Topic 5 - Health and Disease ✅
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
c'est fini 🦖🦖🦖🦖🦖
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
What is health according to W.H.O.
A state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being
Not just the absence of disease
What is the difference between communicable and non communicable diseases?
Communicable diseases are passed directly between individuals
Caused by a pathogen
Non communicable diseases cannot be transmitted between induvial
Generally long-lasting
Caused by lifestyle and genetics
Why does having one diseases lead to higher susceptibility of other diseases
A disease may weaken an individual's immune system, making you more susceptible to other diseases
What is a pathogen
A disease causing organism
Example (4) of pathogen
Virus
Bacteria
Fungi
Protist
Describe cholera
Caused by bacteria
Spread by drinking water that has been contaminated with infectious faeces
Causes diarrhoea
How can cholera be reduced
More access to clean water
Improved sanitation
Describe tuberculosis
Caused by bacteria
Airborne
Causes lung damage
How to reduce the spread of tuberculosis
Improved hygiene and ventilation
Infected individuals should avoid crowded areas
Describe chalara ash dieback
Caused by fungus
Spread airborne by spores
Causes blackened leaves and bark lesions
How to reduce chalara ash dieback
Kill infected plants
Control movement of ash trees
Describe malaria
Caused by protists
Spread by mosquito vectors
Causes damage to blood and liver
How can malaria be reduced
Mosquito nets
Insect repellent
Describe sotmach ulcers
Caused by bacteria called Helicobacter
Transmitted orally by eating infected food
Causes stomach pain and vomiting
How to reduce stomach ulcers
Improve hygiene and sanitation
Describe ebola
Caused by virus
Spread by bodily fluids like blood, semen, saliva
Causes haemorrhagic fever
How to reduce ebola
Improve hygiene
Isolate infected individuals
Describe HIV
Caused by a virus
Spread by bodily fluids during unprotected sex, injecting drugs using unsterilised needles
Causes white blood cells to get destroyed, leading to AIDS
How to reduce HIV
Do not have sex
Do not share needles
Wear a condom
Can viruses survive outside of their host
They need the host cell to reproduce
This can be done in a lytic pathway or a lysogenic pathway
What is the lytic pathway
Using host cell machinery, the virus replicates its DNA
These are assembled to form new virus particles
When the host cell is full of virus particles, it bursts, in a process called lysis
The process is then repeated with nearby cells
What is the lysogenic pathway
The virus uses enzymes to insert its DNA into the host cell DNA
The host cell replicates, and the DNA of the virus is also copied during this process
The lytic cycle begins at this point, starting with the assembly of new viral particles
how are STIs spread
Through sexual contact
They are carried in bodily fluids such as semen and vaginal fluid
how can chlamydia and HIV be reduced
Barrier methods of contraception e.g. Condom
Not having sex
how do plants protect themselves from pests and pathogens using physical barriers
They can use a cellulose cell wall, which is impermeable to many pathogens
Or a waxy cuticle on the surface of the leaf, which acts as a barrier to most pathogens
how do plants protect themselves from pests and pathogens using chemical barriers
Cells of some plants produce antimicrobial chemicals
Some plants release compounds that attract large insects
These feed on the pests and stop them from eating the plant
Humans can extract antimicrobial compounds for these plants to use in medicine and antibiotics
how can plant diseases be detected in the field
Using visible cues
Chalara ash dieback causes malformations and browning of leaves
Aphids causes serious structural damage
Tobacco mosaic virus causes discolouration of leaves
5.11 - how can plant diseases be detected in the lab
Use this method -
Cuttings are taken from diseased plant
The virus causing the disease is grown on an agar plate
The pathogen is tested and identified using a monoclonal antibody testing kit
What are the physical barriers the human body provides
Mucus, cilia and skin
How does mucus protect us
Produced by goblet cells in the airway
Mucus traps bacteria and other pathogens before they reach the lungs and cause infection
How does cilia protect us
Cilia waft away mucus that has trapped pathogens
to be killed by stomach acid
How does skin protect us
Skin cells provide a physical barrier against pathogens
Protecting the tissues and cells beneath it from infection
What are the chemical barriers our bodies have
Lysozymes
Hydrochloric acid
How do lysozymes protect us
Used by white blood cells to kill and digest bacteria
How does hydrochloric acid protect us
Used to kill bacteria in food that reaches the stomach
Prevents infection
5.14 - How does the body respond to an immunisation
In vaccines there is a weakened or dead version of the pathogen
There are antigens on these pathogens
Your body creates antibodies to destroy thee antigens
The antibodies attach to the antigens, meaning the antigens can't harm your body
As your body makes antibodies to fight the pathogen's antigens, it also makes memory cells
This means when your body gets the actual pathogen (not dead or weakened version), the memory cells will know how to fight the pathogen
Advantages of immunisation
Has evidence of eradicating many diseases so far
Immunisation leads to herd immunity, preventing epidemics
Disadvantages of immunisation
There can be side effects like fevers
What is herd immunity
When people are vaccinated it increases the percentage of the population that is immune
The few people that are unvaccinated are then less likely to catch the disease, since the chance of contacting someone infected is low
5.16 - what are antibiotics used to treat + why
Bacterial infections
Because they inhibit cell processes in the bacterium but not the host organism
Name 3 aseptic techniques
Use of an autoclave to prepare sterile growth medium and petri dish
Use of a sterile inoculating loop to transfer microorganisms
The need to keep petri dishes and culture vials covered
formula for cross sectional area of agar jelly
Pi x r2
What does the process of developing new medicines include:
Many stages e.g.
