IOA2 Exam 2 - Retinal Physiology Pt 2
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
In dim light, _______ predominate.
rods
How sensitive are rods to light and what type of vision do they facilitate?
Rods are extremely sensitive in poorly lit conditions, facilitating scotopic vision ("night vision")
The light-sensitive retina allows detection of objects at ________ levels of illumination
low (ability to recognize details is poor)
What colors are perceived in scotopic vision?
Shades of gray
What is the peak wavelength sensitivity of rods?
507 nm
What is the peak lumen/watts of rods?
1700 lumen/watts
What type of lighting conditions produce mesotopic vision?
Conditions intermediate between day (photopic) and night (scotopic)
Which photoreceptors are active during mesopic vision?
Rods and cones
Which photoreceptor activity dominates in photopic vision?
Cone activity
What level of illumination is required for photopic vision?
Bright illumination
What visual functions are enhanced in photopic vision?
Sharp visual acuity and color discrimination
What are the three types of cones, and what wavelengths do they absorb?
Blue (S-cones) - 420 nm
Green (M-cones) --> 531-534 nm
Red (L-cones) --> 564-588 nm
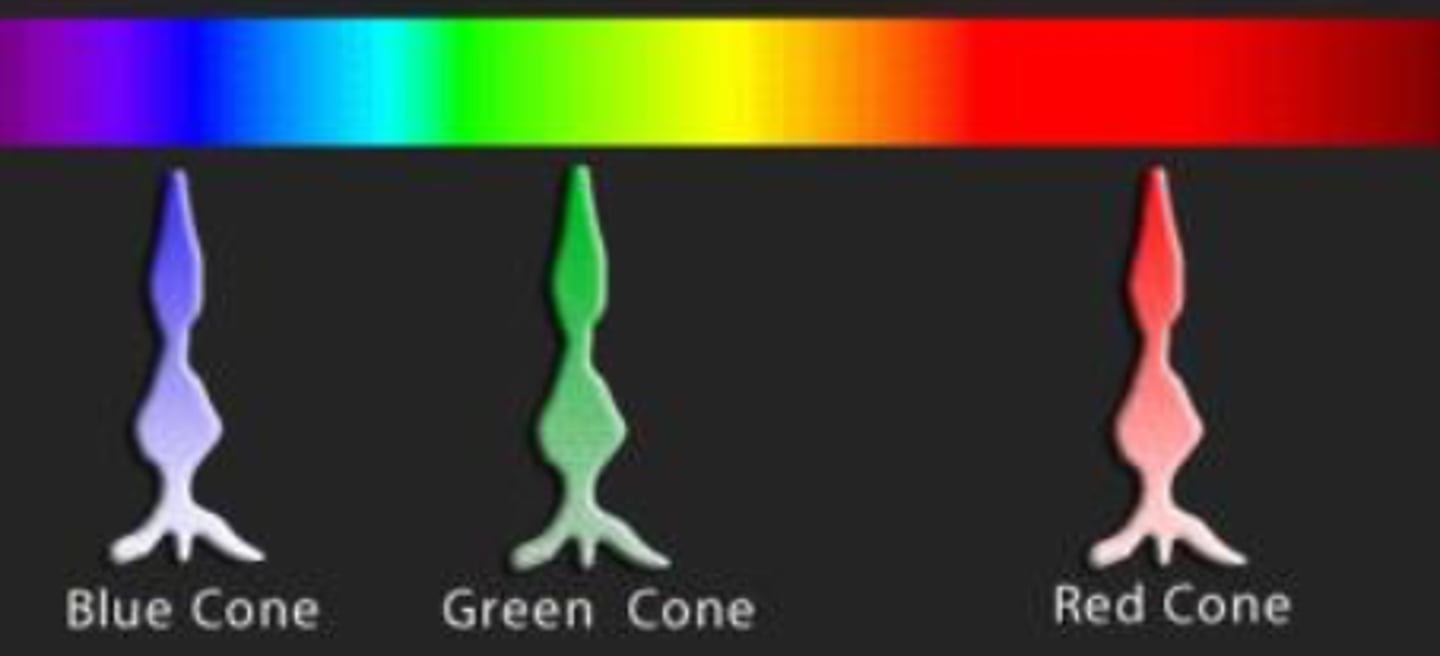
Way to remember the types of cones
SML = small medium large
BGR (burger) = Blue Green Red
What are the two main components of visual pigments in rods and cones?
1) Opsin
2) Chromophore
Opsin
A membrane protein bound to a light-absorbing pigment molecule
What does opsin form?
a long helix that loops back and forth across the membrane seven times
What is the role of opsin in visual pigments?
