ITSS 4370 ITCMF part 1
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
IT management and governance
How decisions are made about adoption, investment, implementation, and deployment of information technology within organizations.
Organizational perspectives on planning and implementation.
Uses the Critical Capabilities of the IT-CMF and ITIL as framework for organizing discussion
Trend from the Field
Focus on Customer Service and the Business
Adapt or Die – keep up with new technologies
Growth in Demand WITH flat or declining budgets
IT as an operational expense
Flattening of the IT Organization
organizing for systems management
IT Organization Design Factors
Infrastructure Design Factors
Infrastructure Departments with Alternative Locations
IT Organization Design Factors
Departmental Responsibilities
Planning Orientation
Infrastructure Processes
Basic IT organization
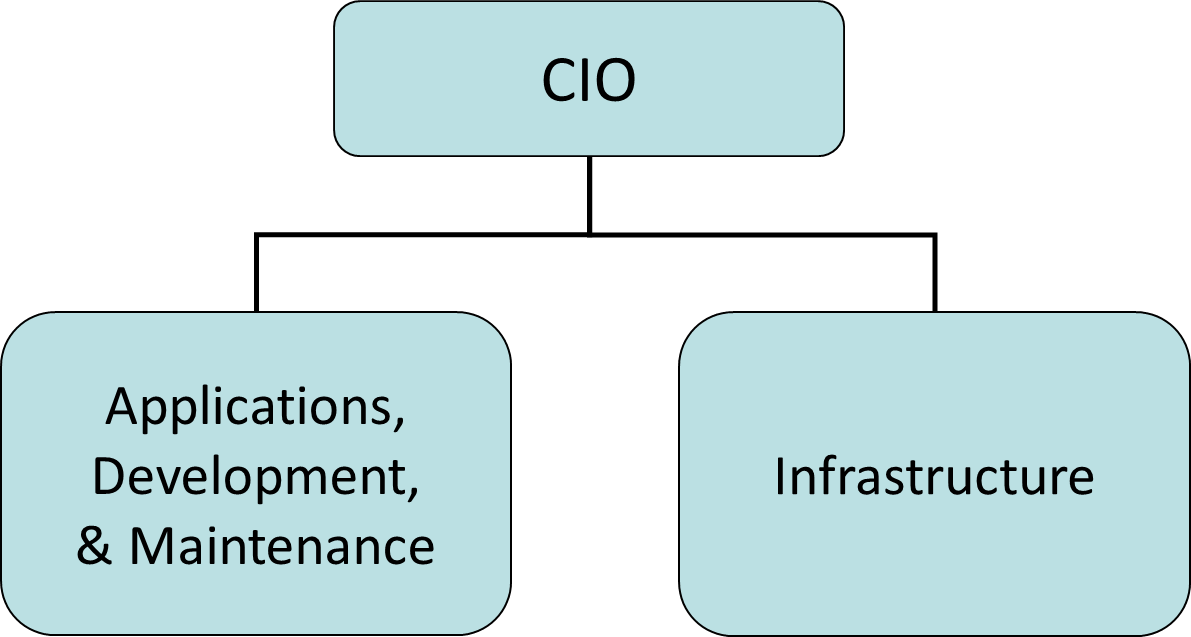
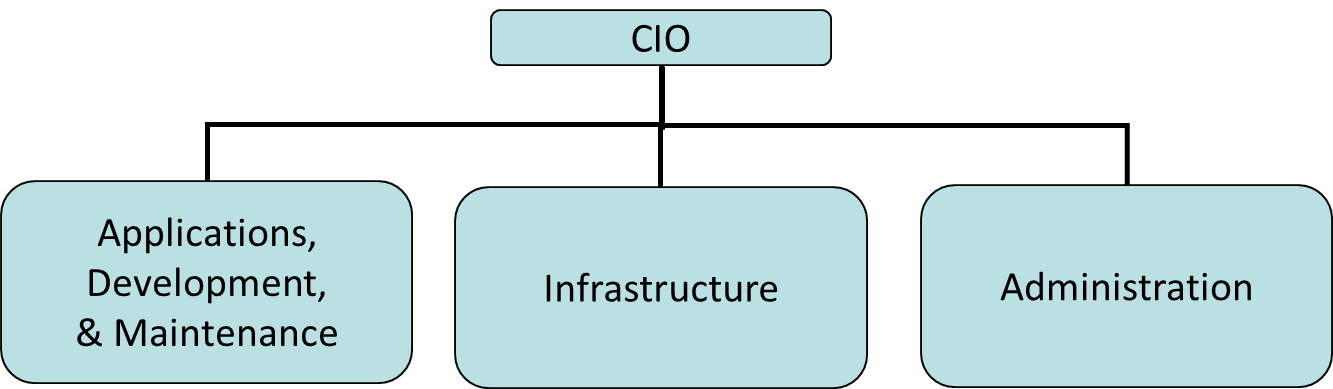
Basic IT Organization with Administration
what does IT CMF define and deliver
business aligned IT improvement strategy based on capability management
what is capability underpinned by
competencies of individuals
capability(org level)
is the organization’s ability to readily mobilize (integrate, reconfigure, acquire, release) resources (tangible and intangible) towards achieving specific outcomes1
Competency (Individual Level)
the demonstrated ability of the individual to apply knowledge, skills, behavior, and attitudes for achieving observable results2
Enterprise IT Capability
is an integration of people (roles), processes, and organizational structure technology that provides IT Services in alignment with strategic intent and investment allocation1.
