LZHS Bio II Animal Kingdom Part 1 (Lower Inverts)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
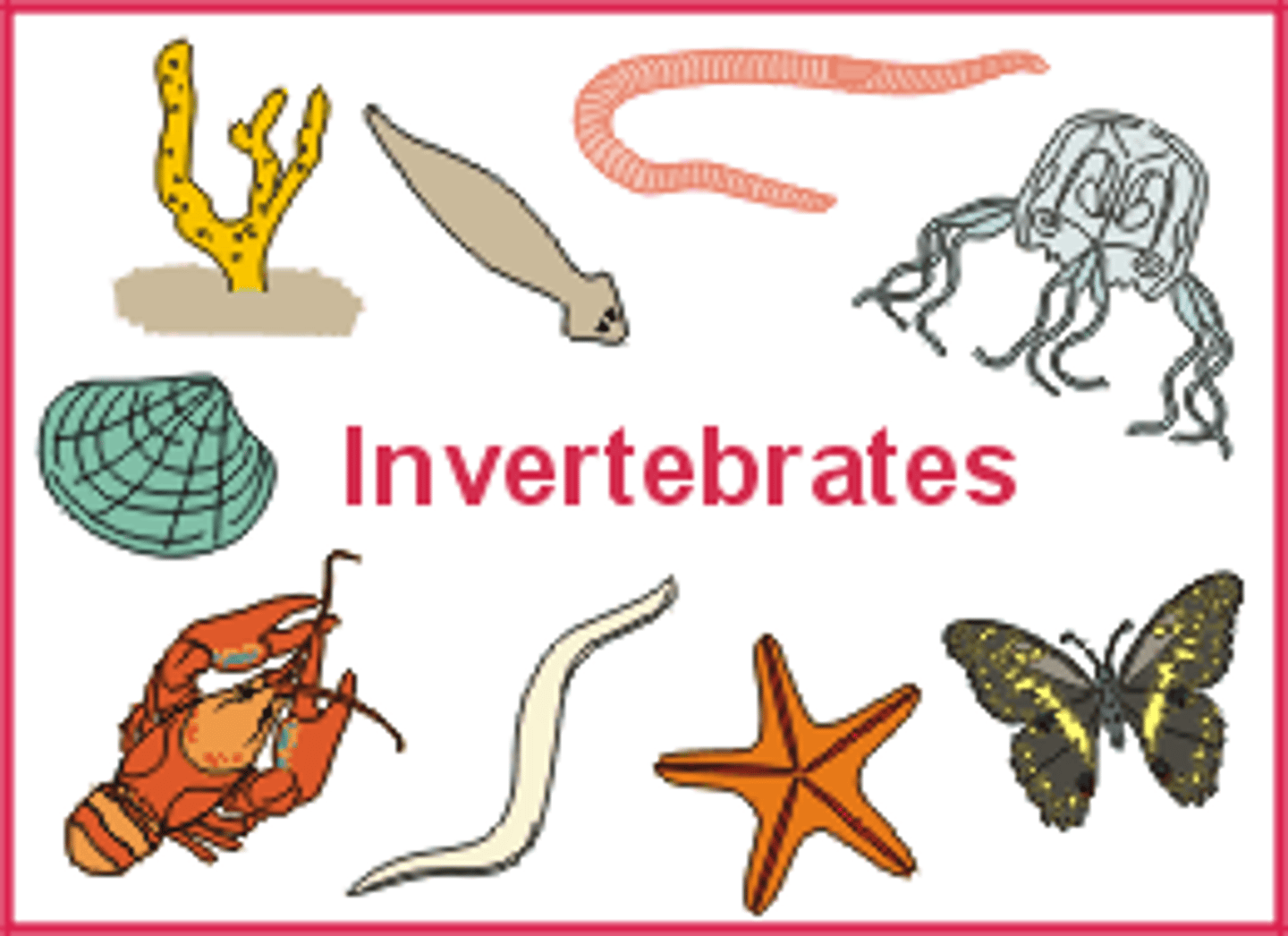
Invertebrates
Majority of animal species are this type of animal

Heterotrophic
(Ingest)
Type of nutrition animals have
(how they get nutrients)

Cell, tissue, organ, organ system
4 Levels of Organization within a multicellular organism (small to large)
Heterotrophic, colonial protists
Type of organism animals are thought to have evolved from
Cephalization
Term for concentration of sensory organs at the anterior or "head" end of an animal
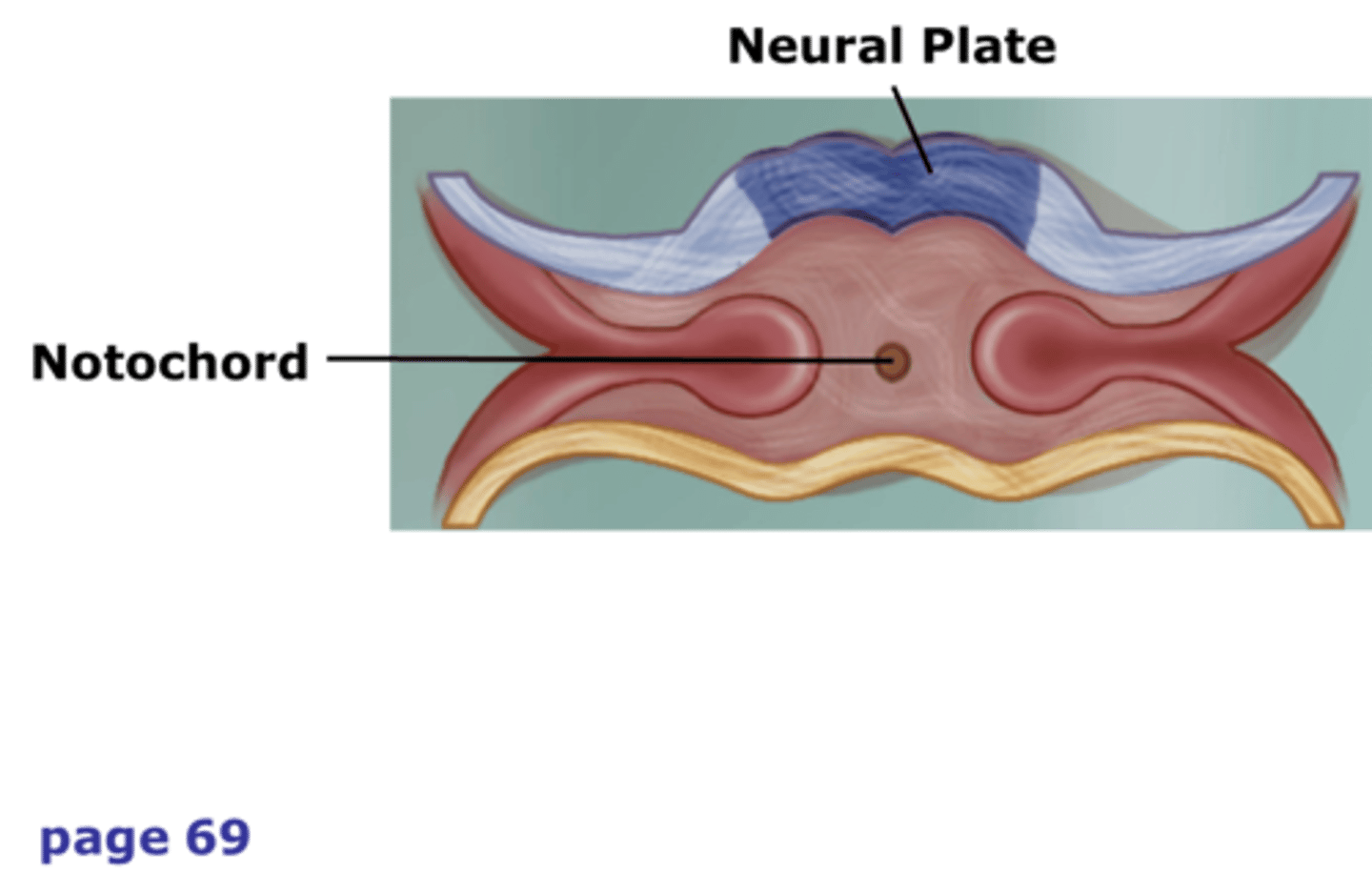
Notochord
Supportive rod along the back of chordates
Acoelomate
The absence of a body cavity
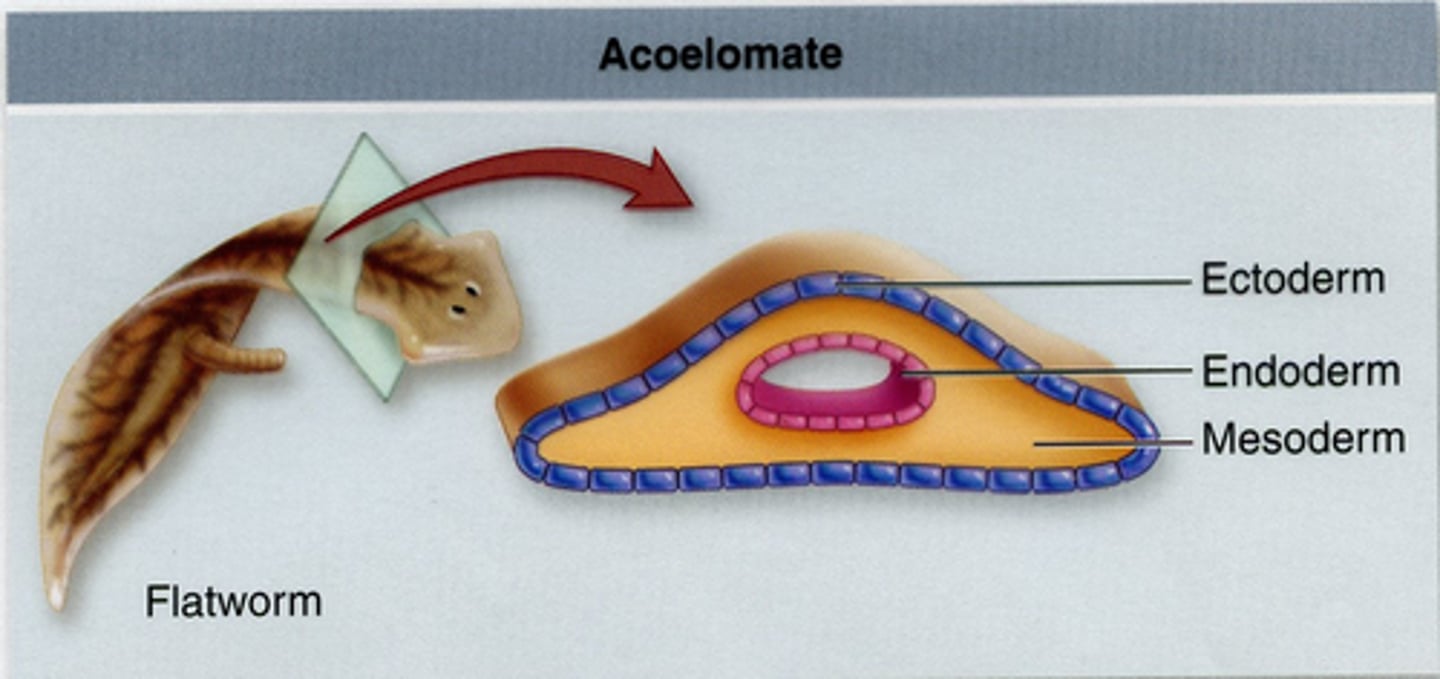
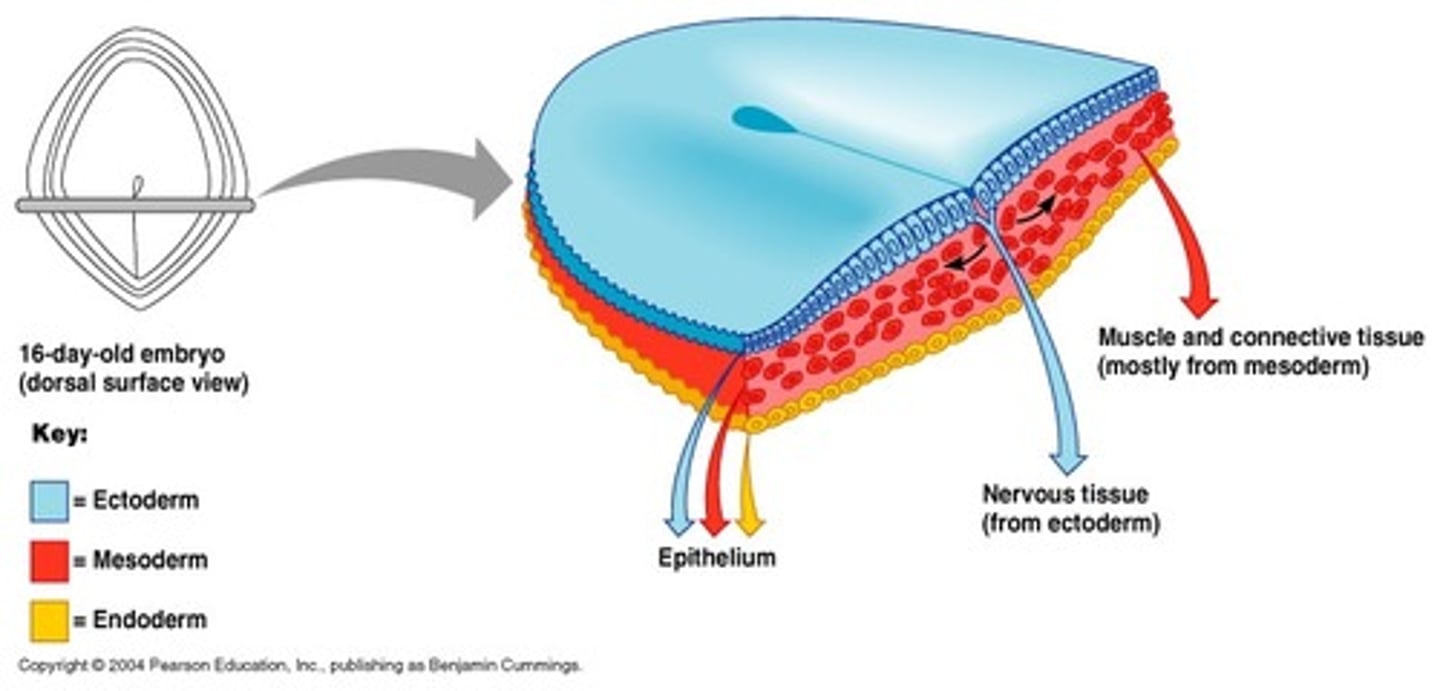
Ectoderm
Germ layer that becomes the nervous system & skin
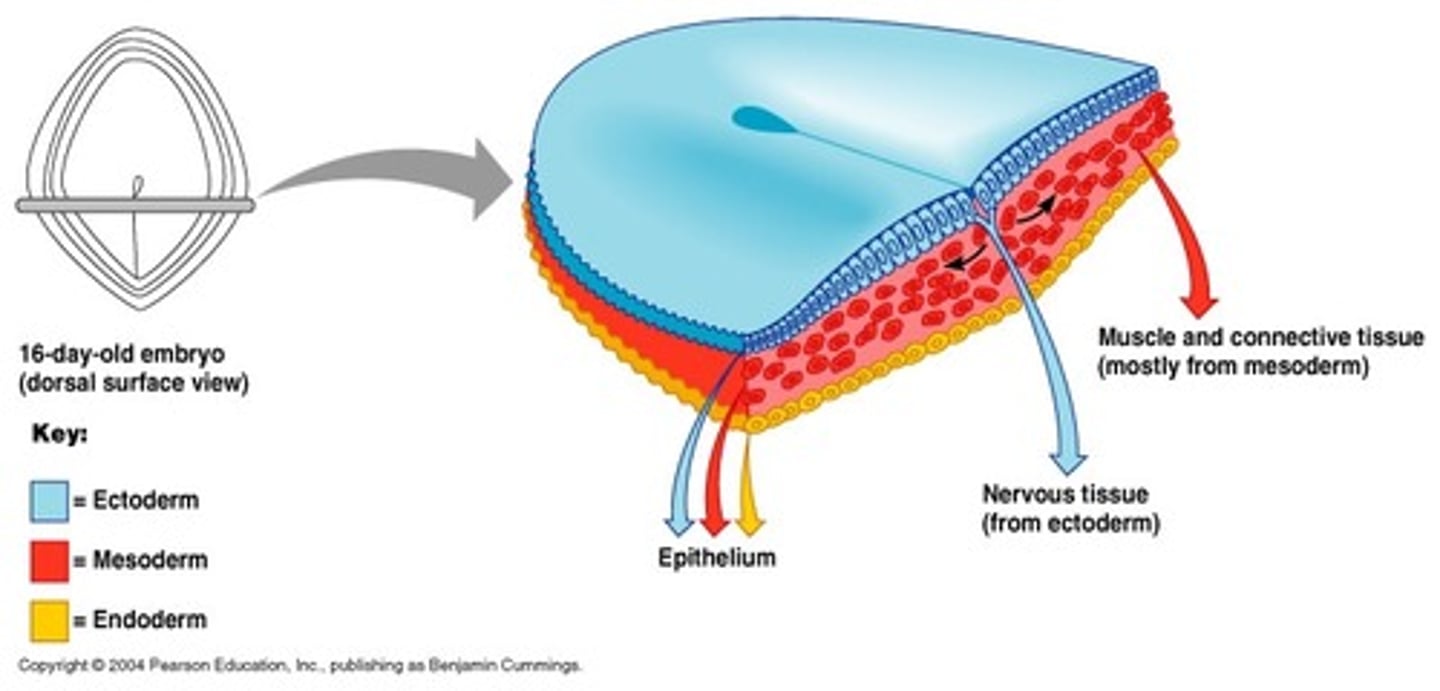
Mesoderm
Germ layer that becomes the muscles
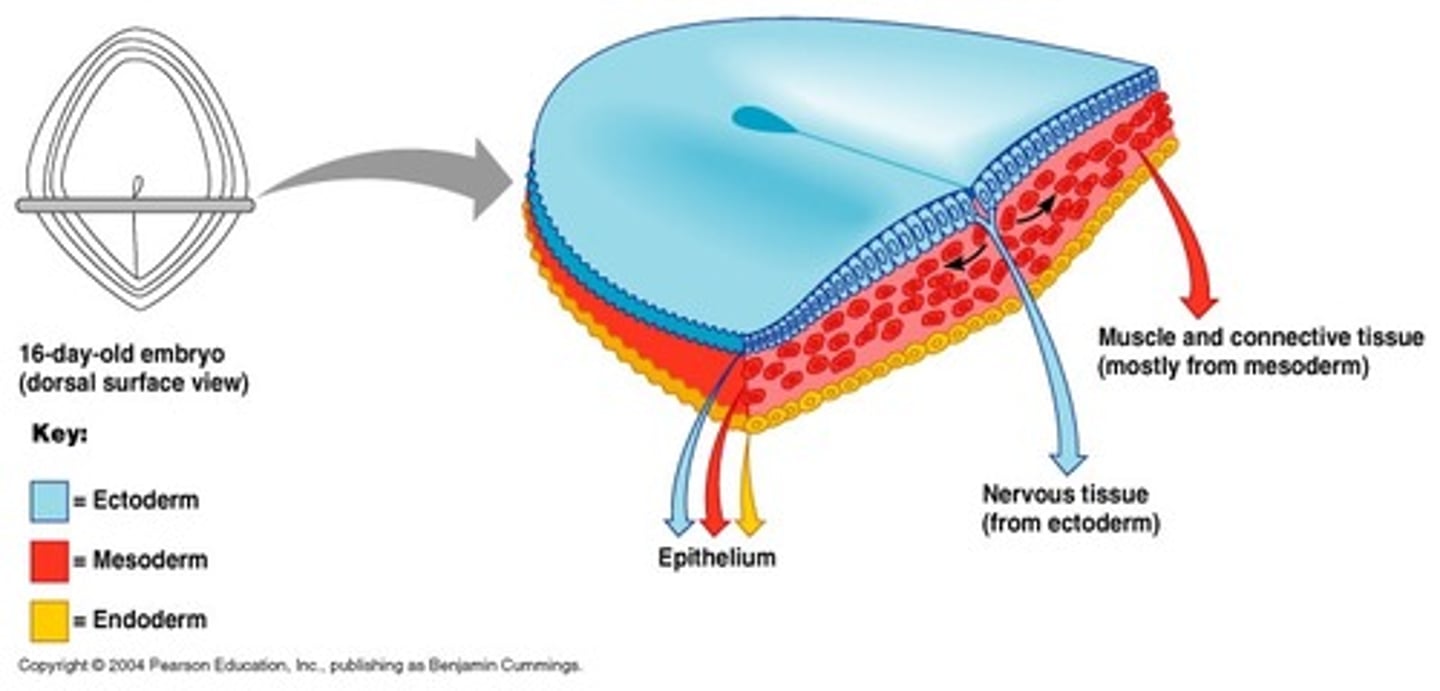
Endoderm
Germ layer that becomes the digestive system
