Chapter 7 End of Chapter Questions
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Knowledge and Comprehension
The thermal death time for a suspension of Bacillus subtilis endospores is 30 minutes in dry heat and less than 10 minutes in an autoclave. Which type of heat is more effective? Why?
Autoclave because high specific heat of water + moist conditions readily transfer heat to cells.
If pasteurization does not achieve sterilization, why is pasteurization used to treat food?
Because it destroys most organisms that cause disease (ex: Listeria, Salmonella, and Escherichia coli) or rapid spoilage of food without significantly affecting the taste or nutritional value, thus extending shelf life and making it safe to consume.
Thermal death point is not considered an accurate measure of the effectiveness of heat sterilization. List three factors that can alter thermal death point.
Innate heat resistance of bacterial strain
Amount of water present
Organic matter present
Clumping of the cells during the test
Past history of the culture (whether it was freeze-dried, wetted, etc.)
Media and incubation temperature used to determine viability of the culture after heating
The antimicrobial effect of gamma radiation is due to ________.
ionizing radiation’s ability to break DNA directly. However, because of the high water content of cells, free radicals (H · and OH ·) that break DNA strands are likely to form.
The antimicrobial effect of ultraviolet radiation is due to ________.
formation of thymine dimers.
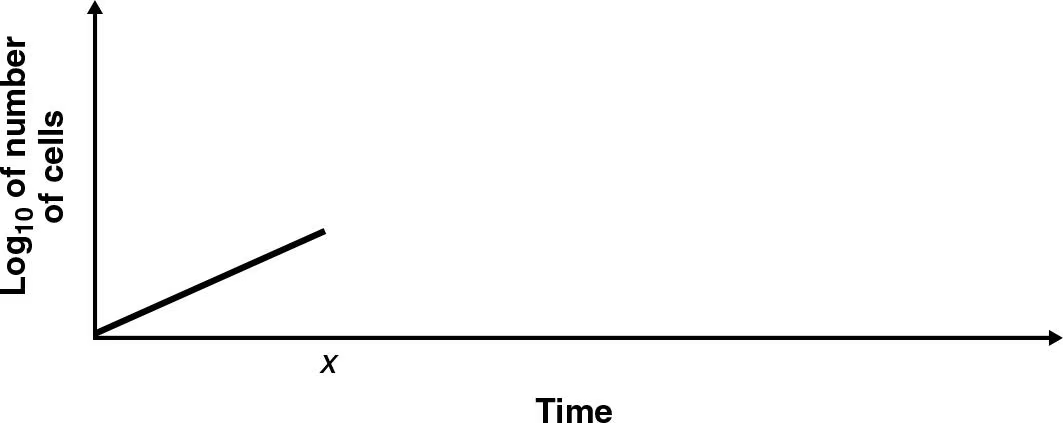
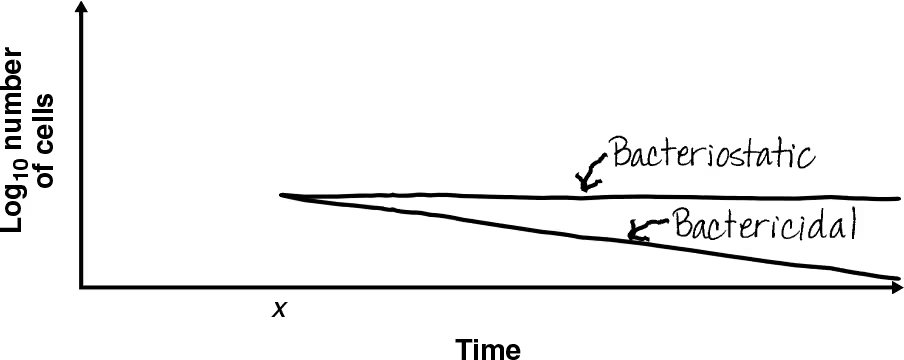
DRAW IT A bacterial culture was in log phase in the following figure. At time x, an antibacterial compound was added to the culture. Draw the lines indicating the addition of a bactericidal compound and a bacteriostatic compound. Explain why the viable count does not immediately drop to zero at x.
