Embryonic Development
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Gestation
The period of time required for full development of a fetus in utero.
Stages and names for the embryo
First two weeks referred to as pre-embryonic stage.
A developing human known as an embryo during week 3-8.
Known as a fetus from the ninth week of gestation until birth.
Pre-implantation embryonic division
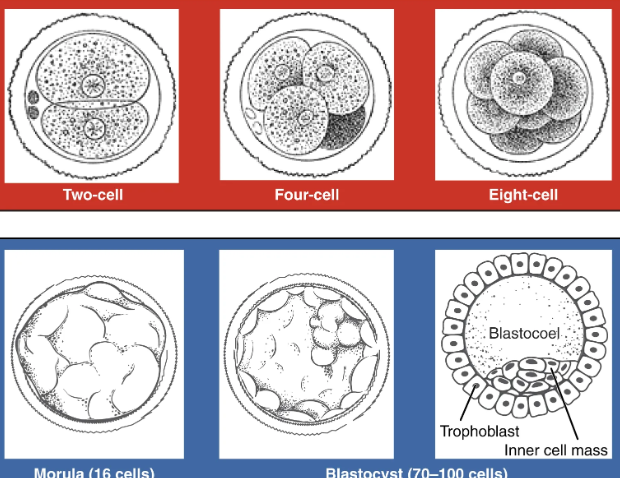
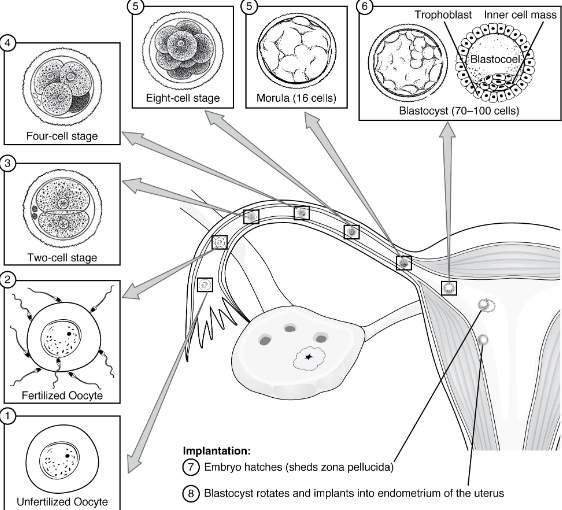
Conceptus continues toward the uterus by peristalsis and beating cilia of epithelial cells of fallopian tube. During the journey, the zygote undergoes five or six rapid mitotic cell divisions. Each cleavage results in more cells but not more volume.
Each daughter cell produced by cleavage is called a blastomere.
Conceptus
Name for zygote and associated membranes following fertilization.
Development of blastocyst
3 days post fertilization, the 16 cell conceptus reaches uterus. This structure is called a morula.
It continues to divide, creating a ball of 100 cells over a few days and feeding from uterine milk (nutritive endometrial secretions) while the uterine lining thickens.
This ball begins to secrete fluid, creating a fluid filled cavity called the blastocoel. It has now become a blastocyst
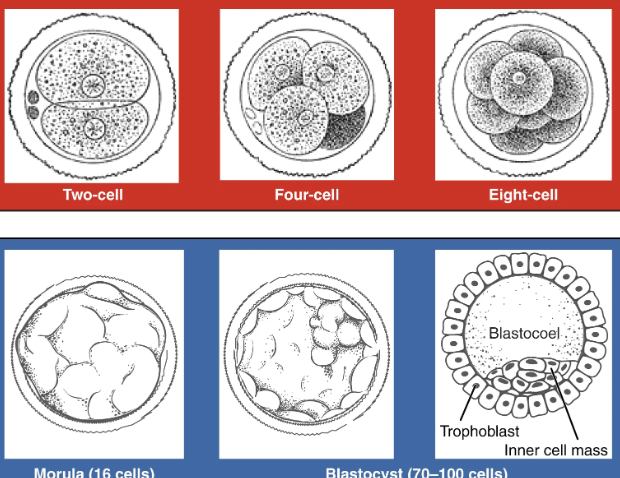
Organization of the blastocyst
Group of cells called inner cell mass are fated to become the embryo.
The cells forming the outer shell are called trophoblasts. These cells will develop into the chorionic sac and fetal portion of the placenta.
The inner mass of embryonic cells is totipotent. Each cell can differentiate into any cell type. Totipotency only lasts for a few days before the cells’ fates are set to become precursors.
Hatching
As the blastocyst forms, the trophoblast excretes enzymes that degrade the zona pellucida. The conceptus breaks free of the zona pellucida in preparation for implantation.
Implantation
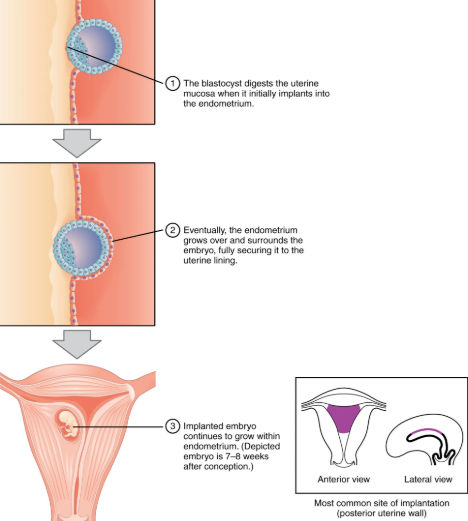
At the end of the first week, the blastocyst adheres to the uterine wall.
Implantation ends the pre-embryonic stage of development.
Implantation is accompanied by minor bleeding. The blastocyst implants in the fundus of the uterus or on the posterior wall. If endometrium not fully developed, the blastocyst will detach and find a better spot.
Failure of implantation
50-75% of blastocysts fail to implant. When this occurs, the blastocyst is shed with the endometrium during menses.
Successful implantation
When blastocyst adheres to endometrium, the superficial cells of the trophoblast fuse with each other, forming syncytiotrophoblast, a multinucleated body that digests endometrial cells to secure blastocyst to uterine wall.
The uterine mucosa rebuilds and envelops blastocyst. The trophoblast secretes human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). hCG accumulates in the maternal bloodstream and is excreted in urine.
Implantation is complete by middle of the second week, just days after implantation, atp the trophoblast has secreted enough hCG for positive pregnancy test result.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
Hormone that directs corpus luteum to survive, enlarge, and continue producing progesterone and estrogen to suppress menses.
Ectopic pregnancy
1-2% of cases, embryo implants outside the uterus or in a region that creates complications for the pregnancy.
Placenta previa
If the embryo implants in the inferior portion of the uterus, the placenta can grow over the opening of the cervix.