Backbone
Distinguishing characteristic of vertebrates
Radial
Type of symmetry with no front/back or left/right; several places to divide in half; Ex: a starfish or an anemone
Bilateral
Type of symmetry with two similar halves on either side of an axis; Ex: a fish or a bear
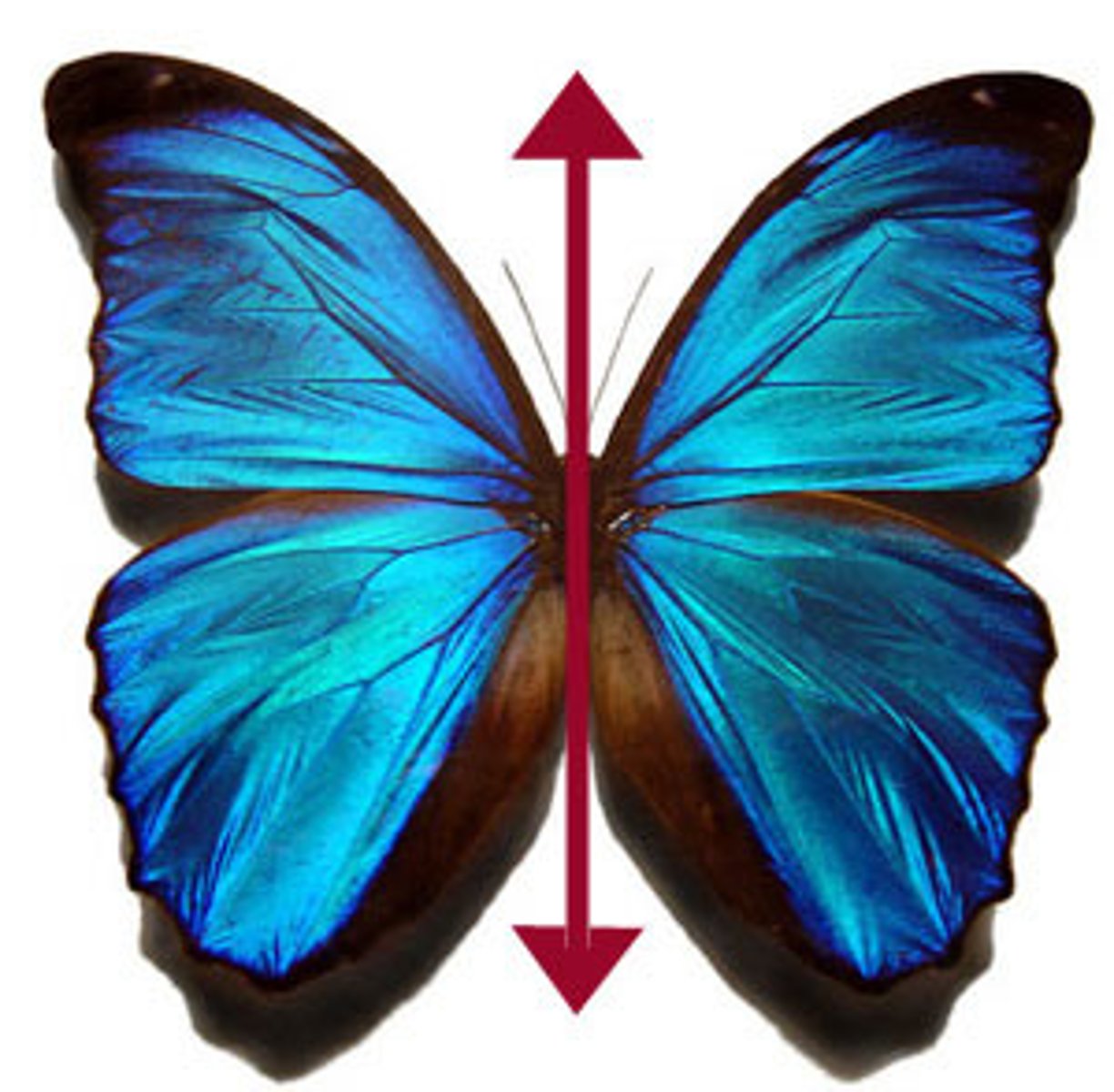

Asymmetry
Lack of symmetry; Ex: a piece of coral or sponge

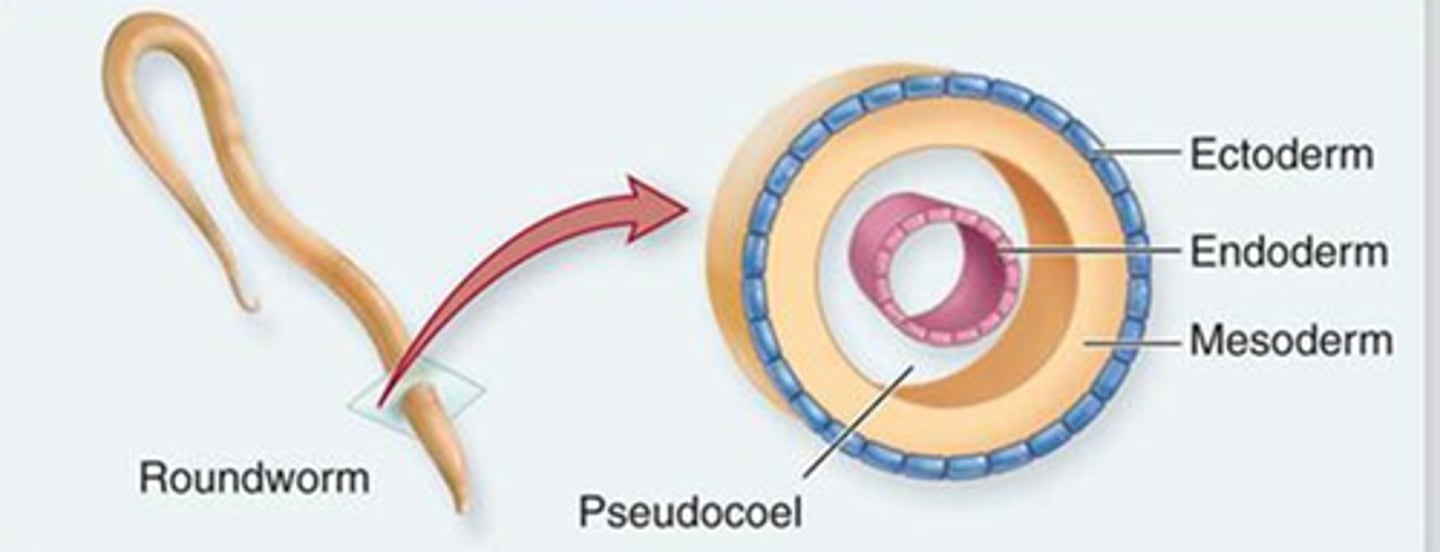
Pseudocoelomate
Presence of a body cavity filled with fluid
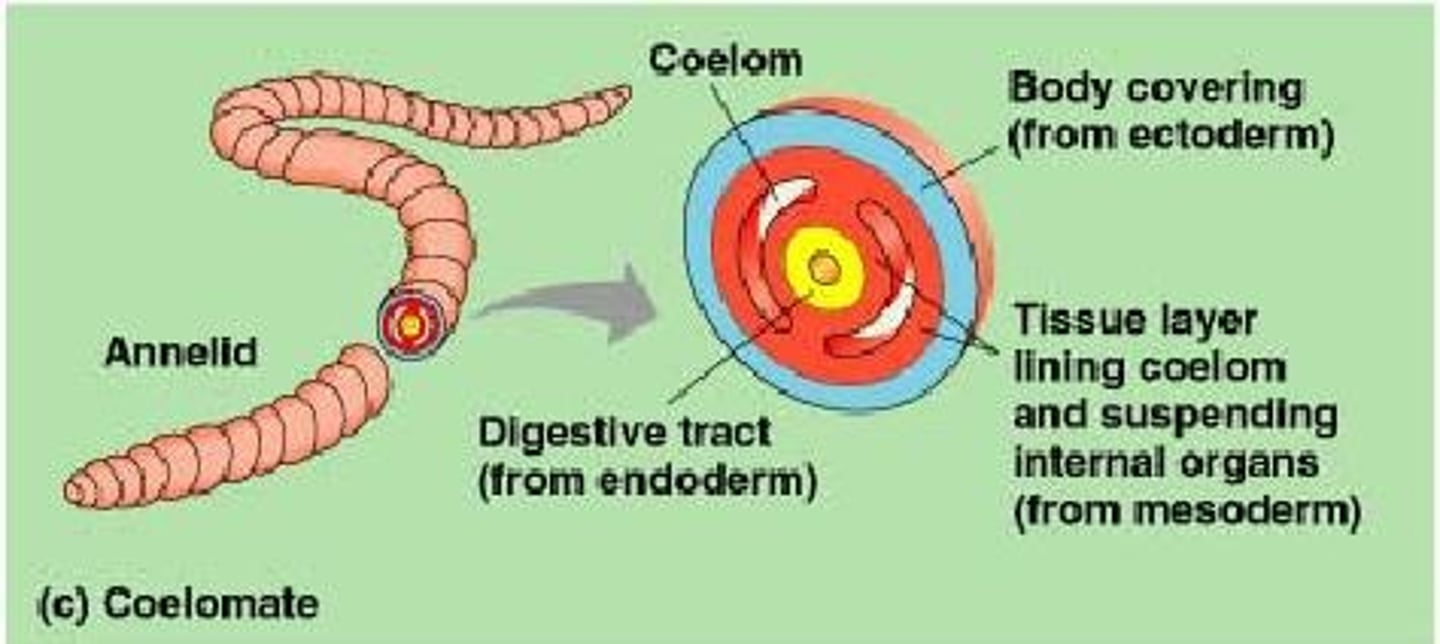
Coelomate
Presence of a body cavity with room for organ development
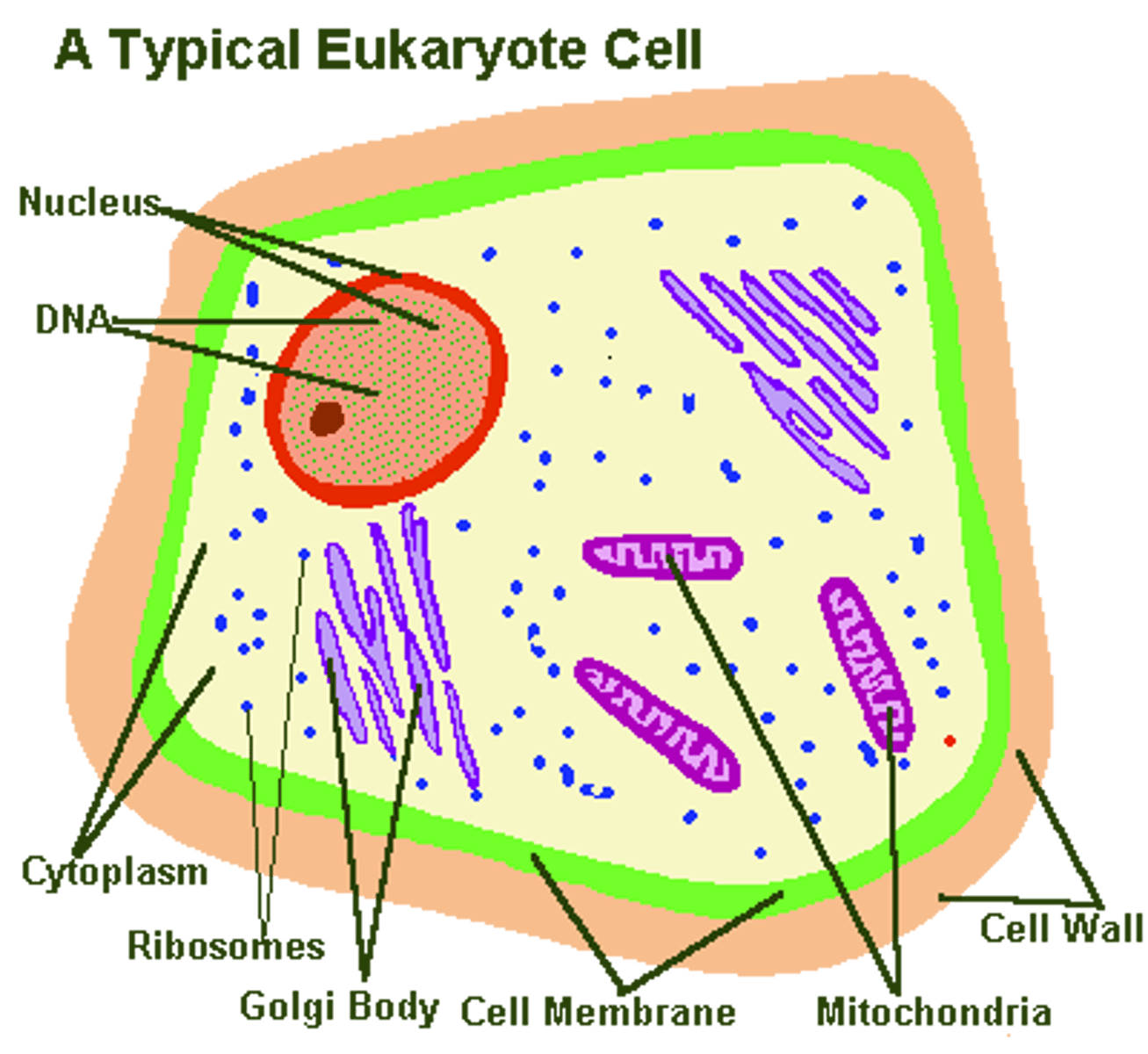
Eukaryotic
Cells that contain a nucleus; such as animal cells (also: plants, protists, fungi)
Posterior
Anatomical term = towards the tail
Anterior
Anatomical term = towards the head
Dorsal
Anatomical term = towards the back
Ventral
Anatomical term = towards the front
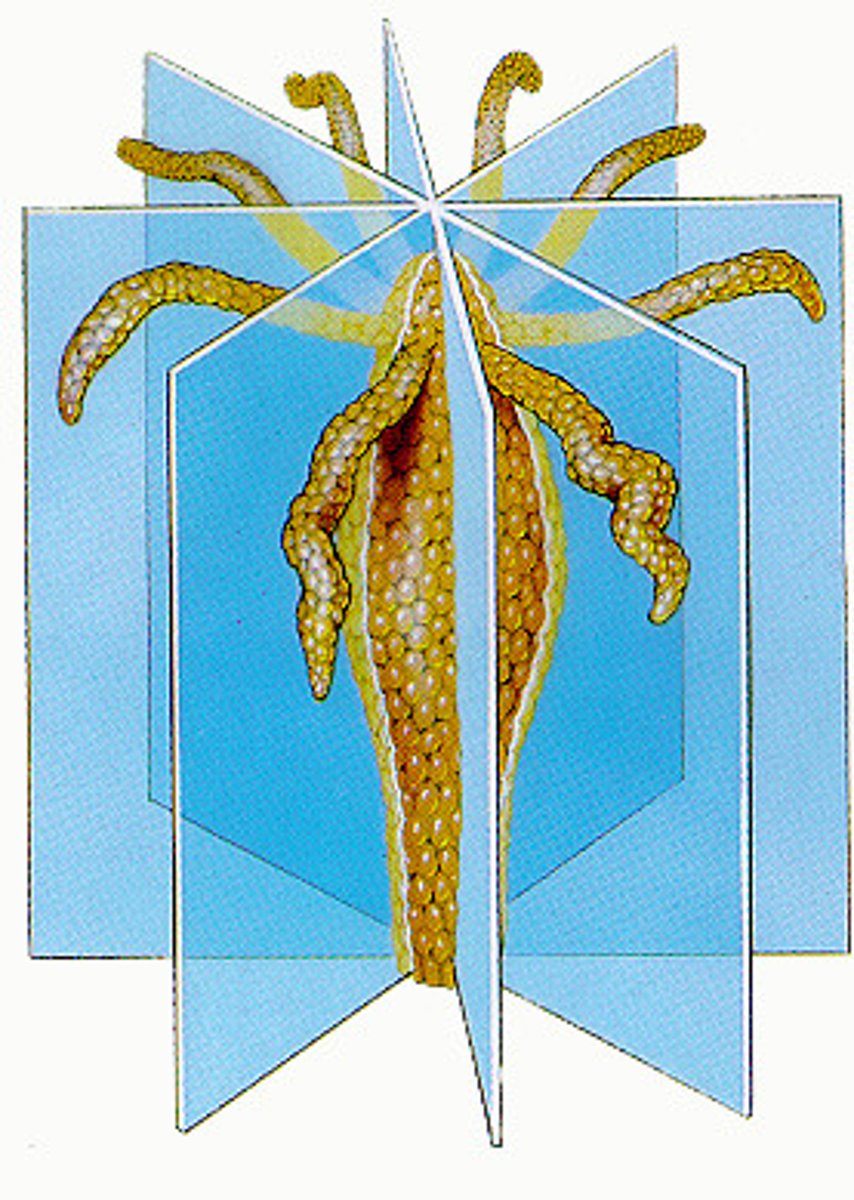
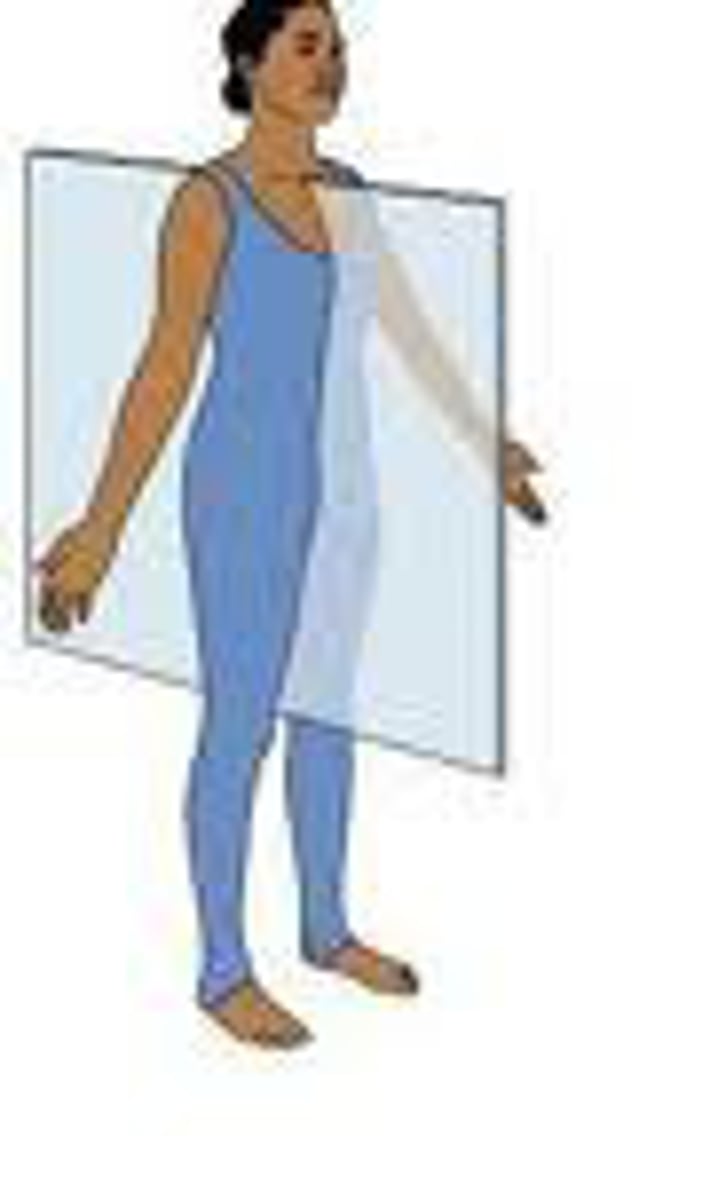
Frontal Plane
Type of plane; vertical cut; divides the organism into front and back
