blood vessels and lymphatics *not diagram heavy
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
163 Terms
the glycocalyx layer on endothelial cells plays a crucial role in the regulation of fluid exchange in capillaries. How does the glycocalyx influence the starling forces involved in capillary fluid dynamics?
it prevents large proteins from exiting the bloodstream, maintaining capillary oncotic pressure and reducing fluid loss
artery
a blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart, where is branches into small vessels
arterioles
smallest arteries that further brach into tiny capillaries where nutrients and waste are exchanged
what is the pathway from artery to vein?
artery
arterioles
capillaries
vein
what is the general appearance of an artery?
thick walls with small lumens
appear rounded
what is the general appearance of a vein?
thin walls will large lumens
appear flattened
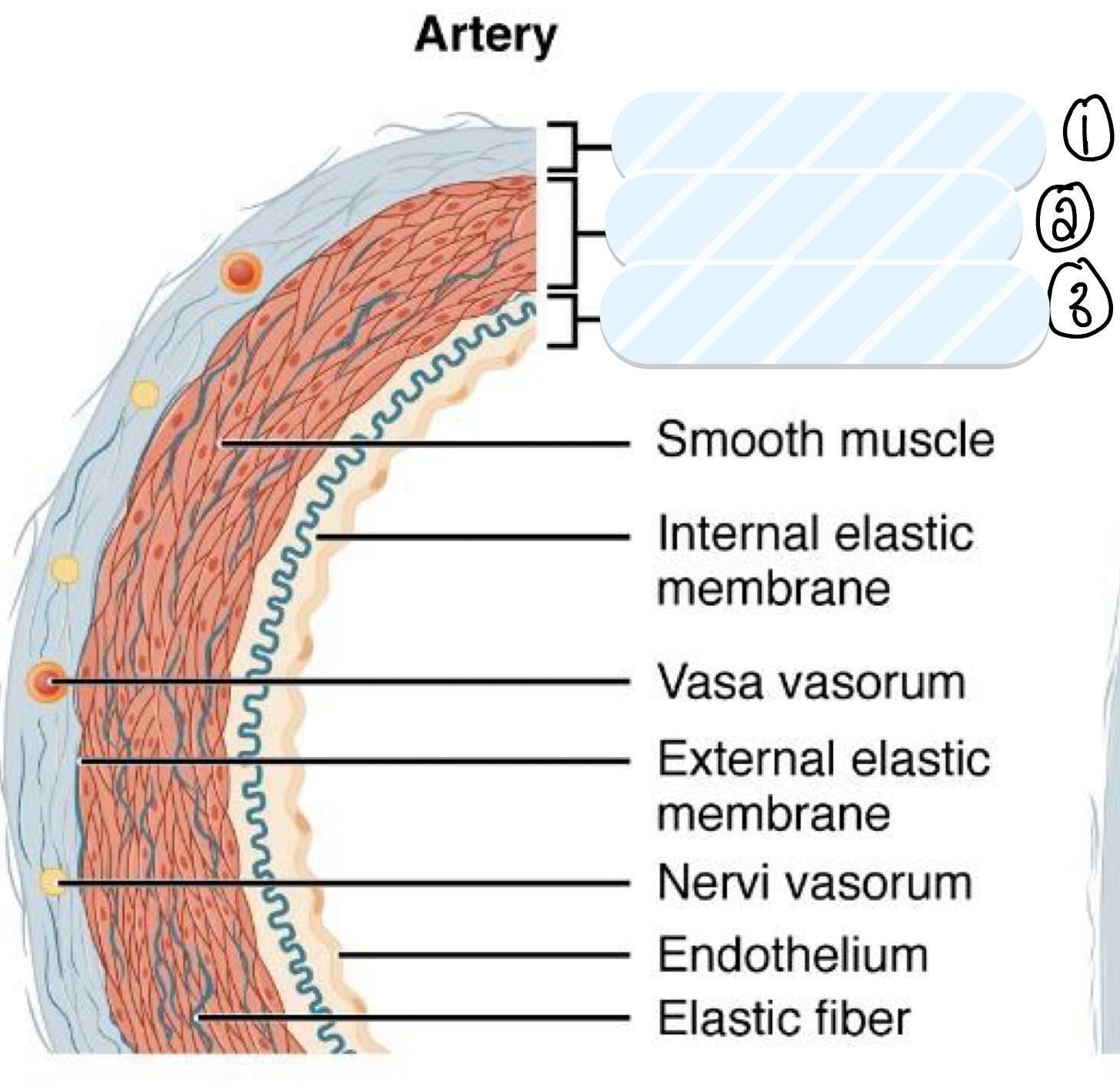
what is layer 1?
tunica externa
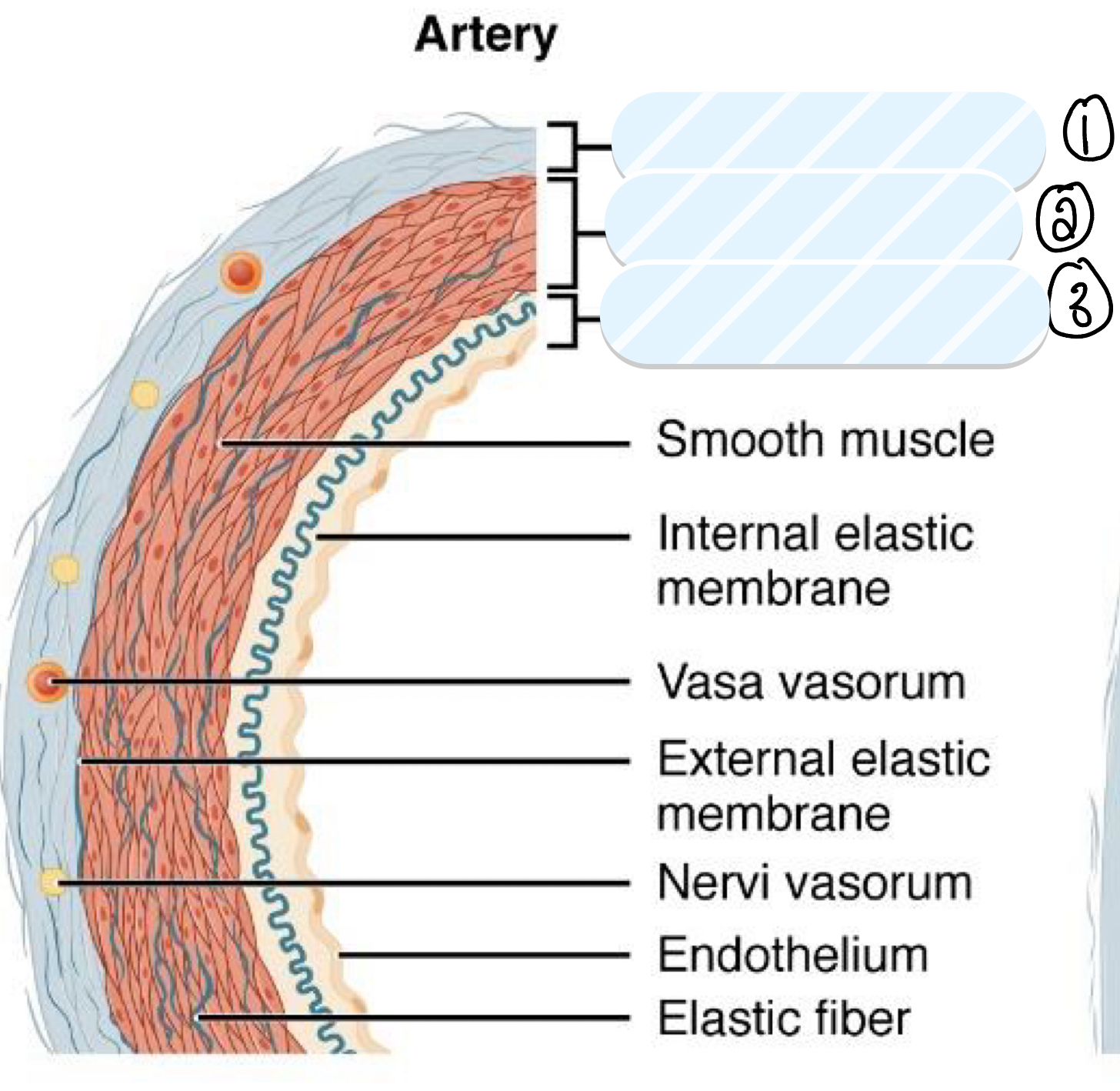
what is layer 2?