IT CMF defines IT capability as
the systematic mobilization of IT resources in support of targeted outcomes.
systemic mobilization
integration reconfiguration gain and release
IT based resources
tangible
intangible
tangible
financial physical infrastructure and human assets
intangible
software, data, intellectual property, branding, culture
IT capability within IT CMF is further defined as
consisting of 37 capability building blocks that an organization needs to develop and mature to constantly deliver business value from its IT resources in support of it business goals
IT Capability comprises the
People
Process
Intellectual
Technology resources
IT Capability is the range of potential output and deliverables from the IT function to the business:
What IT can ‘do’ for the business
Communicated in a common business language
When IT capability is mature, it is understood by business executives, becomes a differentiator in the enterprise, an is integrated into overall corporate strategy
how is IT performance measured
by the business value that the IT organization (and IT itself) can deliver for an organization. This includes IT as a strategic options generator, enabling the business to react quickly to new business opportunities and respond with innovative IT solutions.
Context for defining IT Business Value and Business Benefits: Five Principles1
IT Has No Inherent Value.
Benefits arise when IT enables people to Do Things Differently.
Only the Business - that is, all of an organisation’s managers and individual contributors can release the potential Business Benefits and Business Value of IT.
All IT projects have outcomes, but not all outcomes are benefits.
Benefits must be actively managed for value be obtained.
A process view of IT value generation1
IT’s impact on intermediate business processes on activities in an organisation’s value chain
Management of information
automational effects
The efficiency perspective of value deriving from the role of IT as a capital asset substituting labour, administration and other costs. Here, value results from impacts such as labour savings, productivity improvements, and cost reductions.
informational effects
Emerge from IT’s capacity to collect, store, process, and disseminate information. Value accrues from improved decision quality, decreased use of resources, enhanced organisational effectiveness better quality, and employee empowerment.
transformational effects
The value deriving from IT’s capability to faciliate and support process innovation and transformation. The business value associated with these effects manifests as improved revenue, increased agility, and product enhancement as a result of re-designed organisational structures
IT-CMF defines IT Business Value as
The contribution that IT‐based resources and capabilities make to helping an organization achieve its objectives.”
IT Business Value is captured by
organizing and managing IT such that the potential business benefits arising from the use of IT are actually realised. realized
The realization of IT Business Value and Business Benefits depends on
business changes as well as technology
gaining commitment to achieving the benefits
enabling the success of the IT investment to be judged objectively, based upon relevant and appropriate evidence2
real world benefits of using IT CMF
improvements in it capability and reduction in overall spend
savings in total operating budget for tech innocation and savings of total budget for experiment execution
reduction in set up working time for new servers
IT-CMF is a key measure to track performance over time... Training and certifying senior staff in IT-CMF has significantly improved the quality and consistency of BP’s work
IT-CMF
A strategic partnership between IT and the organization-at-large to unlock the business value of IT
Hierarchy of IT-CMF Artifacts
IT CMF
Macro Capability
Critical Capability (CC)
CC Category
Capability Building Block (CBB)
Practice outcome Metric POM
IT-CMF is comprised of four Macro Capabilities
managing it like a business
managing the IT budget
Managing IT for business values
Managing the IT capability
Managing IT Like a Business
shifting the focus from technology as an end to itself towards the customers and the business problems to which IT can provide solutions
what supports the 4 macro capabilities of IT CMF
the 37 critical capabilities
managing the IT budjet
A proactive and explicit strategy for finding a sustainable economic model for IT products and services.”