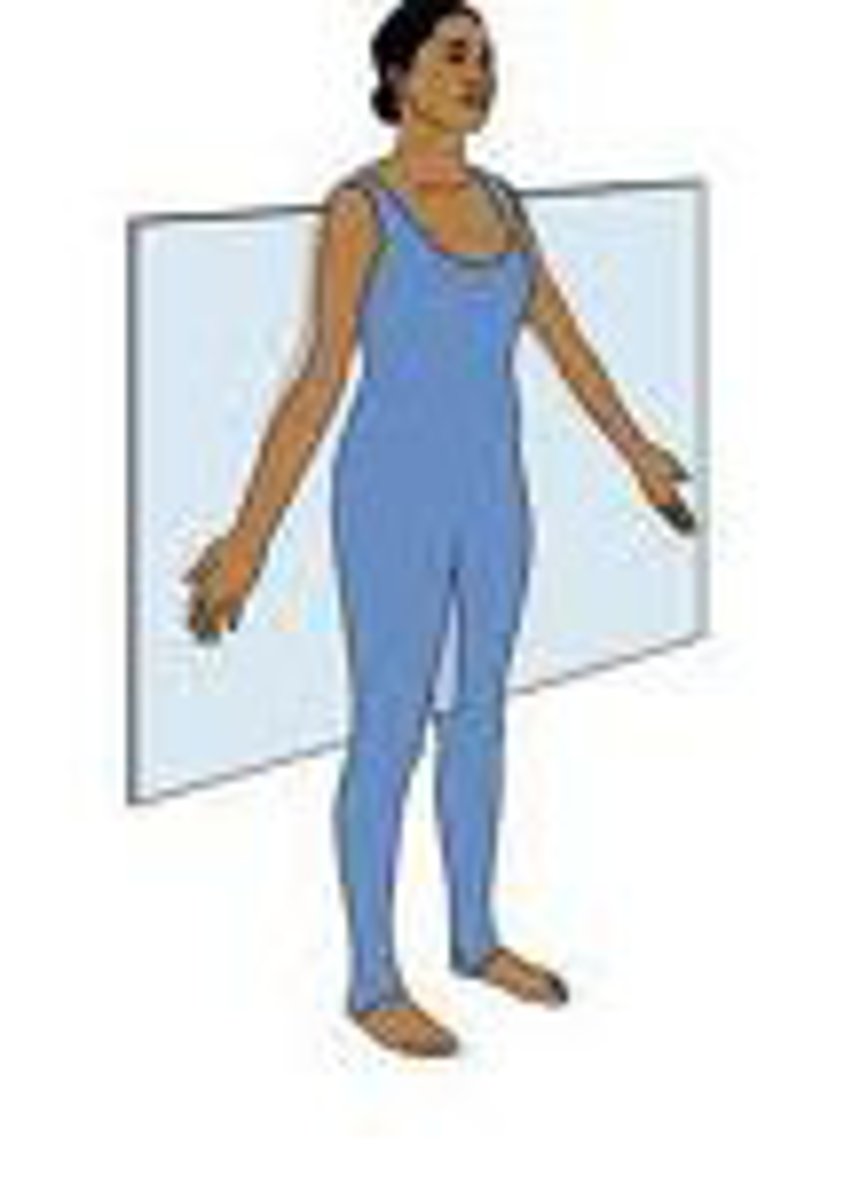

Sagittal Plane
Type of plane; vertical cut; divides the organism into left and right sides
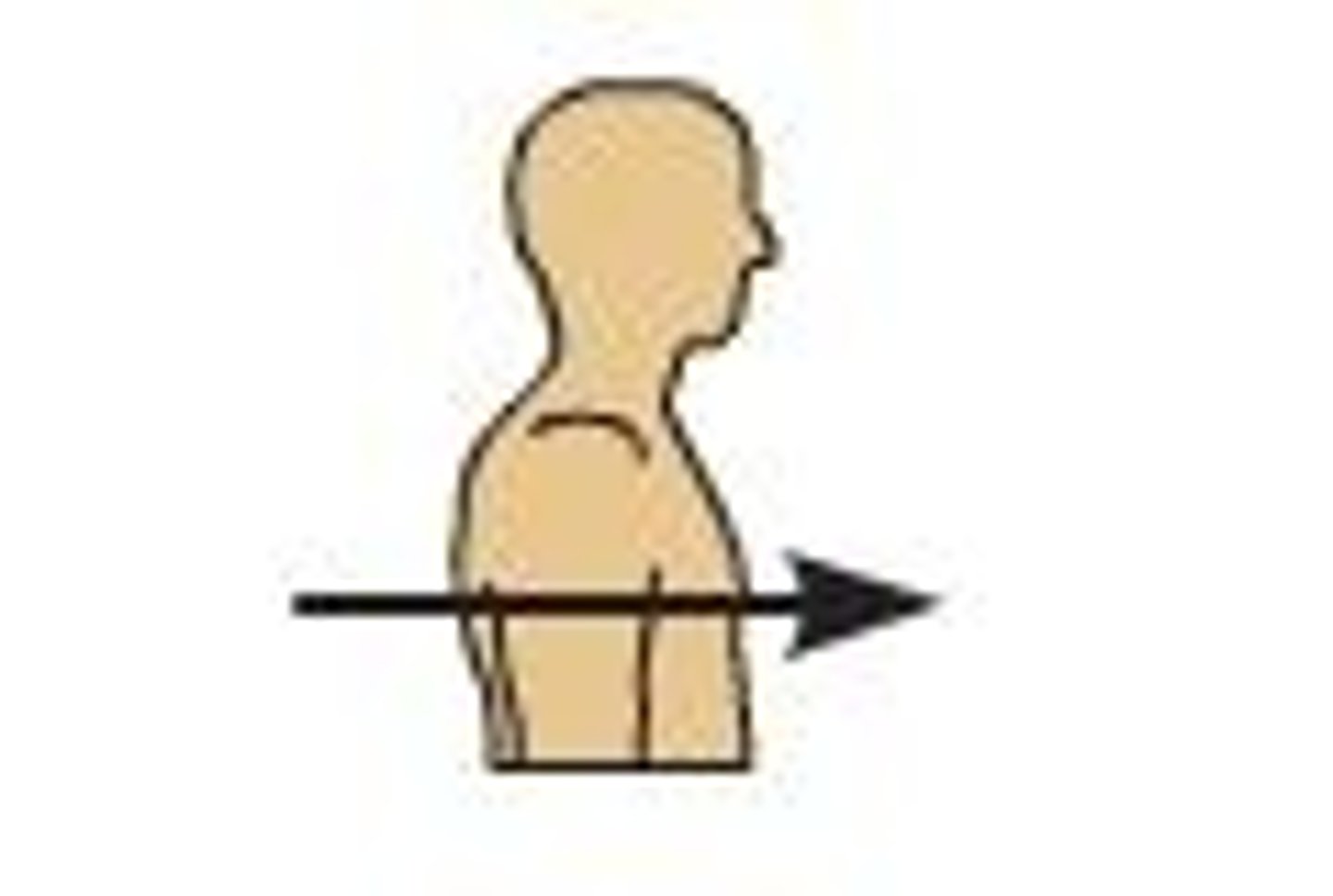
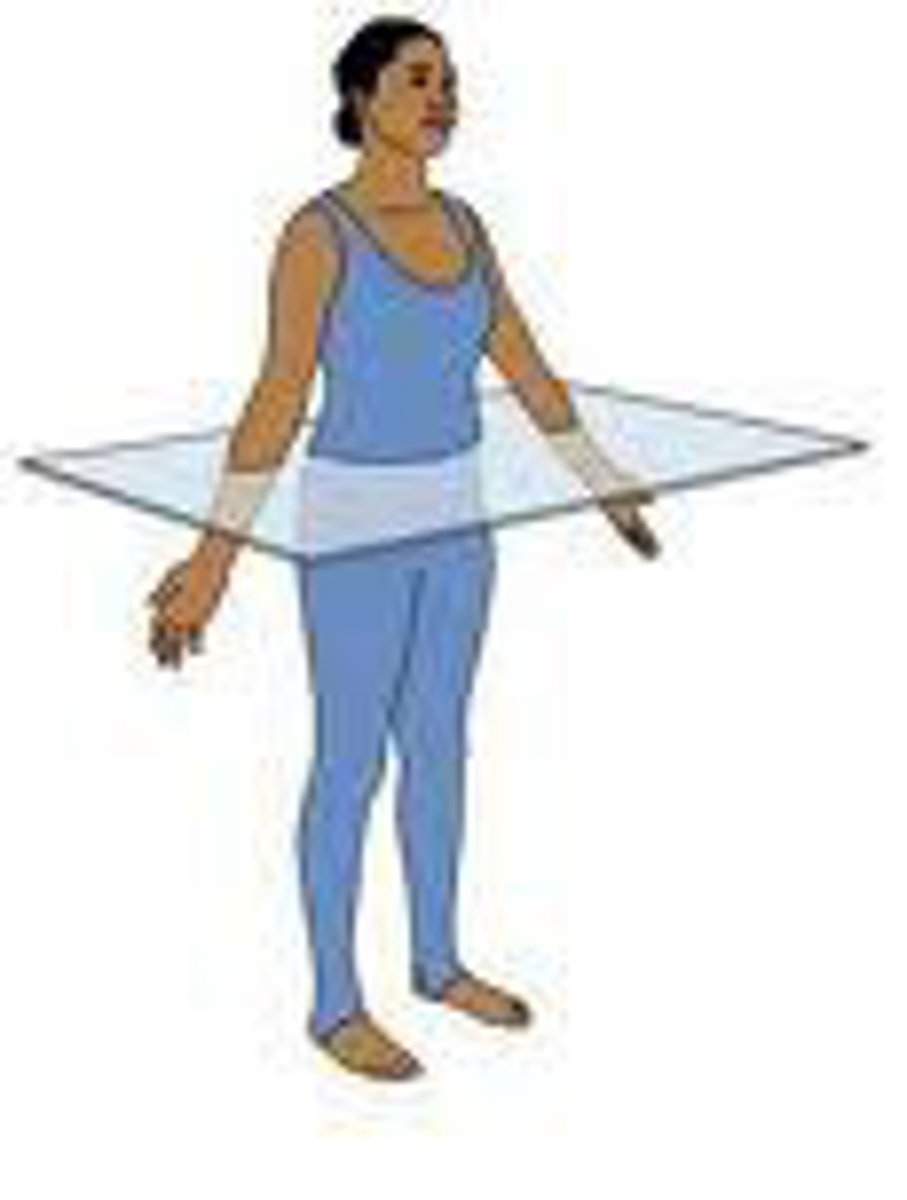
Transverse Plane
Type of plane; horizontal cut; divides the organism into top and bottom
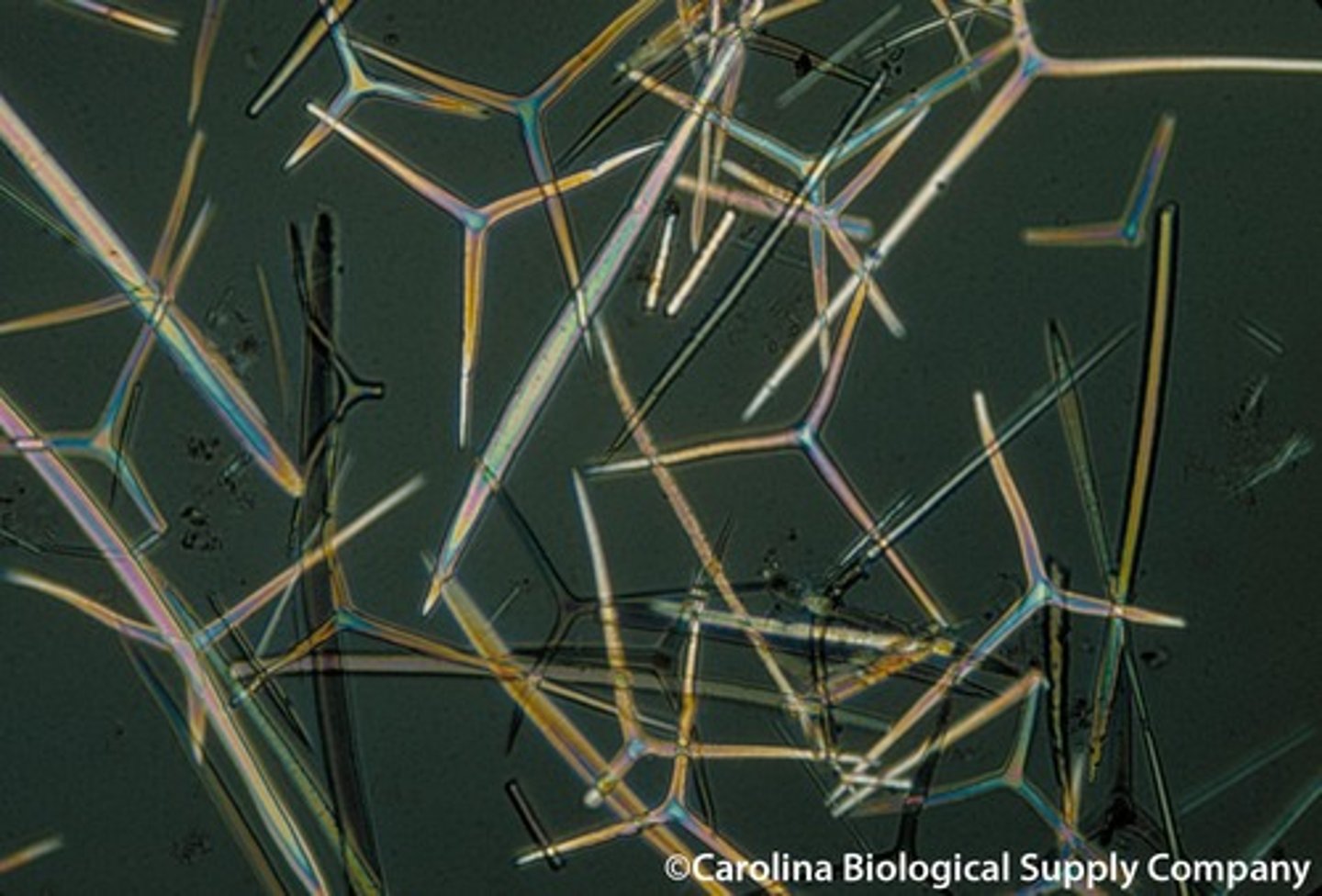
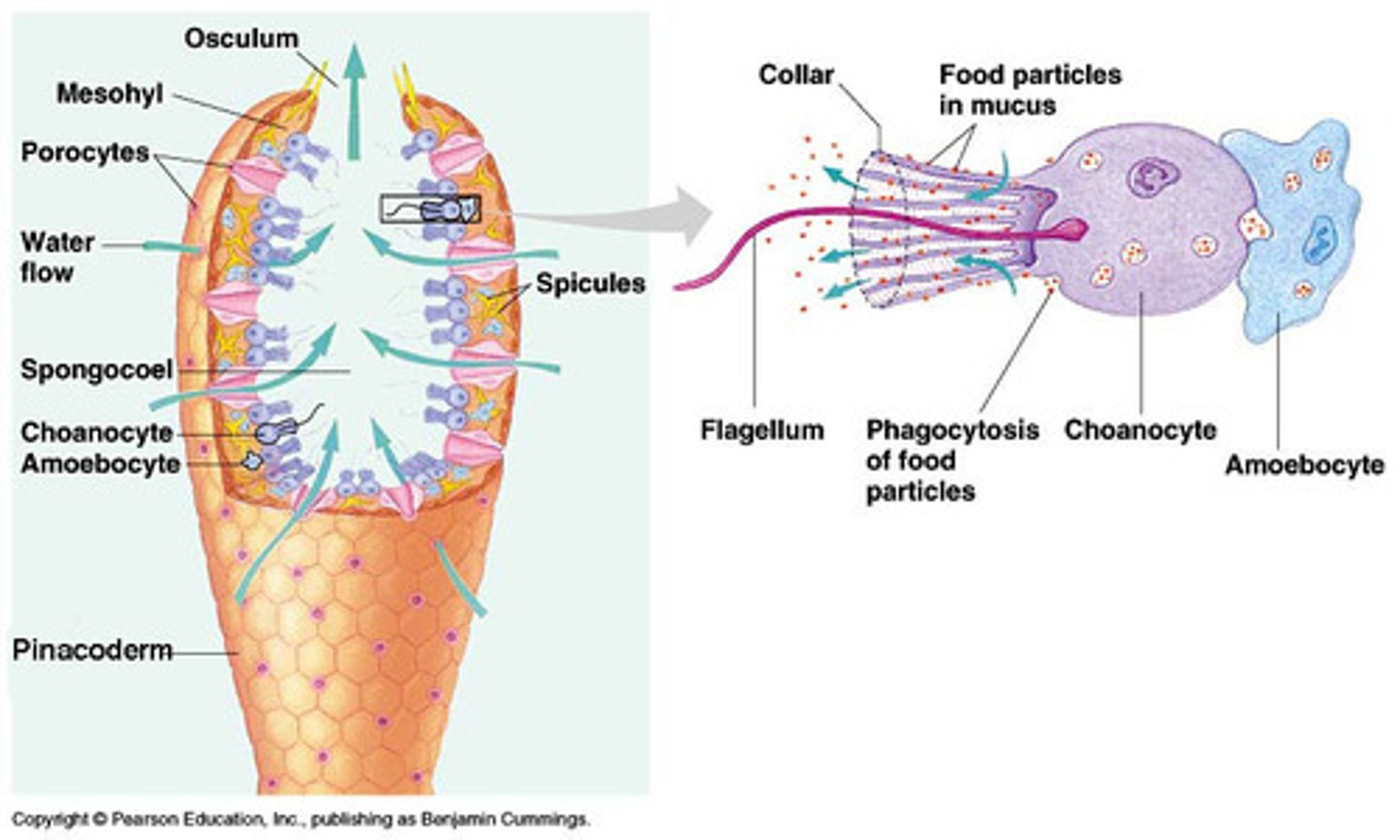
Spicules
Hard needle-like structures that make up the body of a sponge
General Porifera Description
A.K.A. Sponges; asymmetrical, lack true tissue organization, do have cell recognition; filter feeders that are made of bodies with many pores as adults; adults are stationary/sessile

General Cnidarian Description
Have tentacles with stinging cells
(cnidocytes = nematocysts + cnidocils)

General Invertebrate Description
Lack a backbone/vertebral column

The 6 "lower Invertebrate" Phyla
Porifera, Cnidaria (4 classes), Ctenophora
Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, Rotifera
The 4 Classes of Phylum Cnidaria
