World History Final
5.0(1)Studied by 6 people
Card Sorting
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Includes topics such as the French Revolution, Nationalism, Industrial Revolution, Imperialism, and WW1
Last updated 12:50 AM on 6/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
1
New cards
Old Regime
The name for the social structure (the three estates) during the French Revolution
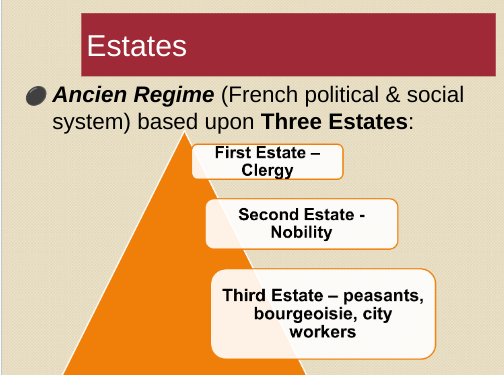
2
New cards
Three Estates
The French political and social system (during French Revolution) which consisted of three social classes, with the top being clergy, middle being nobility, and bottom being peasants, bourgeoisie, and city workers.
3
New cards
Bourgeoisie
Lowest class within the Three Estates whom were heavily taxed by the upper estates even though they were the least wealthy.
4
New cards
sans-culottes
Parisian city workers who wanted more radical change . . . To get rid of monarchy!
5
New cards
King Louis XVI
King of France who put France into heavy debt (for spending a lot of money on military and other things) which upset the citizens of France since they thought he wasn’t a good leader who knew how to spend their money properly. He eventually got executed during the French Revolution when the citizens were upset with monarchy.
6
New cards
Marie Antoinette
Queen of France who was married to King Louis XVI. Nicknamed “Madame Deficit” for her over-spending habits. She essentially “helped put France into debt”. She was eventually executed once citizens turned against monarchy during the French Revolution.
7
New cards
Maximilien Robespierre
Lead the Jacobins (radical revolutionaries) and held a lot of power during the reign of power which was a period of time during the French Revolution, following the creation of the First Republic.
8
New cards
Reign of Terror
Robespierre held power after monarchy was taken down during French Rev. The goal during this time was to create a new society based in civic virtue and they killed any opposition or criticism of the new FR gov’t. They used violence to achieve goals.
9
New cards
Napoleon
Was a great military general of France, who eventually became first consul after monarchy was destroyed during French Rev. The citizens of France overwhelmingly supported his decisions which lead to him gaining much political power. He eventually became emperor of France, invented the Napoleonic Code, and tried to take over all of Europe through military force.
10
New cards
Napoleonic Code
A code invented by Napoleon which defined French laws. Positives: criminal & civil code codified, class privileges abolished, all men equal under the law, and religious freedom
Negatives: Women subservient to fathers & husbands (no property owning rights, no rights to children in divorce)
Slavery reintroduced in the colonies (led to revolution in Haiti)
Negatives: Women subservient to fathers & husbands (no property owning rights, no rights to children in divorce)
Slavery reintroduced in the colonies (led to revolution in Haiti)
11
New cards
Economic causes of French Revolution:
* Government Debt caused by monarchy
* Third estate was heavily taxed while other estates weren’t (wanted tax reform)
* Poor harvest in 1788- led to famine
* Third estate was heavily taxed while other estates weren’t (wanted tax reform)
* Poor harvest in 1788- led to famine
12
New cards
Social causes of French Revolution:
* Bourgeoisie were educated from enlightenment and wanted to implement those ideals
* Lower class wanted equality, liberty, reason
* Lower class wanted equality, liberty, reason
13
New cards
Political causes of French Revolution:
* Bourgeoisie wanted political power
* Citizens were upset with Monarchical government/decisions
* Citizens were upset with Monarchical government/decisions
14
New cards
Tennis Court Oath
3rd Estate, along with a few members of clergy and noblemen, pledged themselves to goal of creating a constitution (limited gov’t!!!) for France.