Bactericidal compounds don’t kill all cells at once
Bacteriostatic compounds simply prevent further growth of bacteria, not necessarily killing.
How do autoclaving, hot air, and ultra-high-temperature
pasteurization illustrate the concept of equivalent treatments?
All 3 processes kill microorganisms but the time required to do so decreases with increasing moisture and/or temperatures
How do salts and sugars preserve foods?
They create a hypertonic environment which draws moisture out of cells and inhibits microorganism growth
Why are salts and sugars considered physical rather than chemical methods of microbial control?
They don’t directly affect cell structures or metabolism, they just alter the osmotic pressure.
Name one food that is preserved with sugar and one preserved with salt.
Sugar: Jams, jellies
Salt: Meats
How do you account for the occasional growth of Penicillium mold in jelly, which is 50% sucrose?
While the 50% sucrose creates a hyperosmotic environment, molds are osmophilic (more capable of growth in higher osmotic pressure) unlike bacteria.
Yeasts/fungi/molds also like higher carbohydrate containing mediums?
The use-dilution values for two disinfectants tested under the same conditions are as follows: Disinfectant A—1:2; Disinfectant B—1:10,000. If both disinfectants are designed for the same purpose, which would you select?
Disinfectant B because it’s stronger even at higher dilutions
A large hospital washes burn patients in a stainless steel tub. After each patient, the tub is cleaned with a quat. It was noticed that 14 of 20 burn patients acquired Pseudomonas infections after being bathed. Provide an explanation for this high rate of infection.
Quaternary ammonium compounds are most effective against gram-positive bacteria.
Gram-negative bacteria stuck in cracks or around the drain wouldn’t have been washed away by the quat.
Some pseudomonads can grow on accumulated quats.
NAME IT What bacteria have porins, are resistant to bisphenols, and survive and may grow in quats?
Pseudomonads (Pseudomonas and Burkholderia)
Multiple Choice
Which of the following does not kill endospores?
autoclaving
incineration
hot-air sterilization
pasteurization
All of the above kill endospores.
4
Which of the following is most effective for sterilizing mattresses and plastic Petri dishes?
chlorine
ethylene oxide
glutaraldehyde
autoclaving
nonionizing radiation
2
Which of these disinfectants does not act by disrupting the plasma membrane?
phenolics
phenol
quats
halogens
biguanides
4
Which of the following cannot be used to sterilize a heat-labile solution stored in a plastic container?
gamma radiation
ethylene oxide
supercritical fluids
autoclaving
short-wavelength radiation
4
Which of the following is used to control microbial growth in foods?
