Week 7 Renal Med Surg 2
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Kidney Function General
regulate extracellular fluid
excrete waste products
control BP
produce erythropoietin
Active Vitamin D
regulate acid-base balance
Glomerulonephritis general
Inflammation of the glomeruli!
3rd cause of ESRD
associated: kidney infection, nephrotoxic drugs, immune disorders, systemic diseases (SLE)
ACUTE
symptoms come and go, temporary or reversible!
Chronic
slowly progressive, leading to irreversible renal failure
Acute Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis (APG) General
Acute!, most common type of Acute GN
common in children, young adults, and adults x>60yrs old
develops 1-2 weeks after an infection of the tonsils, pharynx, or skin by nephrotoxic strains of group A B-hemolytic streptococci; form antibodies to streptococcal antigen
Strep throat (red throat, white lesions, etc)
Acute Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis (APG) Clinical Manifestations
Manifestations:
generalized edema, HTN, oliguria, hematuria, proteinuria, fluid retention!
not expected, indication of kidney damage
periorbital edema —> total body = ascites and peripheral edema
edema around the eyes
smoky urine (bleeding in upper urinary tract)
HTN (increased ECF volume)
abdominal or flank pain
can be asymptomatic; found on routine urinalysis
Acute Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis (APG) Diagnosis
Diagnosis:
H&P
Renal biopsy = confirmation!
Dipstick urinalysis and urine sediment microscopy
erythrocytes/casts
protein
BUN and serum creatinine renal impairments
HIGHER these labs = worse the kidneys
If GFR is lower = worse the kidneys
BUN normal range
10-20
Creatine Normal Range
0.6 - 1.2
GFR normal range
x > 90
Acute Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis (APG) Treatment
treatment
dependent on cause!
diet restriction
restrict diuretics!
kidneys are not working so diuretics won’t work
Rest!
Cause
streptococcal —> give antibiotics!
APG Diet Restrictions
Diet
limit protein and meat foods
limit fluids and sodium
Nephrolithiasis: Risk Factors
Kidney Stones
Risk factors
Metabolic
abnormalities —> increased pH, calcium, oxalate, uric acid
decreased citrate
Climate
warm —> fluid loss —> more concentrated urine
Diet!
increase tea&fruit juice oxalate
excessive protein increase uric acid
low fluid intake = urine more concentrated
Genetic
family hx
Lifestyle
immobile, obesity, sedentary
concentration of supersaturated crystals precipitate and form stones
reduce risk by keeping urine dilute and free flowing!
high in oxalate
nuts, leafy greens
Nephrolithiasis: Types
5 categories:
calcium oxalate
calcium phosphate
cystine
struvite (UTI)
Uric Acid
Calcium most common
Treatment based on what type of stones!
adjust diet or give antibiotics
Nephrolithiasis: Clinical Manifestations
First Symptom
Sudden, severe pain! renal colic
flank area, back, lower abdomen
ureter stretches, dilates, and spasms
can also see nausea and vomiting, dysuria, fever, chills, moist, cool skin
Common Sites of Obstruction
Ureteropelvic Junction (UPJ)
dull costovertebral flank pain or renal colic
Ureterovesical junction (UVJ)
lower abdominal pain; testicular or labial pain
Nephrolithiasis: Diagnostic Studies
Diagnostic Studies
noncontract helical (spiral) CT scan
Ultrasound
Urinalysis
24 hour urine
24 hour urine
For recurrent stones to measure calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sodium oxalate, citrate, cysteine, sulfate, potassium, uric acid, and total urine volume
for nephrolithiasis
retrieval and analysis of stones
Nephrolithiasis: Interprofessional Care
2 Interprofessional Care
Pain Management
acute attack
opioids, NSAIDs, alpha adrenergic blockers
Antibiotics
if indicated
Evaluate cause and prevent further development!