tunica media
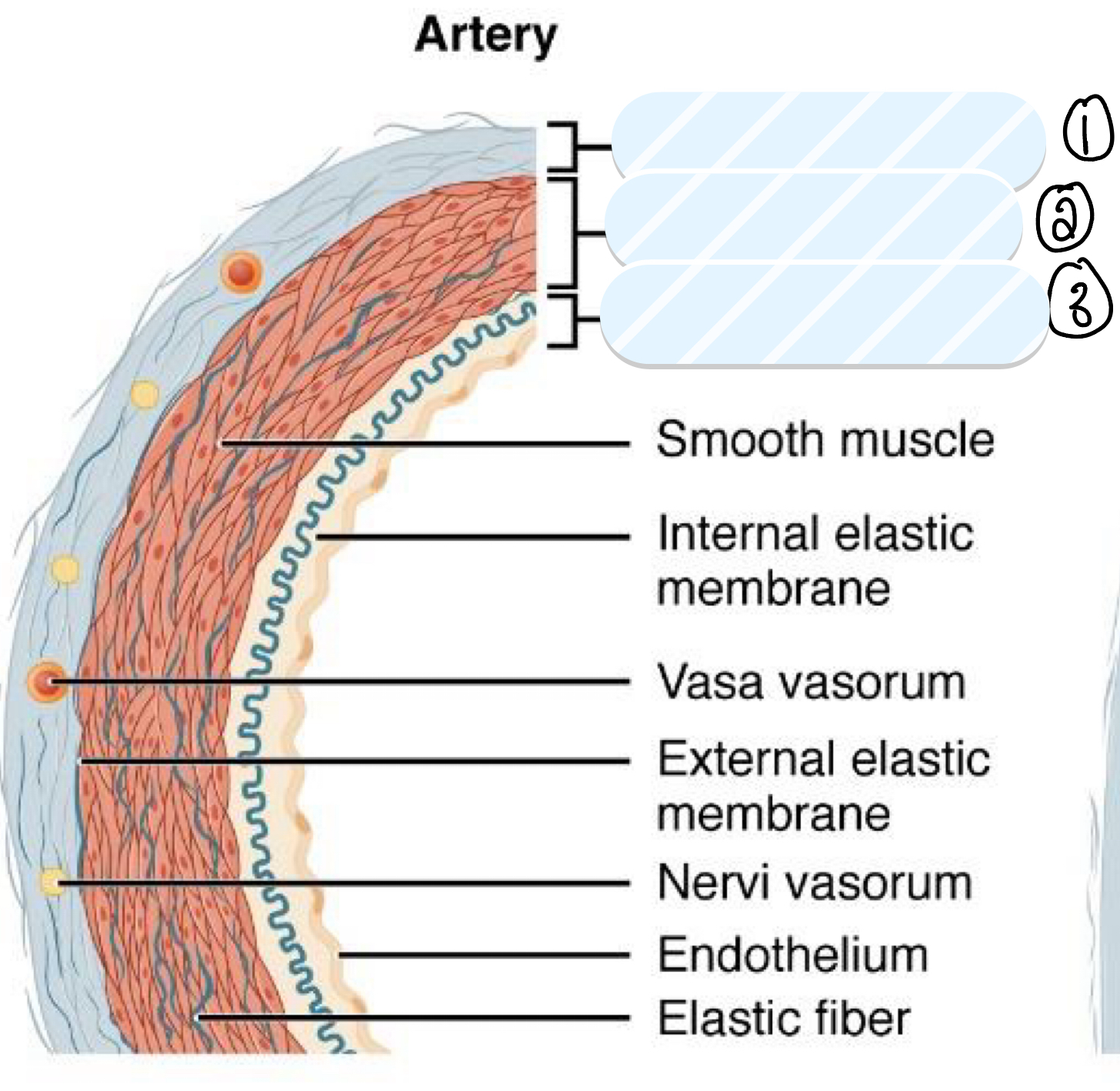
what is layer 3?
tunica intima
describe the tunica intima of arteries
endothelium will appear wavy from constriction of smooth muscle
internal elastic membrane (large vessels)
what is the innermost layer of the tunicas in blood vessels?
tunica intima
what is the middle layer of the tunica in blood vessels?
tunica media
what is the outermost layer of the tunica in blood vessels?
tunica externa
describe the tunica interna in veins
endothelium appears smooth
internal elastic membrane ABSENT
what is normally the thickest layer of the arteries?
tunica media
what is normally thinner than the tunica media besides in large arteries?
tunica externa
what cells dominate in tunica media of arteries?
smooth muscle cells and elastic fibers
what does the proportion of cells depend on in the tunica media of the artery?
vary with distance from heart
what is the thickest layer of tunica in veins?
tunica externa
what cells dominate in tunica media of veins?
smooth muscle cells and collagen fibers