Hydrozoa, Cubozoa, Scyphozoa, Anthozoa
(hydra, jellyfish, sea anemones, coral)
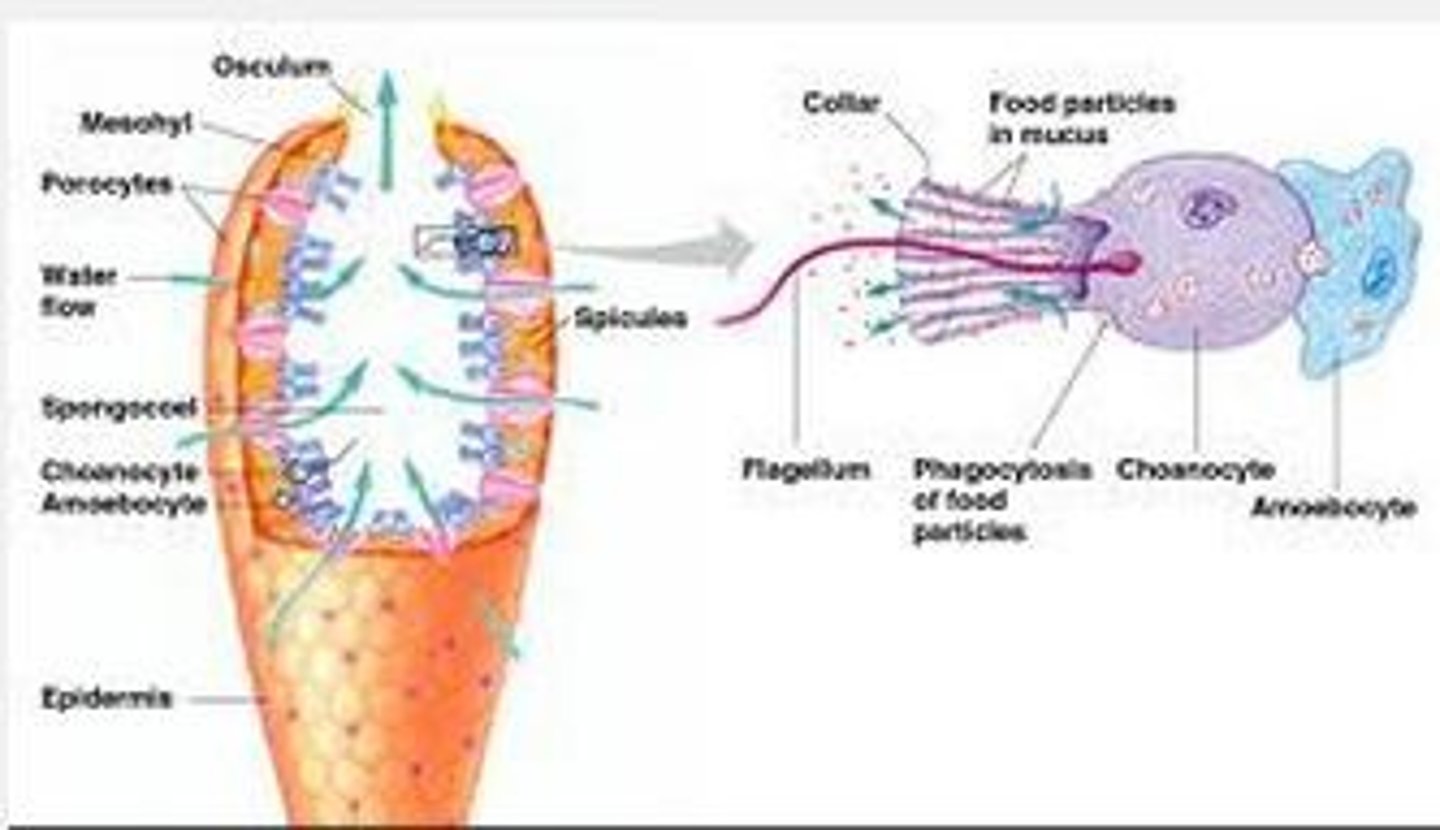
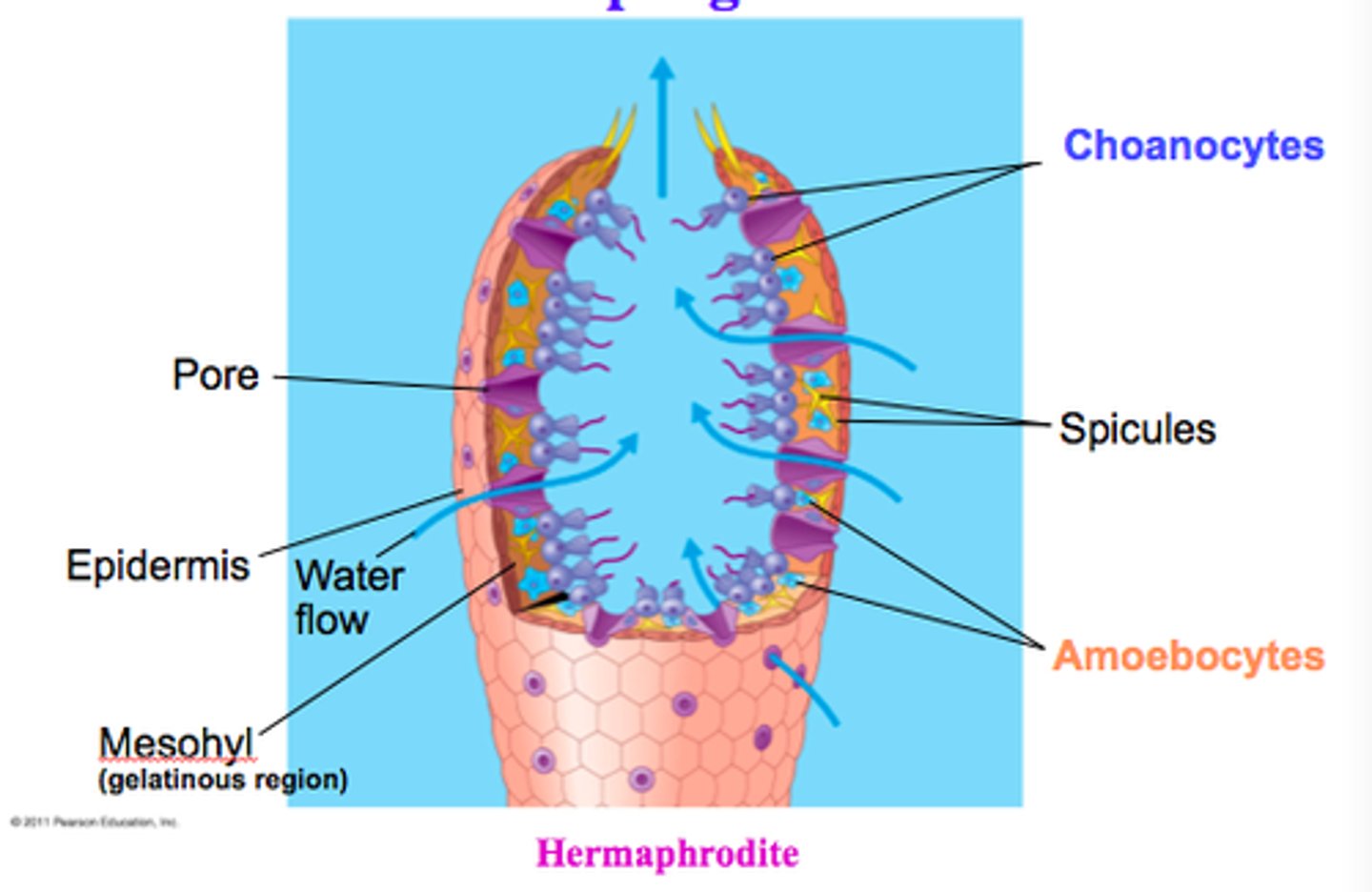
Porocytes
Ring-shaped cells in a sponge;
Form pores (aka ostia)
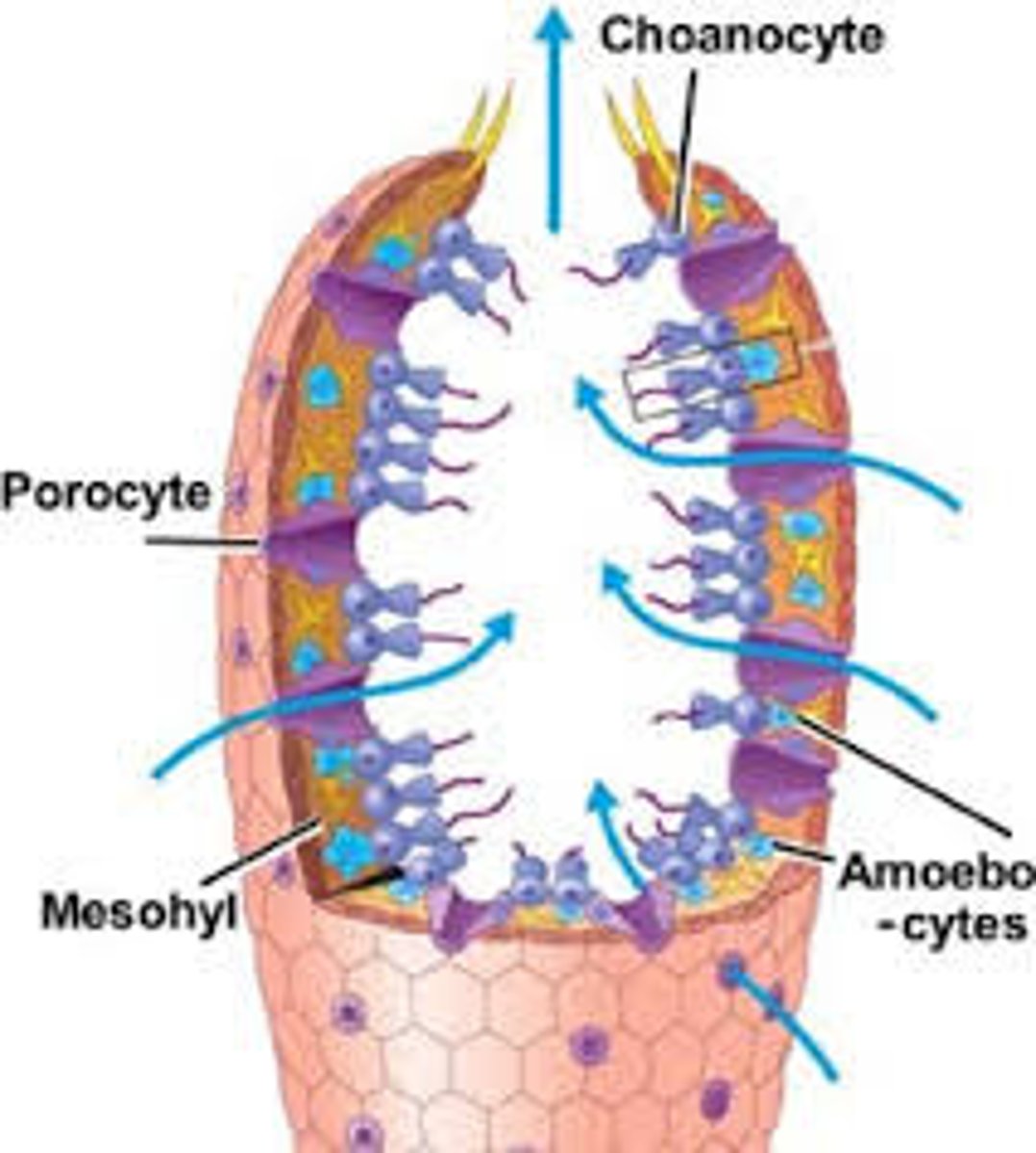
Choanocytes
AKA collar cells of a sponge; face the spongocoel; draw water into the body of the sponge; the flagella create the feeding current
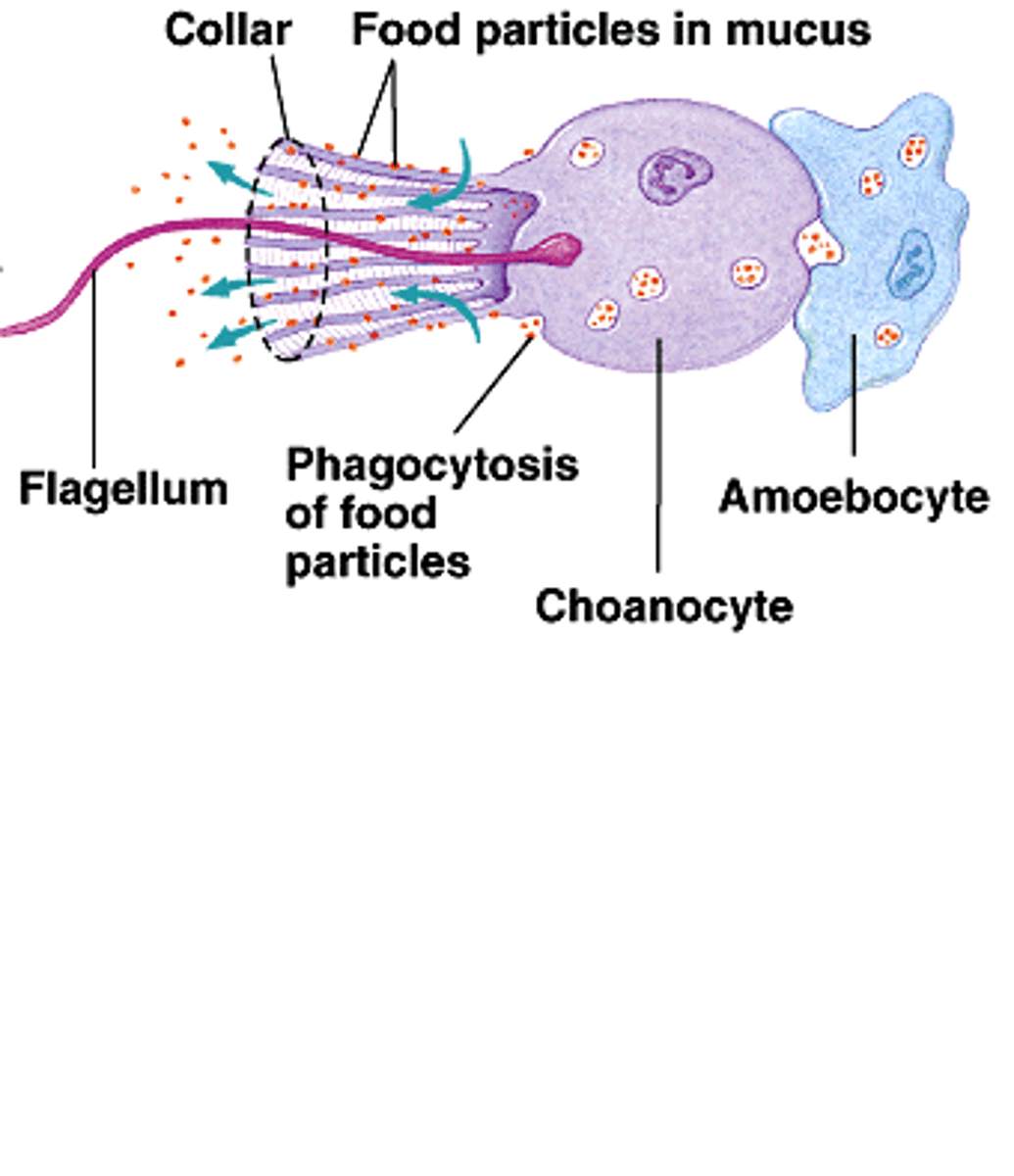
Amoebocyte
Feeding cells in a sponge; they phagocytize and digest food from choanocytes then transport the food where the sponge needs it
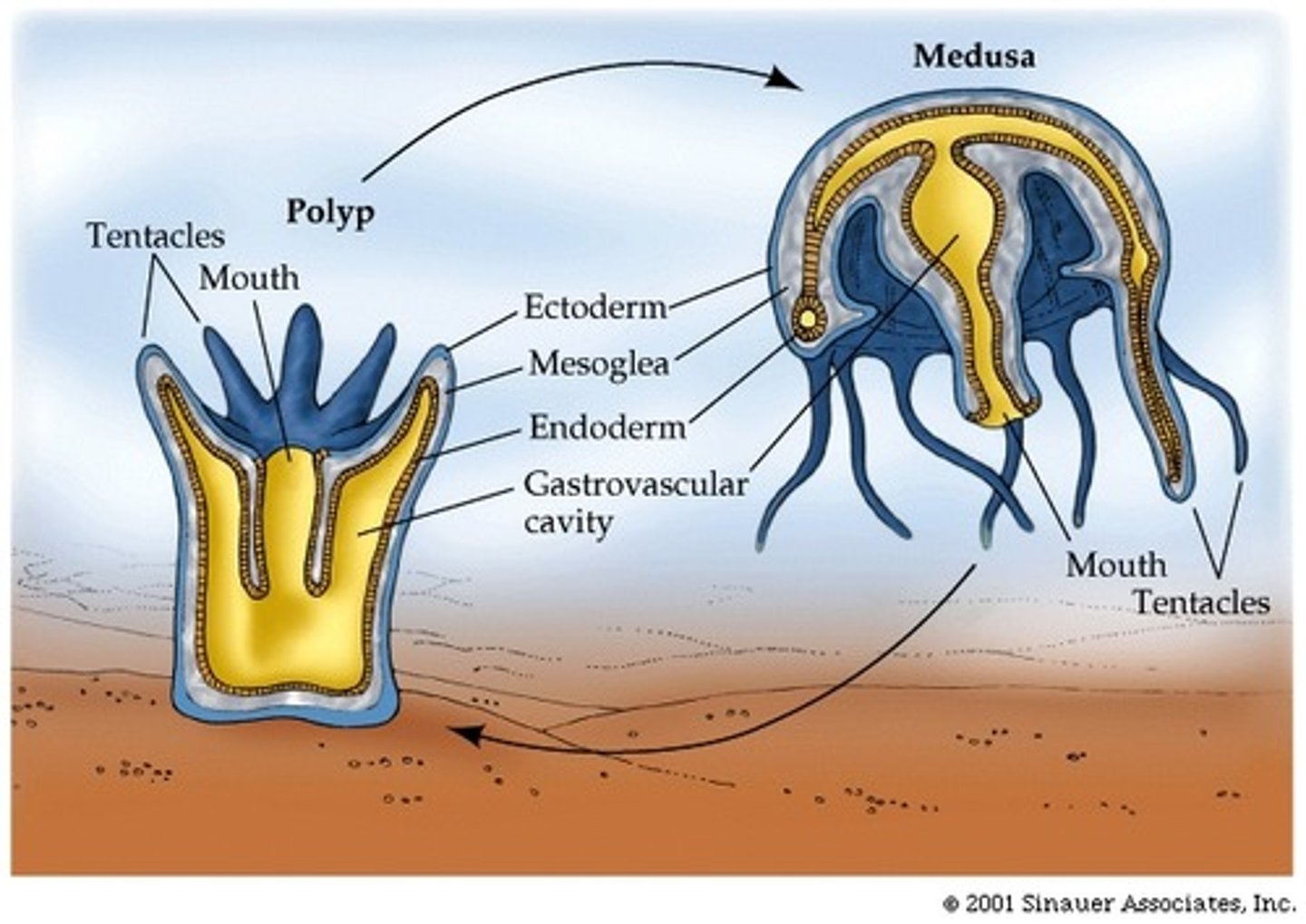
The 2 basic body forms of a cnidarian
Medusa & Polyp
Many cnidarians have these two distinct life stages
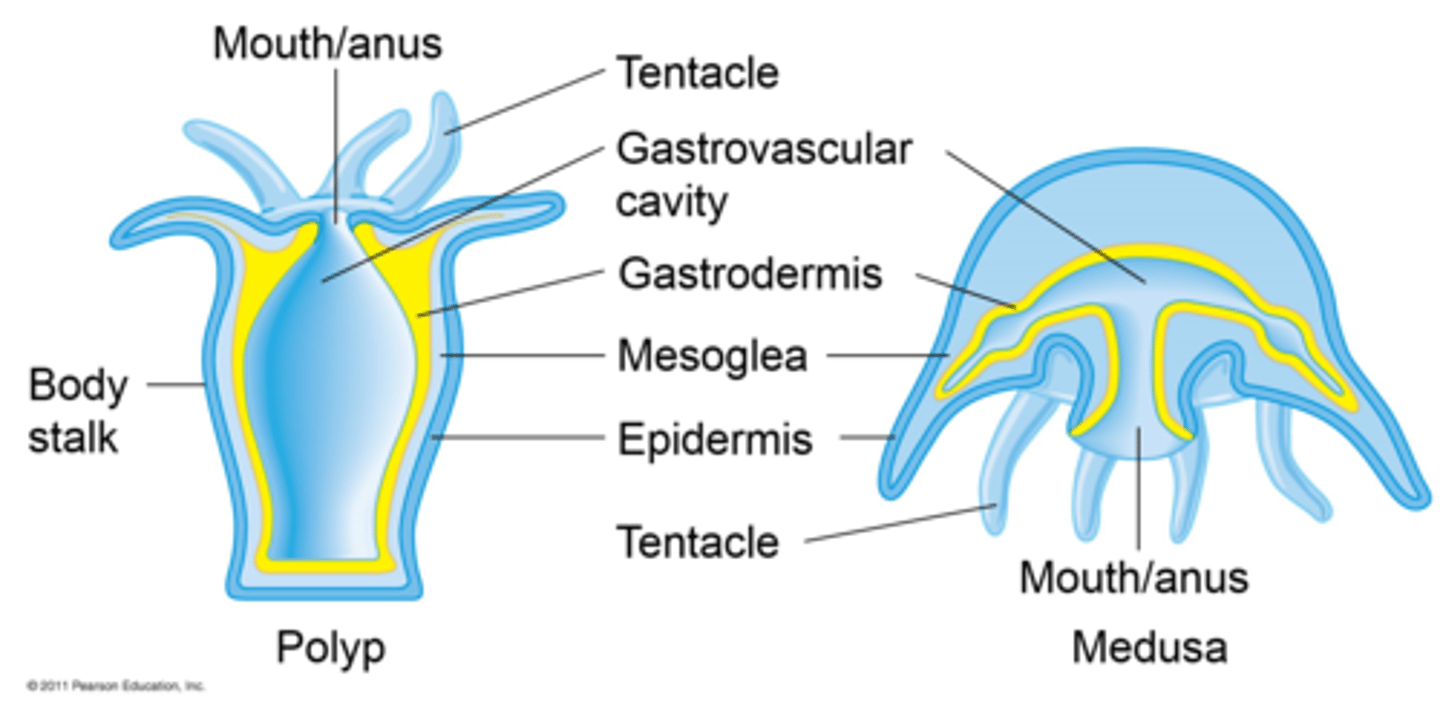
Polyp
Stationary/attached/sessile body form of a cnidarian; "vase-shaped"; primarily asexual reproduction
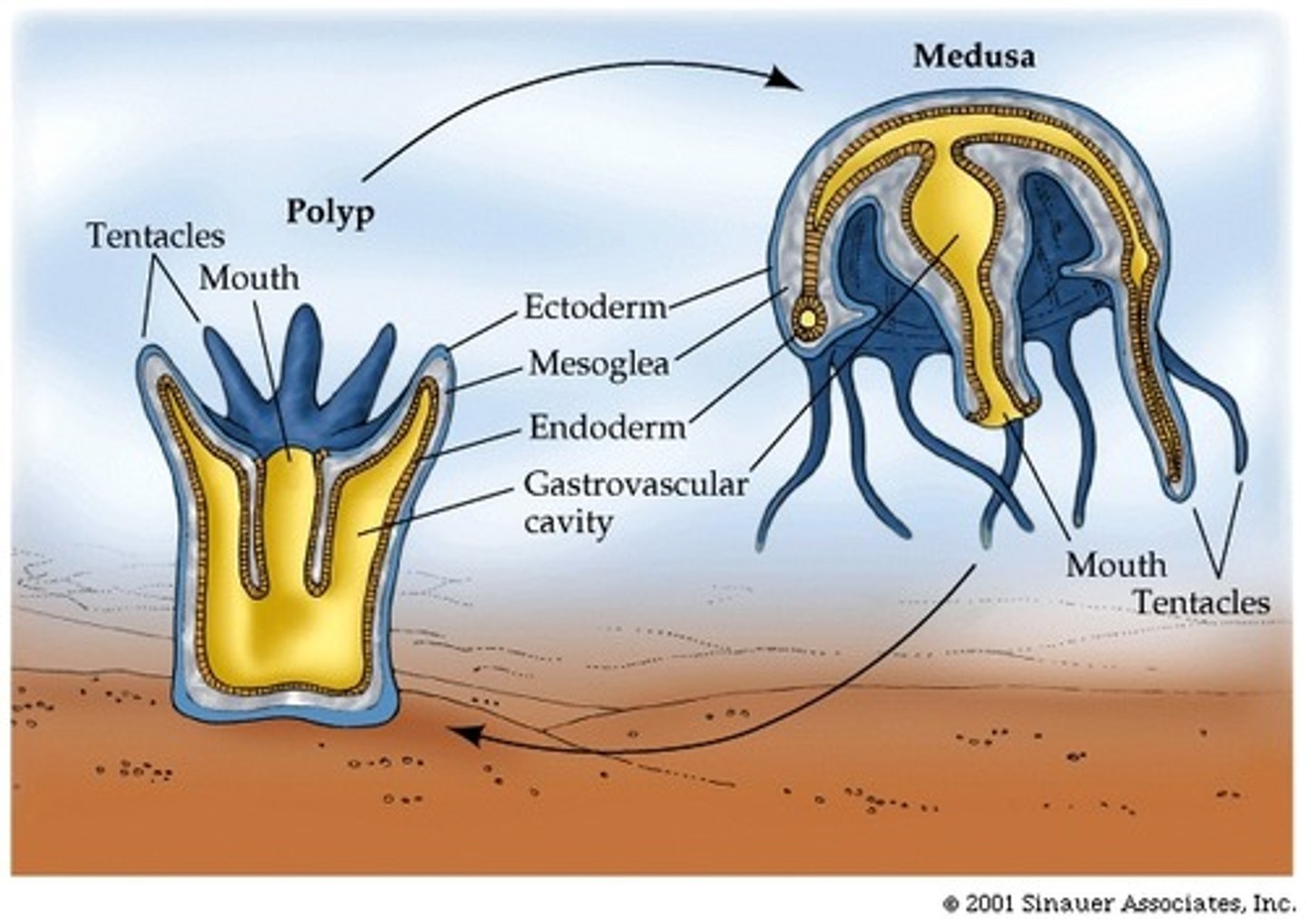
Medusa
Mobile/free-floating body form of a cnidarian; "bell-shaped"; primarily sexual reproduction
