FNR 331 exam 1
1/159
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
160 Terms
Although it wasn't formally recognized a field of science until the ________, understanding the basic tenants of Ecology was critical to early humans.
20th century
Okios means
house
logos means
study of
most major advances of ecology have happened in the last ______
70 yrs (recognized for 60)
ecology is often used as a synonym for
Environmentalism
ecology came of age in the
1960's
ecology
The branch of biological science concerned with the distribution, abundance, and productivity of living organisms and their interactions with each other and with their physical environment
Level 1
cell
level 2
tissue
level 3
organ
level 4
organ system
level 5
organism
level 6
population
level 7
community
level 8
ecosystem
level 9
biosphere
what is an ecosystem?
a functional system that includes an assemblage of interacting organisms and their environment which acts upon them and on which they act
what are the 5 major attributes of an ecosystem?
Structure, function, complexity, interactions and interdependence, temporal change.
Structure:
an ecosystem is composed of biotic and abiotic subsomponents
Function (processes):
within ecosystems there is a constant exchange of matter and energy between the physical environment and the biotic community and within the biotic community
Complexity:
high degree of integration; events and conditions are multiply determined; prediction of change or events difficult
there are only ___ true levels of biological integration:
3; cells, individuals and ecosystems
interactions and interdependence:
large changes in one component may have cascading effects on other components
led to early view of ecosystems/communities as a 'super organism'
temporal change:
ecosystems are not static
the structure and function of ecosystems change through time
Ecosystem change:
ecological succession: process of change after disturbance
mechanisms of successional change
autogenic
allogenic
biogenic
autogenic mechanisms
changes that are caused by the plants that participate in succession. (light, water, nutrients)
allogenic mechanisms
initiated from outside systems; do not initiate from within and are not related to the plant community (fire, wind, climate change)
biogenic mechanisms
biotic organism; include insect epidemics, diseases and the invasion of nonnative (exotic) species.
trophic:
who is eating who, levels
food chains or trophic chains:
who eats who, energy transfer
trophic webs:
chains together to for a web
what are the two type of trophic chains:
grazing and detrital
Grazing:
autotrophs->herbivores->carnivores
detrital:
commences with dead organic matter and involves saprotrophs
who came up with the term food web?
charles elton
