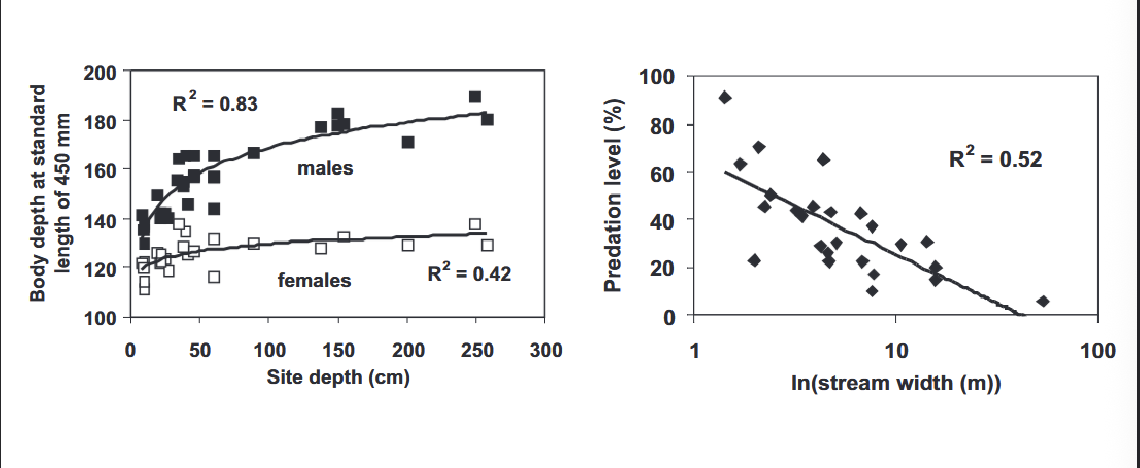
Bears foraging at breeding sites WHAT bigger, deeper-bodied salmon to prey on
Bears foraging at breeding sites WHAT bigger, deeper-bodied salmon to prey on
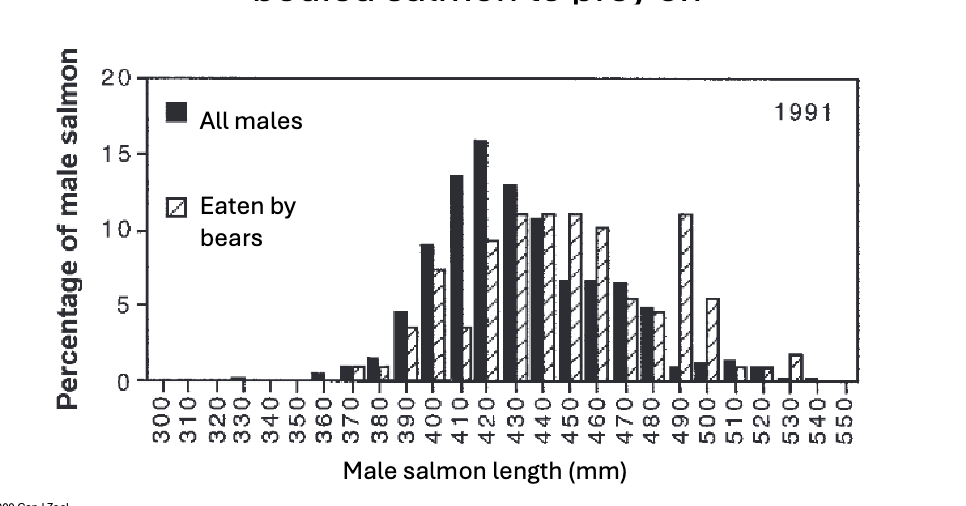
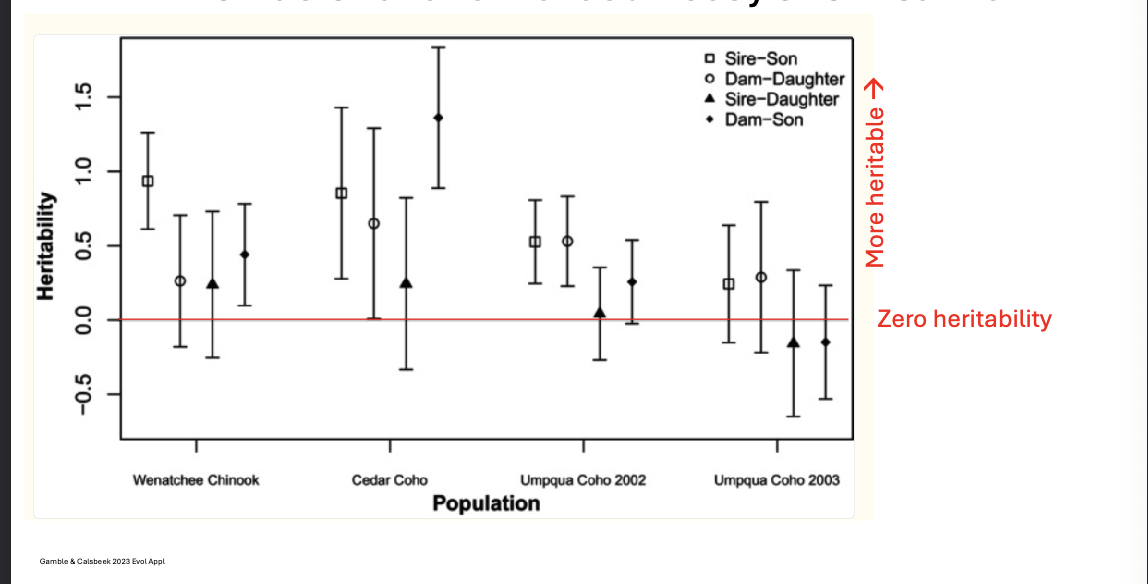
Heritable variation for adult body size in salmon