what is present in the tunica media of veins?
nervi vasorum
vasa casorum
what is absent in the tunica media of veins?
external elastic membrane
what is the composition of the tunica externa in arteries?
collagenous and elastic fibers
what is present in the tunica externa of arteries?
nervi vasorum
vasa vasorum
what cells dominate in tunica externa of veins?
dominate: collagenous and smooth fibers
present: smooth muscle fibers (some)
what is present in the tunica externa of veins?
nervi vasorum
vasa vasorum
why is it good that we have thick smooth muscle in arteries?
controls pressure of blood flow
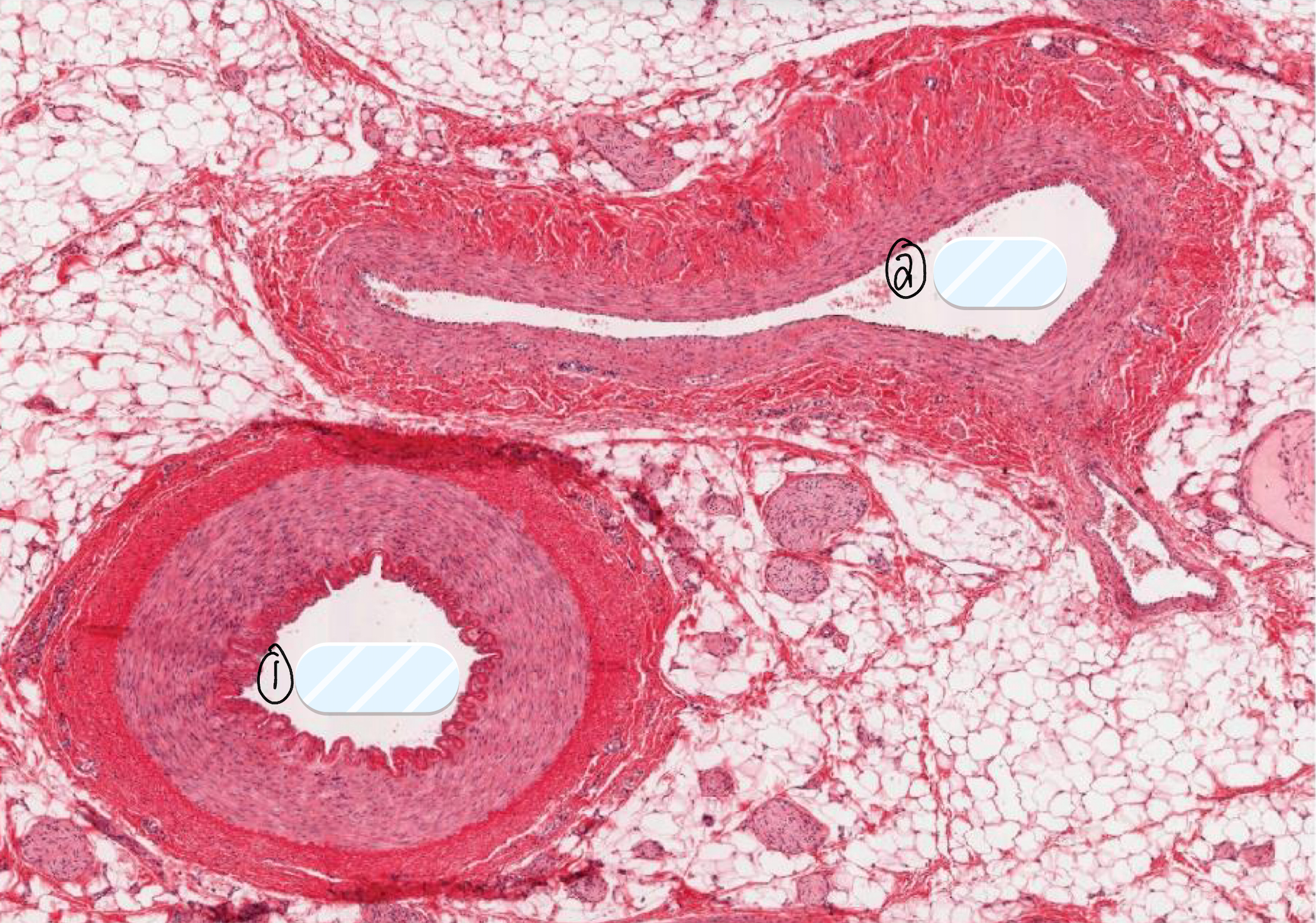
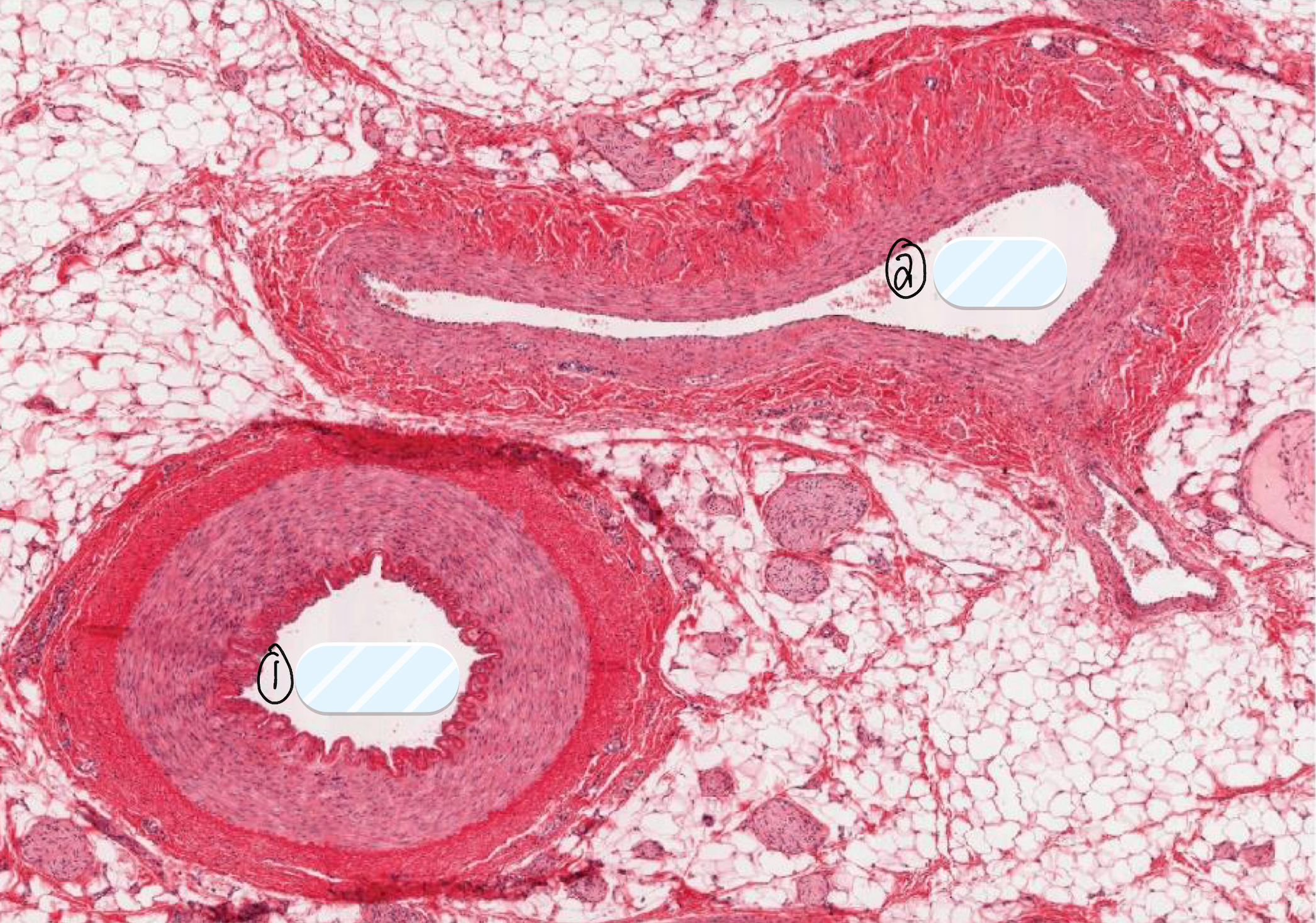
what are structures 1 and 2 in the slide?
artery
vein
what are the tributaries of hepatic portal vein?
cranial mesentaric vein
celiac vein
caudal mesenteric vein
what does swelling of the lymph nodes indicate?
presence of infection in the drainage area
what lymph nodes do you palpate in a routine clinical examination?
superficial lymph nodes
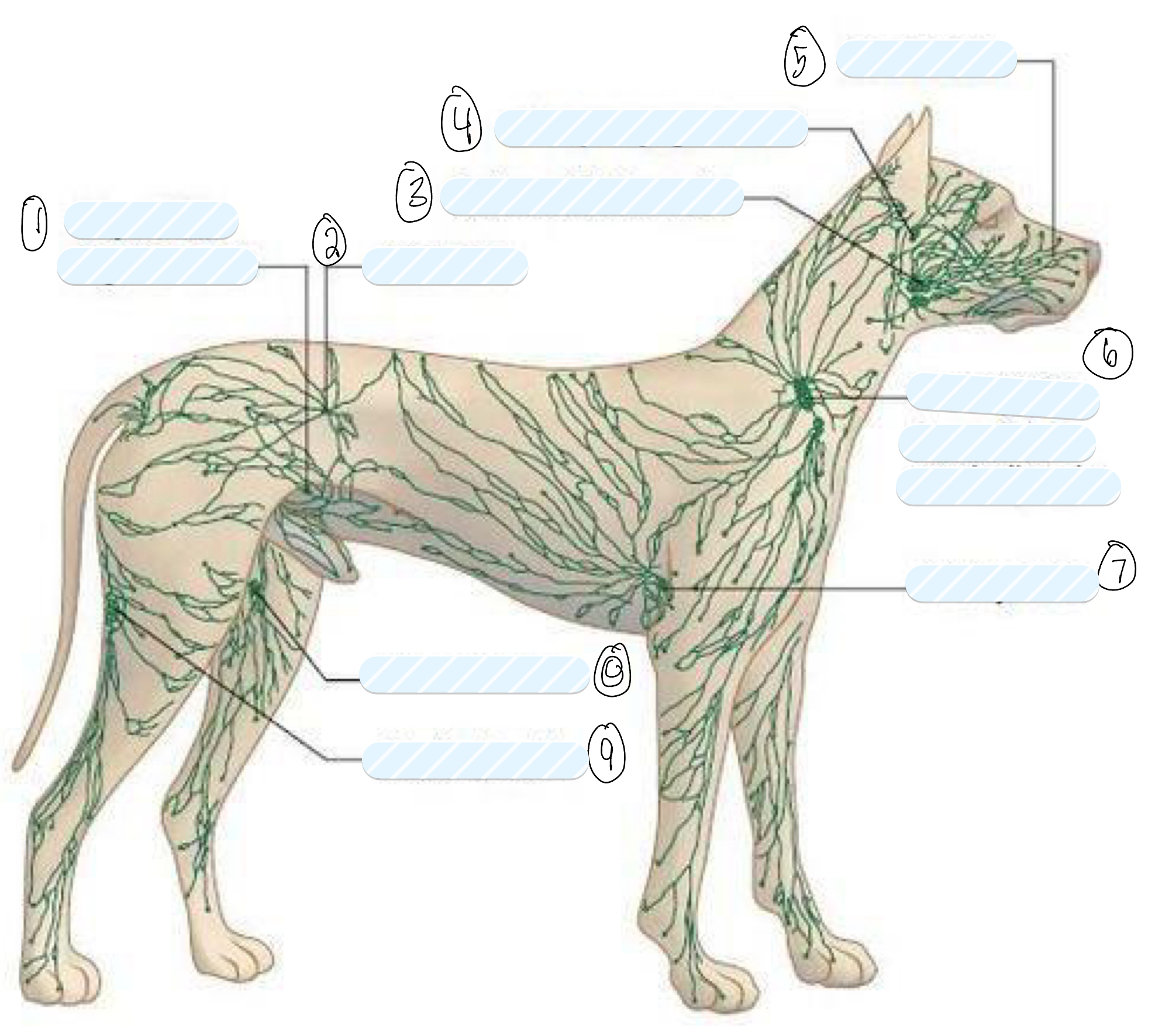
what is 1?