ecological pyramids were developed to
provide a simple representation of trophic function and structure
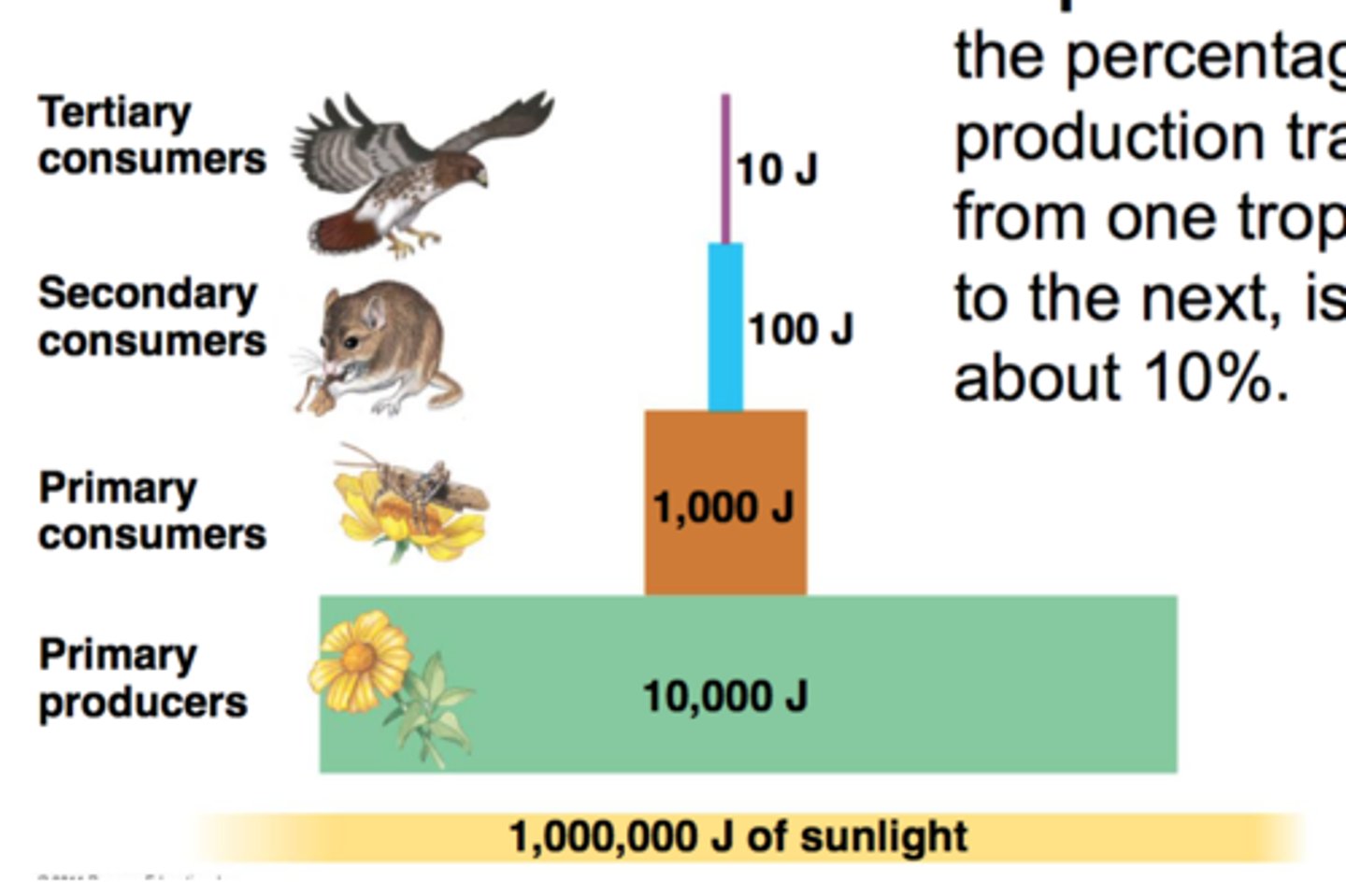
biomass:
total weight of organic material in a population or other given unit
productivity:
production of biomass per unit area per unit time
Alfred J. Lotka
first to consider populations, communities and ecosystems as energy-transforming systems
suggested that an ecological system can be describes by a set of equations that represent exchanges of matter and energy among its components
Eugene P. Odum
strong proponent of ecosystem ecology where the cycling of matter and associated passage of energy through an ecosystem provides a basis for characterizing the systems structure and function
ecosystems can be described based on _______
Energetics
energy is lost with
each transfer from one trophic level to the next
energy is lost as heat
infrared radiation
second law of thermodynamics:
energy systems have a tendency to increase their entropy rather than decrease it through time
trophic efficiency definition:
the ratio of net productivity in one trophic level to the nest production in the previous trophic level
primary production:
organisms that produce their own energy
Net Primary Productivity (NPP):
amount of energy minus the loss in respiration
primary production varies with _____ ______
available nutrients
Aboveground Primary Productivity
increases to a peak at intermediate stand ages, then declines
aboveground biomass
in many forests, constitutes the largest reservoir of biomass
belowground biomass
in many forests, constitutes a much greater annual turnover of organic matter and energy
many species of plants will allocate more primary production to roots on more ______
xeric and nutrient poor sites.
assimilation efficiency
the ratio of assimilation (energy intake) to ingestion
eventually all biomass from other trophic levels ends up in the _____ _____
detritus chain
fungi dominate decomposition in _____ forests
coniferous
bacteria dominate decomposition ______ forests
deciduous
geochemical cycle
chemical cycling between systems
Biogeochemical cycle:
cycling chemicals within the ecosystem
biochemical cycle:
cycling of chemicals within individual organisms
in the geochemical cycle, chemicals move via ___
two pathways the gaseous and sedimentary cycle. (nutrients removed from ecosystem typically do not return)
the gaseous cycle:
predominate form of entry into an ecosystem for N, C, and O. sulfur also cycle as a gas
what causes acid rain?
nitrogen and sulfur oxides
tempurature inversion
a deviation from the normal temperature distribution in the atmosphere, resulting in a layer of cold air temporarily trapped near the ground in a warmer, upper layer
where does air pollution come from?
Nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide emissions
Natural Factors that Predispose Forests to Pollution Effects
•High pressure and frequent air stagnation events;
•Sunlight and heat that increases chemical reactivity;
•Elevation and topography, higher winds, more clouds;
•Rainfall and humidity which enhances deposition & haze;
•Organic emissions from trees (isoprene);
•Low buffering capacity in streams & acid soils
all chemicals are part of _____ cycles
sedimentary
There are three basic mechanisms involved in the movement of material in the sedimentary cycle:
meteorological, biological, geological/hydrological
Meteorological mechanism
inputs from dust and precipitation and outputs result of wind erosion and transportation
Biological mechanisms
Redistribution of nutrients via animal movement or migration
Geological/hydrological mechanisms
•Inputs via chemical weathering of rock and soil or dissolved nutrients moving into the ecosystem in soil water or stream water
The major input of nutrients in many systems is the ____ ____ of weathering erosion and soil solution movement
geological process
hydrologic studies:
•Measure or estimate quantity of nutrients entering the system by meteorological and biological process
•Measure the quantity of nutrients leaving the system in stream water
•The difference is an estimate of weathering input.
biogeochemical cycle
•Continuous exchange of chemicals between the biota and physical environment within an ecosystem.
•Uptake of nutrients by plants is a major component of this cycle.
most forest plants are highly (or completely) dependent upon mutualistic relationship between their ____ & _____
roots and mycorrhiza
what do mycorrhiza do?
•Increase the uptake of nutrients, N, P, K in particular
-increases the volume of soil occupied by the root system thus increasing absorbing surface
-increases the uptake of water
-organic acids secreted by hyphae accelerate decomposition
losses from litter fall and fine roots:
turnover accounts for most of N, Ca, and Mg loss from vegetation
rate of decomposition is influenced by
biota, temperature, chemical composition of leaves, moisture
ex of arthropod herbivore
cicada nymph
ex of arthropod predator
mite
ex of arthropod fungal feeder
springtail
ex of arthropod shredder
millipede
what do soil arthropods and other invertebrates do?
shred organic matter, stimulate microbial activity, mix microbes with their food, mineralize plant nutrients, enhance soil aggregation, burrow, stimulate the diversity of species
how many soil arthropods are there in a square meter of soil?
745k
Understories of most forests are low in biomass compared to the over-story
-Forests with pronounced shrub layer
-Forests with large biomass of bryophytes
Following a major canopy disturbance,
there is a flush of nutrients that become available as plant material on site begins to decompose
Microbial activity increases due to
reduced competition from tree roots and decreased transportation (more soil water available). This may delay nutrient availability to plants but it also reduces loss of nutrients prior to plant uptake.
Nutrients resulting from the assert effect are typically
•taken up rapidly by early successional species, drastically reducing nutrient loss through leaching and runoff.
The Hubbard Brook experiment arrested secondary succession and
prevented vegetation from sequestering nutrients
Because of the strong relationship between _______ ______ and __________, understanding how forest management affects nutrient cycling is critical to sustainable forest management
nutrient cycling (fertility), productivity
maintaining the nutrient capital of a managed forest ecosystem depends upon:
the inherent nutrient capital of the site
how often harvest occur
how much material is harvested
how the substrate is affected
what grows on the site after harvest
fire returns a flush of nutrients to the soil through ____
ash
in nutrient cycling, carbon is lost from the site through _____
combustion
nitrogen may be lost in severe fire through _______
Volatilization
fire is often referred to as a ______ ______
rapid decomposer
geochemical cycle-
Exchanges of chemicals between ecosystems
biogeochemical cycle-
exchanges of chemicals within an ecosystem
biochemical cycle-
redistribution of chemicals within individual organisms
what is retranslocation in the biochemical cycle?
helps to conserve nutrients, but not all nutrients can be reabsorbed equally.
N and S move in the form of amino acids when proteins break down. Mg, K and P also move easily. Ca is incorporated into the cell walls and is highly immobile
the rate of retranslocation is generally greater at _____ ____ sites
nutrient poor
not all nutrients are _____ _____
equally mobile