SBI 3UI Biology - Unit 1 Diversity of Living Things (Chapter 3)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/45
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
1
New cards
What essential services do fungi provide for ecosystems?
* decomposition
* recycling of nutrients
* soil maintenance
* recycling of nutrients
* soil maintenance
2
New cards
Characteristics of Fungi
* Eukaryotic
* Heterotrophic
* Multi-cellular (most)
* Typically not motile
* Have an alternation of generations (can reproduce sexually & asexually)
* Cells have cell walls made of chitin
* Most are terrestrial
* Feed via extracellular digestion
* Heterotrophic
* Multi-cellular (most)
* Typically not motile
* Have an alternation of generations (can reproduce sexually & asexually)
* Cells have cell walls made of chitin
* Most are terrestrial
* Feed via extracellular digestion
3
New cards
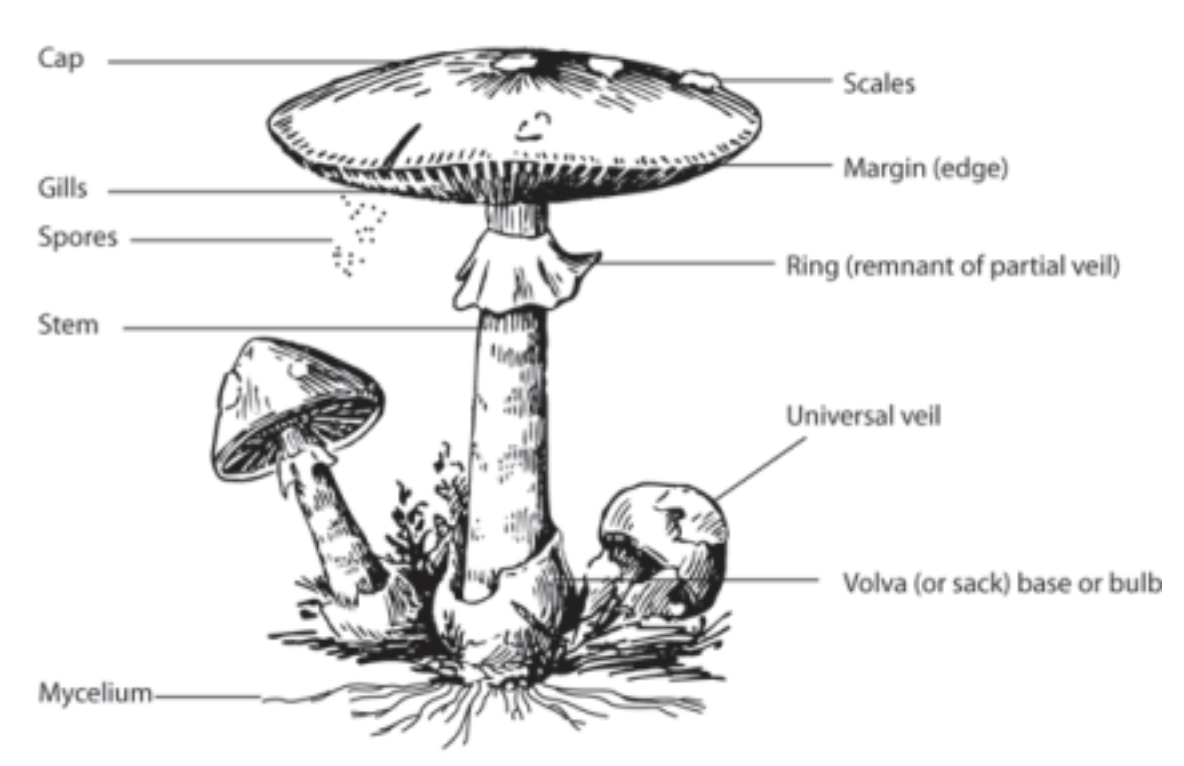
Fruiting Structure (Sporocarp)
The **above ground structure** that houses the spores
* Called the mushroom cap
* On the underside of the cap, spore-producing structures called **basidia** form on the mushroom’s **gills**
* Called the mushroom cap
* On the underside of the cap, spore-producing structures called **basidia** form on the mushroom’s **gills**
4
New cards
Basidia
Spore-producing structures found on the underside of the mushroom cap
5
New cards
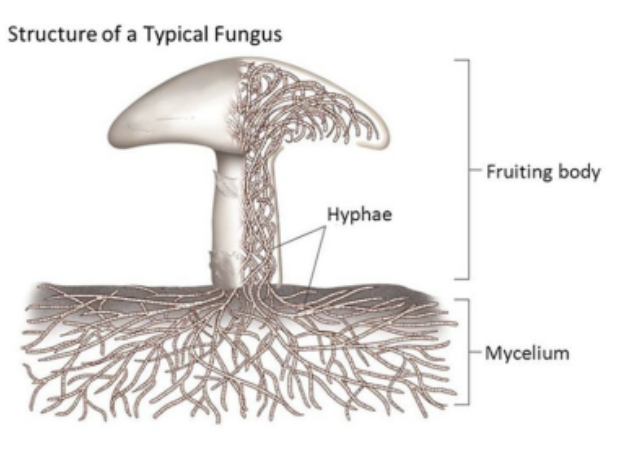
Body (structure of a club fungus)
The main structure of the fungus is located **below ground**.
