Exam 1: Cardiac and Perfusion
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/89
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
1
New cards
Left sided HF S/S
\
think LUNGS
\-paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
\-cough
\-crackles
\-wheezes
\-blood tinged sputum
\-tachypnea
\-tachycardia
\-exertional dyspnea
\-fatigue
\-cyanosis
\-restlessness
\-confusion
\-orthopnea
think LUNGS
\-paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea
\-cough
\-crackles
\-wheezes
\-blood tinged sputum
\-tachypnea
\-tachycardia
\-exertional dyspnea
\-fatigue
\-cyanosis
\-restlessness
\-confusion
\-orthopnea
2
New cards
Right sided HF S/S
Think REST of the body
\-enlarged liver and spleen
\-ascites
\-increased peripheral venous pressure
\-distended JVD
\-anorexia
\-complaints of GI distress
\-weight gain
\-dependent edema
\-fatigue
\-enlarged liver and spleen
\-ascites
\-increased peripheral venous pressure
\-distended JVD
\-anorexia
\-complaints of GI distress
\-weight gain
\-dependent edema
\-fatigue
3
New cards
__Acute Coronary Syndrome: primary cause__
Atherosclerosis
\-Angina occurs when the O2 demand is greater than the oxygen supply
· The heart is working hard (high oxygen demand) but there is poor perfusion to the myocardium (low oxygen supply)
§ Lipids accumulate causing a fatty streak
§ The endothelial lining of the arteries is damaged
\-Angina occurs when the O2 demand is greater than the oxygen supply
· The heart is working hard (high oxygen demand) but there is poor perfusion to the myocardium (low oxygen supply)
§ Lipids accumulate causing a fatty streak
§ The endothelial lining of the arteries is damaged
4
New cards
Acute Coronary Syndrome: RF
§ Smoking
§ Hyperlipidemia
§ HTN
§ Toxins
§ Diabetes
§ Localized inflammatory process
§ Hyperlipidemia
§ HTN
§ Toxins
§ Diabetes
§ Localized inflammatory process
5
New cards
Acute Coronary Syndrome: S/S
§ Palpitations
§ Diaphoresis
§ Anxiety Nausea
§ Angina (chest pain)
· Women confuse chest pain for indigestion
· Men will describe it as an elephant on the chest
· Both genders will complain of arm pain
§ Diaphoresis
§ Anxiety Nausea
§ Angina (chest pain)
· Women confuse chest pain for indigestion
· Men will describe it as an elephant on the chest
· Both genders will complain of arm pain
6
New cards
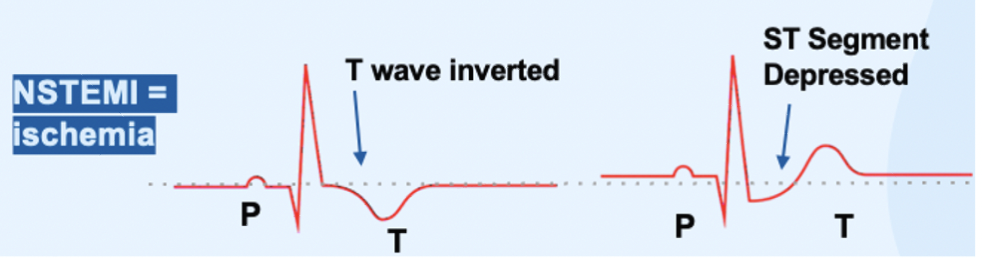
__Non-ST Elevated Myocardial Infarction (NSTEMI):__
§ This is considered Ischemia
· Ischemia means it is lacking O2 NOT tissue death
§ It is reversible
§ Releases cardiac enzymes if damaged
· Ischemia means it is lacking O2 NOT tissue death
§ It is reversible
§ Releases cardiac enzymes if damaged
7
New cards
how will an NSTEMI strip look like?