get H&P, attack the cause
Nephrolithiasis: Treatment and Patient Teaching
Treatment & Patient Teaching
Adequate hydration
NA restriction
Diet Changes
Drugs
can change the pH of urine, prevent excess urinary secretion of a substance or correct primary disease
Struvite stones: antibiotics
Nephrolithiasis: Treatment for Stones
Stone
4mm and less —> pass naturally @ HOME
can take weeks
stone has passed = decrease in pain, and urine must be strained to confirm it has passed
Surgery
if stones are too large
causes injury or infection
Symptoms
extracorporeal shock-wave lithotripsy (ESWL)
Nephrolithiasis: Nutrition Therapy
Nutrition Therapy
Obstructing Stone
adequate fluids to avoid dehydration
forcing fluids not recommended! can increase pain
After Stone Removal!
high intake of fluids (3L/day) = 2.5L urine/day
prevents supersaturation of minerals
reduce risk of dehydration
limit colas, coffee, and tea
Low Sodium Diet
Diet restrictions according to type of stone!
purine, calcium, oxalate
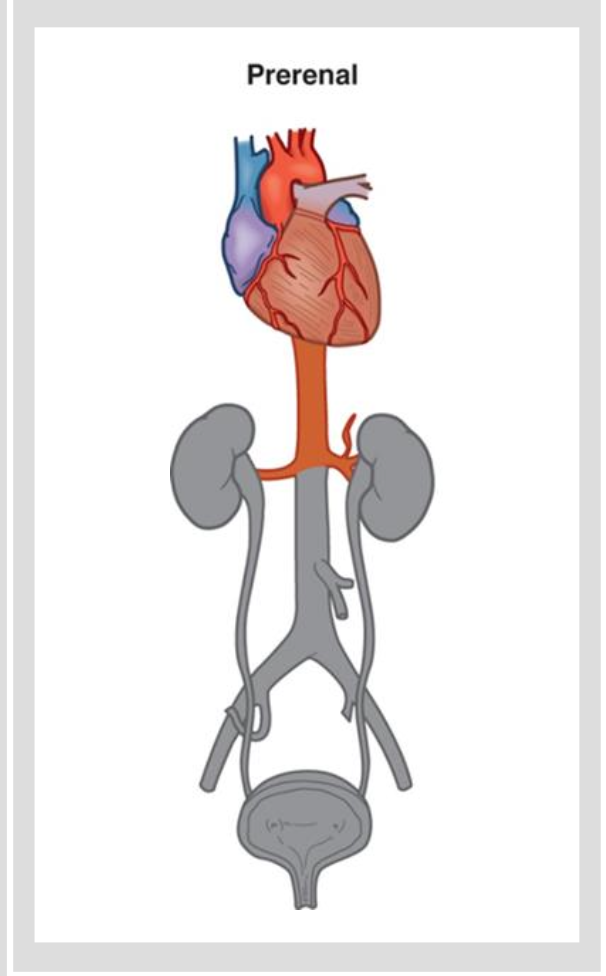
Acute Kidney Injury: Etiology and Pathophysiology Prerenal
Etio and Patho
Prerenal
causes are factors that reduce systemic circulation, causing a reduction in renal blood flow
