5.1 Reaction Rates
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Chemical reactions involve the:
Conversion of reactants with a particular set of properties into products with a whole new set of properties
The investigation of the rate at which reactions occur and the factors that affect them
Chemical kinetics
For most reactions, the rate is ______ at the beginning of the reaction
Greatest
For most reaction, what happens to the rate as the reaction continues?
Decreases
Does the rate change as the reaction proceeds?
Yes
Reaction rates are generally expressed as:
Averages over a particular time period
Why are reaction rates generally expressed as averages over a particular time period?
Because the rate changes as the reaction proceeds
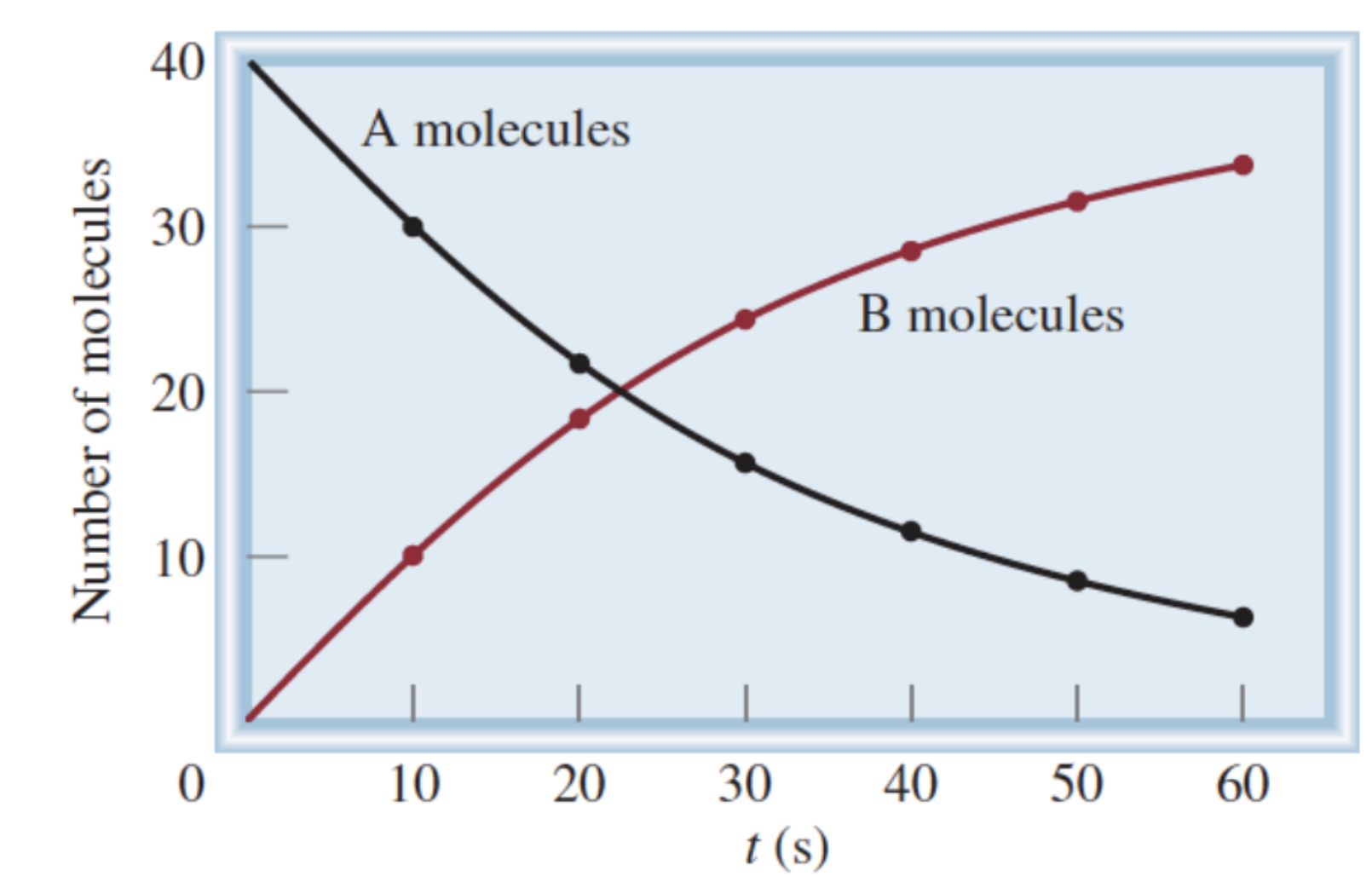
Formula for rate of A molecules:
-(change in [A]) / (change in t)
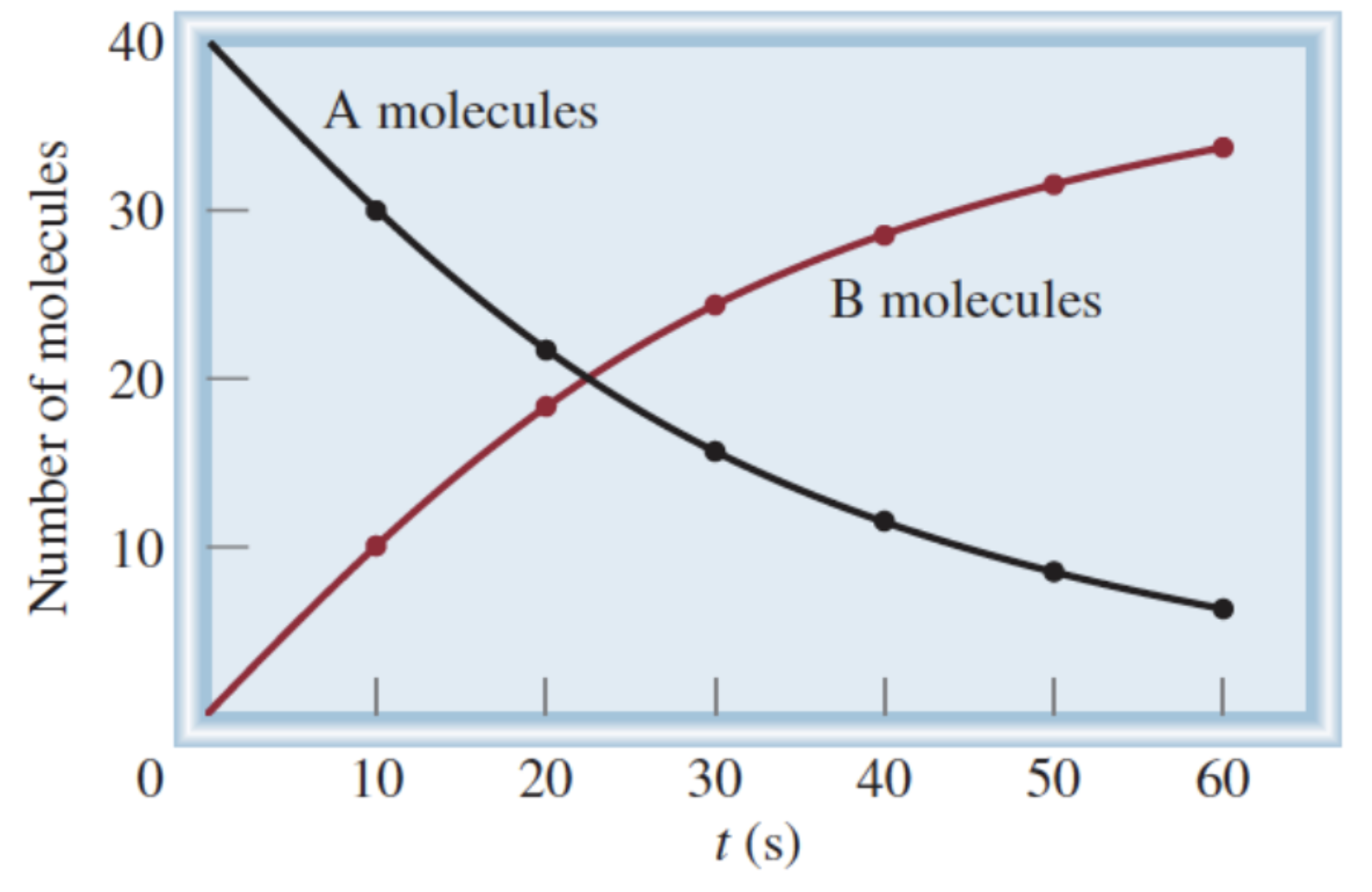
Formula for rate of B molecules:
(change in [B]) / (change in t)
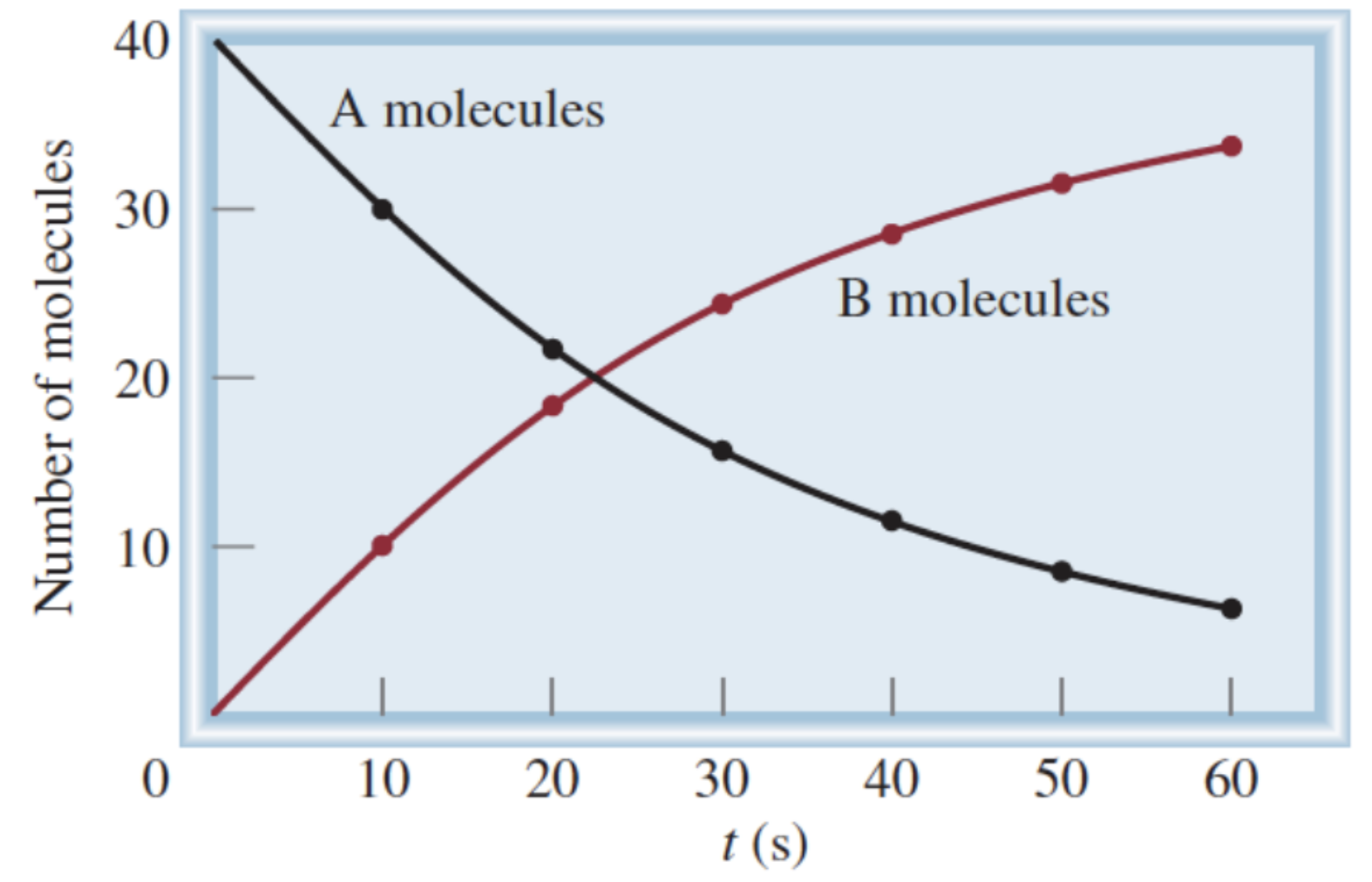
Why do we have a negative sign in the formula for calculating the rate of A molecules?
