Geology 209 Final Chapter 10
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 8:52 PM on 11/17/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
Stratigraphy
The study of the successions of strata and bodies of rocks in the Earth’s interior, represents the key towards understanding the Earth’s geological history
2
New cards
Nicolaus Steno
Discovered that there were two rock sequences in the Earth’s crust separated by a surface of discontinuity, principles of sedimentary layers
3
New cards
Principle of layer superposition
In any sequence of undisturbed layers, the older layer is at the bottom of the succession and the younger layers occupy a progressively higher position according to their age of formation
4
New cards
Principle of successive layer formation
At the time of formation of a layer only fluid was above it. Accordingly, none of the above existing layers in the succession existed at that time, lack traces of soft tissue
5
New cards
Principle of original layer horizontality
Layers were originally horizontal but crustal movements affected their position, older strata will reflect the irregularities of the sea bottom
6
New cards
Principle of lateral layer continuity
Originally deposited strata extend in all directions until they terminate by thinning at the margins of the basin
7
New cards
Steam erosion
Results in valley formation
8
New cards
Mud cracks
Sedimentary structures that form frequently at the surface of the Earth, opening is always upwards and narrows downwards
9
New cards
Ripple marks
Sedimentary structures that form at the top of the layer where unconsolidated particles are rearranged as a result of agitation by water or wind, top of layer indicated by narrow portion of ripple mark
10
New cards
Burrowings
Produced by organisms that develop their life cycles buried in sediments as adaptations to avoid predators or for feeding purposes, present opening indicates top of layer
11
New cards
Unconformities
Breaks in sedimentation and such features
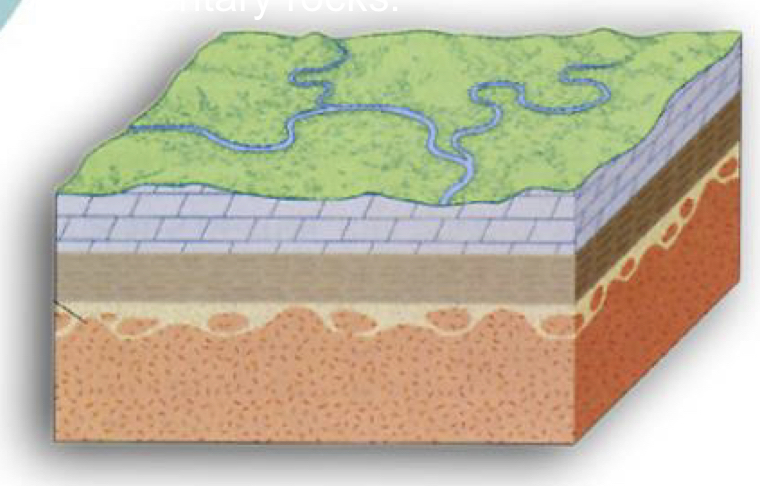
12
New cards
Disconformity
Unconformity between sedimentary rocks which are parallel to each other, no significant crustal movements
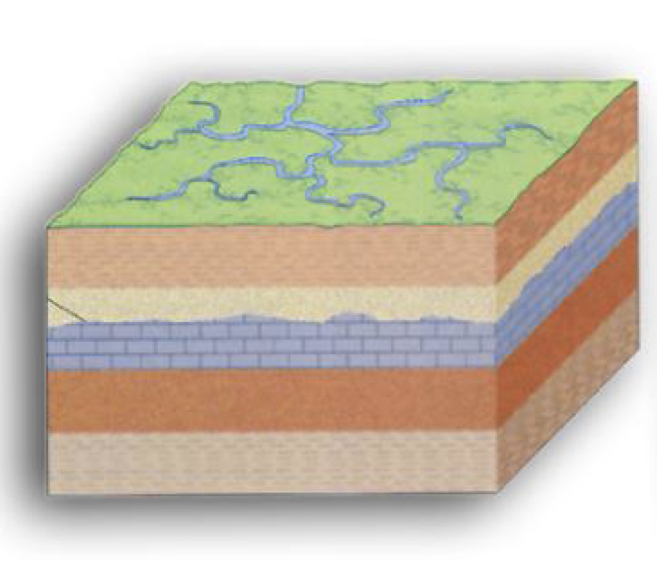
13
New cards
Angular unconformity
Unconformity between sedimentary rocks, the layering below and above the unconformity form a distinct angle, significant crustal movements
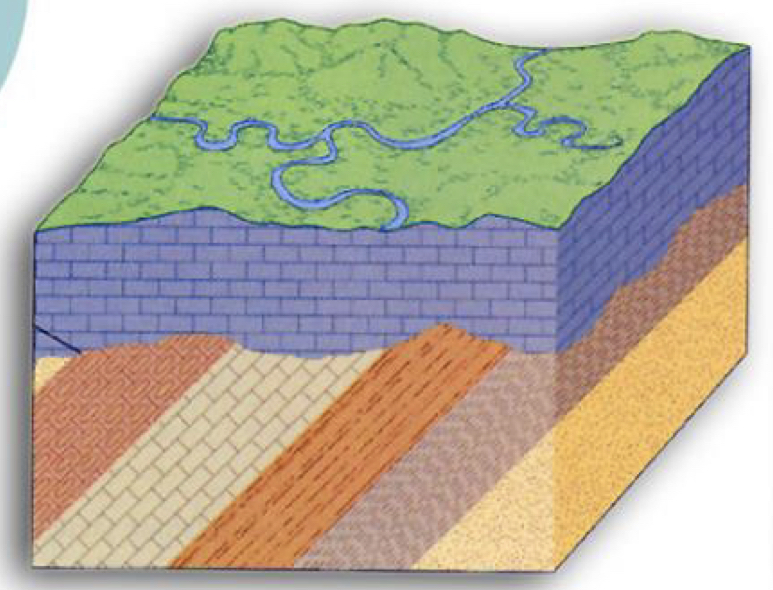
14
New cards
Non-conformities
Unconformity between igneous or metamorphic rocks, encompasses a long time period
15
New cards
Uniformitarianism
The concept that changes at the Earth’s surface are imperceptible and gradual
16
New cards
Actualism
The idea that past geological processes, phenomena and their effects can be understood if we study those actually happening on our planet
17
New cards
Catastrophism