__ST Depression and/or T wave inversion indicating ischemia__
8
New cards
NSTEMI and STEMI- dx and labs
12 lead EKG
myoglobins
creatine kinase MB
Troponin I or T
myoglobins
creatine kinase MB
Troponin I or T
9
New cards
Myoglobins
* earliest marker of injury to cardiac/skeletal muscle
§ No longer evident after 24hrs
§ No longer evident after 24hrs
10
New cards
creatine kinase - MB
§ Peaks around 24hrs after onset of chest pain
§ No longer evident after 3 days
§ No longer evident after 3 days
11
New cards
Troponin I or T
§ If there is any POSITIVE+ value, it means there is cardiac tissue damage and should be reported
12
New cards
__Unstable Angina & NSTEMI MEDS:__
o MONA – Morphine, O2, Nitroglycerine, Aspirin
o give heparin to prevent clot formation of microemboli
o DAPT (dual anti platelet therapy) – ex. Aspirin, clopidogrel, ticagrelor
o PCI (percutaneous coronary intervention) – within 12-72 hrs.
§ This refers to cardiac cath with stent placement
o Notify PCP ASAP if there are any changes in ST segment
o give heparin to prevent clot formation of microemboli
o DAPT (dual anti platelet therapy) – ex. Aspirin, clopidogrel, ticagrelor
o PCI (percutaneous coronary intervention) – within 12-72 hrs.
§ This refers to cardiac cath with stent placement
o Notify PCP ASAP if there are any changes in ST segment
13
New cards
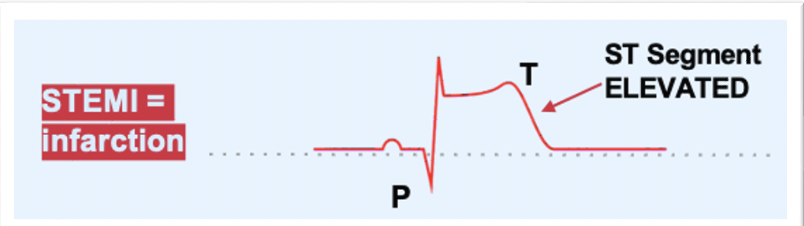
o __ST-Elevated Myocardial Infarction (STEMI):__
§ Infarction – Classic heart attack
§ ST segment is elevated = pt is dying
§ Extensive heart damage
§ This is the only one with an ST elevation
· Tissue is dead and more tissue is continuing to die
§ ST segment is elevated = pt is dying
§ Extensive heart damage
§ This is the only one with an ST elevation
· Tissue is dead and more tissue is continuing to die
14
New cards
§ __STEMI MEDS:__
· PCI (percutaneous coronary intervention) – within 90 mins.
o This refers to cardiac cath with stent placement
· TPA if PCI is not available
o TPA = tissue plasminogen activator = thrombolytic therapy = breaks up existing clots
o This refers to cardiac cath with stent placement
· TPA if PCI is not available
o TPA = tissue plasminogen activator = thrombolytic therapy = breaks up existing clots
15
New cards
o __PRIORITY NURSING INTERVENTIONS FOR ALL CLIENTS WITH ANGINA:__
§ FOR UA, NSTEMI, STEMI
§ FOR UA, NSTEMI, STEMI
· 12-LEAD ECG
· Serial cardiac biomarkers
· Vitals and O2 monitoring HOURLY
· Continuous ECG monitoring
· MONA
· Monitor UOP
· Maintain bed rest
· Limit activity for 12-24hrs.
· Monitor and treat Anxiety
· Serial cardiac biomarkers
· Vitals and O2 monitoring HOURLY
· Continuous ECG monitoring
· MONA
· Monitor UOP
· Maintain bed rest
· Limit activity for 12-24hrs.
