Epithelial Tissues- A&P 1
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
4 tissue types
epithelial, connective tissue, nervous tissue, and muscle tissue
simple
a simple layer
stratisfied
two or more layers
pseudostratisfied
appears to have many layers bc cells are different height and shape. Nuclei appear at different heights
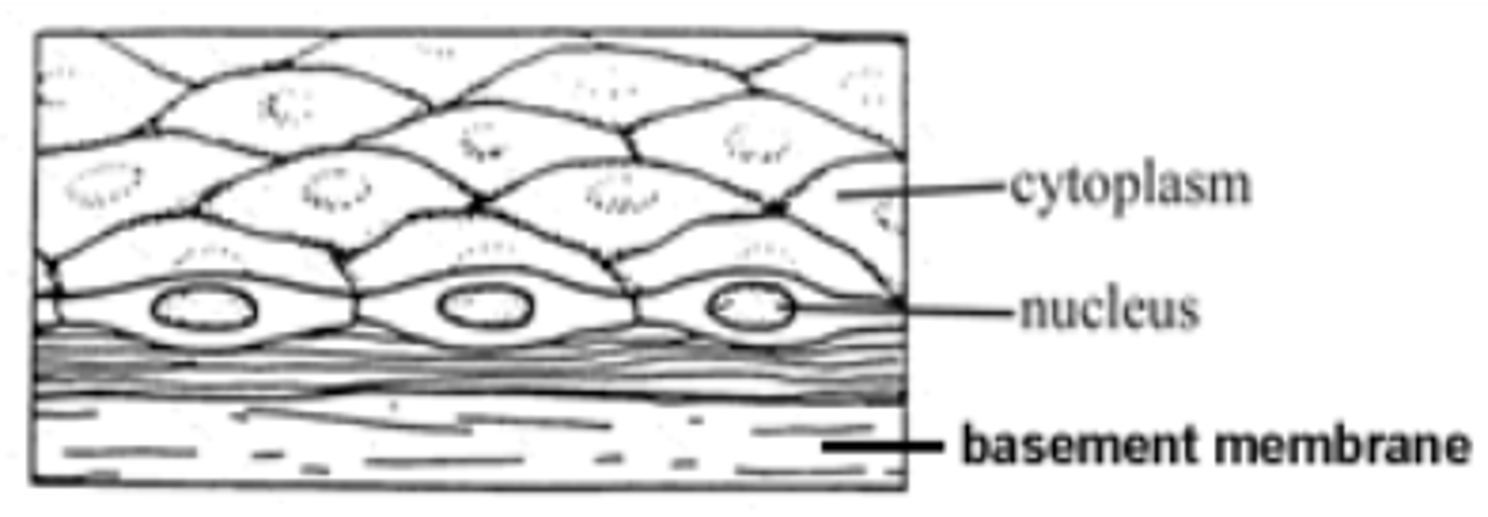
squamous
flat or scalelike cells forming a mosaic pattern
cuboidal
cells appear to be cube-like in cross section
columnar
cells are long and cylindrical like a column
epithelial tissue
covers the body
lines the inside of large body cavities and blood vessls
glandular tissue, made for absorption, excretion, and secretions. ex. sweat
growing on vascular connective tissue
attached to basement membrane
mesothelium
lining internal body cavity
endothelium
lining blood/lymph vessels
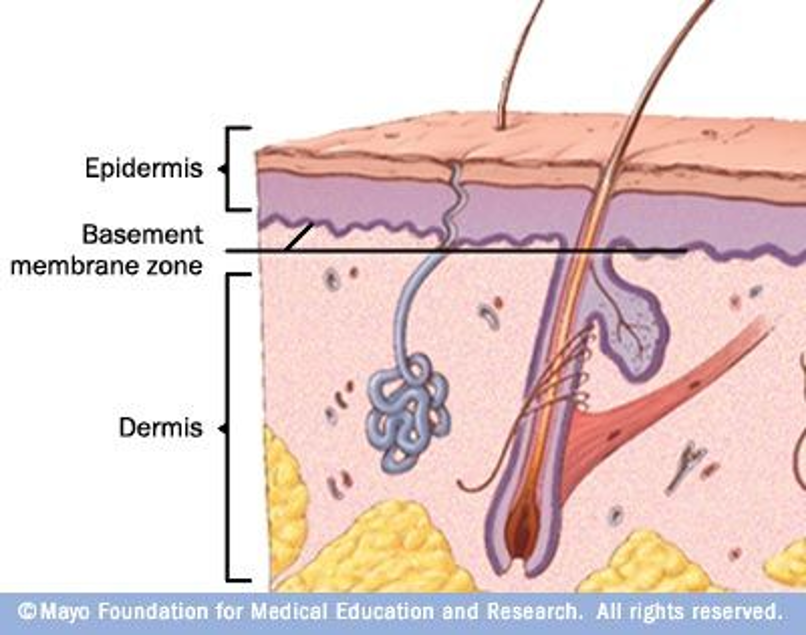
epidermis
keratinized, stratified squamous epithelial cells (usually 4-5 layers)
dermis
connective tissues, blood vessels, oil and sweat glands, nerves, hair follicles
characteristics of epithelial tissue
cells are close together with no intercellular substances
cells reproduce rapidly (rapid healing)
simple squamous function
diffusion and filtration
simple squamous location
lines lungs, kidneys and heart