Change in [A] is a negative number, but rate is always a positive value
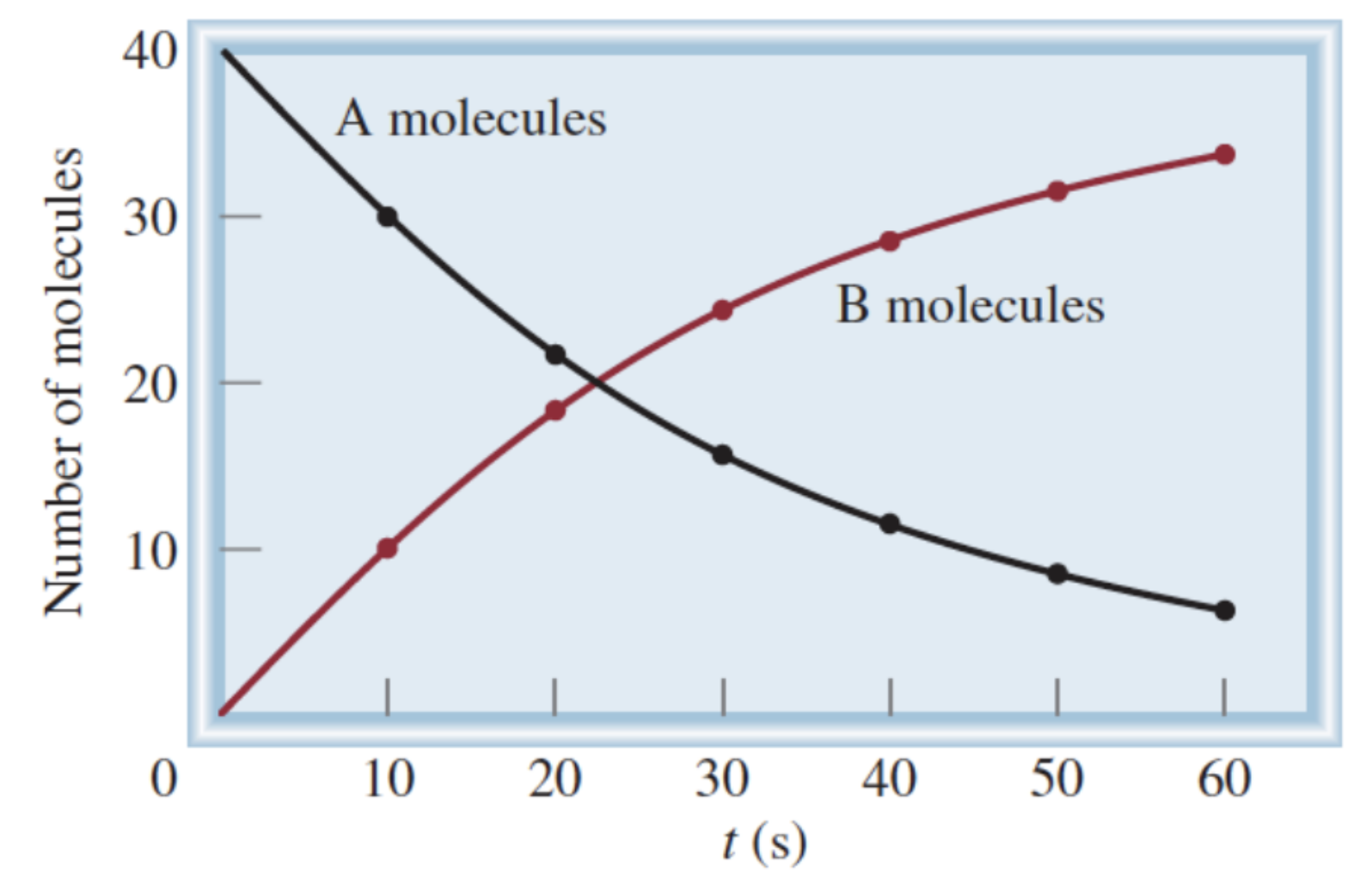
Why is change in [A] a negative number?
Amount of A is decreasing
How to calculate average reaction rate?
Change in a measurable quantity of a chemical species over change in time
Thionyl chloride is a ______ compound
Reactive
Thionyl chloride is used in:
A variety of organic synthesis reactions
Is thionyl chloride controlled?
Yes
What is thionyl chloride controlled under?
Chemical Weapons Convention in the United States
Why is thionyl chloride controlled under the Chemical Weapons Convention in the United States?
It has potential to release dangerous gases explosively on contact with water
Can thionyl chloride be decomposed in solution?
Yes
How can thionyl chloride be decomposed in solution?
By using an organic solvent
Reaction for decomposition of thionyl chloride:
SO2Cl2(solvent) → SO2(g) + Cl2(g)
Can the rate of a compound be calculated relative to other compounds in the reaction?