15
New cards
Storming of the Bastille:
Marks the start of French Rev. People broke into prison to arm themselves for the French revolution.
16
New cards
Declaration of the Rights of Man:
goals/purpose of French Rev. Used ideals from the Enlightenment such as freedom and equality. Also valued “Liberty, equality & fraternity”
17
New cards
Napoleon’s weaknesses:
People were against French rule and did not want to be taken over by France so everyone was against them and they had essentially no allies.
18
New cards
Ways Napoleon promoted French Revolution:
* promoted public education
* created fairer tax laws
* ended serfdom
* created uniform code of law
* religious toleration
* created fairer tax laws
* ended serfdom
* created uniform code of law
* religious toleration
19
New cards
Long lasting affects of French Revolution:
Liberalism: (comes from enlightenment ideals) and purpose was to reform society and give people more rights and freedoms after revolution
Nationalism: people felt more nationalistic for their own countries since they didn’t want to be taken over by Napoleon/French reign.
Nationalism: people felt more nationalistic for their own countries since they didn’t want to be taken over by Napoleon/French reign.
20
New cards
Klemens von Metternich
The King of Austria and the most influential member within the Congress of Vienna. He highly distrusted the democratic ideals of the French Revolution. He wanted to undo liberal ideals.
21
New cards
balance of power
The checking of power so that not one singular country could become a threat/more powerful than the others. This made it impossible for any country to overthrow another without consequences.
22
New cards
legitimacy
If rulers were driven from their throne (by Napoleon during the French Rev) they were entitled to having their power restored after the fact. This was done in hopes that the former monarchs would stabilize political relations among nations. This concept fell on the conservative (traditional) spectrum.
23
New cards
Conservatism
Goals were to preserve traditional ways of doing things and to keep order and stability. Was popular among upper classes. Fought against the ideas of the Enlightenment.
24
New cards
liberalism
Stressed individual freedom, equality, and the belief of progress (that society could improve through reforms). The ideology came from the Enlightenment. Was popular among the rising middle class.
25
New cards
nationalism
Strong feelings of patriotism for a homeland. Usually connected by a common religion, set of traditions, history, or values. Many people began urging for self determination, for example independence & self rule. It can either work to unify people or divide them (ex. it can create a us vs. them mentality). It fueled efforts to build nation-states. Nationalists were loyal to the people, not a king usually. Nationalism could be expressed through either conservative or liberal ideas, it was not just one or the other.
26
New cards
radicalism
Stressed liberty and equality. Grew from ideas from the Enlightenment period and the radical phase of the French Revolution (during the time of the National Convention). Popular among industrial workers (lower class).
27
New cards
Schleswig & Holstein
Two areas that were gained after Prussia and Austria formed an alliance in 1864 and attacked Denmark and took over Schleswig and Holstein. Prussia and Austria however had trouble deciding who would take ownership of which area.
28
New cards
Alsace & Lorraine
In 1871 after the Franco-Prussian War, peace with France helps them gain reparations and these border provinces.
29
New cards
Russification
Forcing all ethnically diverse people within the Russian Empire to stip themselves of one’s ethnic culture so that they can all have a unified singular culture within Russia. (Forced Russian culture on all ethnic groups)
30
New cards
Hapsburgs
The ruling family of Austria; they came from German descent.
31
New cards
Romanovs
the ruling family of the Russian Empire.
32
New cards
Pogrom
An organized massacre of a particular ethnic group; created to achieve unity within the Russian Empire. State orchestrated attacks on Jewish people within Russia because of their difference in culture.