simple squamous description
single layer of flattened cells, disc shaped nuclei, air sacs in lungs specifically

simple cuboidal function
secretion and absorption
simple cuboidal location
kidney tubules, ducts, ovaries

simple cuboidal description
single layer of cubelike cells with large central spherical nuclei. Lumen in the center of ring it forms in the kidney

simple columnar function
secretion, absorption, protection of underlying tissue

simple columnar location
digestive tract (intestines), uterus

simple columnar description
single layer of tall cells with round to oval nuclei.
some have cilia
may contain goblet cells

pseudostratified columnar function
secretion of mucus and moves it with cilia (mucus elevator)

pseudostratified columnar location
trachea

pseudostratified columnar description
single layer of cells at differing heights, nuclei at different levels, may have goblet cells and cilia

stratified squamous function
protection from abrasions

stratified squamous location
esophagus

stratified squamous description
multi layered, cells are the surface are worn and flat compared to the bottom
keratin formed in older cells

stratified cuboidal function
protection

stratified cuboidal location
sweat, mammary and salivary glands

stratified cuboidal description
two layers of cube like cells, forms a lumen

stratified columnar function
protection, secretion

stratified columnar location
rare, male urethra and parts of the pharynx

stratified columnar description
basal cells cuboidal, surface cells elongated

transitional epithelium function
stretchable, blocks diffusion (no leakage)

transitional epithelium location
bladder

transitional epithelium description
resembles stratified squamous and cuboidal, surface cells dome shaped.

purpose of epithelial tissue
tight fitting seal between cells
sits on nonliving basement membrane with CT under it
avascular, no blood suppy
nutrients diffuse up via CT
regenerates quickly
microvilli
small projections of cell membrane that increase surface area for maximal nutrient absorption.

mucus elevator
cilia moves mucus up and out of the trachea. (pseudostratified columnar)

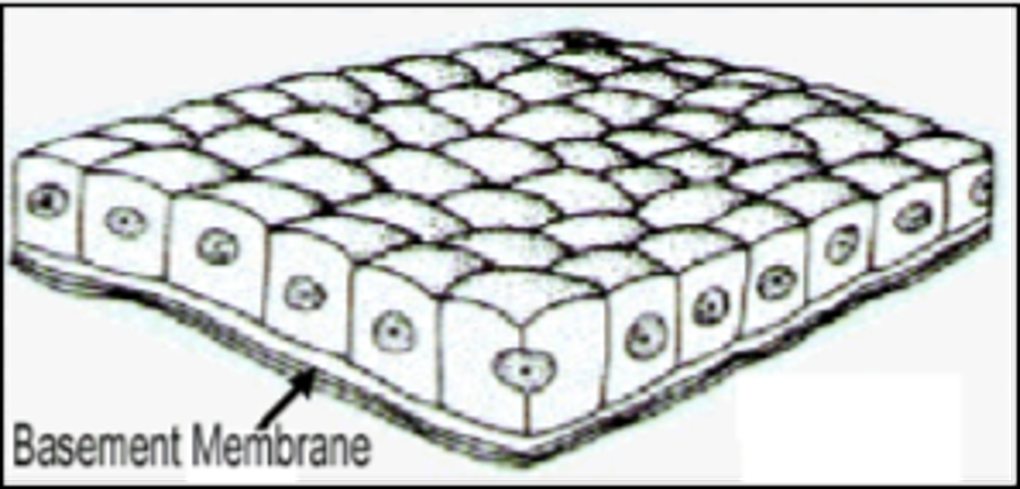
basement membrane
noncellular, nonliving. attached epithelial cells to the dermis. in between epidermis and dermis. made of collagen. CT under it.