severe dehydration, heart failure, decreased CO
Decreases glomerular filtration rate
causes oliguria
Autoregulatory mechanisms attempt to preserve blood flow
RAAS
Associated diseases
addisons
CHF
hypovolemic shock —> GI bleed
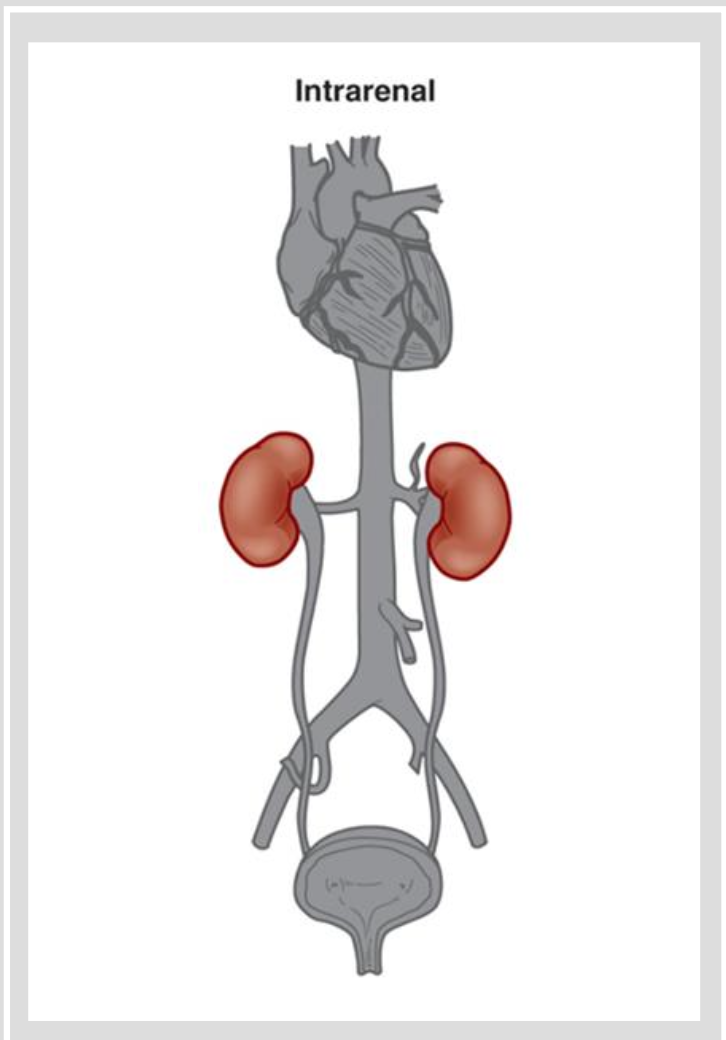
Acute Kidney Injury: Etiology and Pathophysiology Intrarenal
Etio and Patho
Intrarenal
causes include conditions that cause direct damage to kidney tissue
prolonged ischemia
nephrotoxins drugs
vancomycin
metformin
glycoside
oral contrast
chemo drugs
Hemoglobin released from hemolyzed RBC
Myoglobin released from necrotic muscle cells
Nephrotoxic Drugs
vancomycin
metformin
glycoside
oral contrast
chemo drugs
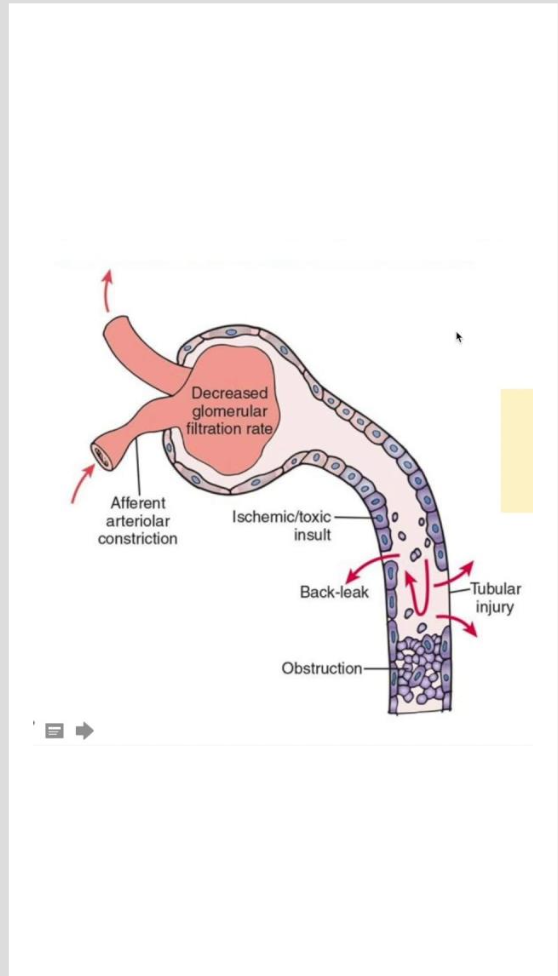
Acute Kidney Injury: Etiology and Pathophysiology Intrarenal ATN
Acute Tubular Necrosis
results from ischemia, nephrotoxins, or sepsis
severe ischemia causes disruption in the basement membrane
nephrotoxic agents cause necrosis of tubular epithelial cells
potentially reversible
If you know the cause —> stop the cause (TREATMENT)
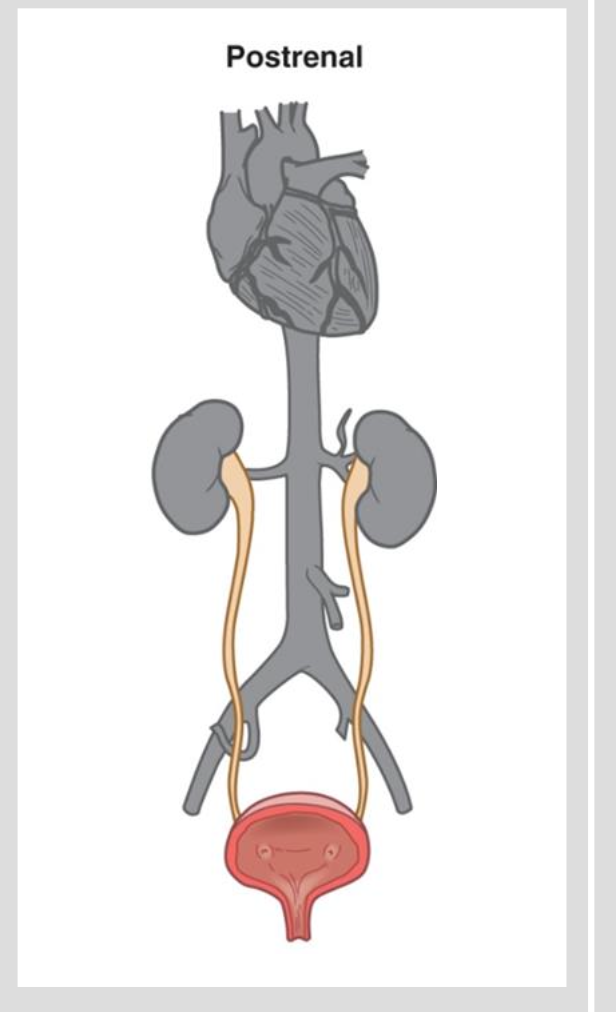
Acute Kidney Injury: Etiology and Pathophysiology Postrenal