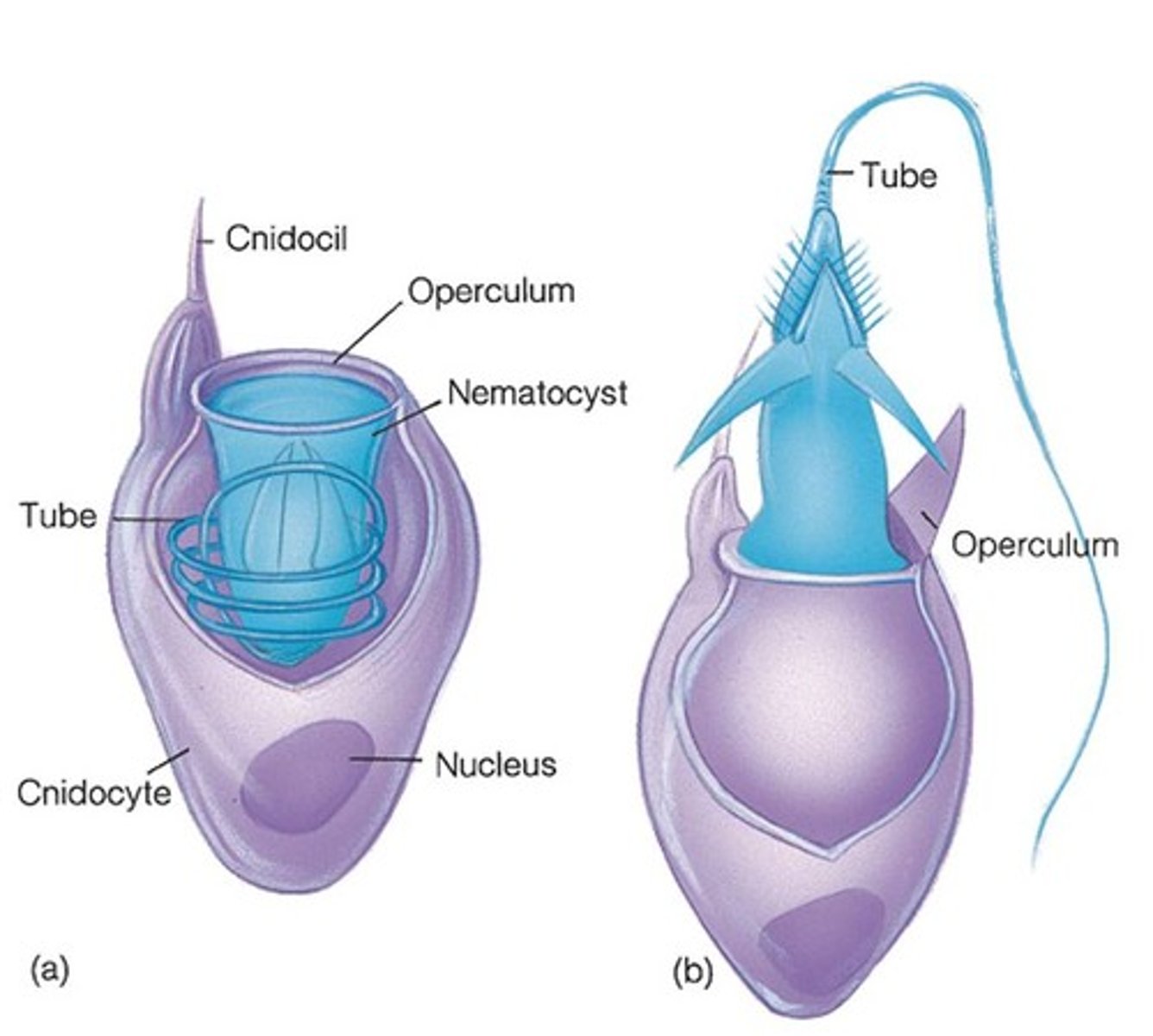
Cnidocyte
A specialized cell used for defense in a cnidarian; has two parts: a cnidocil and a nematocyst
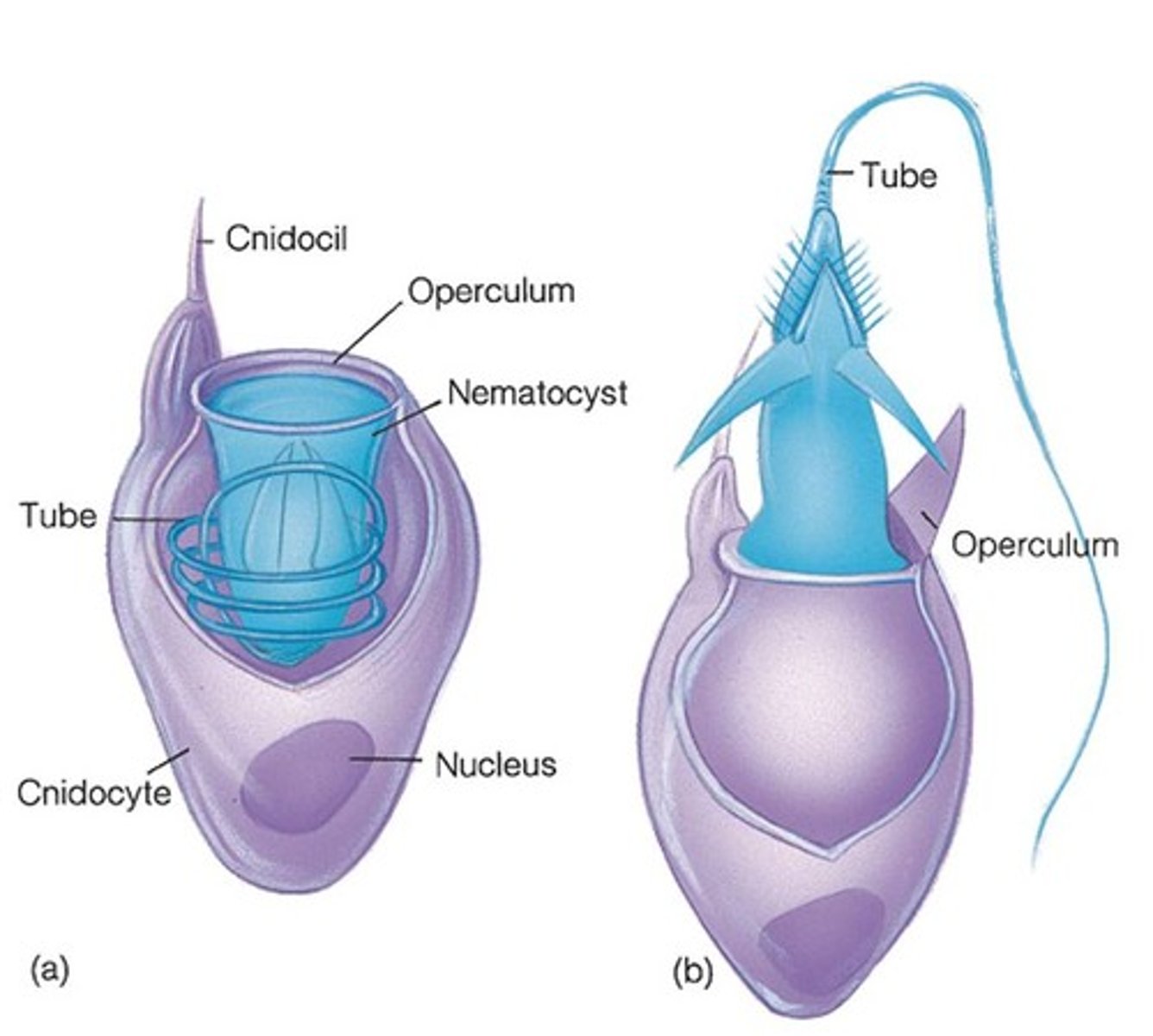
Cnidocil
The hair-like structure on a cnidocyte that acts like a trigger to release the nematocyst
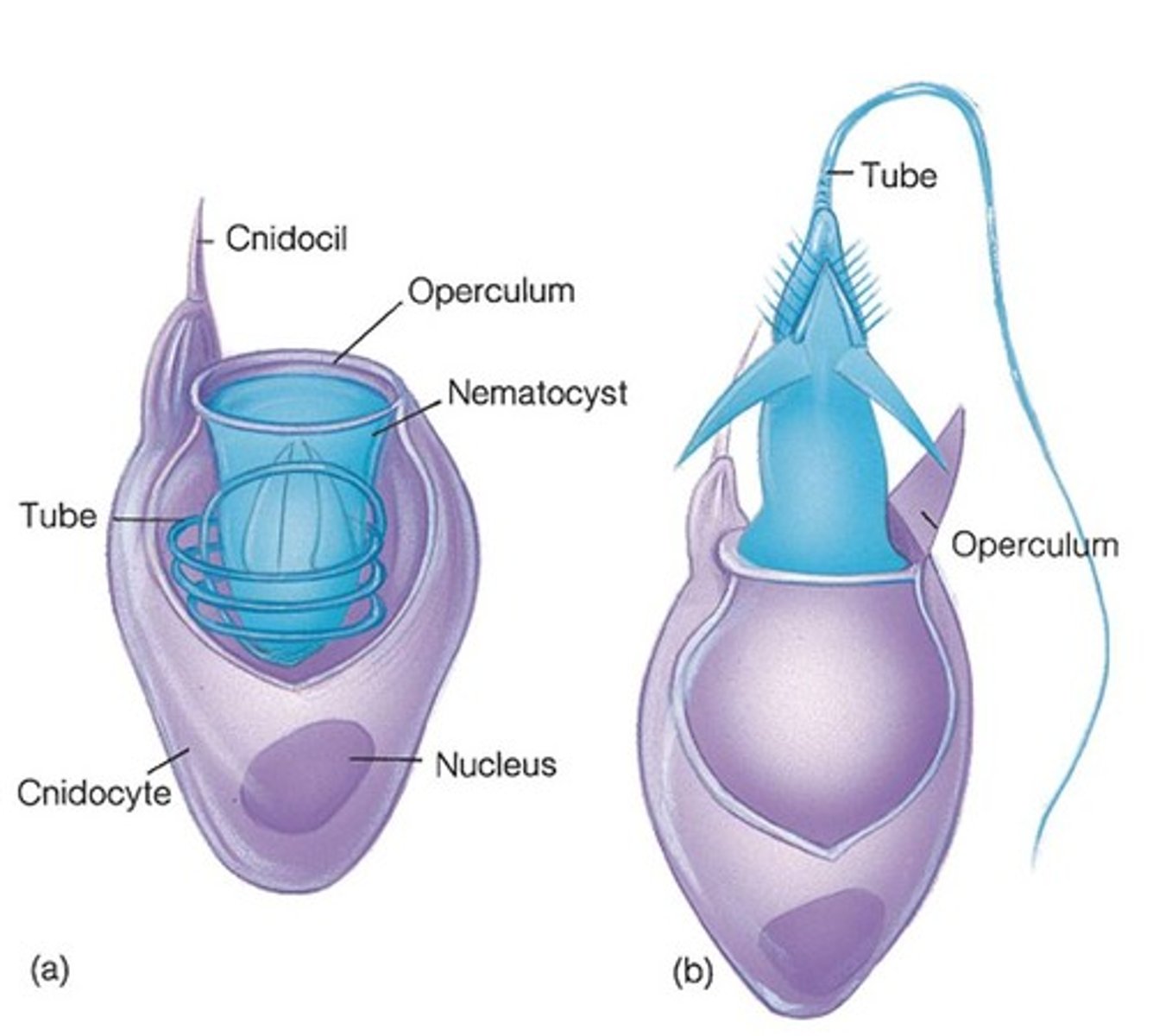
Nematocyst
The coiled filament on a cnidocyte that can have sharp spines of tips to inject poison or wrap around prey; cnidarians use them to capture food (i.e. jellyfish & anemones)
Feeding in Phylum Porifera
"Sponges"
Water current carries food in through the ostia, is captured and directed to the amoebocytes using the coanocytes, the amoebocytes transport the food throughout the sponge, waste is removed and exits through the osculum (opening in the top of the sponge)
Reproduction in Phylum Porifera
"Sponges"
Asexually (form buds)
Sexually (produce sperm & egg; produced at different times to avoid self-fertilization)
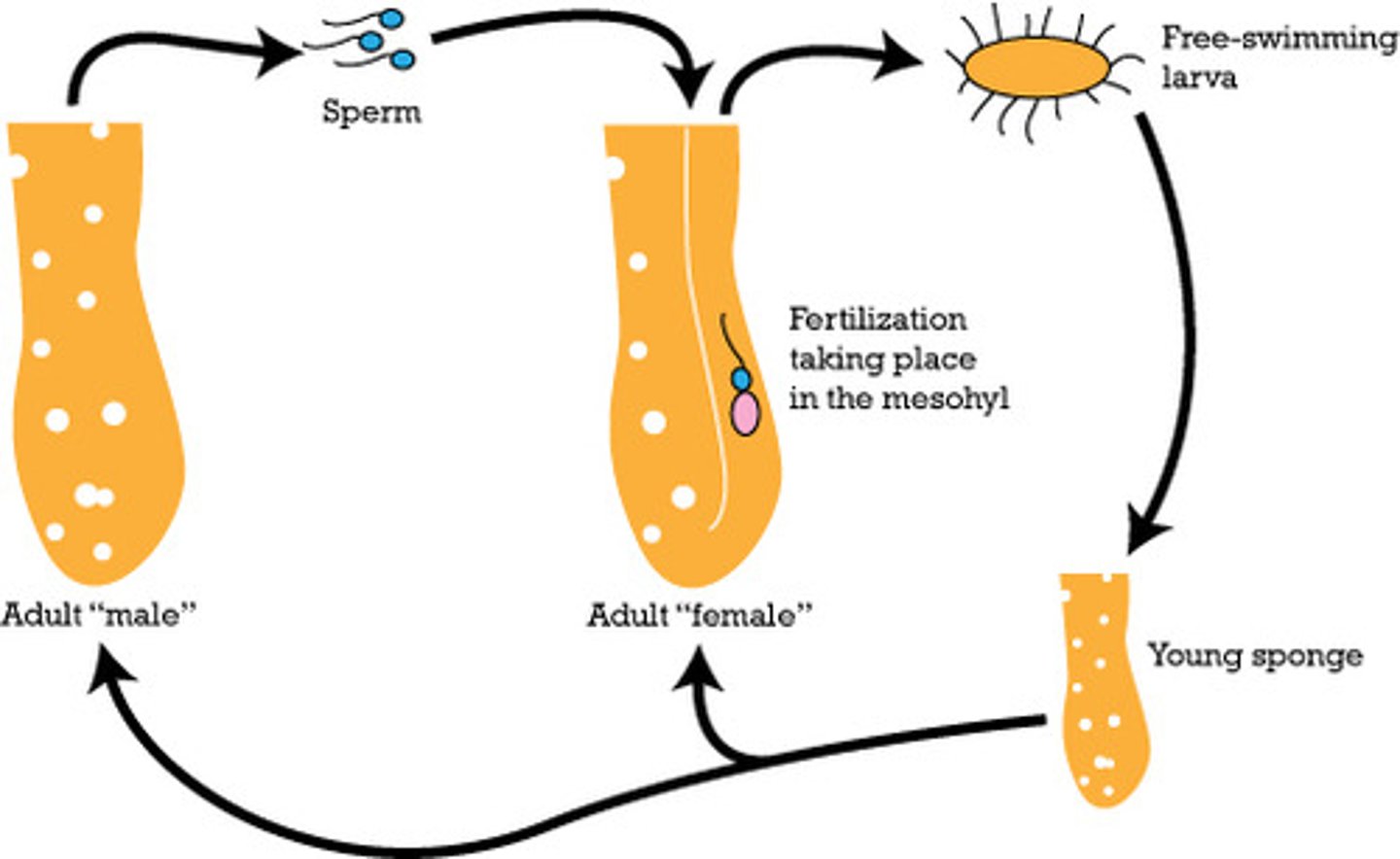
Hermaphrodite
An organism that can produce both sperm and eggs