organic acids
alcohols
aldehydes
heavy metals
all of the above
1
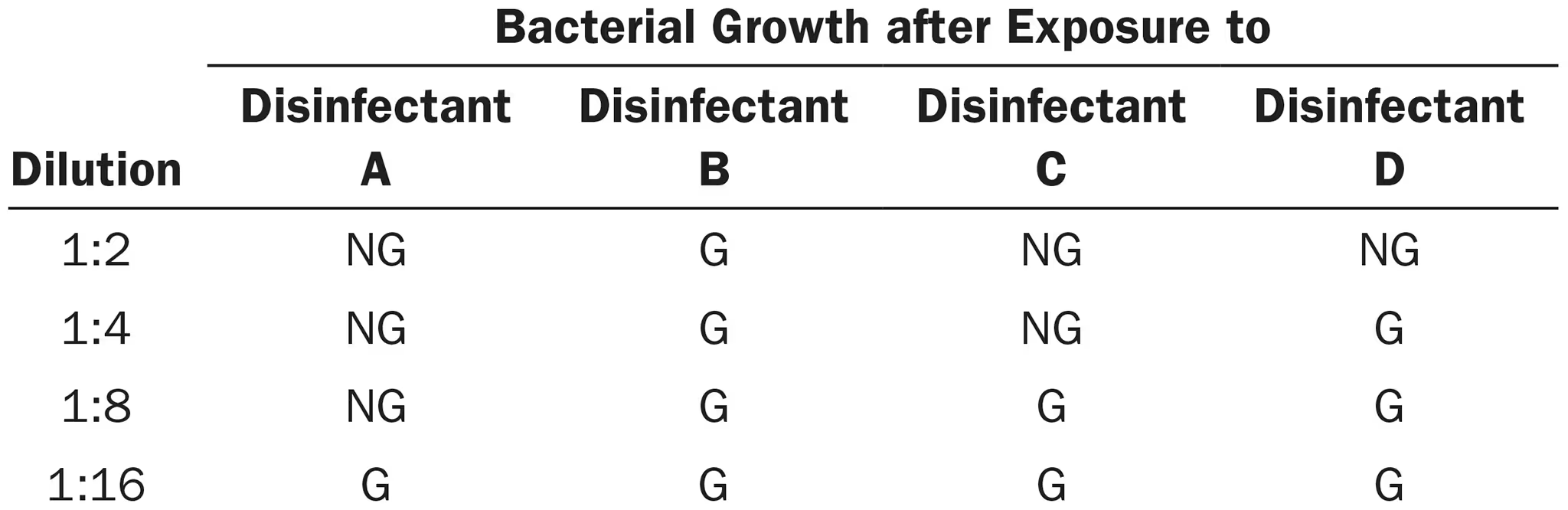
The data were obtained from a use-dilution test comparing four disinfectants against Salmonella Choleraesuis. G = growth, NG = no growth.
Which disinfectant is the most effective?
A
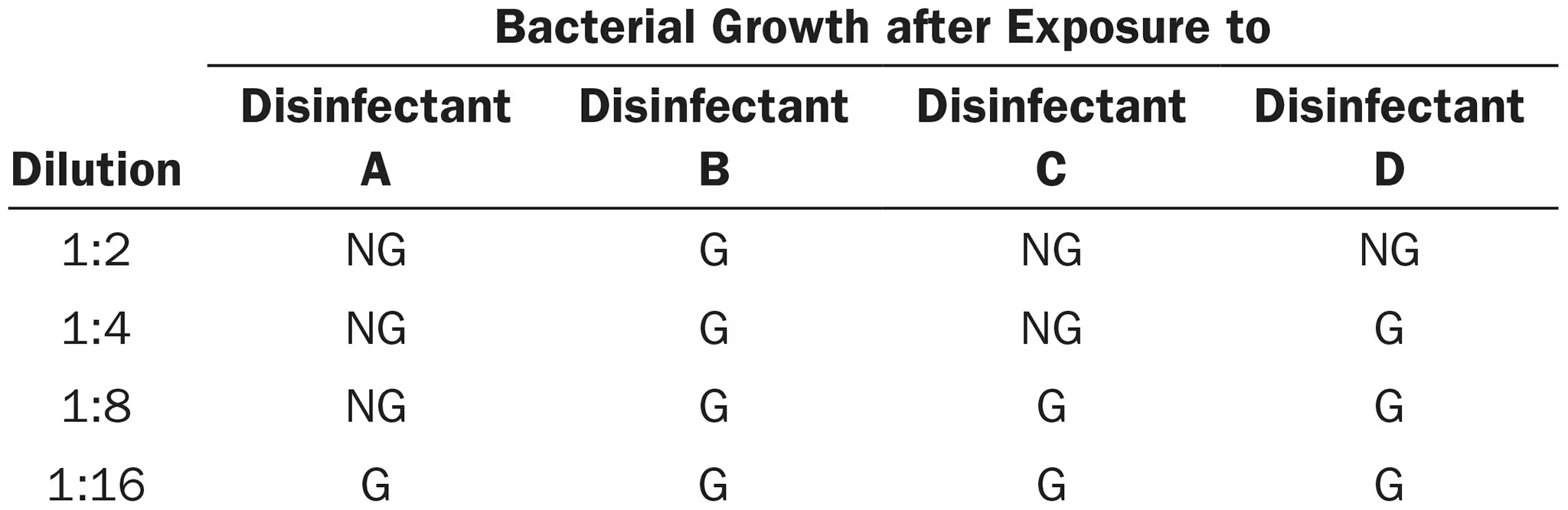
The data were obtained from a use-dilution test comparing four disinfectants against Salmonella Choleraesuis. G = growth, NG = no growth.