superficial inguinal node
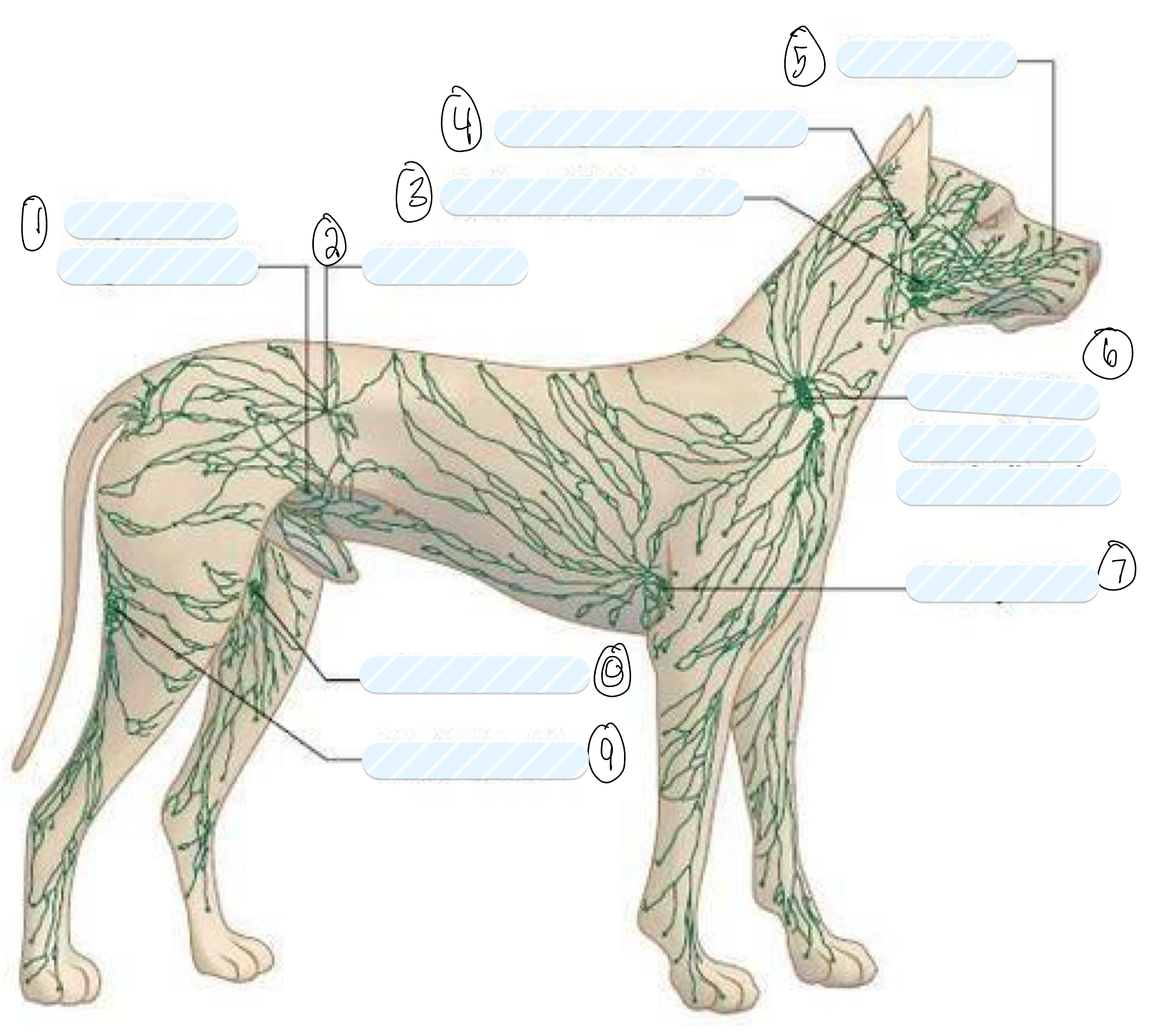
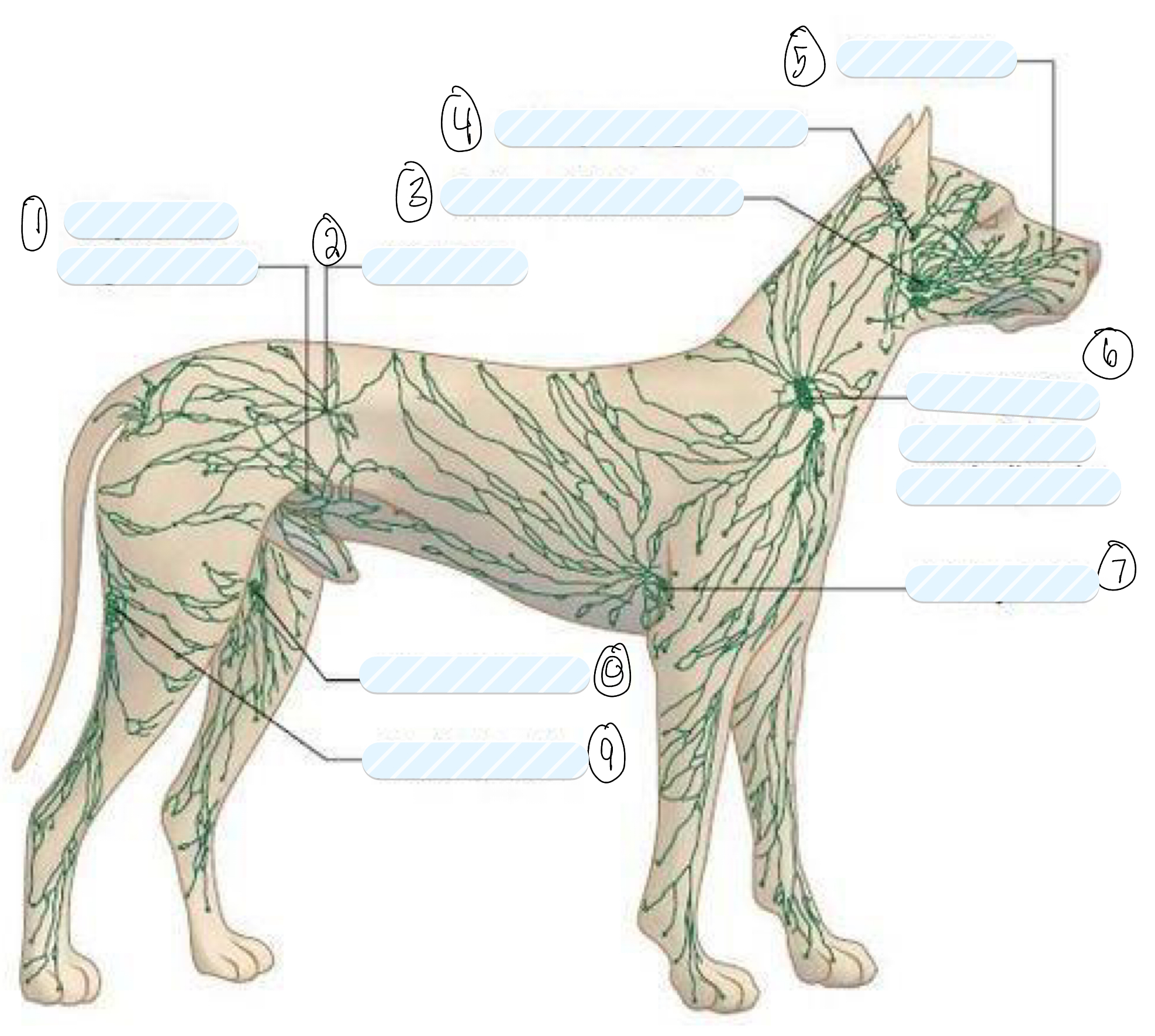
what is 2?
iliac node
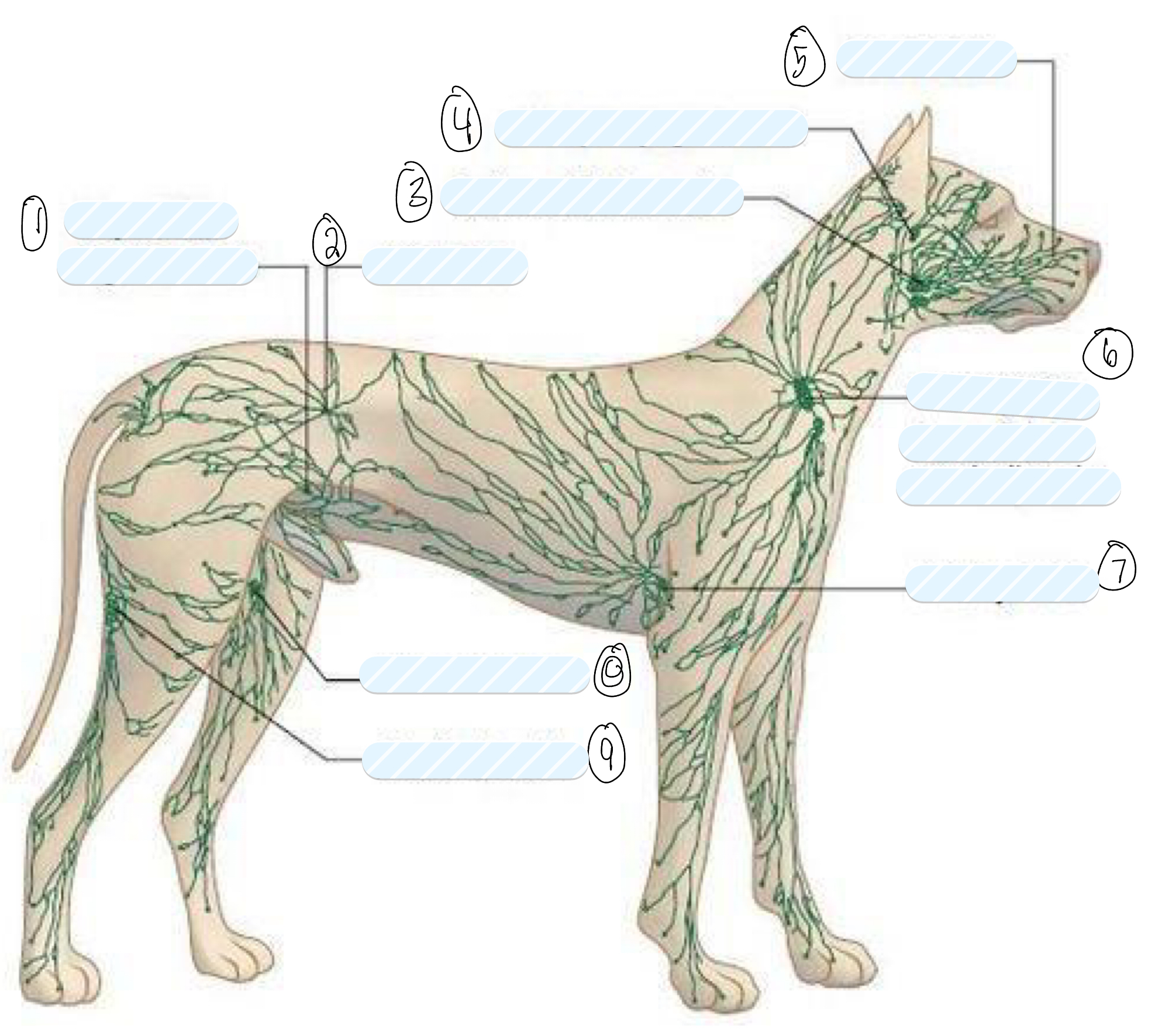
what is 3?