Postrenal
causes include mechanical obstruction of outflow
lacerations
benign prostatic hyperplasia
prostate cancer
calculi
trauma!
extrarenal tumors
bilateral obstruction
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: General
Enlarged Prostate, non-cancerous
70% of men over 60 will have symptoms
hormonal changes associated with aging can contribute
digital rectal exam should be done regularly with older males and can diagnose BPH
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Manifestations
Manifestations
dribbling
sensation to go
oliguria
nocturia
distention
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Diagnostics
Diagnostic
PSA marker —> high case/risk
only way to diagnose = digital rectal exam
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Surgical Treatment
TURP with CBI
transurethral resection of the prostate
Post OP of TURP = can have issues with infection, incontinence, and bleeding
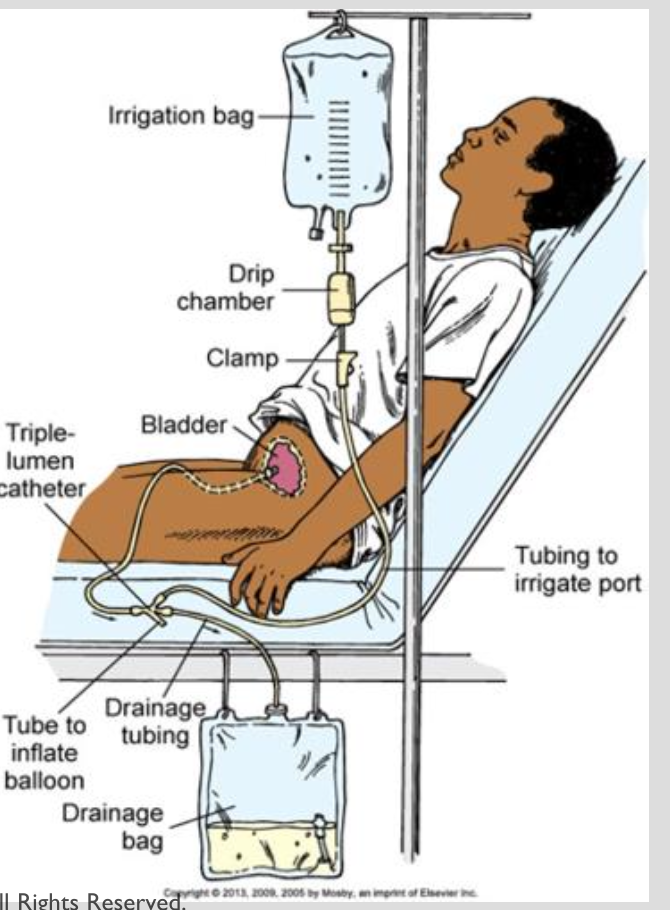
triple lumen catheter is useful for continuous bladder irrigation
can prevent infection and decrease risk of bleeding and clots
Need to take strict I&O’s
Expected
Hematuria!