· Monitor and treat Anxiety
16
New cards
when do STEMI pts go for stent placement
§ goes to cardiac cath lab for stent placement right away; these interventions are happening during transport and procedure preparation
17
New cards
when do NSTEMI and UA pts go for stent placement
will go to cardiac cath within 72h; these interventions are happening until they go to the cath lab
18
New cards
o __ACS Procedures:__ Angiography/Cardiac Catheterization:
· This is an invasive procedure
· Evaluates presence & degree of coronary artery blockage
· Threads a catheter through a peripheral artery into the heart to visualize coronary arteries
· Contrast is used to see blockage
· Evaluates presence & degree of coronary artery blockage
· Threads a catheter through a peripheral artery into the heart to visualize coronary arteries
· Contrast is used to see blockage
19
New cards
use of contrast nursing care
o Assess for allergies: especially contrast dye \n o Perform baseline assessment \n o Withhold food/fluids 6-12 hrs before \n o Assess baseline lab values: cardiac biomarkers & creatinine
o Teach about procedure \n o Give sedative & other drugs
o Teach about procedure \n o Give sedative & other drugs
20
New cards
§ Post Angiography Site Care:
· Monitor vitals
· Assess for bleeding
· Assess for hematomas
· Assess neurovascular checks (5 P’s – Pain, Paresthesia, Pallor, Pulse, Paralysis)
o Check every 15 min for the 1st hour (4 times)
o Check every 30 min for the 2nd hour (2 times)
o Check every hour for the next 4 hours (4 times)
o Check every 4 hours
· Bed Rest
o Pt must lay flat, supine
o Extremity must be straight for the prescribed time
o Pt cannot walk
o Pt cannot sit up to eat
· Assess for bleeding
· Assess for hematomas
· Assess neurovascular checks (5 P’s – Pain, Paresthesia, Pallor, Pulse, Paralysis)
o Check every 15 min for the 1st hour (4 times)
o Check every 30 min for the 2nd hour (2 times)
o Check every hour for the next 4 hours (4 times)
o Check every 4 hours
· Bed Rest
o Pt must lay flat, supine
o Extremity must be straight for the prescribed time
o Pt cannot walk
o Pt cannot sit up to eat
21
New cards
ACS MEDS - drug action - *Vasodilators – Nitroglycerin -*
o Prevents coronary artery vasospasm
o Reduces preload and afterload, decreasing myocardial oxygen demand
o Decreases BP
o Reduces preload and afterload, decreasing myocardial oxygen demand
o Decreases BP
22
New cards
ACS MEDS - nursing action - *Vasodilators – Nitroglycerin -*
o Monitor for orthostatic hypotension
o Teach pt headaches are common
o Withhold drug if pt is taking phosphodiesterase inhibitor for erectile dysfunction within the last 24-48hrs – can cause severe hypotension
o Educate to take 1 tablet every 5 mins x 3
o If chest pain continues after first dose and 5 mins have passed, take 2nd tablet and call 911
o When taking this medication pt should be sitting down
o Teach pt headaches are common
o Withhold drug if pt is taking phosphodiesterase inhibitor for erectile dysfunction within the last 24-48hrs – can cause severe hypotension
o Educate to take 1 tablet every 5 mins x 3
o If chest pain continues after first dose and 5 mins have passed, take 2nd tablet and call 911
o When taking this medication pt should be sitting down
23
New cards
ACS MEDS - drug action - *Analgesic – Morphine*
o Pain relief (chest pain)
o Decreased O2 consumption (Reduces the demand for O2)
o Calms anxiety
o Decreased O2 consumption (Reduces the demand for O2)
o Calms anxiety
24
New cards
ACS MEDS - nursing action - *Analgesic – Morphine*
o Monitor for decreased RR
o Monitor for hypotension
o N/V
o Monitor for hypotension
o N/V
25
New cards
ACS MEDS - drug action - *Betablockers – Metoprolol* (end in LOL)
o Antidysrhythmic & antihypertensive
§ decrease O2 demand by reducing afterload and slowing HR
o Acute MI: decrease infarct size
§ improves short- and long-term outcomes
§ decrease O2 demand by reducing afterload and slowing HR