33
New cards
Congress of Vienna
A group of main European heads of government (the main four being Czar Alexander 1st from Russia, King William III from Prussia, Klemens von Metternich from Austria, and Castlereagh from Great Britan; France was technically also a main power within the Congress of Vienna as well, but it was not as included as the others since it had great power due to the French Revolution) that had ==a goal of maintaining long lasting peace and stability within Europe after the defeat of Napoleon. This group maintained peace by balancing one another’s power so that not one in particular could become more powerful than the others.== ==They also strived to regain control and return to monarchical governments, previous to the French Revolution reforms. Essentially, trying to return to conservative ideas.==
34
New cards
How nationalism both created and destroyed nations:
Created: Brought people with commonalities (ex. religion, culture, ethnicity, etc) together in unification
Destroyed: Caused people who were unalike to essentially ‘segregate’ from one another and became extremely divided. Example: Pogroms were organized in Russia to attack Jewish people due to their difference in culture.
Destroyed: Caused people who were unalike to essentially ‘segregate’ from one another and became extremely divided. Example: Pogroms were organized in Russia to attack Jewish people due to their difference in culture.
35
New cards
Otto von Bismark
Bismark became prime minister of Prussia under the rule of William I in 1862. Bismark was a junker and a realpolitik (meaning he had many conservative ideals). He declared himself (with the king’s approval) able to rule without the consent of parliament, going against Prussia’s constitution at the time. Bismark started a lot of wars for Prussia against many other countries at the time (Franco-Prussian War, Seven Weeks war).
36
New cards
Realpolitik
The politics of reality; used to describe tough power politics with no room for ideals, basically desiring results without the consideration of ethics. (Ex. Bismark was a Realpolitik)
37
New cards
German Wars of Unification:
\
Denmark
* PR & AUS declared war v. Denmark over Danish claims to provinces of Schleswig & Holstein
* Denmark easily defeated; AUS & PR disagreed over governance of Schleswig & Holstein
* Seven Weeks War v. Austria, 1866
* PR defeated AUS
* Formed North German Confederation
* Cementing PR dominance of German peoples
Denmark
* PR & AUS declared war v. Denmark over Danish claims to provinces of Schleswig & Holstein
* Denmark easily defeated; AUS & PR disagreed over governance of Schleswig & Holstein
* Seven Weeks War v. Austria, 1866
* PR defeated AUS
* Formed North German Confederation
* Cementing PR dominance of German peoples
38
New cards
Camillo di Cavour
In 1852, he became prime minister of Italy and worked to expand Piedmont-Sardinia’s (a large Italian State’s) power. In 1858, Napoleon III agreed to help Cavour drive Austria out of Northern Italy, together they easily took over all of Italy with Napoleon III’s help with just 2 battles. Cavour was a crucial part of uniting Italy.
39
New cards
Giuseppe Garibaldi
In 1860, a small army of Italian Nationalists (the red shirts) led by soldier, Giuseppe Garibaldi, captured Sicily. Garibaldi agreed to unite the Southern areas of Italy and soon took over Piedmont-Sardinia, he however allowed king Victor Emanuel II to rule in March 1861, stepping down from his leadership. He helped unite Italy.
40
New cards
Laissez Faire
‘Hands off’ government!
41
New cards
urbanization
People moving in large masses from rural areas to cities.
42
New cards
Proletariat
member of the working class
43
New cards
Labor unions
Worked to change..
* Length of workday
* Wages Health & safety concerns
* Benefits / compensation
* Child labor
* Length of workday
* Wages Health & safety concerns
* Benefits / compensation
* Child labor
44
New cards
Socialism
collective or governmental ownership and administration of the means of production and equal distribution of goods/wealth
45
New cards
Suffrage
the right to vote
46
New cards
Agricultural Revolution
Advances in agricultural technology caused there to be a food surplus which also caused the British population to improve
47
New cards
Why did the Industrial Revolution start in Great Britain?
Because they had access to…
1\. Labor force
2\. Natural resources – i.e. coal & iron ore, rivers, harbor, plus colonies!
3\. Investment capital (growth of middle class entrepreneurs)
4\. Markets – empire & increased demand
5\. Gov’t support & stability
1\. Labor force
2\. Natural resources – i.e. coal & iron ore, rivers, harbor, plus colonies!
3\. Investment capital (growth of middle class entrepreneurs)
4\. Markets – empire & increased demand
5\. Gov’t support & stability
48
New cards
Wealth of Nations by Adam Smith
valued capitalism, private ownership, competition, profit, and free market.