Which disinfectant(s) is (are) bactericidal?
A,B,C, and D
A,C, and D
A only
B only
none of the above
2
Which of the following is not a characteristic of quaternary ammonium compounds?
bactericidal against gram-positive bacteria
sporicidal
amebicidal
fungicidal
kills enveloped viruses
2
You and your classmates are trying to determine how a disinfectant might kill cells. You observe that when you spill the disinfectant in a tube of reduced litmus milk, the litmus turns blue again. You suggest to your classmates that
the disinfectant might inhibit cell wall synthesis.
the disinfectant might oxidize molecules.
the disinfectant might inhibit protein synthesis.
the disinfectant might denature proteins.
the disinfectant might damage DNA.
2
The correct answer is "the disinfectant might oxidize molecules." Reduced litmus milk turns blue when it becomes oxidized. If the disinfectant causes the litmus to turn blue, it suggests that the disinfectant has oxidizing properties, which means it may be working by oxidizing cellular components like proteins, lipids, or nucleic acids, thereby disrupting cell function and leading to cell death.
Which of the following is most likely to be bactericidal?
membrane filtration
ionizing radiation
lyophilization (freeze-drying)
deep-freezing
all of the above
2
Analysis

The disk-diffusion method was used to evaluate three disinfectants. The results were as follows: (view image)
Which disinfectant was the most effective against the organism?
Can you determine whether compound Y was bactericidal or bacteriostatic?
Disinfectant Z
You can't really determine it because it could be either or.
For each of the following bacteria, explain why it is often resistant to disinfectants.
Mycobacterium
Has a cell wall that’s hydrophilic, waxy, and rich in mycolic acids
For each of the following bacteria, explain why it is often resistant to disinfectants.
Pseudomonas
Has the ability to pump out antibiotics, contain proteins called porins which show little permeability for hydrophilic solute and change their structure to escape from antibacterial pressure.
For each of the following bacteria, explain why it is often resistant to disinfectants.
Bacillus
They have an endosperm, a protective barrier/layer against biocides.