Unexpected
A lot of serosanguinous blood
low VS —> hypovolemic shock —> call doctor
Acute Kidney Injury Phases
Oliguric —> Diuretic —> Recovery
Can turn into Chronic Kidney Disease if not handled
AKI: Clinical Manifestations Oliguric
Oliguric Phase
Urinary changes — oliguria
less than 400 mL/day
w/in 1-7 days after injury
lasts 10 to 14 days (longer + poor prognosis)
Urinalysis may show casts, RBCs, WBCs
AKI: Clinical Manifestations Oliguric Phase: Metabolic Acidosis
Metabolic Acidosis
impaired kidney cannot excrete H- ions
Serum bicarbonate is decreased!
Severe acidosis develops!!
Will show Kussmaul respirations: rapid, deep respirations in an effort to compensate by increasing the exhalation of carbon dioxide (acid)
Metabolic Acidosis
Increased H- ions
Bicarbonate is low
AKI: Clinical Manifestations Oliguric Labs
Labs
Sodium balance
increased excretion of sodium! —> hyponatremia
Potassium excess
Impaired ability of kidneys to excrete sodium —> hyperkalemia
usually asymptomatic
may have weakness
ECG changes
AKI: Clinical Manifestations Oliguric Hematologic & Waste & Neurologic
Hematologic Disorders
leukocytosis: result of infection
Waste Product Elimination
Elevated BUN and Serum creatinine levels (indicative of kidney injury) and low GFR
Neurologic Disorders d/t nitrogenous waste products in brain and nervous tissues
fatigue and difficulty concentrating
seizures, stupor, coma
AKI: Diuretic Phase Clinical Manifestations
Manifestations
Urine output —> 3L or 5L (polyuria)
dumping of electrolytes
increased urea concentrations —> osmotic diuresis
Monitor for hyponatremia, hypokalemia, and dehydration
give fluids and maybe electrolyte replacements
AKI: Recovery Phase
GFR increases, BUN and Creatinine decreases
First 2 weeks = major improvement!
Can take up to 12 months for kidney function to stabilize!!
Influenced by comorbidities
Older Adults affected, may not recover completely
AKI: Diagnostic Studies
Diagnostic Studies
thorough history
serum creatinine
Urinalysis
urine sediment containing abundant cells, casts, or proteins suggests intrarenal disorders
Kidney ultrasonography
kidney disease or obstruction
Renal scan
assess abnormalities in kidney blood flow, tubular function, and the collecting system
CT scan
identify lesions, masses, obstructions, vascular anomalies
Renal Biopsy
confirming intrarenal causes of AKI
AKI: Contraindicated Diagnostic Studies!
Contraindicated
MRI WITH CONTRAST MEDIUM
Magnetic Resonance ANgiography (MRA) with gadolinium contrast medium
Contrast-induced nephropathy (CIN)
Hyperkalemia Therapies
Temporary: move K+ into cells!