o Acute MI: decrease infarct size
§ improves short- and long-term outcomes
26
New cards
ACS MEDS - nursing action - *Betablockers – Metoprolol* (end in LOL)
o Monitor for bradycardia and hypotension
o Hold if apical pulse < 60
o Monitor asthma & heart failure pts
o Monitor for decreased LOC, crackles, chest discomfort
o Check heart rate before admin
§ 60 or less hold med call pcp
o Hold if apical pulse < 60
o Monitor asthma & heart failure pts
o Monitor for decreased LOC, crackles, chest discomfort
o Check heart rate before admin
§ 60 or less hold med call pcp
27
New cards
ACS MEDS - drug action - *Thrombolytic Agent – Alteplase*
o Breaks up clots in the blood
28
New cards
ACS MEDS - nursing action - *Thrombolytic Agent – Alteplase*
o Monitor for bleeding
o Monitor labs – PTT and PT
o Not indicated for pts with NSTEMI
o Indicated for pts with STEMI and PCI is not an option
o Monitor labs – PTT and PT
o Not indicated for pts with NSTEMI
o Indicated for pts with STEMI and PCI is not an option
29
New cards
ACS MEDS - drug action - *Antiplatelet Agents – Aspirin, Clopidogrel (Plavix)*
\
\
o Prevent platelets from sticking together
o Aspirin should be given with nitro on onset of symptoms due to its ability to prevent vasoconstriction
o Aspirin should be given with nitro on onset of symptoms due to its ability to prevent vasoconstriction
30
New cards
ACS MEDS - nursing action -*Antiplatelet Agents – Aspirin, Clopidogrel (Plavix)*
o Monitor for tinnitus (toxicity)
§ Ringing of the ears
o Watch out for bleeding
§ Ringing of the ears
o Watch out for bleeding
31
New cards
ACS MEDS - drug action - *Anticoagulants – Heparin and Enoxaparin*
o Prevent clot growth
o Prevent new clot formation
o Prevent new clot formation
32
New cards
ACS MEDS - nursing action - Anticoagulants – Heparin and Enoxaparin
o Monitor for bleeding
o PT/ INR, PTT, CBC
§ Platelet count comes from CBC
o Thrombocytopenia & Anemia
o Risk for bleeding and bruising
o PT/ INR, PTT, CBC
§ Platelet count comes from CBC
o Thrombocytopenia & Anemia
o Risk for bleeding and bruising
33
New cards
ACS MEDS - drug action - *Lipid Lowering Statin – Atorvastatin (end in STATIN)*
o Block synthesis of cholesterol and increase LDL receptors in liver
o Decreases LDL
o Decreases triglycerides
Increases HDL (in small amounts
o Decreases LDL
o Decreases triglycerides
Increases HDL (in small amounts
34
New cards
ACS MEDS - nursing action - *Lipid Lowering Statin – Atorvastatin (end in STATIN)*
o Monitor liver enzymes and creatine kinase
§ Will be decreased
§ if muscle weakness or pain occurs
o Give at night
§ Will be decreased
§ if muscle weakness or pain occurs
o Give at night
35
New cards
ACS – Nutrition
· NPO except water until stable
· Low sodium diet
· Low saturated fat diet
· Low cholesterol diet
· No Fast food
· No Canned food
· No prepackaged food
· Low sodium diet
· Low saturated fat diet
· Low cholesterol diet
· No Fast food
· No Canned food
· No prepackaged food
36
New cards
ACS - exercise
· Low Impact activity
37
New cards
ACS - nursing considerations
Administer stool softener
o Prevent straining
o Drink plenty of water
o Include fiber in diet
o Prevent straining
o Drink plenty of water
o Include fiber in diet
38
New cards
__Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)__
o Surgical procedure to restore vascularization of the myocardium & improve client quality of life
o Most effective when EF is less than 50%
o Open chest procedure
o ICU monitoring
o Most effective when EF is less than 50%
o Open chest procedure
o ICU monitoring
39
New cards
CABG - Pre-Op Nursing Considerations
o Informed consent
o Discontinue meds prior to sx (educate pt)
o Meds to continue until morning of sx (educate pt)
o Discontinue meds prior to sx (educate pt)
o Meds to continue until morning of sx (educate pt)
40
New cards
CABG - PRE-OP - Discontinue meds prior to sx
§ Diuretics - 2-3 days prior to sx
§ Aspirin and other anticoagulants – 1 week prior to sx