Yes
How can the rate of a compound be calculated relative to other compounds in the reaction?
By using the stoichiometric equation for the reaction
In a reaction with equimolar relationships, the calculated reaction rates of all the compounds are:
The same
Are reaction rates absolute values?
No
Why are reaction rates not absolute values?
They depend on chemical chosen
The chemical chosen to calculate reaction rates is usually the one that is:
The easiest to measure
Can units vary depending on the measurements being made?
Yes
Fe(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
What are the units of measurements possible when measuring reaction rates in this reaction?
Change in [HCl] over time, change in pH over time, Change in volume of H2 over time, Change in pressure of H2 over time, change in mass of H2 over time
Fe(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
How to measure change in [HCl] over time?
By titrating it
Fe(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Unit obtained when measuring change in [HCl] over time:
M/s
Fe(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
How to measure change in pH over time?
By using a pH meter
Fe(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Unit obtained when measuring change in pH over time:
pH units/s
Fe(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
How to measure change in volume of H2 over time?
By using a eudiometer
Fe(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Unit obtained when measuring change in volume of H2 over time:
mL/s
Fe(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
How to measure change in pressure of H2 over time?
By using a manometer
Fe(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Unit obtained when measuring change in pressure of H2 over time:
kPa/s
Fe(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
How to measure change in mass of H2 over time?
By using a balance in an open system
Fe(s) + 2 HCl(aq) → FeCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
Unit obtained when measuring change in mass of H2 over time:
g/s
Molecular bromine is ______ in color
Reddish-brown
Br2(aq) + HCOOH(aq) → 2Br-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + CO2(g)
What are the colors of the species in the reaction, other than molecular bromine?
Colorless
Br2(aq) + HCOOH(aq) → 2Br-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + CO2(g)
What happens to the concentration of Br2 as the reaction progresses?
Decreases
Br2(aq) + HCOOH(aq) → 2Br-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + CO2(g)
What happens to the color of Br2 as the reaction progresses?
Fades
Br2(aq) + HCOOH(aq) → 2Br-(aq) + 2H+(aq) + CO2(g)
The loss in color and concentration of Br2 as the reaction progresses can be monitored with a:
Spectrometer
A spectrometer registers the:
Amount of visible light absorbed by bromine
a A + b B → c C + d D
How can the average rate be calculated using each of the species?
-1/a x change in [A] over change in time
-1/b x change in [B] over change in time
1/c x change in [C] over change in time
1/d x change in [D] over change in time
Factors affecting reaction rate:
Increasing surface area of reactants, increasing concentration of reactants, increasing pressure of reaction, increasing temperature of reaction, using a catalyst in the reaction
Collision theory states that, for a reaction to occur, what must happen?
Particles must collide with the correct orientation and with sufficient energy
How do different factors affect the rate of reaction?
By affecting the frequency of particle collisions, and/or the proportion of collisions that have enough energy to react
How does increasing surface area change the frequency of collisions?
Increases
How does increasing surface area change the percent of successful collisions?
No change
Increasing surface area to increase reaction rate must be for what type of reactants?
Solid
How does increasing surface area of solid reactants increase frequency of particle collisions?
Number of particles exposed and available to react is increased
How does increasing concentration of reactants change frequency of collisions?
Increases
How does increasing concentration of reactants change percent of successful collisions?
No change
Increasing concentration of reactants to increase rate of reaction must only happen in:
Solutions
Why does increasing the concentration of reactants in solution increase rate of reaction?
There are a greater number of particles available to react
How does increasing pressure of reaction change frequency of collisions?
Increases
How does increasing pressure of reaction change percent of successful collisions?
No change
Increasing pressure of reaction to increase reaction rate must only happen in a reaction involving:
Gases
Why does increasing pressure of a reaction increase frequency of particle collisions?
Forces gas particles closer together
How does increasing temperature of reaction change frequency of collisions?
Increases
How does increasing temperature of reaction change percent of successful collisions?
Increases
Why does increasing temperature of reaction increase frequency of collisions and percent of successful collisions?
Kinetic energy of particles is increased
A catalyst provides an:
Alternate route for a reaction
The alternate route for a reaction provided by a catalyst has a:
Lower activation energy
Lower activation energy means that:
Particle collisions need less energy in order for a reaction to occur
Having a lower activation energy increases/decreases the rate of reaction
Increases