submandibular node
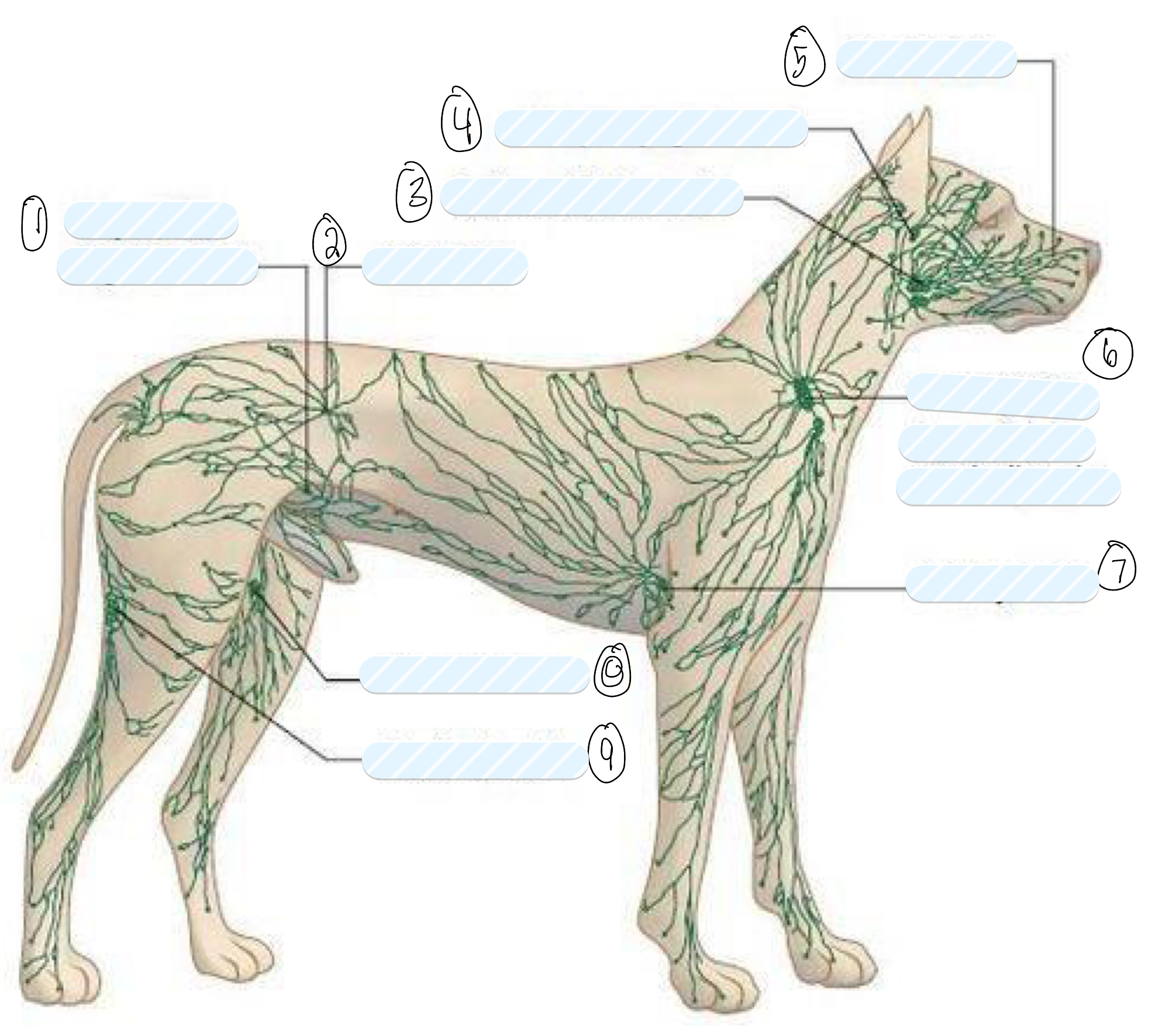
what is 4?
retropharyngeal node
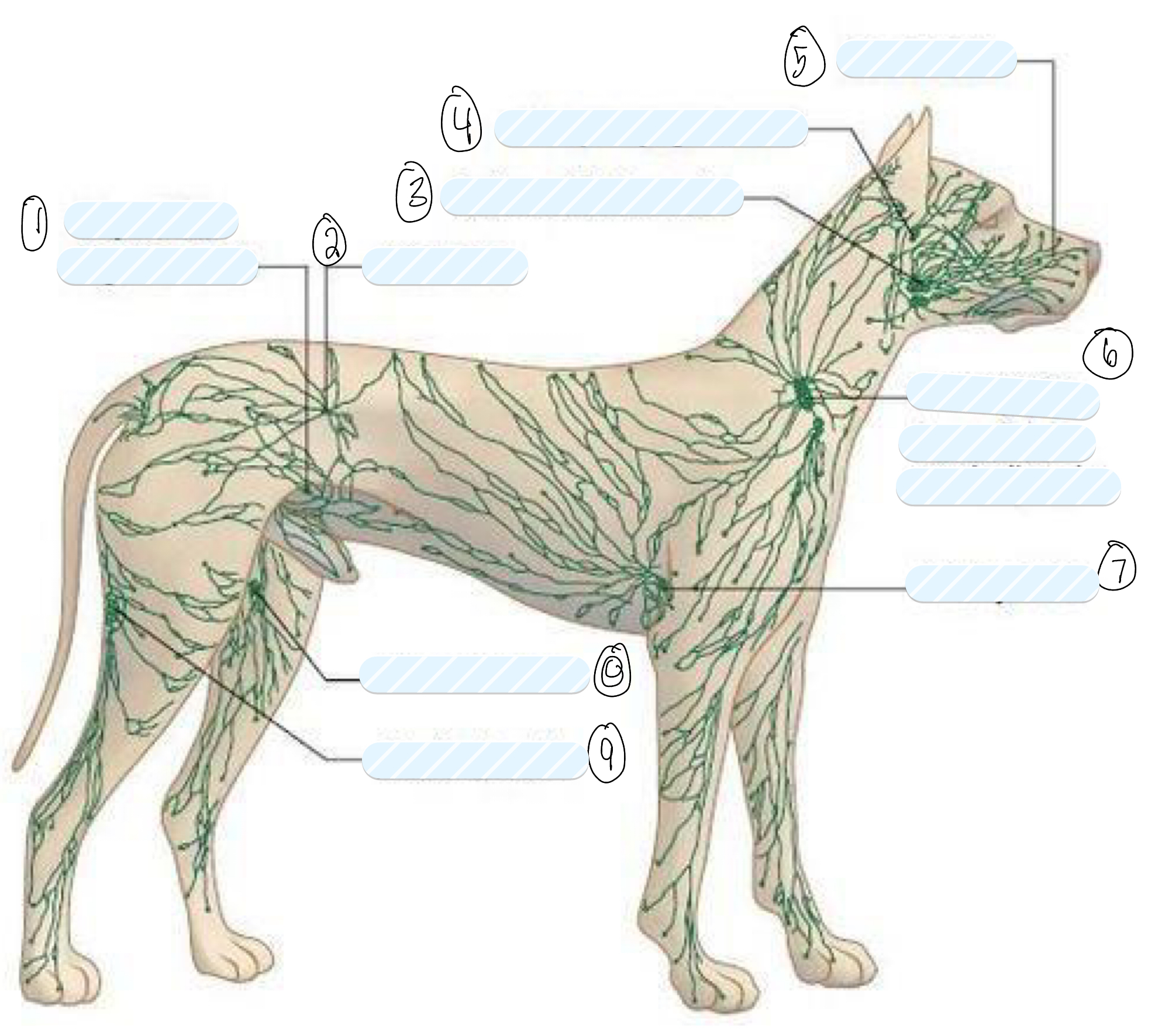
what is 5?