§ Aspirin and other anticoagulants – 1 week prior to sx
41
New cards
CABG - PRE-OP - continue meds prior to sx
§ Potassium supplements
§ Antidysrhythmic
§ Antihypertensives
§ Insulin
§ Antidysrhythmic
§ Antihypertensives
§ Insulin
42
New cards
CABG - Post-Op Nursing Considerations:
o ICU for 24-36 hours
o Monitor hemodynamics – tight BP control
§ Arterial line for BP monitoring
· Hypotension
o Can be due to the graft collapsing
· Hypertension
o Can be due to bleeding at graft or suture sites
o ECG for heart rhythms
o Epicardial pacing wire for emergency pacing
o Chest tube care
o Endotracheal / Mechanical vent care
o Foley cath
o NGT for gastric decompression
o Splinting for coughing and deep breathing
o Early mobility
o Monitor hemodynamics – tight BP control
§ Arterial line for BP monitoring
· Hypotension
o Can be due to the graft collapsing
· Hypertension
o Can be due to bleeding at graft or suture sites
o ECG for heart rhythms
o Epicardial pacing wire for emergency pacing
o Chest tube care
o Endotracheal / Mechanical vent care
o Foley cath
o NGT for gastric decompression
o Splinting for coughing and deep breathing
o Early mobility
43
New cards
CABG - Complications - Pulmonary
· Atelectasis
· Pneumonia
· Pulmonary Edema
· Pneumonia
· Pulmonary Edema
44
New cards
CABG - Complications - Pulmonary - prevention
· Early Ambulation
· Turning
· Deep breathing exercises
· Turning
· Deep breathing exercises
45
New cards
CABG - Complications - Pulmonary - recognize cues
· Abnormal lung sounds
· Unequal lung sounds
· Crackles
· Unequal lung sounds
· Crackles
46
New cards
CABG - Complications - Pulmonary - interventions
· Administer O2
· Notify PCP
· Potentially prepare for chest tubes/ diuretics
· Notify PCP
· Potentially prepare for chest tubes/ diuretics
47
New cards
CABG - Complications - hypothermia
· Vasoconstriction
· Metabolic acidosis
· Metabolic acidosis
48
New cards
CABG - Complications - hypothermia - prevention
· Monitor Temp
· Keep pt warm
· Keep pt warm
49
New cards
CABG - Complications - hypothermia - recognizing cues
· Decreased capillary refill
· Cool extremities
· HTN
· Cool extremities
· HTN
50
New cards
CABG - Complications - hypothermia - intervention
· Check ABG’s
· Bear hugger
· Warming blanket
· Warming fluids
· Bear hugger
· Warming blanket
· Warming fluids
51
New cards
CABG - Complications - heart (decreased cardiac output)
· Dysrhythmias – AFIB
· Cardiac Tamponade (Causes restrictive pressure around heart which reduces its ability to pump = decreased cardiac output)
· Hypovolemia
· Left Ventricular Failure
· Myocardial Infarction (MI)
· Cardiac Tamponade (Causes restrictive pressure around heart which reduces its ability to pump = decreased cardiac output)
· Hypovolemia
· Left Ventricular Failure
· Myocardial Infarction (MI)
52
New cards
CABG - Complications - heart - Dysrhythmias – AFIB __Intervention__
§ Administer BB soon after sx
53
New cards
CABG - Complications - heart - cardiac tamponade __Intervention__
§ Sternotomy or pericardiocentesis
54
New cards
CABG - Complications - heart - hypovolemia __Intervention__
§ Carefully replace fluids, colloids
55
New cards
CABG - Complications - heart - left ventricular failure __Intervention__
§ Vasopressors and positive inotropes
56
New cards
CABG - Complications - heart - MI __Intervention__
§ Call MD
§ MONA
§ MONA
57
New cards
CABG - Complications - *Electrolyte Disturbances*
· K and Magnesium depletion
58
New cards
CABG - Complications - *Electrolyte Disturbances - recognizing cues*
§ Fatigue
§ Muscle cramps
§ Tingle
§ Numbness
§ Heart palpitations
§ Muscle cramps
§ Tingle
§ Numbness
§ Heart palpitations
59
New cards
CABG - Complications - *Electrolyte Disturbances - intervention*
o give K + and Mag replacements
§ SAFETY for IV potassium- how fast can we give K+?
§ 10 mEq/hr
§ Must use IV pump
§ Must be on cardiac monitor
§ NEVER PUSH IV
§ SAFETY for IV potassium- how fast can we give K+?