* The body is a mesh-like structure, made up of a branching network of filaments that are collectively called **mycelium**.
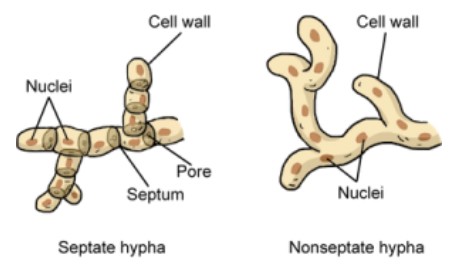
* The individual mycelium filaments are called **hyphae** (singular: hypha) The hyphae are microscopically thin. They consist of long tubes of cytoplasm containing many nuclei. The cell wall is composed of **chitin**
* The hyphae tubes are sometimes separated into cell-like compartments by cell walls called **septa** (singular: septum) The walls are not solid and contain large pores and the cytoplasm is therefore continuous from end to end
* The body is a mesh-like structure, made up of a branching network of filaments that are collectively called **mycelium**.
* The individual mycelium filaments are called **hyphae** (singular: hypha) The hyphae are microscopically thin. They consist of long tubes of cytoplasm containing many nuclei. The cell wall is composed of **chitin**
* The hyphae tubes are sometimes separated into cell-like compartments by cell walls called **septa** (singular: septum) The walls are not solid and contain large pores and the cytoplasm is therefore continuous from end to end
6
New cards
Mycelium
The body of a club fungus made up of a branching network of filaments
7
New cards
Hyphae
The individual mycelium filaments
* Consist of long tubes of cytoplasm containing many nuclei. The cell wall is composed of **chitin**
* Hyphae tubes are sometimes separated into cell-like compartments by cell walls called **septa**. Cells walls are not solid and contain large pores → cytoplasm is continuous
* Consist of long tubes of cytoplasm containing many nuclei. The cell wall is composed of **chitin**
* Hyphae tubes are sometimes separated into cell-like compartments by cell walls called **septa**. Cells walls are not solid and contain large pores → cytoplasm is continuous
8
New cards
Fungus Life Cycle
1. Mycelium of the body pushes above the ground to form the fruiting body. The mycelium fibres run up through the stem into the cap.
2. Spores are released. Each spore that is released is haploid (containing only one copy of each chromosome).
3. Spores grow and produce hyphae with one nucleus.
4. When two hyphae come in contact, two of their cells can fuse, forming a dikaryotic cell (a cell with two separate nuclei – the nuclei do not join)
5. The dikaryotic hyphae grows into mycelium which produces the mushroom cap when it is mature. Inside the basidia gills, the two haploid nuclei fuse forming a zygote. The zygote divides and produces 4 haploid spores.