facial node
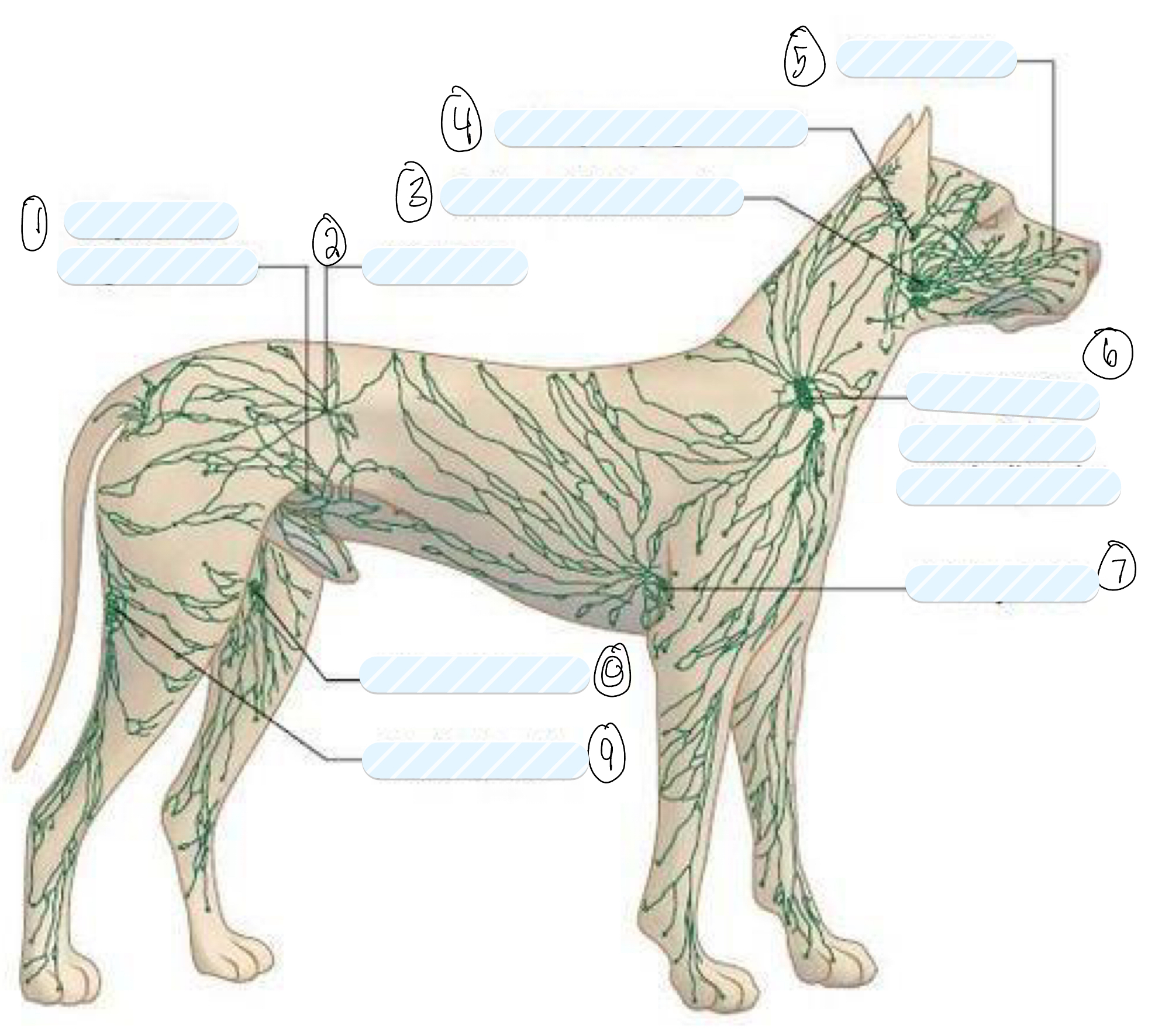
what is 6?
prescapular (superficial cervical) node
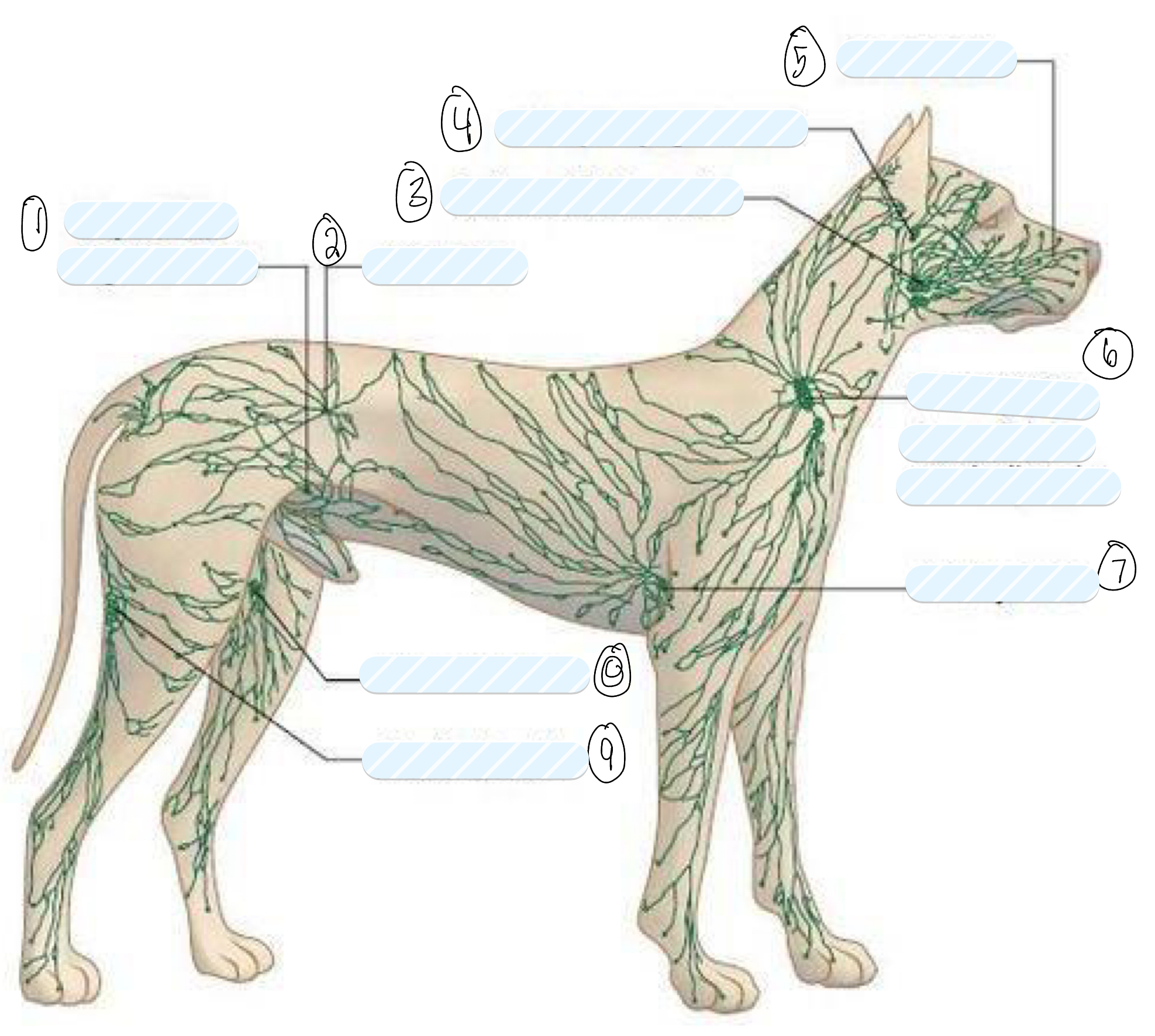
what is 7?