The idea that the present day Earth was shaped through catastrophes such as volcanic eruptions and earthquakes
18
New cards
Stratigraphical range
The idea that certain fossils occur in certain layers
19
New cards
How do you classify the stratigraphical range of a fossil?
By its first appearance and extinction, once a species is extinct, it does not appear in high stratigraphical layers
20
New cards
Principle of inclusion
States that the inclusion within an igneous rock are older than the rock that includes them
21
New cards
Principle of cross-cutting relationships
States that a cross-cutting rock is younger than the cross-cut one
22
New cards
Xenolith
An inclusion in igneous rocks
23
New cards
Principle of rock-cooking
states that an igneous rock which thermally alters a layer of body of rocks is younger than them
24
New cards
Sills
Rock layer that cook the rocks below and above them
25
New cards
Hadean
The oldest eon in Earth’s history, began with the formation of our planet and has no rock record, only molten matter existed
26
New cards
Archean
Includes the oldest rocks on Earth, devoid of fossils
27
New cards
Hadean/Archean boundary
Given by the age of the oldest rocks in the stratigraphical record
28
New cards
Proterozoic
Stratigraphical interval with the oldest fossils on Earth, fossils were microscopic, larger fossils were found in the later part of this period
29
New cards
Phanerozoic
Youngest eon, visible large sized fossils can be found in many of the sedimentary rocks accumulated during this interval
30
New cards
Paleozoic
Oldest in the Phanerozoic eon, small resemblances between fossils in this era and the modern floras and faunas
31
New cards
Mesozoic
Contains fossils that present some resemblances to modern life forms
32
New cards
Cenozoic
Fossil debris discovered in these sediments present clear resemblances with modern life forms
33
New cards
Radioactivity
The natural properties of some atoms to transform spontaneously into one or two different atoms in order to achieve a more stable nucleus structure
34
New cards
Radioactive decay
The idea that some isotopes are stable and others are not, unstable ones can be transformed spontaneously into an isotope with a stable nucleus configuration
35
New cards
Parent atoms
Stable isotopes before radioactive decay
36
New cards
Daughter atoms
Stable atoms after radioactive decay
37
New cards
Half-life
The _____ of a radioactive element represents the time it takes for one half of the atoms of the original unstable parent element to decay to atoms of a new and more stable daughter element
38
New cards
Paelozoic/Mesozoic boundary
Given by the most severe crisis in the history of life where 90% of the species in the seas and oceans became extinct
39
New cards
Mesozoic/Cenozoic boundary
Given by the meteorite impact that led to the dinosaur extinction