49
New cards
Principle of Population by Thomas Malthus
expressed the idea that people should stop helping the poor (since they should reduce the poor population) and wanted to stop feeding the poor.
50
New cards
Jeremy Bentham and Utilitarianism
Emphasized greatest good for the greatest number
51
New cards
Robert Owen
Created Industrial Empire (good Capitalist) and set a standard that you could make a profit while still treating workers humanely
52
New cards
Emmeline Pankhurst
Women’s Social and Political Union (WSPU) leader, fought for women’s suffrage (right to vote for women)
53
New cards
Charles Darwin On the Origin Of Species
Created the theory of evolution and natural selection (species that have most adapted to their environment survive or “Survival of the fittest”)
54
New cards
Communist Manifesto by Karl Marx
Went against capitalism, and rather than reforming the capitalist system, wanted to overthrow it. It also created the idea of Communism which was a **form of complete socialism in which all property and means of production were owned by the people & shared equally.**
55
New cards
Goal of Communism
to overthrow capitalism and instead share all property and means of production equally by the people in society. It was an extreme form of socialism.
56
New cards
Louis Pasteur
\
discovered bacteria in fermentation process, which led him to discover that heat could kill germs (pasteurization process) (GERM THEORY OF DISEASE)
discovered bacteria in fermentation process, which led him to discover that heat could kill germs (pasteurization process) (GERM THEORY OF DISEASE)
57
New cards
Joseph Lister
encouraged sterilization of surgical wards to prevent bacteria growth & disease (GERM THEORY OF DISEASE)
58
New cards
Henry Ford
Came up with system of interchangeable parts & cars were built on an assembly line , this allowed things (such as cars) to be produced faster and cheaper.
59
New cards
Wright Brothers
invented the airplane
60
New cards
Marie Curie
discovered that some atoms release powerful charges and that atoms are not solid, but instead they can be divided (RADIOACTIVITY)
61
New cards
Alexander Graham Bell
inventor of the telephone
62
New cards
Thomas Edison
inventor of the light bulb
63
New cards
Sigmund Freud
Inventor of “Talk Therapy”
* pioneered a new social science, psychology
* Maintained that the human subconscious is active on our conscious mind
* Studied the dream world & the subconscious fears, desires of individuals
* pioneered a new social science, psychology
* Maintained that the human subconscious is active on our conscious mind
* Studied the dream world & the subconscious fears, desires of individuals
64
New cards
Working and living conditions impacted by industrialization:
Things and technology became cheaper/more accessible, machines started taking over the jobs of humans
65
New cards
Social Darwinism
* Westerners applied Charles Darwin’s ideas about natural selection & survival of the fittest to society
* Social Darwinists claimed white, European racial superiority
* Social Darwinists claimed white, European racial superiority
66
New cards
Hindus
people who follow the religious belief of Hinduism (note that they view certain forms of meat as sacred)
67
New cards
Muslims
followers of Islam (note that they view pork as a forbidden food/sacred)
68
New cards
Economic Dependence
Colonies had little economic independence from their mother countries and had no choice but to depend on their mother country for the economy.
69
New cards
geopolitics
politics, especially international relations, as influenced by geographical factors.