Managing the IT Capability
What IT can do for the organization... Includes the knowledge, skills, tools, processes, abilities, and motivation available in the IT department to support or perform enterprise business activities.”
Managing IT for Business Value
An integrated process of selecting and implementing investments in IT that will likely bring the highest value to the organization
IT-CMF Critical Capabilities (CCs)
represent the key activities and procedures that must be defined and controlled to enable an IT organization to plan and deliver IT solutions, and to measure the business value outcomes of its initiatives and daily activities
Each CC defines a particular
domain, function, set of processes, or roles within the IT organization
Each CC refers to a specific set of integrated activities required to deliver specific outcomes in support of value creation
Behaviours
Actions
Methods
Metrics
each critical capability has what to support it?
rich documentation
Managin IT for business value (critical capabilities)
BAR: benefits assessment and realization
PPM: project portfolio management
TCO: total cost of ownership
BAR Value
The Benefits Assessment and Realization (BAR) capability helps an organization forecast and manage the realization of benefits from IT-enabled change initiatives
BAR Goal
The Benefits Assessment and Realization (BAR) capability aims to forecast, crystalize, and sustain the business benefits arising from IT-enabled change initiatives.
BAR
is the ability to establish an outcomes focus for the selection and management of IT-enabled business change initiatives to ensure that their potential value is delivered. BAR addresses the cultural and behavioural change needed to create and to sustain value from those initiatives. In this way, BAR ensures that business benefits are planned, dynamically adjusted, and actually achieved.
Bar Covers
Increase organizational awareness, understanding, and commitment to creating a value mind-set/culture and sustaining value from IT-enabled business change across the full life cycle of the investment.
Promote the message that benefits do not come from technology itself, but rather from the change that technology shapes and enables.
Manage how organizational change is effected to achieve business benefits.
Focus management on outcomes of IT-enabled change initiatives and measurable benefits rather than on change activities.
Create a common language for describing business benefits from IT.
Promote understanding of the potential business benefits from innovation, collaboration, flexibility, and agility enabled through the adoption of digital technologies and approaches.
Optimize the flow of benefits to support the organization‘s strategy
BAR key artifacts
Library of business value indicators
Benefits plan
A business case template
A benefits dependency map
PPM VALUE
helps ensure that the status of project portfolio components (projects, programmes, or sub-portfolios) is closely tracked to support early identification of potential issues and to minimize program delivery conflicts.
BAR Goal
aims to monitor and report on the status of an investment portfolio of IT programs
Project Portfolio Management PPM
Ability to select, approve, and balance project portfolio components (projects, programmes, or sub-portfolios) to deliver the organization’s strategic objectives and its operational needs.
Managing the project portfolio will prioritize, monitor, track, analyse, report, and as necessary, terminate project portfolio components that plan to, or that currently consume organizational resources.
PPM alignment with strategic Objectives
Alignment with strategic objectives
Performing due diligence by ensuring that the organization has a shared understanding of and commitment to the execution of its strategic objectives.
Identifying paths and progression steps for the delivery and execution of the organization’s strategic objectives.
Establishing an agreed quantitative model to assess and provide clarity on the strategic contribution that project portfolio components make to strategic objectives.
Responding to any changes in the organization’s strategic direction.
Assessing and prioritizing programmes and projects based on their alignment with business objectives and operational needs.
PPM Oversight and management
Oversight and management
Managing portfolio risk.
Managing portfolio communications.
Monitoring and tracking of the progress and impact of programmes, within the portfolio.
Reviewing the programmes in the portfolio for adherence to the original business case.
Maintaining an up-to-date portfolio status, including any deviations beyond a defined threshold on progress and expected impact.
PPM Operational
Establishing a governance model that facilitates flexible control and management of the projects’ portfolio.
Prioritizing and authorizing project portfolio components, and establishing a running order in which they are to be executed.