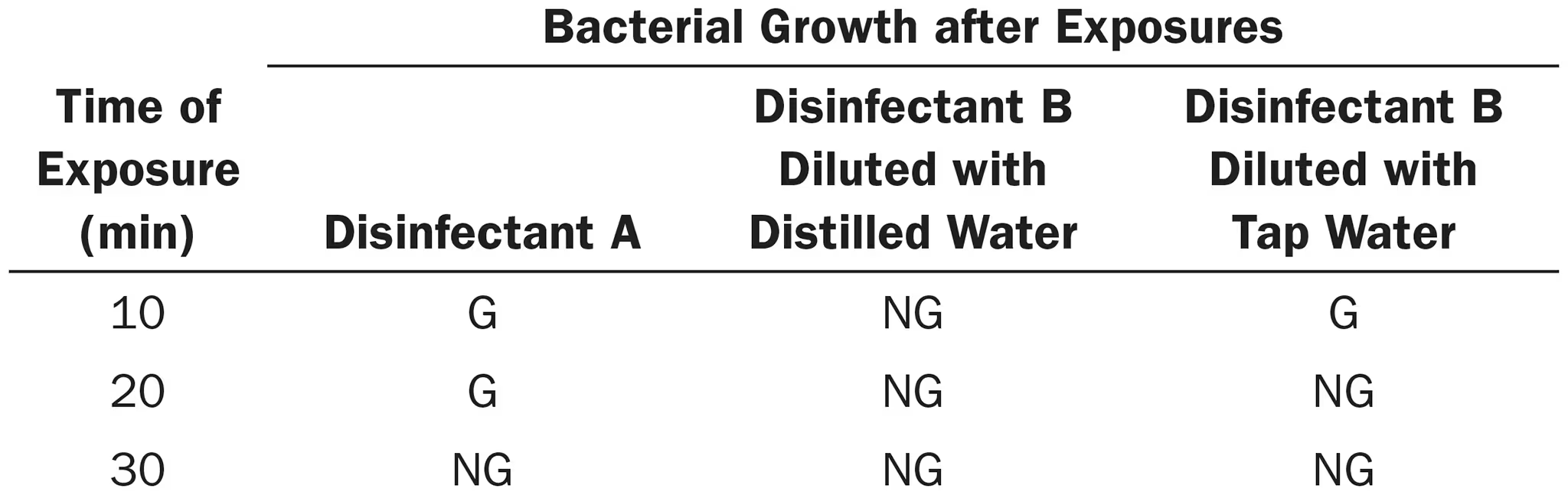
A use-dilution test was used to evaluate two disinfectants against Salmonella Choleraesuis. The results were as follows:
Which disinfectant was the most effective?
Which disinfectant should be used against Staphylococcus?
B diluted with distilled water
The test results for Salmonella choleraesuis cannot be directly applied to Staphylococcus, as different pathogens may have different sensitivities to disinfectants. Therefore, a separate analysis is required to determine which disinfectant is most effective against Staphylococcus. The same use-dilution test can be conducted using Staphylococcus as the target pathogen.
^ or answer might be all of them since they could all be considered bactericidal and disinfectants that kill salmonella could also be used against S. aureus
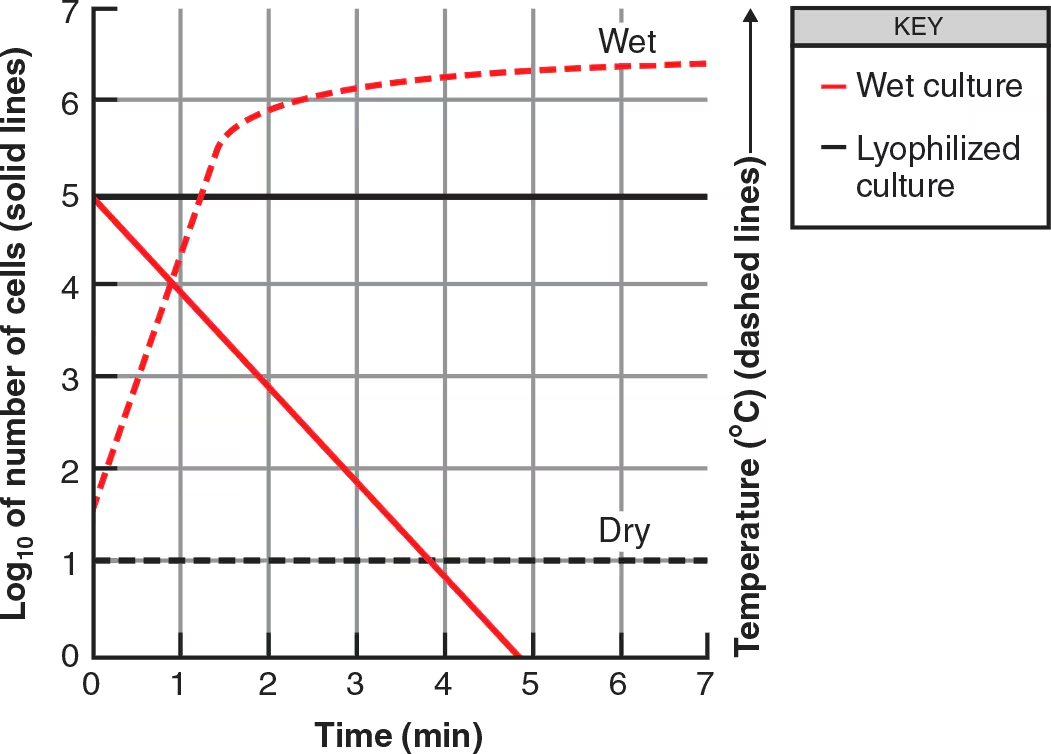
To determine the lethal action of microwave radiation, two 105 suspensions of E. coli were prepared. One cell suspension was exposed to microwave radiation while wet, whereas the other was lyophilized (freeze-dried) and then exposed to radiation. The results are shown in the following figure. Dashed lines indicate the temperature of the samples.
