Caring for the neonate
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
history of breastfeeding
Newborns and mothers have natural reflexes at birth.
Most cultures breastfed for 2–3 years.
Alternatives emerged: substitute milk, wet nursing, then formula.
Breastfeeding is rising again.
In developed countries, mothers who are older, more educated, and higher SES are more likely to breastfeed.
Benefits of breast-feeding
• Physical and cognitive well-being
• No evidence of emotional or social relationship benefits
• WHO recommends breast-feeding for 2 years
•Especially important in developing countries
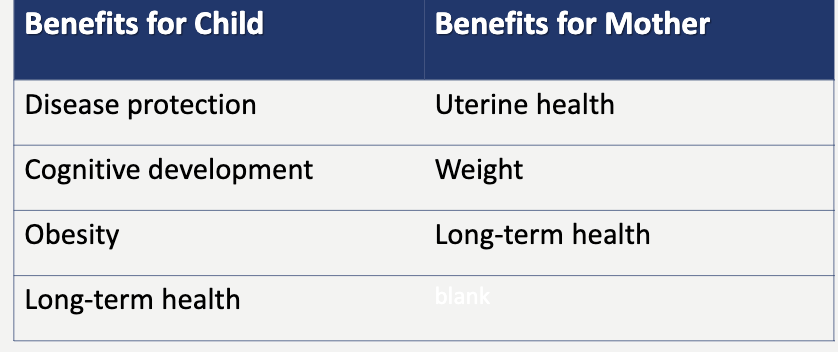
benefits of breast feeding for child and mother
Obstacles to breast feeding
Some women have difficulty
• Employment
• Harder for fathers to feed
• Infectious diseases
transmitted by mother
• Marketing claims by formula
makers
crying
Crying
• Three distinct crying signals
•Fussing: soft volume, unsteady whimper
•Anger: large volume of air
•Pain: sudden onset
• Also classified as basic if no distinctive cry is noted
• Crying curve relates to crying frequency
soothing
Soothing and Responding To Cries
• Variation in duration and intensity of crying
• Swaddling babies has been shown to reduce crying
• Ten percent of Western babies are colicky with no known cause
• Soothing includes lifting baby to the shoulder, soothing repetitive
movements, soothing sounds, distraction
• Common theme is new source of stimulation
swaddling

bonding myth and truth
Mother-Infant Bonding
• No support that first hour is critical for bonding in
mother and infant
•Imprinting identified in birds, not humans
• Hospitals now encourage close contact
immediately after birth
postpartum depression
In some cases, birth can cause postpartum depression
•Combination of hormonal changes and deep feelings of anxiety,
sadness, and difficulty sleeping
• Increased risk if previous episodes of depression
• May impact child development
challenges
Low socioeconomic status or poverty
– Access to basic needs (food, shelter, health care)
– Stability
– Support (family)
– Stress
– Education
– At both family level and community level
• Rural vs. urban poverty
Affluence
– Support (family)
– Stress
– Leisure time and financial means
supports
• Family and extended family
• Family rituals – such as family dinner time
• Access to clean water and food
• Good health care system
and puppies!