Responding to any positive or negative changes in the expected benefits of the project portfolio components.
Approving and terminating portfolio components in accordance with the governance model and the charters of the specific project portfolio components.
PPM People/leadership/Resource
Identifying and involving key personnel in selecting programmes and projects.
Providing and maintaining leadership and inspiration for the duration of the portfolio which may span multiple years or even decades.
Maintaining oversight of financial, people, and technical resources.
Providing a suite of tools and appropriate infrastructure to support staff to successfully deliver the portfolio’s objectives
PPM key artifacts
Portfolio reporting
Portfolio dashboard
Scenario analysis models
TCO Value
capability analyses the life cycle costs associated with IT assets and IT-enabled business services. It facilitates investment selections, drives service improvements, and helps control costs.
TCO goal
aims to collect, analyze, and disseminate data on all costs associated with an IT asset or IT-enabled business service throughout its life cycle, from initial acquisition, to deployment, operations, and maintenance, to its eventual removal.
Total cost of ownership TCO
Ability to identify, compare, and control all direct and indirect costs associated with IT assets and IT-enabled business services
TCO covers
Identifying and analyzing IT costs across asset and service life cycles, from acquisition to operations, enhancements and end of life
Identifying all costs that both directly and indirectly affect the bottom line – including, for example, hardware and software acquisition, management and support, communications, training, end-user expenses, opportunity costs of downtime and other productivity losses
Establishing a common methodology for comparing costs within and across IT assets, processes and services
TCO key artifacts
Total cost of ownership policy and models
Cost tracking database
Configuration management database (CMDB)
Managing IT like a business (capabilities)
accounting and allocation
business planning
business process and management
capacity forecasting and planning
demand and supply management
enterprise information and management
governance
green IT
leadership
innovation management
organizational change management
organization design and planning
risk management
service analytics and intelligence
sourcing and supplier management
strategic planning
Accounting and allocation value
capability assigns costs of IT services proportionally and transparently to the users of those services, improving cost awareness and responsible usage behaviours.
Accounting and allocation goal
aims to allocate the consumption of IT services to business units and to calculate the associated costs for chargeback/showback purposes.
Accounting and allocation
Ability to define and manage the policies, processes and tools used for calculating the costs of IT and distributing them across the organization.
Accounting and allocation covers
Establishing policies for measuring the consumption of IT services by business units and for the chargeback/showback of associated IT costs to those units
Managing how the chargeback/showback for IT service consumption is allocated
Influencing the demand for IT services
Accounting and allocation Key artifacts
IT accounting model
Chargeback/showback model
IT services catalog
Business Planning Value
links the IT strategy with operational delivery. It enables the development of multi-year investment roadmaps and plans to ensure that the IT strategy is successfully implemented.
Business Planning Goal
capability aims to link the IT strategy with IT operational planning. It represents the next level in planning detail following on from defining the IT strategy, ensuring that the necessary financial and other resources are allocated for implementation.
Business Planning
Ability to produce an approved document that provides implementable detail for the IT strategy, setting out the IT function’s tactical objectives, the operational services to be provided, and the financial and other resources and constraints that apply in the coming planning period
Business Planning Covers
Allocating responsibility to specific employees for IT business planning
Managing appropriate financial and non-financial resources and their capacities for ongoing IT business planning activities
Specifying the requirements for each activity in the IT business plan
Seeking support of relevant stakeholders for the IT business plan
Reviewing the IT business plan against actual performance
Business Planning key artifacts
IT business plan
Business-as-usual (BAU) commitments database
Comprehensive requirements catalog
Business Process Management Value
helps to make business activity flows more effective, more efficient, and more responsive to evolving business objectives.
Business Process Management goal
capability helps create an understanding of business activity flows so they can be more readily understood and developed, and so that errors can be reduced and risks mitigated.
Business Process Management
Ability to identify, design, document, monitor, optimize, and assist in the execution of both existing and new organizational processes
Business Process Management covers
Implementing process improvement initiatives and driving cultural change for business process improvement
Selecting, developing, and applying methods governance models, technologies, and skills, roles, and communications materials that support the organization’s processes
Developing and applying graphical representations of processes
Adopting technologies that automate and assist with business process management
Business Process Management key artifacts
BPM policy
BPM governance model
BPM technology (suite)
Business process model and notation
Capacity Forecasting and Planning Value
capability anticipates the shifting needs for IT resources so that capacity can be cost-effectively added or reduced in a timely manner to meet changes in demand.