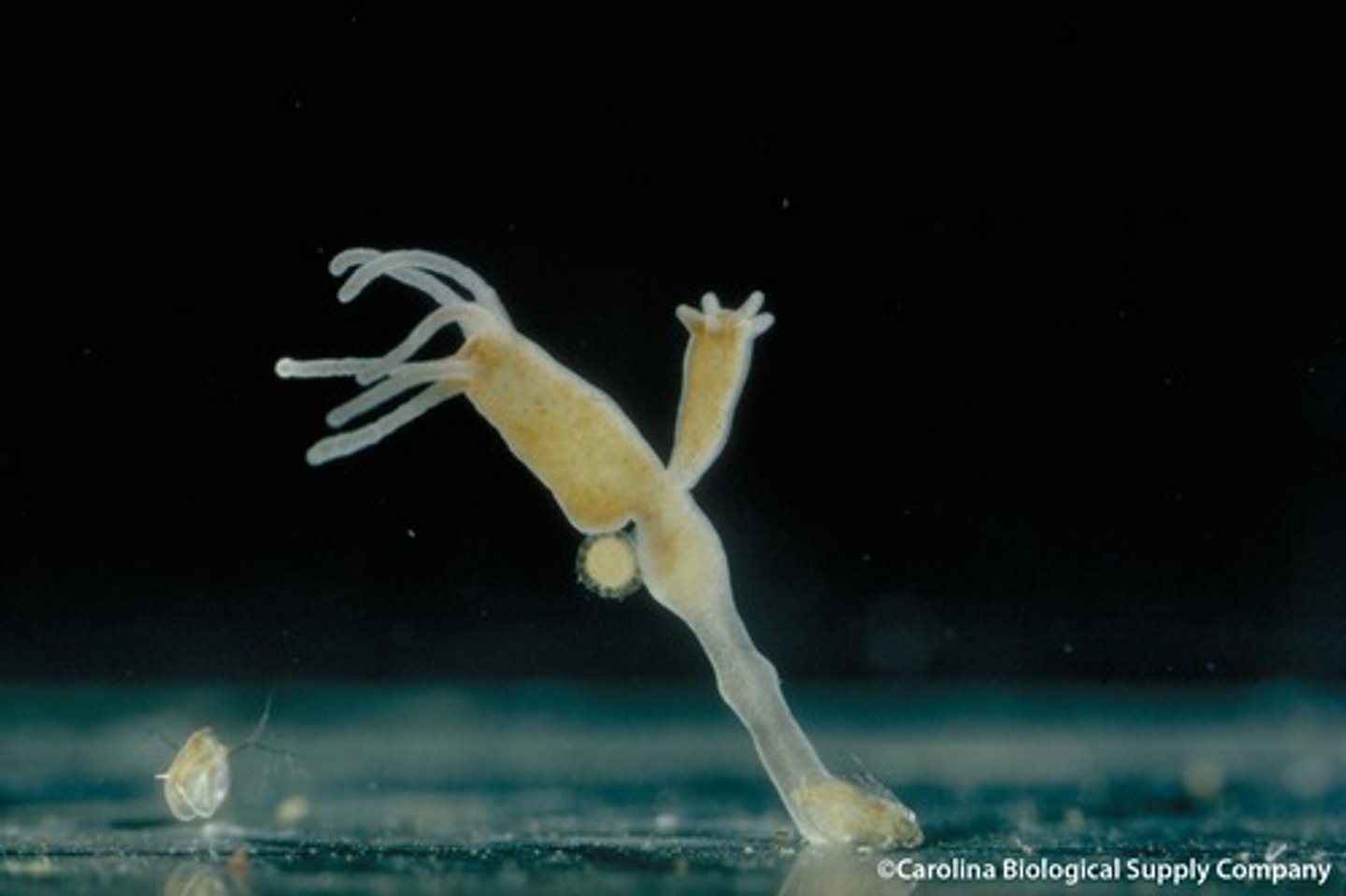
Class Hydrozoa
1 of 4 classes from Phylum Cnidaria
Hydra are stationary polyps; Portuguese man-of war are mobile or floating polyps

Class Cubozoa
"Box Jellies"
1 of 4 classes from Phylum Cnidaria
Adults are mobile medusa; cube shaped with tentacles at the corners of the cube; no polyp form has been identified
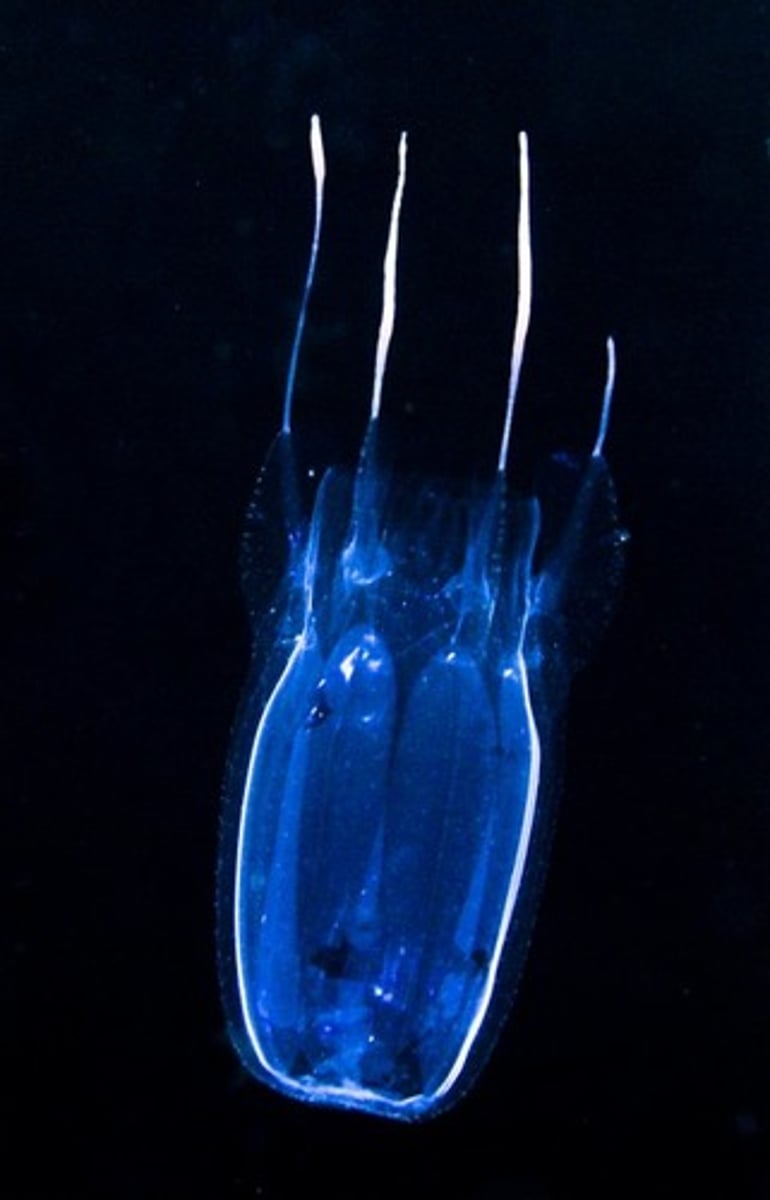
Class Scyphozoa
"Jellyfish"
1 of 4 classes from Phylum Cnidaria
Adults are mobile medusa; Medusa form is how jellyfish spend most of their life; polyp form is seen during life cycle
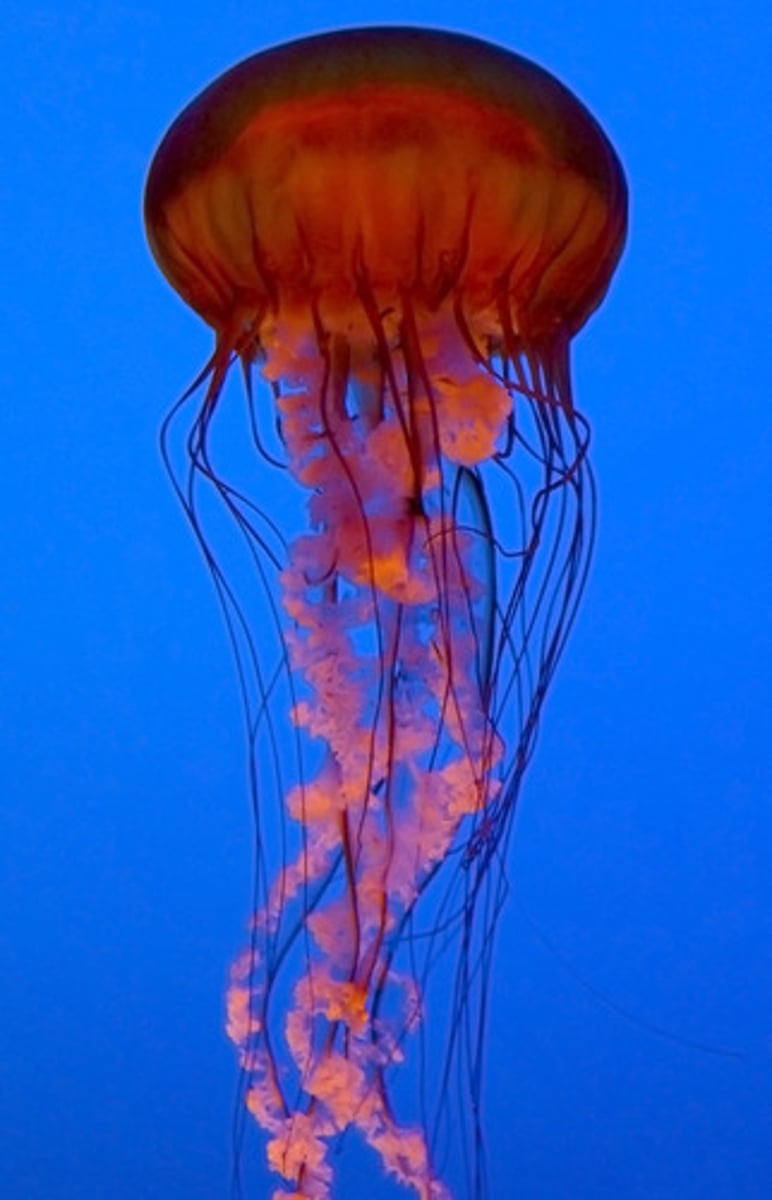

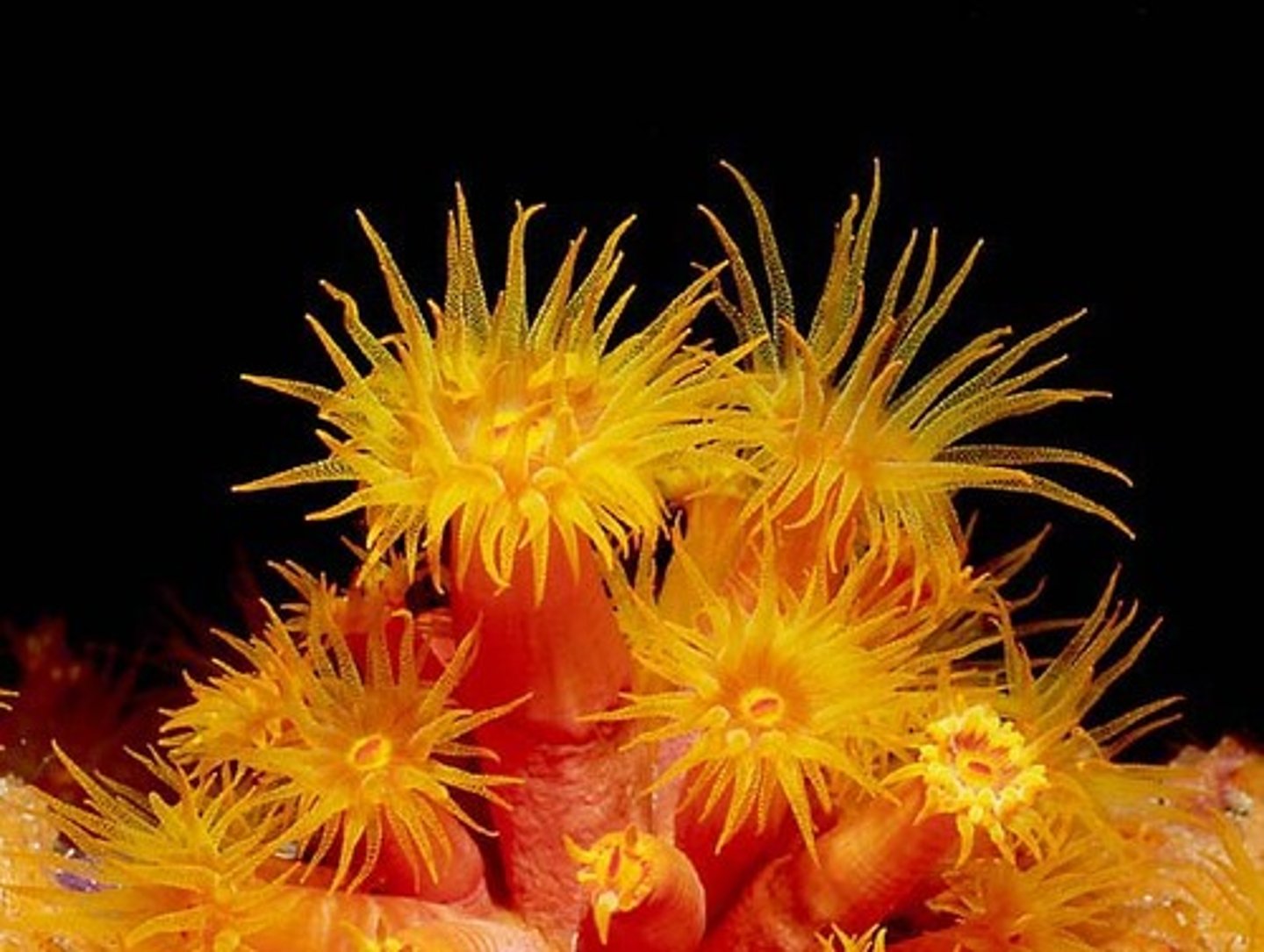
Class Anthozoa
"Flower Animals"
1 of 4 classes from Phylum Cnidaria
Adults exist only as stationary/sessile polyps; secrete walls of calcium carbonate (CaCO3)
Ex: sea anemones & coral

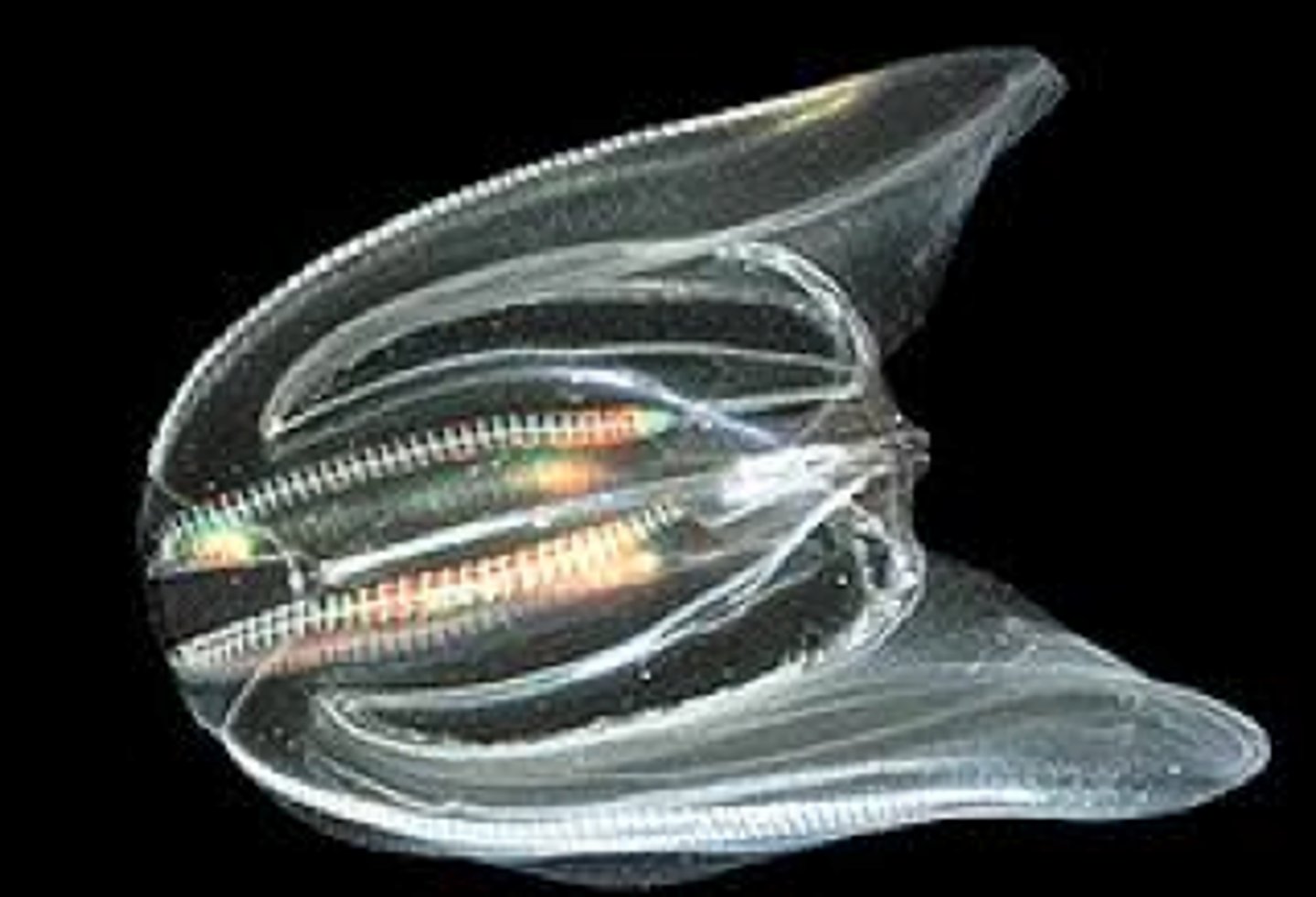
Phylum Ctenophora
Comb Jellies; have 8 rows of cilia used for movement (largest organism to move using cilia), have biting glue cells called coloblasts