axillary node
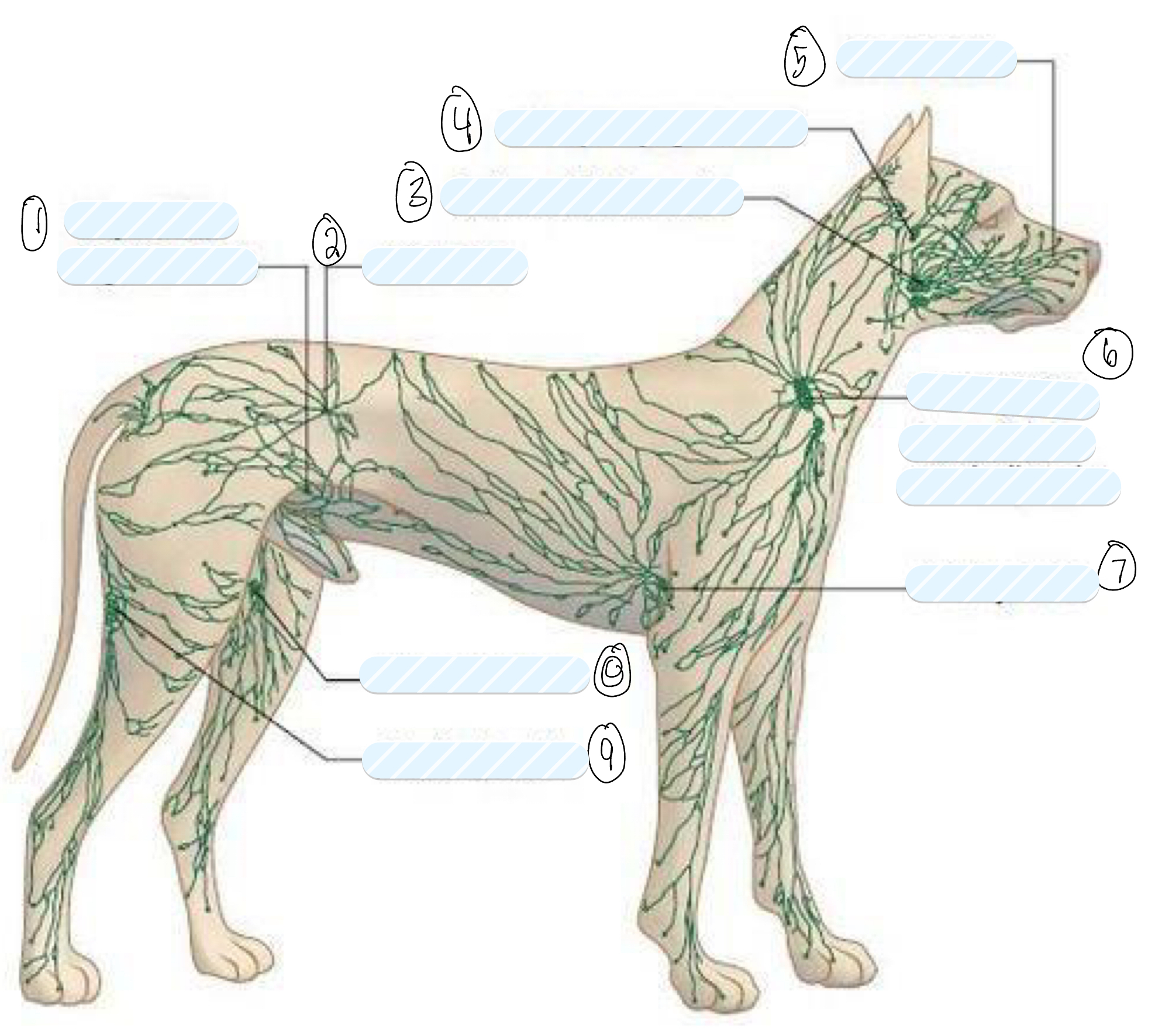
what is 8?
femoral node
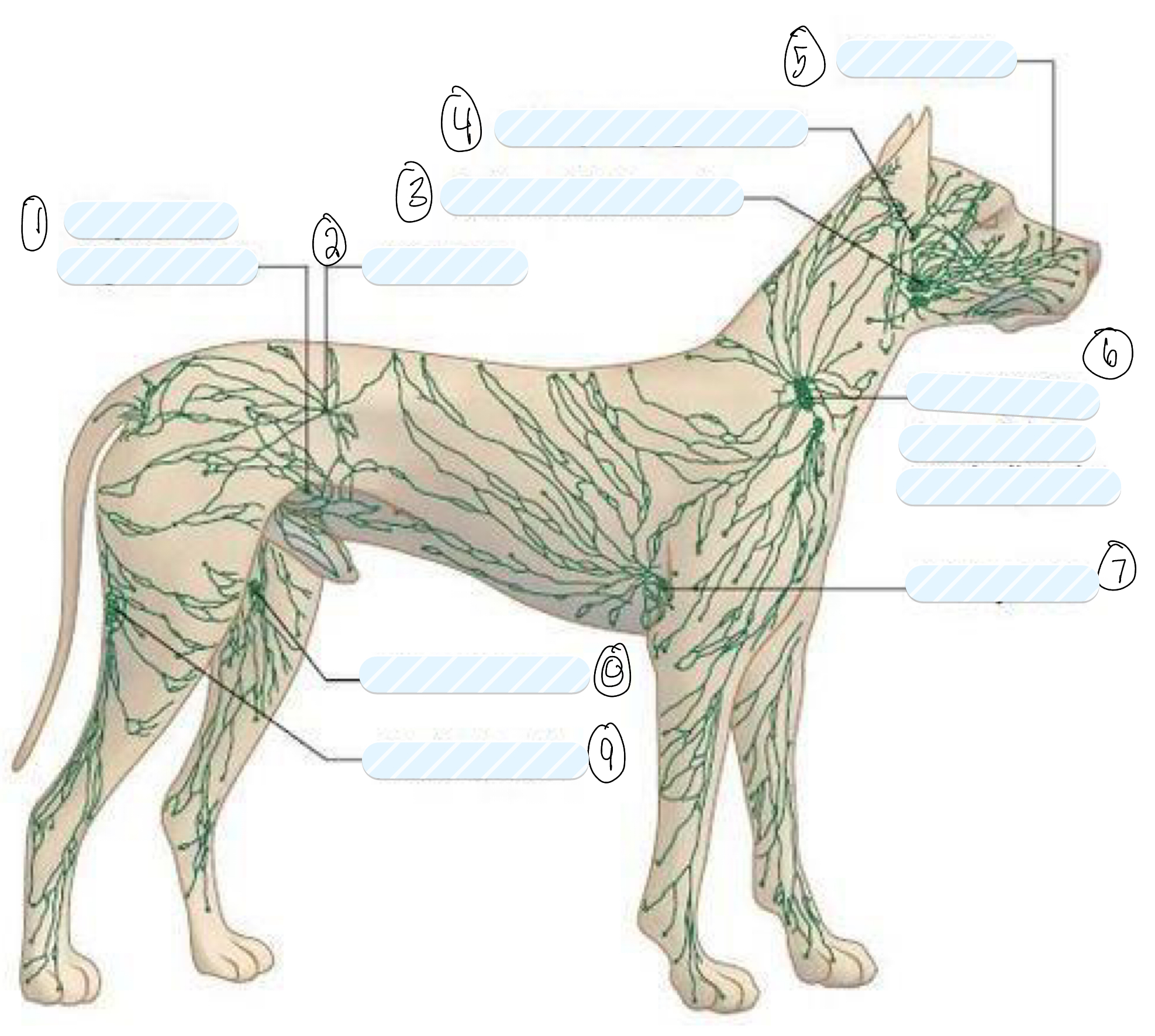
what is 9?
popliteal node
is the tracheal duct/trunk paired or unpaired?
paired
is the thoracic duct/trunk paired or unpaired?
unpaired
where is the tracheal duct/trunk located?
in the neck, on both sides of the trachea
what structure is the tracheal duct/trunk located within?
carotid sheath
what structure does all lymph from the body drain into?
left external jugular vein
where is the cranial part of the thoracic duct located?
the left side around the 5/6th thoracic vertebra
what does the thoracic duct open into?