9
New cards
Haploid
Contains only one copy of each chromosome
10
New cards
Dikaryotic cell
A cell with two separate nuclei
11
New cards
Symbiotic Relationships
Fungi + Trees (any plant)
Fungi + Trees (any plant)
* Fungi increases the surface area of the trees roots → tree is able to get more food and water
* The tree produces food in the leaves and sends it towards the roots → fungi can use as food
* The tree produces food in the leaves and sends it towards the roots → fungi can use as food
12
New cards
Symbiotic Relationships
Fungi + Cyanobacteria = Lichens
Fungi + Cyanobacteria = Lichens
* The fungus provides structural support, carbon dioxide, and water to the cyanobacteria
* The cyanobacterium shares its carbohydrates with the fungus
* The cyanobacterium shares its carbohydrates with the fungus
13
New cards
Zygospore Fungi (Zygomycota)
* Reproduce asexually & sexually
* during sexual reproduction produce **zygospores**
* Ex: Bread moulds
* during sexual reproduction produce **zygospores**
* Ex: Bread moulds
14
New cards
Club Fungi (Basidiomycota)
* Have short lived reproductive structures called **basidiocarps** (fruiting bodies) that form basidiospores
* Reproduce asexually by either budding or asexual spore formation
* Ex: Mushrooms, bracket, fungi, puffballs
* Reproduce asexually by either budding or asexual spore formation
* Ex: Mushrooms, bracket, fungi, puffballs

15
New cards
Sac Fungi (Ascomycota)
* Reproduce both sexually (forms sacs) and asexually (produces spores)
* Identified by fingerlike sacs called **asci** which form during sexual reproduction.
* In asexual reproduction, **spores** are produced at the tip of hyphae
* Ex: Mildews, morels, truffles, yeast
* Identified by fingerlike sacs called **asci** which form during sexual reproduction.
* In asexual reproduction, **spores** are produced at the tip of hyphae
* Ex: Mildews, morels, truffles, yeast

16
New cards
Imperfect Fungi
* Imperfect because they do not have a sexual phase
* Ex: Penicillium makes the drug penicillin, P. roquefort makes blue cheese, deuteromycetes used to make soya sauce, cyclosporine is a drug used in transplant patients
* Ex: Penicillium makes the drug penicillin, P. roquefort makes blue cheese, deuteromycetes used to make soya sauce, cyclosporine is a drug used in transplant patients

17
New cards
Characteristics of Animals
* Eukaryotic
* Cells have no cell wall
* Multicellular
* Heterotrophs that ingest food
* Mobile at some point in their life cycle
* Form a hollow ball of cells called a **blastula** during the embryological development
* Cells have no cell wall
* Multicellular
* Heterotrophs that ingest food
* Mobile at some point in their life cycle
* Form a hollow ball of cells called a **blastula** during the embryological development
18
New cards
Classifying Animals
Body Organization
Body Organization
* Specialized cells are organized into tissues, organs, and organ systems
* The development of nerves is a key early innovation important for coordinating movements and sensing changes in the environment.
* Members of the Porifera phylum (sponges) are the only animals that lack a nervous system and other tissue types.
* The development of nerves is a key early innovation important for coordinating movements and sensing changes in the environment.
* Members of the Porifera phylum (sponges) are the only animals that lack a nervous system and other tissue types.
19
New cards
Classifying Animals
Body (Germ) Layers
Body (Germ) Layers
There are three different layers of cells in a developing embryo that give rise to the specialized tissues:
* Ectoderm (outer layer e.g. skin, nervous system)
* Endoderm (inner layer e.g. lining of body cavity)
* Mesoderm (middle layer e.g. circulatory, reproductive, muscular systems)
* Ectoderm (outer layer e.g. skin, nervous system)
* Endoderm (inner layer e.g. lining of body cavity)
* Mesoderm (middle layer e.g. circulatory, reproductive, muscular systems)
20
New cards
Ectoderm
Outer layer (e.g. skin, nervous system)
21
New cards
Endoderm
Inner layer (e.g. lining of body cavity)
22
New cards
Mesoderm
Middle layer (e.g. circulatory, reproductive, muscular systems)
23
New cards
Classifying Animals
Coelom
Coelom
* Fluid-filled body cavity
* Allows for the development of more complex organ systems
* **Acoelomate** animals have a flattened body
* **Coelomate** animals have a body cavity in which complex internal organs can develop
* Allows for the development of more complex organ systems
* **Acoelomate** animals have a flattened body
* **Coelomate** animals have a body cavity in which complex internal organs can develop
24
New cards
Acoelomate
Animals that have a flattened body
25
New cards
Coelomate
Animals that have a body cavity in which complex internal organs can develop
* gives muscles a structure to brace against
* allows for the development of more complex organs
* gives muscles a structure to brace against
* allows for the development of more complex organs
26
New cards
Classifying Animals
Digestive Tract or Gut
Digestive Tract or Gut
* One opening (bag digestive system) (ex. hydra)
* Two openings (tube digestive system) (ex. earthworm)
* Two openings (tube digestive system) (ex. earthworm)
27
New cards
Classifying Animals
Body Symmetry
Body Symmetry
* **Asymmetrical**: Animals which have __no symmetry__ at all
* **Radial Symmetry**: Animals that are shaped like a c__ylinder or bowl__ in which their body parts are arranged around an __imaginary central axis__
* **Bilateral Symmetry**: Animals that have __mirror-image__ right and left sides. This is the most common type of symmetry. Animals have a distinct head and tail, back and bottom surfaces and two side surfaces.