(NOT stinging cells called cnidocytes)

Spongin
Provides support in a sponge; made of a network of protein fibers

Planarians
Free living flatworm; Phylum Platyhelminthes; Class Turbellaria; Incomplete digestive tract (one opening) "Pharynx"
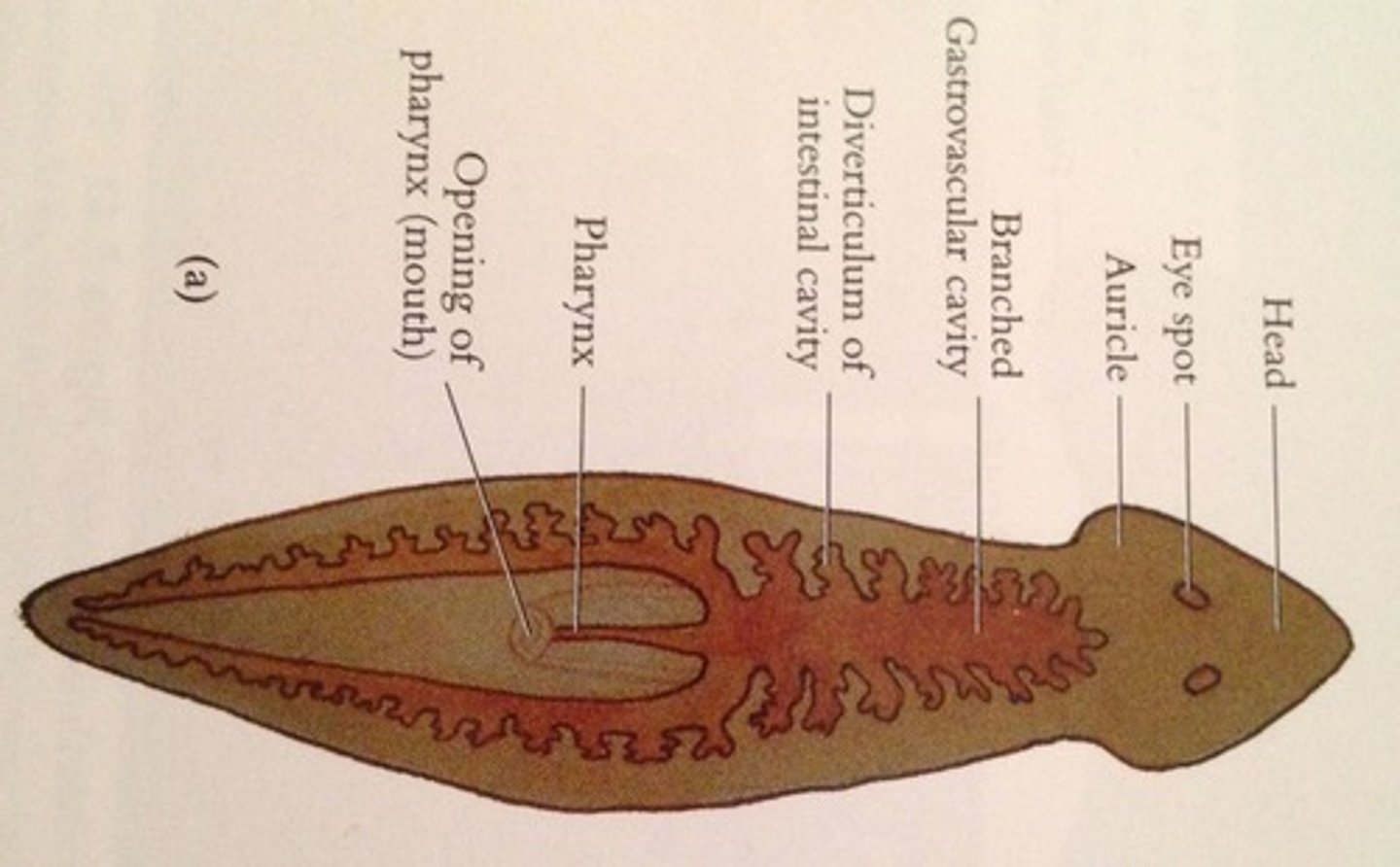
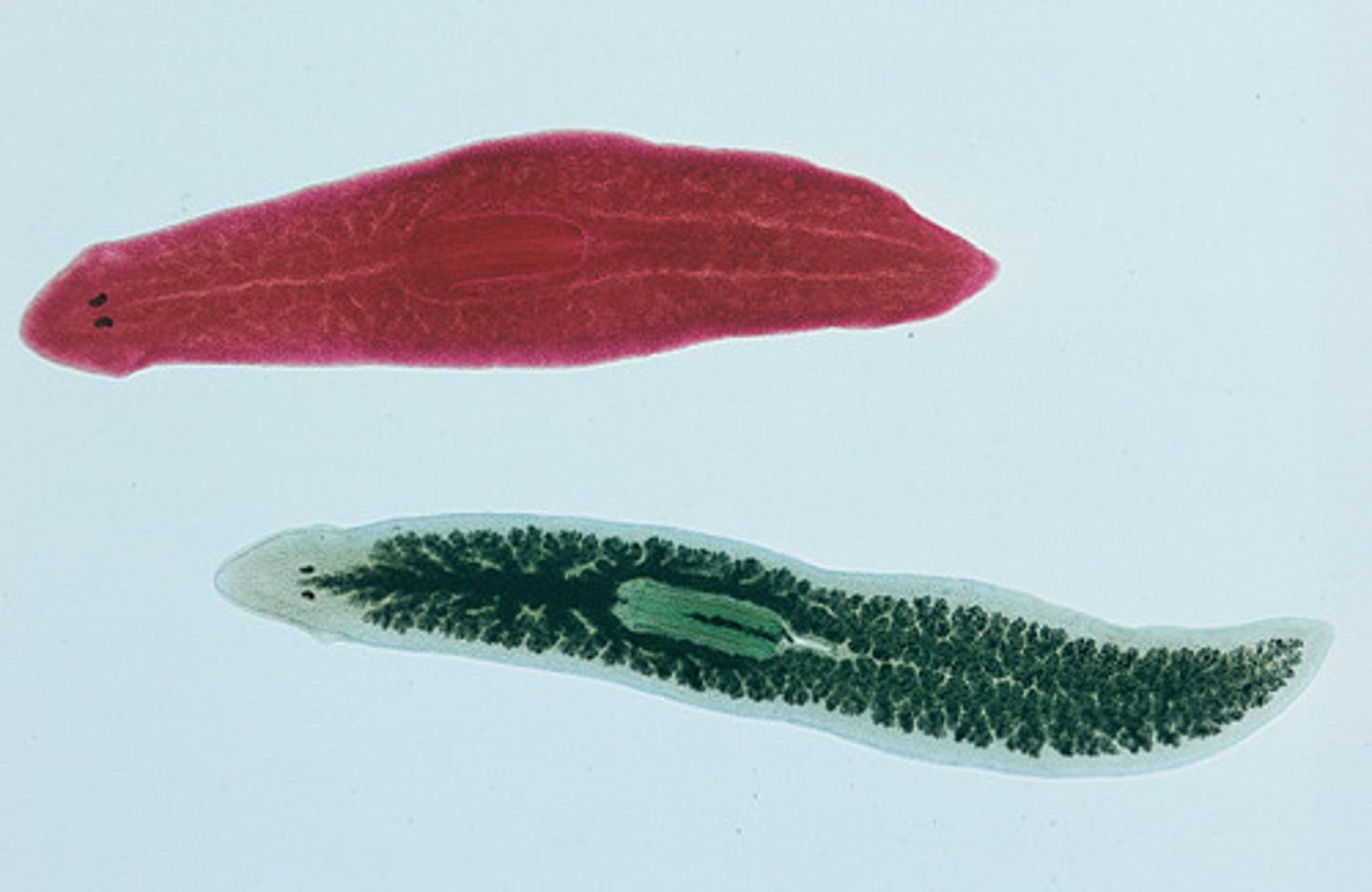
Phylum Platyhelminthes
(Nickname = Flatworms)
4 Classes; Most are parasitic; acoelomate; reproduce asexually by fission, fragmentation or regeneration; NO circulatory /respiratory system (all cells are close to surface to exchange material)
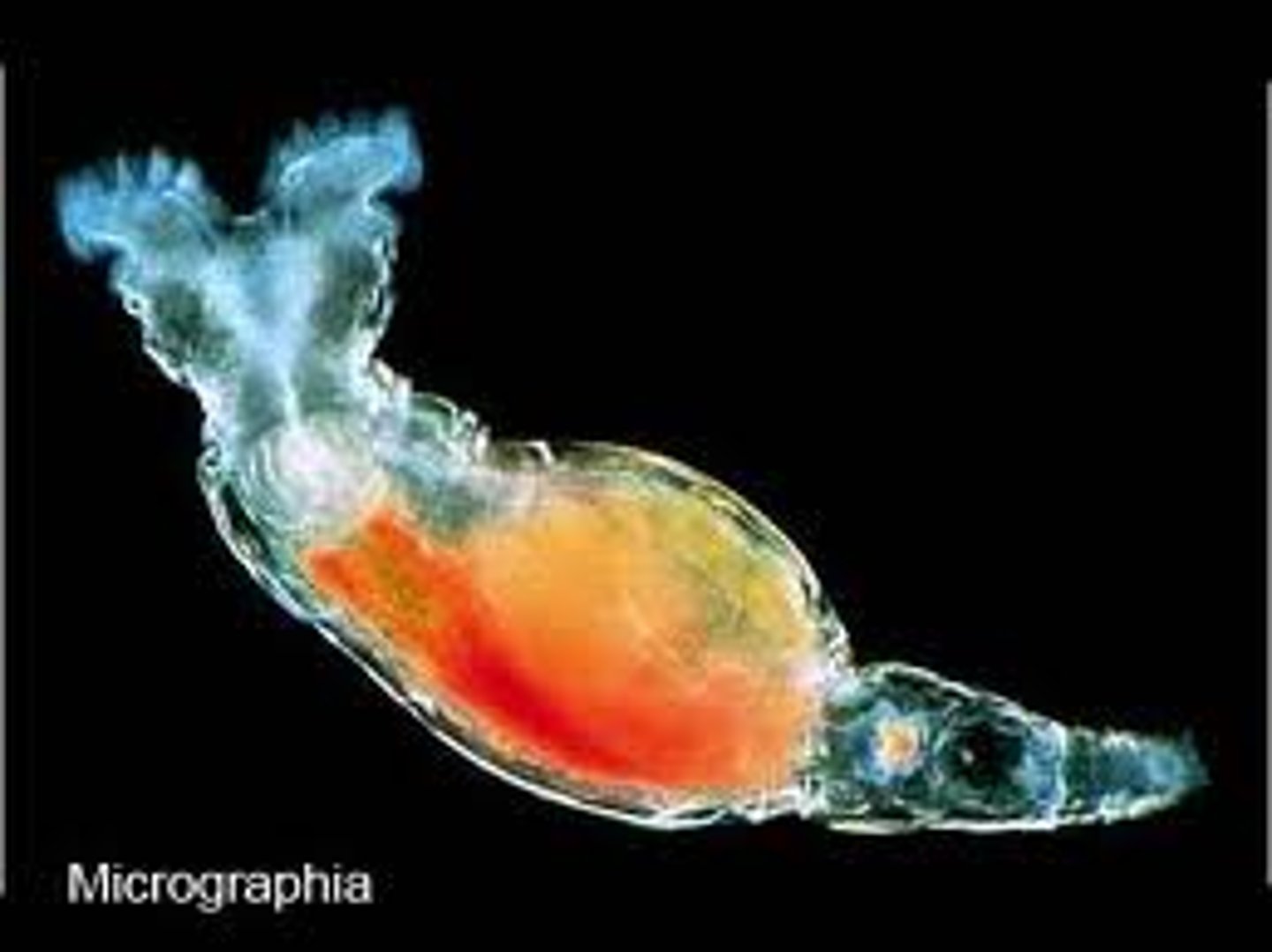
Phylum Rotifera
(Nickname = Wheel Bearers)
Complete digestive tract (two openings); Use "flame cells" as primitive kidneys to remove excess water; Use ring of cilia around mouth "sweep" food into the organism; free living
Phylum Nematoda
(Nickname = Roundworms)
Have a Pseudocoelom; Have a complete digestive system (2 openings: mouth ->anus); Are parasitic (Ascaris, Necator, Trichinella); 1st Phylum discussed with a body cavity...