left external jugular vein/cranial vena cava
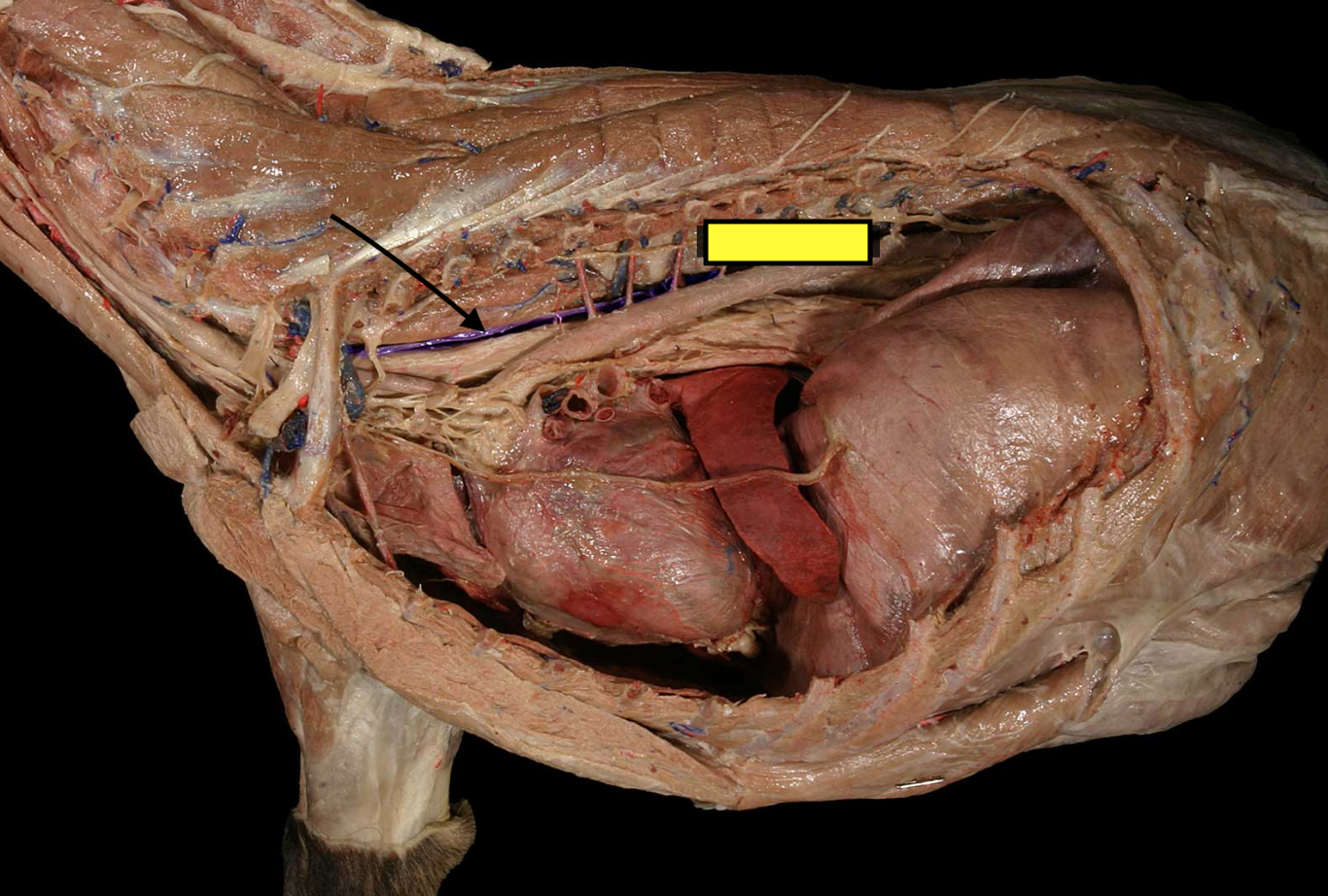
what is the black arrow pointing to? (blue line)
thoracic duct
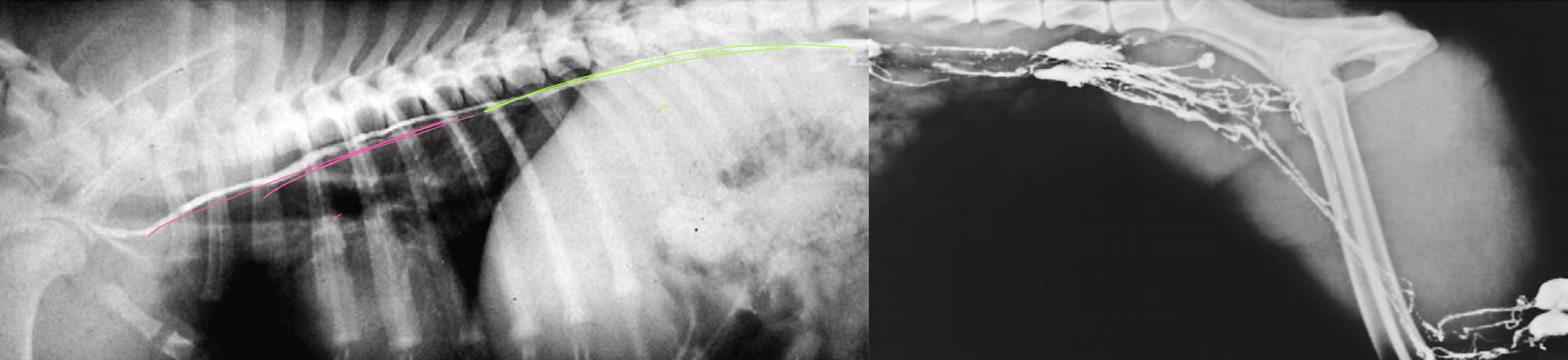
what does the pink line represent?
left thoracic duct
what does the green line represent?
right thoracic duct
what are the vascular components of the lymphatic system?
lumbar trunks
cisterna chyli
thoracic duct
tracheal ducts/trunks
what is the lympho-center in the horse?
rather than having one large lymph node, horses have an collection of several smaller lymph nodes
list the flow of lymph in order
organ
lymph node
other lymph node
venous system
cranial vena cava or left jugular vein
what is the flow of lymph?
UNIDIRECTIONAL FLOW
afferent lymphatic vessels
carry lymph into the lymph node
efferent lymphatic vessels
carry lymph away from the lymph node
where does the tracheal trunk bring lymph from?
brings lymph from head, neck, and forelimb before joining thoracic duct
what is the flow of lymph from lumbar trunk?
lumbar trunk collects lymph from the lower limbs and pelvis
transported chyle cistern
drained into the thoracic duct
what are the superficial veins used for venipuncture?
cephalic vein
femoral vein
saphenous vein
external jugular vein
coccygeal vein
lymphatic system components
vascular component
lymph nodes
lymph organs
In studies on canine gastric perfusion, how could the use of NSAID affect endothelial function in stomach?
it impairs the production of prostaglandins, which can reduce mucosal blood flow and increase susceptibility to gastric lesions
what is the correct sequence of the blood flow in systemic circulation?
heart
body
heart
blood from which organs is drained by the hepatic portal vein?
stomach
intestines
pancreas
spleen
which additional veins, via portal circulation, provide blood to the avian kidney?
external iliac and ischiatic vein
what is there more of in the limbs of animals: veins or arteries?
veins
what is not present in the forelimb?
there is no cephalic artery, they have superficial veins
what vein converges to form the caudal vena cava?
common iliac veins
what are the tributaries of the common iliac vein?
deep circumflex iliac vein
gonadal vein
renal vein
phrenicoabdominal vein
hepatic vein
external and internal veins are…
tributaries of the common iliac veins
deep circumflex iliac vein
paired
location: parietal
gonadal vein
paired
visceral
what does the left gonadal vein open into?
renal vein
renal vein
paired
location: visceral
phrenicoabdominal vein
paired
location: parietal
where will the blood of the GI tract travel?
liver
caudal vena cava
what tributary of the vena cava will not be present in venous return and why?
cranial mesentaric artery since they go to liver
adventitia
the outermost layer of the blood vessel that provides support and anchors vessel to surrounding tissue
what is the composition of the adventitia?
connective tissue
cells
extracellular matrix
what type of connective tissue makes up adventitia?
loose and dense irregular connective tissue with collagen and elastin fibers
what is the function of the connective tissue in the. adventitia?
anchor vessel to surrounding tissues
what cells are present in the adventitia?
fibroblasts
macrophages
stem cells
myofibroblasts
pericytes
what is the composition of the extracellular matrix of the adventitia?
rich in proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans
what is the purpose of the extracellular matrix of the adventitia?
contributes to structural integrity and flexibility of the vessel wall
vasa vasorum
contain tiny blood vessels present in the adventitia that supply larger vessels to supply oxygen and nutrients to outer portion of vessel wall
what else does the vasa vasorum contain besides tiny blood vessels?
lymphatic vessels to help drain excess fluid from vessel wall
Defense and hemodynamic
nervi vasorum
are small nerves present in the adventitia that regulate smooth muscle contraction influencing vasomotor controland sensory functions of blood vessels
function of large elastic arteries
steady blood flow
function of median muscular arteries
distribution
function of smaller arteries or arterioles
resistance and pressure
function of small veins or venules
draining
function of medium veins
unidirectionality and venous return
function of large veins
veinous return
do veins or arteries flow away from the capillary beds?
veins
do veins or arteries flow towards the capillary beds?
arteries
what are the different portal systems of systemic circulation in the body?
hepatic portal system
pituitary hypothalmic system
renal portal system
adrenal glands portal system
in which species is the renal portal system present?
birds and reptiles
what is the pathway for pulmonary circulation?
right ventricle
main pulmonary artery
lungs
pulmonary vein
left atrium of heart
what is the pathway for systemic circulation?
left ventricle
aorta
body tissues
superior and inferior vena cavae
right atrium of heart
what structure in the heart is responsible for collecting deoxygenated blood from organs?
cranial vena cava
caudal vena cava
azygous vein
renal veins
return of deoxygenated filtered blood (kidney used the oxygenated blood!)