AQA A level Chemistry 3.3.15: NMR
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
What does NMR stand for? (1)
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.
What is NMR used for? (1)
To deduce the entire chemical structure
Why are analytical techniques important in confirming new compounds? (1)
They provide precise molecular information
How does carbon-13 NMR differ from proton NMR? (1)
Carbon-13 NMR gives simpler spectra as carbon atoms do not exhibit splitting from adjacent atoms
Why is the delta scale used for in NMR spectroscopy? (1)
- It is used to record chemical shift
- Measuring the resonance frequency relative to a standard
What can be found using NMR spectroscopy? (4)
- The number of proton environments by how many peaks.
- How many hydrogens in a nearby environment by peak splitting.
- How many hydrogens in that environment by the integration ratio.
- Information about the nature of the environment by the chemical shift.
For proton NMR, what must be remembered? (1)
If a carbon isn't attached to a hydrogen, don't consider it when counting the number of environments
How do you use IR and NMR spectroscopy to deduce a molecule? (3)
1. Work out the empirical and molecular formula.
2. Use IR spectroscopy to identify the main groups.
3. Use NMR spectroscopy to give details of the carbon chain
Why do hydrogen atoms on neighbouring carbons affect resonance? (1)
They create their own magnetic fields, impacting the resonance conditions of protons
What is the integration trace in NMR? (1)
It gives the relative number of hydrogens in each environment.
What is Carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy? (2)
- Works the same as proton NMR but detects C-13 nuclei.
- Provides the number and type of carbon environments but is less reliable
What is chemical shift in NMR? (4)
- Measured in ppm with a standard of 0 from Si(CH3)4.
- More shielding reduces the chemical shift.
- Electrons around hydrogens create a shielding effect.
- Thinned electrons (e.g., near an electronegative O) cause a smaller magnetic field.
What is the (n+1) rule? (1)
Peak splitting = Number of hydrogens on neighbouring carbons + 1
How does the molecular environment affect chemical shift? (1)
Highly electronegative atoms deshield the nucleus, increasing the s-value.
What are the rules for proton NMR when deducing a molecule? (4)
1. Number of peaks.
2. Chemical shift.
3. Integration trace (ratios).
4. Splitting pattern.
How does resonance occur in NMR? (2)
- Protons flip between high and low energy orientations under the right magnetic field strength and radio-frequency.
- Absorption peaks are produced during resonance
How is NMR spectroscopy prepared? (3)
1. Dissolve the sample in an inert solvent (e.g., CCl4 or CDCl3).
2. Use solvents with no H atoms.
3. Deuterated solvents like CDCl3 can be used.
Why must the sample be dissolved in an inert solvent for NMR? (1)
The solvent contains no protons, so it doesn't create interference peaks
What solvents are used for NMR spectroscopy? (3)
- TMS.
- CCl4 (non-polar, for non-polar organic molecules).
- CDCl3 (polar, for polar organic molecules).
How does NMR spectroscopy work? (3)
- Hydrogen nuclei act as spinning protons with a magnetic field.
- When placed in a magnetic field, hydrogen nuclei align along magnetic force lines.