Capacity Forecasting and Planning Goals
capability aims to understand what resources will be required to support IT services based on current and projected organizational demands
Capacity Forecasting and Planning
Ability to model and forecast demand for IT services, infrastructure, facilities and people
Capacity Forecasting and Planning covers
Collecting capacity-related strategic and operational information
Designing and advancing IT capacity forecasting models
Modeling the current and future capacity requirements across all IT resources
Using forecasting models to determine the impact on IT resources of business forecasts
Communicating insights from capacity planning to relevant stakeholders
Capacity Forecasting and Planning key artifacts
IT forecast plan
IT utilization reports
Capacity Management Information Systems (CMIS)
Capacity forecasting models and modeling tools
Demand and Supply Management Value
The Demand and Supply Management (DSM) capability can improve the business value that IT services deliver by reducing or eliminating supply surpluses and missed fulfillment opportunities.
Demand and Supply Management Goals
The Demand and Supply Management (DSM) capability aims to balance the business demand for
IT services and the supply of those services.
Demand and Supply Management
Ability to manage the IT services portfolio in such a way that there is a balance between the demand for and the supply of IT services
Demand and Supply Management Covers
Analyzing and managing current and future demand for IT services
Analyzing and managing the current and future supply of IT services
Proposing response to address gaps between demand and supply
Fostering collaboration between IT and the business to manage the IT services portfolio
Understanding the trade-offs between satisfying demand and the cost of supply
Demand and Supply Management Key artifacts
Demand models
IT services portfolio
IT services catalog
Shared operations catalog (IT & business)
Supply models
Enterprise Information Management Value
The Enterprise Information Management (EIM) capability provides appropriate operational data for business transactions, and consistently enables timely and informed decision making.
Enterprise Information Management Goal
The Enterprise Information Management (EIM) capability ensures that quality data is available to support the business activities of the organization.
Enterprise Information Management
Ability to establish effective systems for gathering, analyzing, distributing, exploiting and disposing of data and information, covering strategic, operational and security aspects of information management for the enterprise
Enterprise Information Management Covers
Establishing an information management strategy, policies, standards and controls
Establishing information governance mechanisms
Performing information valuations
Defining and maintaining master data
Making infrastructure and storage decisions
Managing information quality
Enterprise Information Management Key artifacts
Information management strategy
Information governance policy
Access controls policy
Governance
The Governance (GOV) capability is the ability to evaluate, direct, and monitor the current and future use of an organization’s IT resources in support of strategic objectives.
Governance Goals and Objectives
Establish IT governance as a central component of effective corporate governance and provide appropriate guidance regarding the effective, efficient, and acceptable use of IT.
Establish appropriate IT decision-making bodies and processes, including mechanisms for escalation of IT issues and compliance with obligations.
Establish decision boundaries, decision rights, and decision inputs; and delegate authority and accountability for aspects of IT governance in line with what is appropriate for the organization’s context.
Governance
Improve confidence in, and the agility and transparency of, IT decision-making.
Ensure that distributed IT decisions support the organization’s strategic goals and objectives.
Provide broad oversight on the performance of IT in the organization.
Governance Key artifacts
Documented IT decision-making process
Decision-making responsibility and accountability matrix
Formal charters for governance bodies (IT steering committee or enterprise governance council)
Green IT Value
The Green Information Technology (GIT) capability enables organizations to minimize their impact on the environment by using IT to deliver Triple Bottom Line (TBL) results - environmental (planet), and social (people), and financial (profit).
Green IT Goal
The Green Information Technology (GIT) capability aims to manage IT operations in an environmentally sensitive manner, and to leverage IT to minimize the environmental impact of the wider business activities.
Green IT
Ability to minimize the environmental impact of IT, and to make the best use of technology the minimize the environmental impact across the organization
Green IT Covers
Developing a green IT strategy and aligning it to business requirements
Planning how to meet IT’s environmental sustainability goals
Implementing environmental compliance within IT governance
Providing relevant measurement and reporting
Aligning organizational capabilities, people and culture for ensuring environmentally sustainable computing
Green IT Key Artifacts
Environmental sustainability strategy
Green IT roadmap
Green IT targets