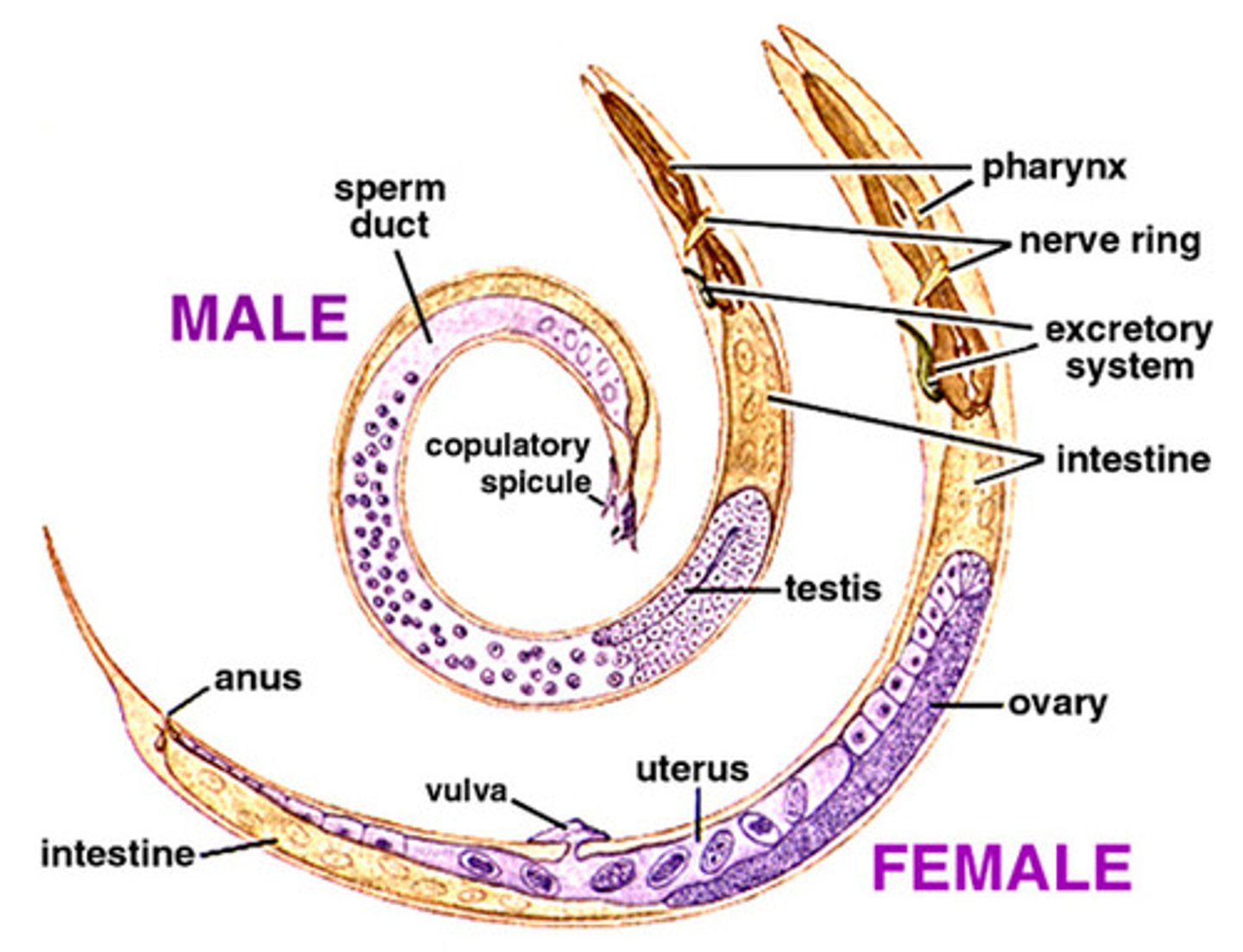
Importance of a body cavity
Fluid in the cavity helps to circulate material; Fluid in the body can make the body rigid, allowing for use of muscles (movement); Organ function improves when there is room to move in a cavity
Tegument
Thick protective layer covering the body of endoparasites; helps to keep them from being digested by their host
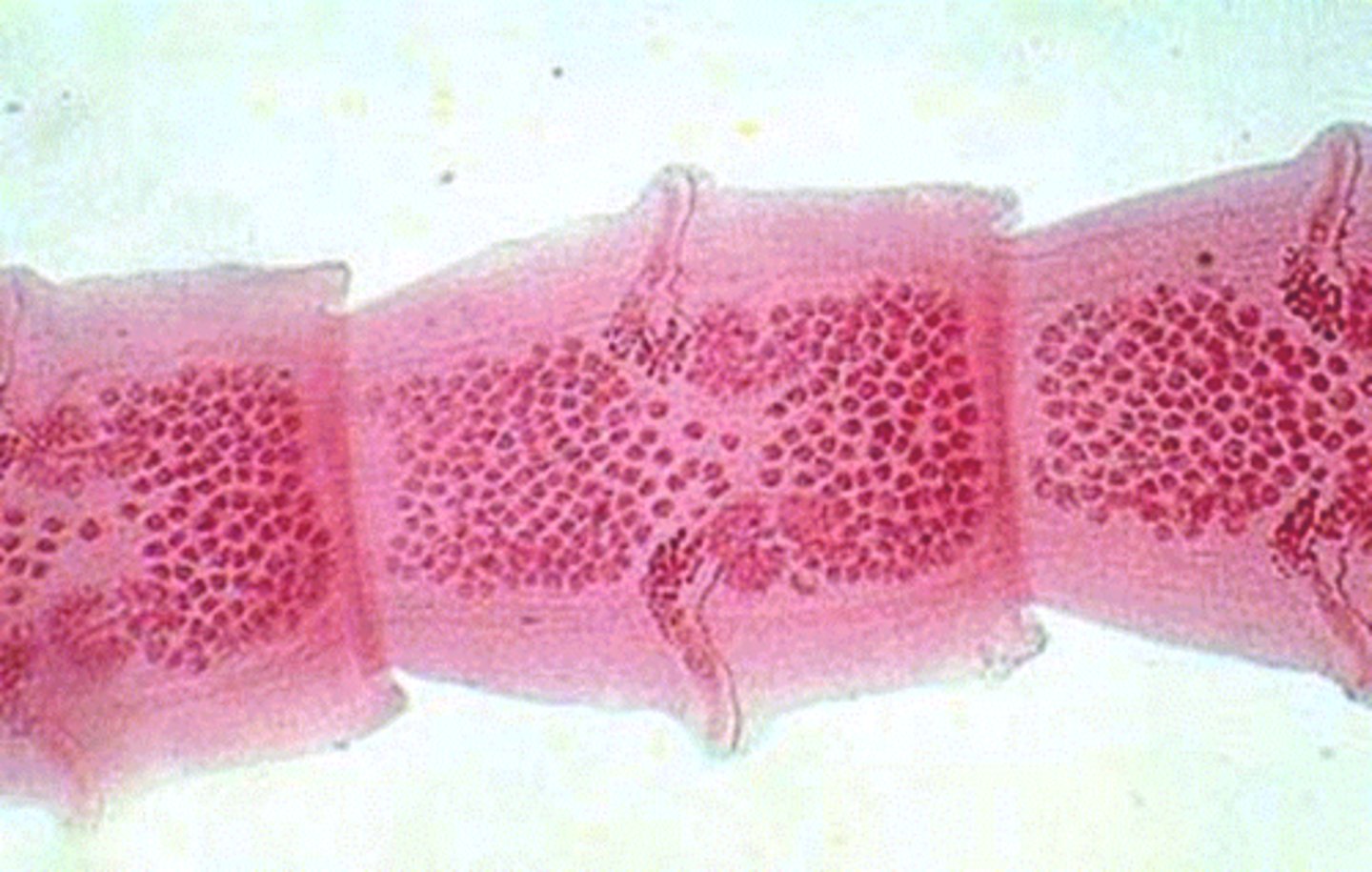
Proglottids
Rectangular sections of a tapeworm; Phylum Platyhelminthes; Class Cestoda
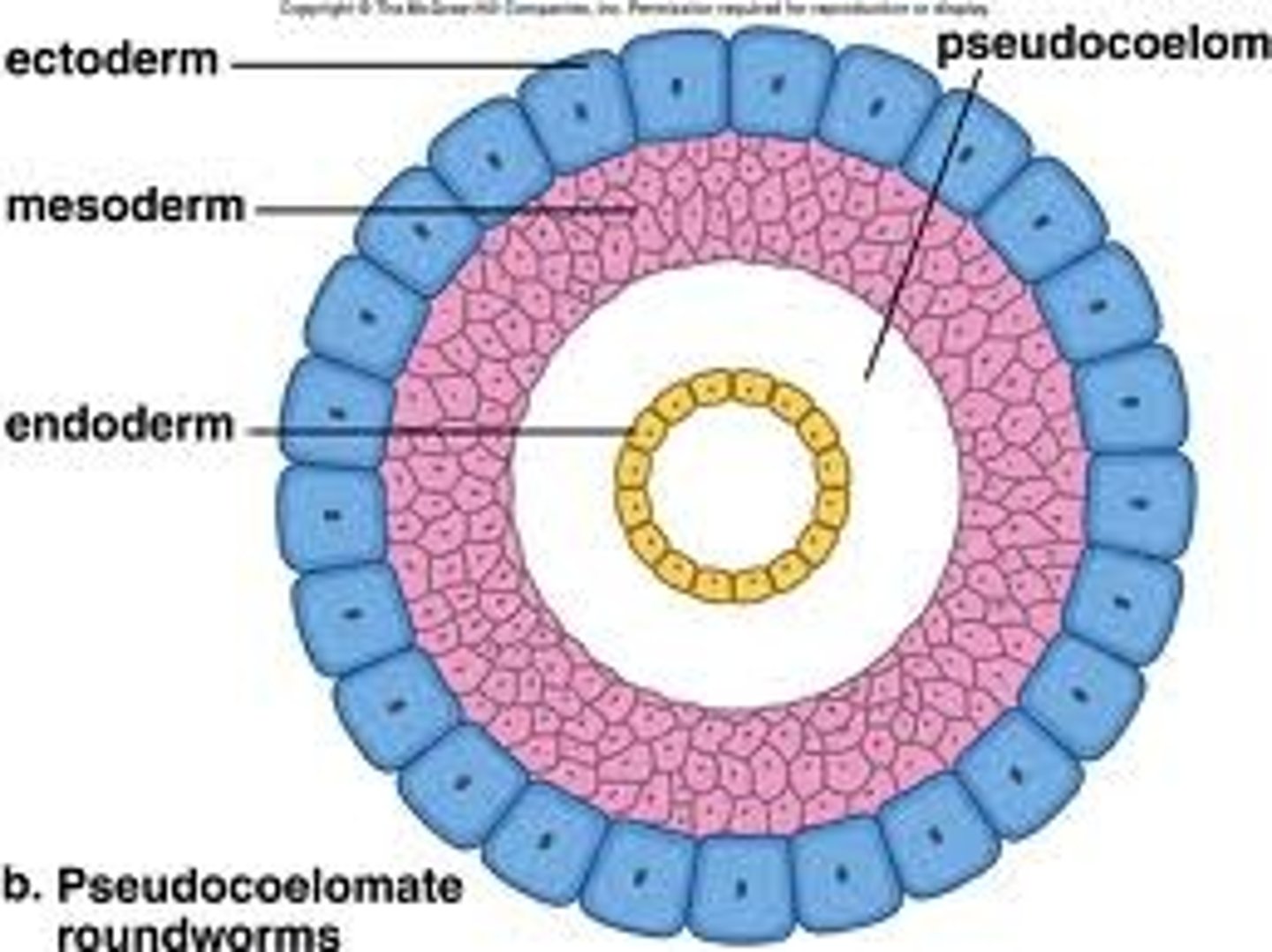
Psuedocoelom
Fluid filled cavity between the gut and the body wall
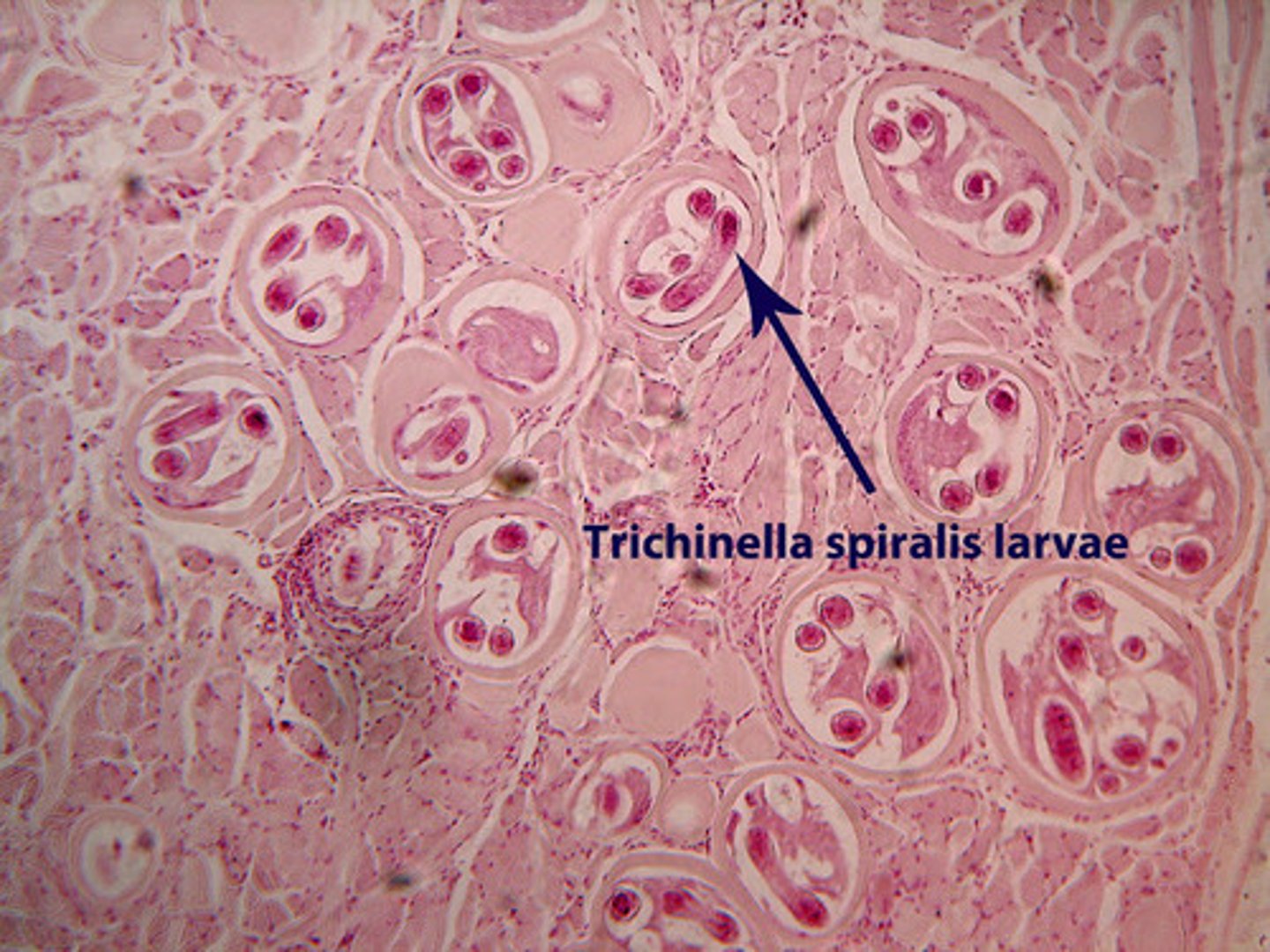
Trichinosis
Infection caused by a roundworm; acquired by eating raw or under-cooked meat
4 Classes of Flatworms
(Phylum Platyhelminthes)
Class Turbellaria (Free living)
Class Trematoda (Parasitic Fluke)
Class Monogenea (Parasitic Fluke)
Class Cestoda (Parasitic Tapeworm)
Examples of parasitic roundworms
Ascaris, Necator, Trichinella