- High-energy orientation is achieved by absorbing photons
What is meant by equivalent hydrogen environments? (1)
Both carbon groups give the same peak in the spectrum
Draw a table to show NMR peak splitting patterns (4)
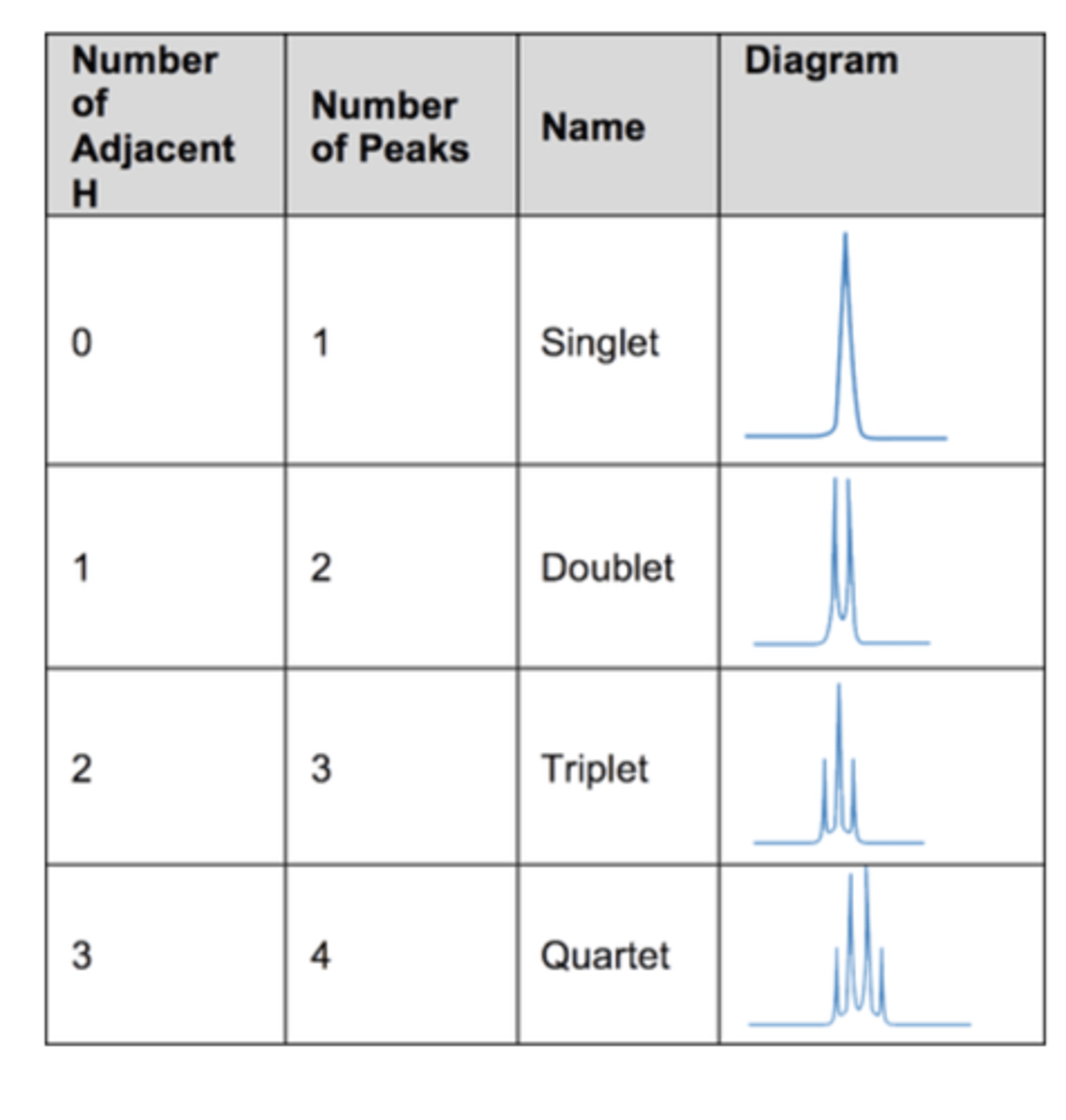
What does singlet peak splitting mean? (1)
No adjacent hydrogen environments
What does doublet peak splitting mean? (1)
1 adjacent hydrogen environment
What does triplet peak splitting mean? (1)
2 adjacent hydrogen environments
What does quartet peak splitting mean? (1)
3 adjacent hydrogen environments
What is tetramethylsilane (Si(CH3)4) used for? (1)
It acts as a standard in NMR as it produces a single peak
Why is TMS used, and why is it suitable? (6)
- Produces one signal.
- Signal is away from other H signals.
- Strong signal allows for a small amount of sample.
- Non-toxic.
- Inert.
- Low boiling point, easy removal from the sample.