* Many of these animals have numerous repeating body parts called **segments**
* The segments can become specialized for specific functions
* These animals also tend to have **paired limbs**
\
Animals that have bilateral symmetry also have **cephalization**, the location of the majority of the sense organs and nerve cells in the head region.
\
Bilaterally symmetrical animals are further divided into two major branches:
* **Protostomes**: During embryonic development the __mouth__ forms first
* **Deuterostomes**: During embryonic development the __anus__ forms first
* **Radial Symmetry**: Animals that are shaped like a c__ylinder or bowl__ in which their body parts are arranged around an __imaginary central axis__
* **Bilateral Symmetry**: Animals that have __mirror-image__ right and left sides. This is the most common type of symmetry. Animals have a distinct head and tail, back and bottom surfaces and two side surfaces.
* Many of these animals have numerous repeating body parts called **segments**
* The segments can become specialized for specific functions
* These animals also tend to have **paired limbs**
\
Animals that have bilateral symmetry also have **cephalization**, the location of the majority of the sense organs and nerve cells in the head region.
\
Bilaterally symmetrical animals are further divided into two major branches:
* **Protostomes**: During embryonic development the __mouth__ forms first
* **Deuterostomes**: During embryonic development the __anus__ forms first
28
New cards
Asymmetrical
No symmetry
* Ex. sponges
* Ex. sponges
29
New cards
Radial Symmetry
Animal’s body parts are arranged around an imaginary central axis
* Ex. starfish
* Ex. starfish
30
New cards
Bilateral Symmetry
Animals that have mirror-image right and left sides
* Ex. beetles
* Ex. beetles
31
New cards
Protostomes
During embryonic development the __mouth__ forms first
32
New cards
Deuterostomes
During embryonic development the __anus__ forms first
33
New cards
Invertebrates
* This group has the majority of animals (over 98%)
* They __do not have a backbone__
* Ex. leaches, clams, insects
* They __do not have a backbone__
* Ex. leaches, clams, insects
34
New cards
Vertebrates (Chordata)
* Have a notochord for at least part of their life cycle (a rodlike cord of cells that forms the main axial support i.e. backbone)
35
New cards
Agnathans
Jawless fishes
36
New cards
Gnathostomata
Jawed animals
37
New cards
Porifera
* None
* Acoelomate (flattened body)
* No Symmetry
* No Digestive System
* Filters nutrients from the environment
* No Nervous System
* No Respiratory System
* No Circulatory System
* Ex: glass sponge, commercial sponge
* Acoelomate (flattened body)
* No Symmetry
* No Digestive System
* Filters nutrients from the environment
* No Nervous System
* No Respiratory System
* No Circulatory System
* Ex: glass sponge, commercial sponge
38
New cards
Cnidaria
* None
* Acoelomate
* Radial Symmetry
* Bag Digestive System
* Hunts for food w/ tentacles around mouth
* Yes Nervous System
* No Respiratory System
* No Circulatory System
* Ex: jellyfish, sea anemone
* Acoelomate
* Radial Symmetry
* Bag Digestive System
* Hunts for food w/ tentacles around mouth
* Yes Nervous System
* No Respiratory System
* No Circulatory System
* Ex: jellyfish, sea anemone
39
New cards
Platyheminthes
* Protostomes (mouth forms first)
* Acoelomate
* Bilateral Symmetry
* Bag Digestive System
* Eat by catching food through their mouths
* Yes Nervous System
* No Respiratory System
* No Circulatory System
* Ex: flatworms, tapeworms, liverflukes
* Acoelomate
* Bilateral Symmetry
* Bag Digestive System
* Eat by catching food through their mouths
* Yes Nervous System
* No Respiratory System
* No Circulatory System
* Ex: flatworms, tapeworms, liverflukes
40
New cards
Nemotoda
* Protostomes (mouth forms first)
* Pseudocoelomate (body cavity isn’t fully lined but isn’t hollow)
* Bilateral Symmetry
* Tube Digestive System
* Gulps food whole and crushes in pharynx or slurps food through a “stylet” drinking straw