Discovery
Development
Preclinical testing
Clinical testing
5.21 - how are monoclonal antibodies made
The rat is injected with antigens.
Then it makes lymphocytes, which make antibodies to fight the antigens.
The cells are taken out of the rat. In a lab, cancer cells are added to the cell.
The cancer cell fuses with the lymphocyte to make a hybridoma cell.
The hybridoma cells copy themselves and produce antibodies.
The antibodies are called monoclonal antibodies because they came from a single cloned cell.
The monoclonal antibodies are created to be harvested and used for different purposes.
How are monoclonal antibodies used in pregnancy testing
Pregnancy test kits use monoclonal antibodies.
These have been designed to bind with a hormone called HCG which is found only in the urine of pregnant women.
Monoclonal antibodies are attached to the end of a pregnancy test stick onto which a woman urinates.
If she is pregnant, HCG will be present in her urine and will bind to the monoclonal antibodies on the test stick.
This will cause a change in colour or pattern which will indicate pregnancy.
These specific monoclonal antibodies in the pregnancy test will only bind with HCG.
How are monoclonal antibodies used to analyse blood
Monoclonal antibodies are modified so that they will bind to the molecule you are looking for
They are bound to a fluorescent dye
If the molecules are in the sample, then the antibodies bind it to it, and the dye can be observed
Advantages of monoclonal antibodies compared to drug and radiotherapy treatments
They only bind to target cells, meaning healthy ones are not affected
What is the effect of exercise and diet on obesity
Eating more calories than you burn causes you to put on weight
Eating a large excess of calories, especially if a lot of them come from saturated fat, can lead to obesity
Obesity can lead to CVD and high blood pressure, as well as type 2 diabetes
To avoid obesity, eat a diet with less sugar, less processed food, and less saturated fat
How to calculate BMI
mass / height2
What is the effect of alcohol on liver diseases
A high alcohol intake can lead to liver disease
Fatty liver, common in alcoholics, can lead to liver cancer
To reduce your chances of liver disease, try and drink less than 14 units of alcohol a week
What is the effect of smoking on cardiovascular disease
Smoking increases the risk of lung cancer, COPD and CVD
Cigarettes contain over 40 chemicals; they all have different effects - from lung cancer to heart failure
You should quit smoking if you want to avoid CVD
What are some different treatments for CVD
Life long medication
Surgical procedures
Lifestyle changes
Life long medication as a way to treat CVD
There are medications to reduce cholesterol or reduce blood pressure
People with high blood pressure may have to take multiple medications to reduce it
Surgical procedures as a way to treat CVD
Coronary arteries supply the heart with oxygen
If these are blocked, a coronary artery bypass can be performed
Another method involves using a metal stent to widen arteries that have been narrowed by plaque
Name 3 lifestyle changes as a way to treat CVD
Reducing salt in diet
helps prevent high blood pressure from developing
Maintaining a healthy BMI (achieved by exercise)
reduces strain on the heart
Reducing the amount of fat you eat
reduces the risk of fat deposits in the arteries
Stages of drug development
1. Screening for potential drugs
2. Preclinical trials
3. Clinical trials
4. Approval by a medical agency
What is a blind trial
• Where participants don't know whether they are receiving the new drug or the placebo
• Prevents patient being biased
What is a double blind trial
• Neither the participants nor the doctors know who is receiving the new drug or the placebo
• Prevents bias from doctors
Name the aseptic technique and why it is used - a t p s g m a p d
Autoclave to prepare sterile growth medium and petri dishes
• If this step does not take place, they are likely to be contaminated with other microorganisms
• This can potentially produce a new pathogen
Name the aseptic technique and why it is used - s i l
Sterile inoculating loop
• Kills unwanted microorganisms by passed incoculating loop through a flame
Name the aseptic technique and why it is used - p d s u d
Petri dish storage upside down
• This is to prevent condensation from the lid landing on the agar jelly and disrupting growth
Core practical - investigating the effects of antibiotics on microbial cultures METHOD
Take a petri dish
Sterilise it in an autoclave
Use a permanent marker to draw 3 degments
Place different antiseptics on filter paper discs, then use forceps to apply the filter paper disc onto to agar plate
Tape down the lid
Incubate at 25o C for 2 days
Calculate the area of the zones using pi r2
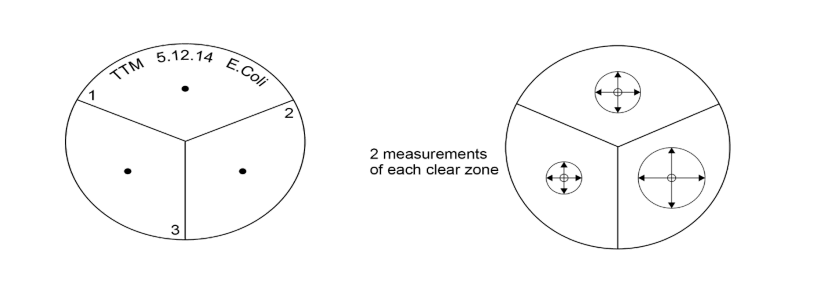
Independent variables for core practical
Different antibiotics or antiseptics
Dependent variable for core practical
Area of the zone of inhibition
Control variables for core practical
• Area of filter paper disc
• Species of bacteria
• Concentration of antiseptic
What are non communicable human diseases caused by
An interaction of a number of factors
Causes of CVD
• High intake of saturated fats
• Inactive lifestyle
Causes of lung and breast cancer
• Smoking for lung cancer
• Age and genetics for breast cancer
Causes of lung and liver disease
• Smoking
• High alcohol intake