IV Insulin and Sodium bicarbonate
D50 stabilizes the blood glucose
Low Dysrhythmias — stabilizes myocardium
calcium gluconate
Remove K+ from body
Sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) or Patiromer (Veltassa)
Dialysis
AKI: Interprofessional Care Nutritonal Therapy
Nutritional Therapy
Maintain adequate caloric intake
mostly carbs and fat: prevent ketosis from endogenous fat breakdown and gluconeogenesis from muscle protein breakdown
Restrict Sodium: prevent edema, HTN, and HF
Increase Dietary Fat: non protein calories
Parenteral nutrition: if GI tract nonfunctional to provide adequate nutrition
AKI: Gerontologic Considerations
More susceptible to AKI
dehydration
hypotension
diuretic therapy
aminoglycoside therapy
obstructive disorders
surgery
infection
Chronic Kidney Disease General
leading cause
diabetes 50%
HTN 25%
goes undiagnosed until later stage
progressive, irreversible kidney damage —> pathologic abnormalities
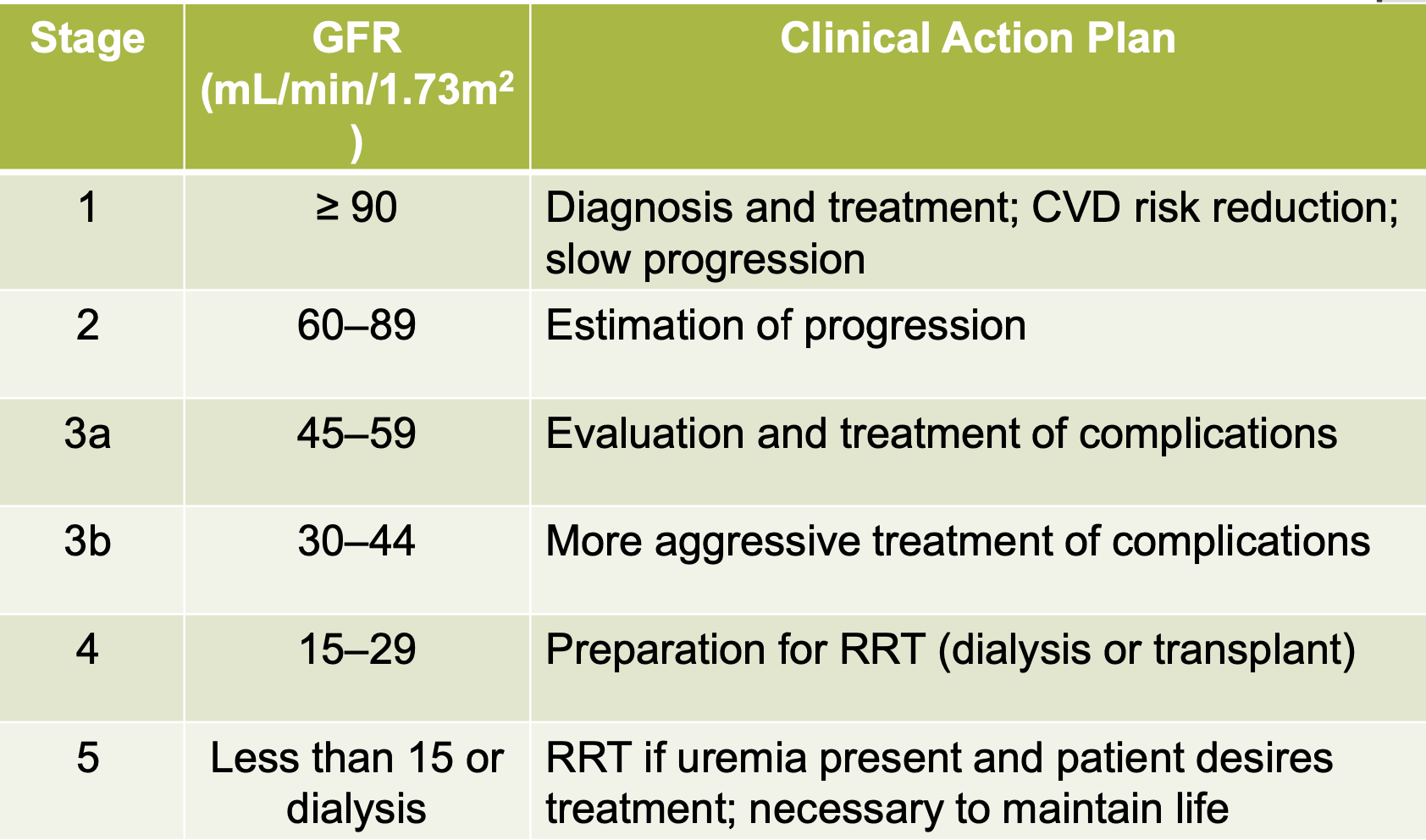
disease staging based on decrease in GFR
ESRD: x < 15 mL/min
Chronic Kidney Disease
stage
Chronic Kidney Disease: Clinical Manifestations
Uremia
syndrome in which kidney function declines to the point = systemic!