70
New cards
colony
a land controlled by another nations
71
New cards
protectorate
Local rulers left in place with the understanding that they would defer to mother country in foreign affairs & economy
* Did not require as much military & financial commitment
* Did not require as much military & financial commitment
72
New cards
Direct vs Indirect Rule
\
* **Direct Rule (French model) – all ruling officials from France; imposed French culture in colonies; essentially wanted to create French provinces of area**
* **Indirect Rule (British model) – created ruling class within colony by using locals to govern & educating these elite in England**
* **Direct Rule (French model) – all ruling officials from France; imposed French culture in colonies; essentially wanted to create French provinces of area**
* **Indirect Rule (British model) – created ruling class within colony by using locals to govern & educating these elite in England**
73
New cards
Sphere of Influence
* An area in which an outside power claimed exclusive investment and/or trading privileges
* Ex. Open Door Policy in China (Europeans & Americans in China)
* Monroe Doctrine & Roosevelt Corollary (U.S. in Latin America)
* Ex. Open Door Policy in China (Europeans & Americans in China)
* Monroe Doctrine & Roosevelt Corollary (U.S. in Latin America)
74
New cards
Causes of Imperialism
EMPIRES
__**E**__**xploratory** - Industrial Revolution enabled Europeans to travel to places previously unreachable
__**M**__**ilitary Interests**
* Needed naval bases around world
* National security & prestige of possessing colonies
__**P**__**olitical**
* Nationalism encouraged quest for empire
* Balance of power issue – competing with rival nation states
__**I**__**deological** - desire to spread western values (philosophies, habits, laws, values)
* “civilizing” mission - referred to as “the White Man’s Burden”
__**R**__**eligious -** spread Christianity
__**E**__**conomic Interests**
* Industrial Revolution created need for resources & markets and also stimulated venture capital to fund missions
* Industrial Revolution also empowered & enabled Europeans to conquest parts of the globe previously unreachable (new weapons, medicines & forms of transportation)
__**S**__**ocial Darwinism**
* Westerners applied Charles Darwin’s ideas about natural selection & survival of the fittest to society
* Social Darwinists claimed white, European racial superiority
__**E**__**xploratory** - Industrial Revolution enabled Europeans to travel to places previously unreachable
__**M**__**ilitary Interests**
* Needed naval bases around world
* National security & prestige of possessing colonies
__**P**__**olitical**
* Nationalism encouraged quest for empire
* Balance of power issue – competing with rival nation states
__**I**__**deological** - desire to spread western values (philosophies, habits, laws, values)
* “civilizing” mission - referred to as “the White Man’s Burden”
__**R**__**eligious -** spread Christianity
__**E**__**conomic Interests**
* Industrial Revolution created need for resources & markets and also stimulated venture capital to fund missions
* Industrial Revolution also empowered & enabled Europeans to conquest parts of the globe previously unreachable (new weapons, medicines & forms of transportation)
__**S**__**ocial Darwinism**
* Westerners applied Charles Darwin’s ideas about natural selection & survival of the fittest to society
* Social Darwinists claimed white, European racial superiority
75
New cards
Sepoy Rebellion
Sepoys (Indian soldiers employed by the British East Indian Company) were upset that their gun cartridges were greased with animal fat (since they needed to bite the cartridges) and it went against their religious beliefs (since India consisted predominately of Hindus and Muslims who viewed pork and beef as sacred)
76
New cards
Indian National Congress & Muslim League
organizations that protested for the rights against British rule, they tried to gain independence for India
77
New cards
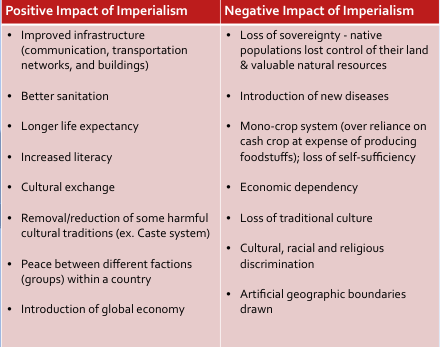
Positives and Negatives of Imperialism
78
New cards
arms race
**military build up among great powers that increased tension**
79
New cards
Kaiser Wilhelm II
German ruler during WW1
80
New cards
Militarism\*
War was looked at as a ‘good thing’ where men would go and prove themselves. It gave people and eagerness to go to war.