What is the most likely method of lethal action of microwave radiation?
How do you suppose these data might differ for Clostridium?
The heat produced acts upon the E. coli cells, unlike in the dehydrated samples where the cells didn’t experience elevated temperature.
Clostridium species contain heat resistant endospores so the microwave’s radiation will be less effective and take a longer period of time to kill all the cells. All other lines on the graph should be the same as that of E. coli.
Clinical Applications and Evaluations
Entamoeba histolytica and Giardia duodenalis were isolated from the stool sample of a 45-year-old patient, and Shigella sonnei was isolated from the stool sample of an 18-year-old patient. Both patients experienced diarrhea and severe abdominal cramps. Prior to onset of digestive symptoms, both had been treated by the same chiropractor, who had administered colonic irrigations (enemas) to them. The device used for this treatment was a gravity-dependent apparatus using 12 liters of tap water. There were no check valves to prevent backflow, so all parts of the apparatus could have become contaminated with feces during each colonic treatment. The chiropractor provided colonic treatment to four or five patients per day. Between patients, the adaptor piece that is inserted into the rectum was placed in a “hot-water sterilizer.”
What two errors did the chiropractor make?
improper adapter apparatus sterilization
used tap water in apparatus instead of sterile water
there’s no valves to prevent backflow which could contaminate the treatment
Between March 9 and April 12, five chronic peritoneal dialysis patients at one hospital became infected with P. aeruginosa. Four patients developed peritonitis (inflammation of the abdominal cavity), and one developed a skin infection at the catheter insertion site. All patients with peritonitis had low-grade fever, cloudy peritoneal fluid, and abdominal pain. All patients had permanent indwelling peritoneal catheters, which the nurse wiped with gauze that had been soaked with an iodophor solution each time the catheter was connected to or disconnected from the machine tubing. Aliquots of the iodophor were transferred from stock bottles to small in-use bottles. Cultures from the dialysate concentrate and the internal areas of the dialysis machines were negative; iodophor from a small in-use plastic container yielded a pure culture of P. aeruginosa.
What improper technique led to this infection?
Aliquots of the iodophor were transferred from stock bottles to small in-use bottles —» potential contamination
You are investigating a national outbreak of Ralstonia mannitolilytica associated with use of a contaminated oxygen-delivery device among pediatric patients. The device adds moisture to and warms the oxygen. Each hospital followed the manufacturer’s recommendation to use a detergent to clean the reusable components of the device between patients. Tap water is permitted in the device because the device uses a reusable 0.01-μm filter as a biological barrier between the air and water compartments. Ralstonia is a gram-negative rod commonly found in water.
Why did disinfection fail?
What do you recommend for disinfecting? The device cannot be autoclaved.
The disinfectant used isn’t very effective in Gram Negative bacteria since they have the extra outer membrane and usually most disinfectants can’t bypass that.
Gaseous sterilization with ethylene oxide