* Yes Nervous System
* No Respiratory System
* No Circulatory System
* Ex: roundworms, heartworm, human whipworm
* Pseudocoelomate (body cavity isn’t fully lined but isn’t hollow)
* Bilateral Symmetry
* Tube Digestive System
* Gulps food whole and crushes in pharynx or slurps food through a “stylet” drinking straw
* Yes Nervous System
* No Respiratory System
* No Circulatory System
* Ex: roundworms, heartworm, human whipworm
41
New cards
Annelida
* Protostomes (mouth forms first)
* Coelomate (have a body cavity in which complex internal organs can develop)
* Bilateral Symmetry
* Tube Digestive System
* Eats food w/ a mouth and takes food from decaying animals and plants
* Yes Nervous System
* Yes Respiratory System
* Yes Circulatory System
* Ex: earthworm, leeches
* Coelomate (have a body cavity in which complex internal organs can develop)
* Bilateral Symmetry
* Tube Digestive System
* Eats food w/ a mouth and takes food from decaying animals and plants
* Yes Nervous System
* Yes Respiratory System
* Yes Circulatory System
* Ex: earthworm, leeches
42
New cards
Molluscs
* Protostomes (mouth forms first)
* Coelomate (have a body cavity in which complex internal organs can develop)
* Bilateral Symmetry
* Tube Digestive System
* Have microscopic teeth that allow them to catch and hunt their prey
* Yes Nervous System
* Yes Respiratory System
* Yes Circulatory System
* Ex: snail. slug
* Coelomate (have a body cavity in which complex internal organs can develop)
* Bilateral Symmetry
* Tube Digestive System
* Have microscopic teeth that allow them to catch and hunt their prey
* Yes Nervous System
* Yes Respiratory System
* Yes Circulatory System
* Ex: snail. slug
43
New cards
Anthropods
* Protostomes (mouth forms first)
* Coelomate (have a body cavity in which complex internal organs can develop)
* Bilateral Symmetry
* Tube Digestive System
* Hunting for food or catching it in its web
* Yes Nervous System
* Yes Respiratory System
* Yes Circulatory System
* Ex: spider, crayfish
* Coelomate (have a body cavity in which complex internal organs can develop)
* Bilateral Symmetry
* Tube Digestive System
* Hunting for food or catching it in its web
* Yes Nervous System
* Yes Respiratory System
* Yes Circulatory System
* Ex: spider, crayfish
44
New cards
Echinodermata
* Deuterostome (anus forms first)
* Coelomate (have a body cavity in which complex internal organs can develop)
* Radial as adults, bilateral as larvae
* Tube Digestive System
* Attaches to and consumes prey
* Yes Nervous System
* No Respiratory System
* No Circulatory System
* Ex: starfish, sea urchin
* Coelomate (have a body cavity in which complex internal organs can develop)
* Radial as adults, bilateral as larvae
* Tube Digestive System
* Attaches to and consumes prey
* Yes Nervous System
* No Respiratory System
* No Circulatory System
* Ex: starfish, sea urchin
45
New cards
Chordates
* Deuterostome (anus forms first)
* Coelomate (have a body cavity in which complex internal organs can develop)
* Bilateral Symmetry
* Tube Digestive System
* Hunts and eats food, chews w/ hinged mouth
* Yes Nervous System
* Yes Respiratory System
* Yes Circulatory System
* Ex: dog, turtle, wolf
* Coelomate (have a body cavity in which complex internal organs can develop)
* Bilateral Symmetry
* Tube Digestive System
* Hunts and eats food, chews w/ hinged mouth
* Yes Nervous System
* Yes Respiratory System
* Yes Circulatory System
* Ex: dog, turtle, wolf
46
New cards
Rotifera
* Protostomes (mouth forms first)
* Pseudocoelomate (body cavity isn’t fully lined but isn’t hollow)
* Bilateral Symmetry
* Tube Digestive System
* Hunts and eats with a mouth
* Yes Nervous System
* No Respiratory System
* No Circulatory System
* Ex: prarotatoria, monogononta
* Pseudocoelomate (body cavity isn’t fully lined but isn’t hollow)
* Bilateral Symmetry
* Tube Digestive System
* Hunts and eats with a mouth
* Yes Nervous System
* No Respiratory System
* No Circulatory System
* Ex: prarotatoria, monogononta