81
New cards
Causes of WW1
MANIA
**Militarism- War was looked at as a ‘good thing’ where men would go and prove themselves. It gave people and eagerness to go to war.**
**Alliance Systems- Alliance system reinforced feelings of anxiety, fear & distrust; “us v. them” mentality**
**Nationalism- France bitter about their loss to Germany in the Franco-Prussian War; Balkan Peninsula saw surge of nationalism in the wake of the decline of old empires (Hapsburgs & Ottomans)**
**Imperialism / Rivalries-** Competition for the largest, wealthiest empires fueled tension and conflict, deepening rivalries
**A**ssasination (immediate spark)- Serbia dissatisfied over the fact that Austria-Hungary controlled Bosnia, where many ethnic Serbs lived
* Bosnians, supported by the Serbian terrorist group known as **Black Hand,** plotted death of **Archduke Franz Ferdinand** (heir to AH throne)
* June 28, 1914 **Gavrilo Princip** shot Franz Ferdinand & wife Sophie while they were visiting Sarajevo (capital of Bosnia)
**Militarism- War was looked at as a ‘good thing’ where men would go and prove themselves. It gave people and eagerness to go to war.**
**Alliance Systems- Alliance system reinforced feelings of anxiety, fear & distrust; “us v. them” mentality**
**Nationalism- France bitter about their loss to Germany in the Franco-Prussian War; Balkan Peninsula saw surge of nationalism in the wake of the decline of old empires (Hapsburgs & Ottomans)**
**Imperialism / Rivalries-** Competition for the largest, wealthiest empires fueled tension and conflict, deepening rivalries
**A**ssasination (immediate spark)- Serbia dissatisfied over the fact that Austria-Hungary controlled Bosnia, where many ethnic Serbs lived
* Bosnians, supported by the Serbian terrorist group known as **Black Hand,** plotted death of **Archduke Franz Ferdinand** (heir to AH throne)
* June 28, 1914 **Gavrilo Princip** shot Franz Ferdinand & wife Sophie while they were visiting Sarajevo (capital of Bosnia)
82
New cards
Stalemate
no progress in war from either side
83
New cards
total war
everyone is involved in war, even citizens
84
New cards
armistice
the agreement to stop fighting (not a surrender)
85
New cards
14 Points
Peace Keeping Organization (League of Nations) and particularly emphasized points by Woodrow Wilson were, Freedom of the Seas, Free trade, self determination, no secret treaties, and demilitarization/arm reduction
86
New cards
Paris Peace Conference
A meeting of all the Nations who fought in WW1 after WW1 which tried to make amends after the war
87
New cards
Impact of new technology in WW1
Deadlier weapons= more deaths
88
New cards
Trench Warfare Impacts
* Shell Shock
* Unsanitary environment
* Rats
* Cold and wet
* dead bodies everywhere
* Unsanitary environment
* Rats
* Cold and wet
* dead bodies everywhere
89
New cards
Reasons for American involvement in WW1
Unrestricted submarine Warfare:
* Germany used submarines to attack cargo ships which happened to host American citizens, this angered the U.S.
Zimmerman Note:
* German minister (Zimmerman) wrote to Mexico that they would help them gain territory back from the U.S. if they helped them in WW1, this was intercepted by the U.S. which further angered them.
* Germany used submarines to attack cargo ships which happened to host American citizens, this angered the U.S.
Zimmerman Note:
* German minister (Zimmerman) wrote to Mexico that they would help them gain territory back from the U.S. if they helped them in WW1, this was intercepted by the U.S. which further angered them.
90
New cards
Treaty of Brest Litovsk
Treaty that ended Russian involvement in WW1 (they ended before their allies)
91
New cards
Geographic changes in Europe after WW1
* gain of new smaller countries
* Large countries lost land
* Large countries lost land
92
New cards
Peace conditions/punishments for Germany (article 231)
They humiliated Germans by blaming WW1 entirely on them.
* GER lost territory and colonial possessions, reparations, war guilt, and military reduction
* GER lost territory and colonial possessions, reparations, war guilt, and military reduction
93
New cards
Map
Identify the following places, France, Great Britain, Germany, Belgium, Italy, Denmark, Austria, Hungary, Serbia, Bosnia, Greece, Russia, Turkey, Egypt, Morocco, South Africa, Tanzania, Somalia, India, China, Vietnam, Philippines.