often occurs when GFR x<15mL/mi
Results of retained substances
urea, creatinine, hormones, electrolytes, water
CKD: Clinical Manifestations Neurologic System
Expected as kidney disease progresses
result of
increased nitrogenous waste products
electrolyte imbalances
metabolic acidosis
atrophy and demyelination of nerve fibers
CKD: Clinical Manifestations Cardiovascular System
Clinical Manifestations:
fluid overload
hyperlipidemia
HTN
dysrhythmias
heart failure
CKD: Clinical Manifestations Respiratory System
Resp System:
uremic halitosis
urine-like odor of the breath
shortness of breath
tachypnea
crackles
kussmaul respirations
CKD: Clinical Manifestations Hematologic System
Hematologic
anemia
decrease production of erythropoietin
decrease functioning of renal tubular cells
decreased iron stores
folic acid lost in dialysis
bleeding tendences!
defect in platelet function
CKD: Clinical Manifestations GI system
GI
cause: excessive urea!!
stomatitis with ulcerations
blood in stools
vomiting
constipation
CKD: Clinical Manifestations Integuementary System
Skin
pruritus
intense itching
blood loss or infection
uremic frost
urea crystalizes on skin
CKD: Clinical Manifestations Infection
Infection
changes in WBC function
altered immune response and function
hyperglycemia and external trauma
CKD: Clinical Manifestations Electrolyte/Acid-Base Imbalances
Metabolic Acidosis
results from kidneys impaired ability to excrete excess acid (primary ammonia)
defective reabsorption and regeneration of bicabonate
CKD: Diagnostic Studies
Diagnostic Studies
H&P
Dipstick evaluation of protein
urinalysis
renal ultrasound, scan, ct scan, biopsy
LABS
all mostly low
potassium usually high
CKD: Drug Therapies
Hypertension
ACE-inhibitors (-pril) and ARB agents (-tan)
not beta blockers, these meds help the kidneys
Anemia
erythropoietin (EPO)
iron supplements
folic acid sipllements
avoid blood transfusions
increase the development of antibodies
only cure is transplant, and multiple transfusions = rejection of transplant
Dyslipidemia
statins (atorvastatin)
fibrates (gemfibrozil)
Complications
drug toxicity
digoxin, diabetic agents
antibiotics
opioid medications
CKD: Nutritional Therapy
Nutritional Therapy
protein intake
fluid restriction
Sodium restriction
from 2 to 4 g/day
salt substitutes should be avoided
POtassium Restriction
2 to 3g / day
high potassium foods be avoided!
Dialysis: General
Two methods
peritoneal
hemodialysis
Gfr X < 15
blood is filtered and cleaned in a machine and ran back into the machine
Dialysis: Peritoneal Dialysis
Catheter through anterior abdominal wall —> peritoneal space
Aseptic technique!
BIGGEST COMPLICATION —> INFECTION!
peritonitis —> infection
Peritoneal Dialysis: Solutions and Cycles
3 Phase
can be done manually by gravity or by a machine
1- Inflow (fill): 2 to 3L over 10 minutes!
2- Dwell (equilibration): 20 to 30 minutes → 8 Hours
3- Drain: 15 to 30 minutes
Cycle is repeated
Called an exchange
volume depends on size of peritoneal cavity
Unexpected
cloudy —> infection
blood —> ripping/tearing
fecal matter —> tear in intestines
less drainage than what we put in
Expected
greenish brown color
more drainage than what we put in
Peritoneal Dialysis Complications
Complications
exit site infection
peritonitis
hernias
lower back problems
bleeding
pulmonary complication
protein loss
only kidney complication where we increase protein!