Determines the wavelength absorption
Chromophore
Molecule that absorbs the photon of light
What is the chromophore in both rod and cone visual pigments?
11-cis-retinal (derivate of vitamin A)
How do cones differ from rods in terms of opsin?
Cones have three different types of opsins, while rods have only one (rhodopsin)
How do the three opsin photopigments in cones differ?
Differ in amino acid composition that binds 11-cis retinal
What color is the S-cone cell sensitive to?
Blue
What color is the M-cone cell sensitive to?
Green
What color is the L-cone cell sensitive to?
Red
What is the result of these different opsins in cones?
They cause the chromophore's absorption to diferent wavelengths
What % of amino acids are identical between all cones and rhodopsin?
~40%
What % of amino acids are identical between blue cones vs. green and red cones?
~40%
What % of amino acids are identical between green and red cones?
~95%
Where is rhodopsin pigment located?
Disc membrane
What induces the constant replacement of photoreceptors?
Damage of the photoreceptors in the outer segment due to light absorpition induces a constant replacement
When are rod outer segments shed and what removes them?
In the morning, removed by RPE phagocytosis mechanisms
When are cone outer segments shed and renewed?
In the evening
What happens to Vitamin A in the RPE?
Oxidized in the RPE to give retinal access to the RPE via diffusion thru the large capillary fenestrations in the choriocapillaris
Nerve transduction of information between retinal neurons occurs by:
ion channel activity at gap junctions
What is a gap junction and how does it work in the retina?
An electrical synapse that allows current to pass directly between cells for rapid signal transmission
In gap junctions, no _______ is necessary.
chemical mediator
Between which types of retinal cells are gap junctions (electrical synapses) found?
1) Photoreceptor and photoreceptor
2) Photoreceptors and horizontal cells
3) Horizontal cells and horizontal cells
4) Bipolar axon and amacrine cells
Between which types of retinal cells are chemical synapses found?
-Amacrine and ganglion cells
-Bipolar and ganglion cells
How do chemical synapses transmit signals in the retina?
Neurotransmitter binds to specific sites at the postsynaptic membrane, eliciting an excitatory or inhibitory change in that neuron
Excitatory neurotransmitter in the retina
Glutamate
Which types of retinal cells release glutamate?
All photoreceptors, bipolar cells, and most ganglion cells
Inhibitory neurotransmitter in the retina
GABA and glycine
Which types of retinal cells release GABA and Glycine?
Most amacrine cells and horizontal cells
Chemicals that alter neuron transmission
Neuromodulators
Name the neuromodulators of the retina
Dopamine
Acetylcholine
What is the role of dopamine in retinal function?
changes the conductance of gap junctions between horizontal cells
Acetylcholine is synthesized by
starburst amacrine cells (SACs)
How does acetylcholine affect visual function?
Acetylcholine, along with GABA, helps modulate visual function in the inner plexiform layer (IPL)
Process by which a photon of light is. changed to an electrical signal
Phototransduction
Phototransduction occurs in the
photoreceptors
What triggers phototransduction and the start of the process of vision?
The absorption of light (outer segment) by rhodopsin
During phototransduction, a series of biochemical changes follow light absorption, causing the cell to
hyperpolarize
What is the immediate result of photoreceptor hyperpolarization?
It starts an electrical current flow through the retina
After the photoreceptors, which cells receive the signal in the retina?
Bipolar and horizontal cells
After bipolar and horizontal cells, where is the signal transferred to?
Amacrine and ganglion cells
Which retinal cells' axons carry the visual message to the brain cortex upon activation?
Ganglion cell
What is the resting membrane potential of photoreceptors?
-40 mV
Why do photoreceptors hyperpolarize instead of generating action potentials?
Dependent on potassium influx
Photoreceptors maintain a _________ electrical charge, of about ________mV in the dark.
slight negative electrical charge = -40 mV
What maintains the negative electrical charge of photoreceptors in the dark?
Active transport of cations (sodium and calcium) from within to outside the cell
CGN channels
Cyclic Gated-Nucleotide Channels
in the outer segment; are repsonsible for the light-induced changes in the electrical activity of photoreceptors
Cyclic GMP gated-channels
What pump is located on the inner segment plasma membrane, and what does it do?
Na/K ATPase pump; it uses ATP to pump Na+ out of the inner segment while moving K+ inside
Na+ then re-enters the photoreceptor via ________ in the __________.
Na channels; outer segment
What is the dark current in photoreceptors?
The flow of sodium and other cations into and out of the cell while in the dark