§ 10 mEq/hr
§ Must use IV pump
§ Must be on cardiac monitor
§ NEVER PUSH IV
60
New cards
CABG - Complications - neuro deficits
· CVA (stroke) from transient HTN
· hypotension
· blood clot
· hypotension
· blood clot
61
New cards
CABG - Complications - neuro deficits - recognizing cues
§ balance issues
§ eyesight issues
§ facial droop
§ arm weakness
§ speech difficulties
§ eyesight issues
§ facial droop
§ arm weakness
§ speech difficulties
62
New cards
CABG - Complications - neuro deficits - interventions
o Protect airway
o Call MD
o Code stroke
o Call MD
o Code stroke
63
New cards
pacemakers indication
o Help control abnormal heart rhythms with low-electrical pulses to prompt heart to beat at normal rate
64
New cards
transcutaneous pacemaker
●Fully external
●Symptomatic bradycardia when pt is unresponsive to atropine
●Painful d/t large amount of electricity
●Temporary
65
New cards
epicardial pacemaker
●Pulse generator outside of body
●Leads threaded through chest directly to heart
●Common after open-heart surgery
●Temporary
66
New cards
endocardial (transvenous) pacemaker
●Pulse generator implanted under skin/muscle
●Wires threaded through a large vein and lodged into the wall of the heart
●Permanent (pulse generator will be changed as needed)
●\*Some also function as a defibrillator
67
New cards
Implantable Cardioverter/Defibrillator (ICD):
o CONTAINS AN INTERNAL GENERATOR TO DELIVER SHOCK IF NEEDED
§ For pt’s with ventricular dysrhythmias who are at risk of needing D-FIB
§ Ventricular Tachydysrhythmias
§ MI with left ventricular dysfunction
§ For pts who survive sudden cardiac death / ventricular dysrhythmias
§ Stronger shock – will feel like a blow to the chest
§ For pt’s with ventricular dysrhythmias who are at risk of needing D-FIB
§ Ventricular Tachydysrhythmias
§ MI with left ventricular dysfunction
§ For pts who survive sudden cardiac death / ventricular dysrhythmias
§ Stronger shock – will feel like a blow to the chest
68
New cards
pacemaker on demand
pacemaker will deliver electricity when the HR falls below a predetermined rate
69
New cards
fixed pacemaker
the pacemaker will deliver electricity at a fixed rate (less common)
70
New cards
reasons to put a pacemaker in
§ Symptomatic bradycardia
§ Complete heart block
§ Sick sinus syndrome
§ Cardiac arrest
§ Atrial tachydysrhythmias
§ Complete heart block
§ Sick sinus syndrome
§ Cardiac arrest
§ Atrial tachydysrhythmias
71
New cards
pacemaker spikes
expected
\
§ shows when electricity is being sent to the heart
\
§ shows when electricity is being sent to the heart
72
New cards
pacemaker - ECG Monitoring For Malfunction - failure to sense
\
· Doesn’t sense pt HR
· Causes inappropriate/random firing
· Doesn’t sense pt HR
· Causes inappropriate/random firing
73
New cards
pacemaker - ECG Monitoring For Malfunction - failure to capture
§ due to leads not connected appropriately
§ Electricity is not caught by the heart
§ Leads to bradycardia or asystole
§ Electricity is not caught by the heart
§ Leads to bradycardia or asystole
74
New cards
pacemaker - ECG Monitoring For Malfunction - failure to pace
§ battery issue
§ Pacemaker is not sending electricity
§ Pacemaker is not sending electricity
75
New cards
Pacemaker Complications
o Infection- Endocarditis
o Hematoma Formation
o Pneumothorax
o Atrial Or Ventricular Septum Perforation
o Lead Misplacement
o Hiccups
o Hematoma Formation
o Pneumothorax
o Atrial Or Ventricular Septum Perforation
o Lead Misplacement
o Hiccups
76
New cards
Pacemaker Complications - why do hiccups occur?
**§ Pacemaker is sitting low in the heart – near the diaphragm (tickling the diaphragm)**
77
New cards
Pacemaker FACTS - pt education
\-Regular pacemaker function checks
\-Report any signs of infection at incision site
\-Keep incision dry for 4 days after implantation, or as ordered.
\- AVOID LIFTING arm on pacemaker side above shoulder until approved by cardiologist.
\-Avoid close proximity to high-output electric generators
\-Monitor pulse and tell your HCP if heart rate drops below predetermined rate.
\-Always wear a Medic Alert ID device
\-Always carry your pacemaker information card and a current list of drugs.