Peritoneal Dialysis Effectiveness of Chronic PD
Short training program
Advantages
simplicity
home based program
increasing patient participation
no need for special water systems
equipment set-up is relatively simple
Hemodialysis General
Vascular Access sites
types of access
arteriovenous fistulas and grafts
temporary vascular access
Fistula and Graft
combining a vein and an artery
hear a bruit
same thing except another device combines them
has a thrill
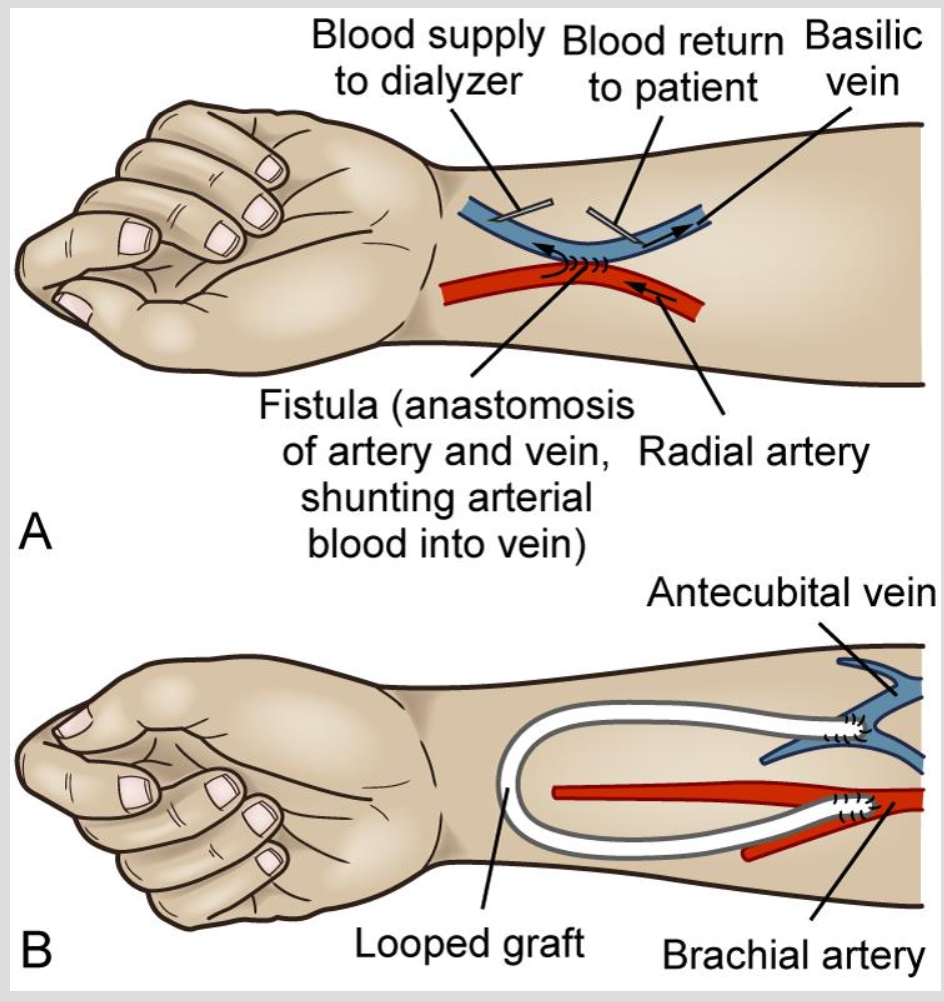
Hemodialysis Procedure
two needles placed in fistula or graft
pulls blood from circulation to HD machine
used to return dialyzed blood to the patient
Heparin is added to prevent clotting
BIGGEST COMPLICATION: HYPOVOLEMIA
Hemodialysis Pre Procedure
Before
assess fluid status
weight, BP, peripheral edema, heart and lung sounds
weight from last postdialysis and current
assess vascular access
assess temperature
monitor VS every 30 to 60 minutes
Hemodialysis Settings and Schedules
Majority treated at an outpatient center
dialyzed for 3 to 4 hours
3 days per week
Other schedule options
short daily HD
Long nocturnal HD
home HD
Kidney Transplant
live (27%) or deceased (73%) donors
monitor patient after procedure for fluid and electrolyte imbalance
hydration is key!
placed on immunosuppressive therapy for live to prevent rejection!
infection is a high risk!!
contraindications
advanced cancer, refractory/untreated herat disease
chronic respiratory failure, extensive vascular disease
chronic infection
unresolved psychosocial disorders
HIV+ or hep B or C are not contraindicated