\-Report any signs of infection at incision site
\-Keep incision dry for 4 days after implantation, or as ordered.
\- AVOID LIFTING arm on pacemaker side above shoulder until approved by cardiologist.
\-Avoid close proximity to high-output electric generators
\-Monitor pulse and tell your HCP if heart rate drops below predetermined rate.
\-Always wear a Medic Alert ID device
\-Always carry your pacemaker information card and a current list of drugs.
78
New cards
Pacemaker MYTHS - pt education
Okay to resume boxing / bar fights
All pacemakers are MRI safe
Microwave ovens interfere with pacemaker function.
Travel is restricted
79
New cards
Aneurysm definition
o Weakness in a section of a dilated artery that causes a widening or balloon in the wall of the blood vessel
80
New cards
aneurysm RF
o Male
o Atherosclerosis (most common cause)
o Hypertension
o Smoking
o Hyperlipidemia
o Genetics
o Age (loss of elastin in artery walls causes stiffening/thickening, & progressive fibrosis; more prone to aneurysms & higher mortality rate), etc.
o Atherosclerosis (most common cause)
o Hypertension
o Smoking
o Hyperlipidemia
o Genetics
o Age (loss of elastin in artery walls causes stiffening/thickening, & progressive fibrosis; more prone to aneurysms & higher mortality rate), etc.
81
New cards
aneurysm types
saccular
fusiform
fusiform
82
New cards
aneurysm types - saccular
affect only one side of the artery
83
New cards
aneurysm types - fusiform
Affect the complete circumference of the artery
84
New cards
aneurysm - recognizing cues for thoracic aortic aneurism
§ Severe back pain (most common)
§ Hoarseness
§ Cough
§ SOB
§ Difficulty swallowing
§ Decrease in urinary output d/t hypovolemic shock
§ Hoarseness
§ Cough
§ SOB
§ Difficulty swallowing
§ Decrease in urinary output d/t hypovolemic shock
85
New cards
aneurysm - recognizing cues for __Abdominal Aortic Aneurism:__
§ Constant gnawing
§ abdominal pain
§ flank or back pain
§ pulsating abdominal mass (do not palpate)
§ abdominal pain
§ flank or back pain
§ pulsating abdominal mass (do not palpate)
86
New cards
aneurysm - recognizing cues for __Iliac Aortic Dissection:__ (EMERGENCY)
§ Sudden tearing, ripping, stabbing abdominal or back pain
§ Hypovolemic shock
· Decreased BP
· Tachycardia
§ Hypovolemic shock
· Decreased BP
· Tachycardia
87
New cards
__Aneurism Nursing Care: (PRIORITY)__
o Assess ABC - circulation!!
o Vitals Q15 min
o Decrease SBP to 100 to 120mm Hg with b-blockers or CCB
o Monitor UOP
o Prepare for emergency surgery for rupturing aneurysm
o Vitals Q15 min
o Decrease SBP to 100 to 120mm Hg with b-blockers or CCB
o Monitor UOP
o Prepare for emergency surgery for rupturing aneurysm
88
New cards
__Aneurism Complication: rupture__
§ Can result in massive hemorrhage, shock & death
§ Treatment is resuscitation & immediate surgical repair
§ Older clients with > 6 cm aneurysm & hypertension have greater risk of death
§ Treatment is resuscitation & immediate surgical repair
§ Older clients with > 6 cm aneurysm & hypertension have greater risk of death
89
New cards
__Aneurism Complication: thrombus__
§ Can form inside aneurysm, emboli can dislodge causing ischemia
§ Assess circulation distal to aneurysm (pulses, color, & temperature)
§ Assess circulation distal to aneurysm (pulses, color, & temperature)
90
New cards
__Aortic Aneurysm Repair__
o Graft
§ Report graft rupture or occlusion:
· Absent pulses, coolness of extremities, signs of hypovolemia (hypotension, decreased UOP)
§ Implement general post op nursing care – ex. turning, deep breathing, splinting
§ Report graft rupture or occlusion:
· Absent pulses, coolness of extremities, signs of hypovolemia (hypotension, decreased UOP)
§ Implement general post op nursing care – ex. turning, deep breathing, splinting