immunology and serology review antibody structure and function exam 1
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
memorize this set
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Antibody functions
• Neutralization (binding inhibits activity)
• Opsonization (enhances phagocytosis)
• Complement activation (triggers complement activity)
• Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
• Cells (NK cells, macrophages, neutrophils) recognize antibody bound to target cell and release substances to destroy target cell.
What is the function of CSFs? Colony stimulating factors?
Induce and control differentiation of cells in bone-marrow.
What are the classes (isotypes) of antibody
IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE, IgD
What is the definition of an antibody
Antibodies (immunoglobulin) are proteins that specifically binds to an antigen and targets its destruction
What band do antibodies normally appear? And what is their serum electrophoresis pH?
gamma (γ) band with serum electrophoresis at pH 8.6
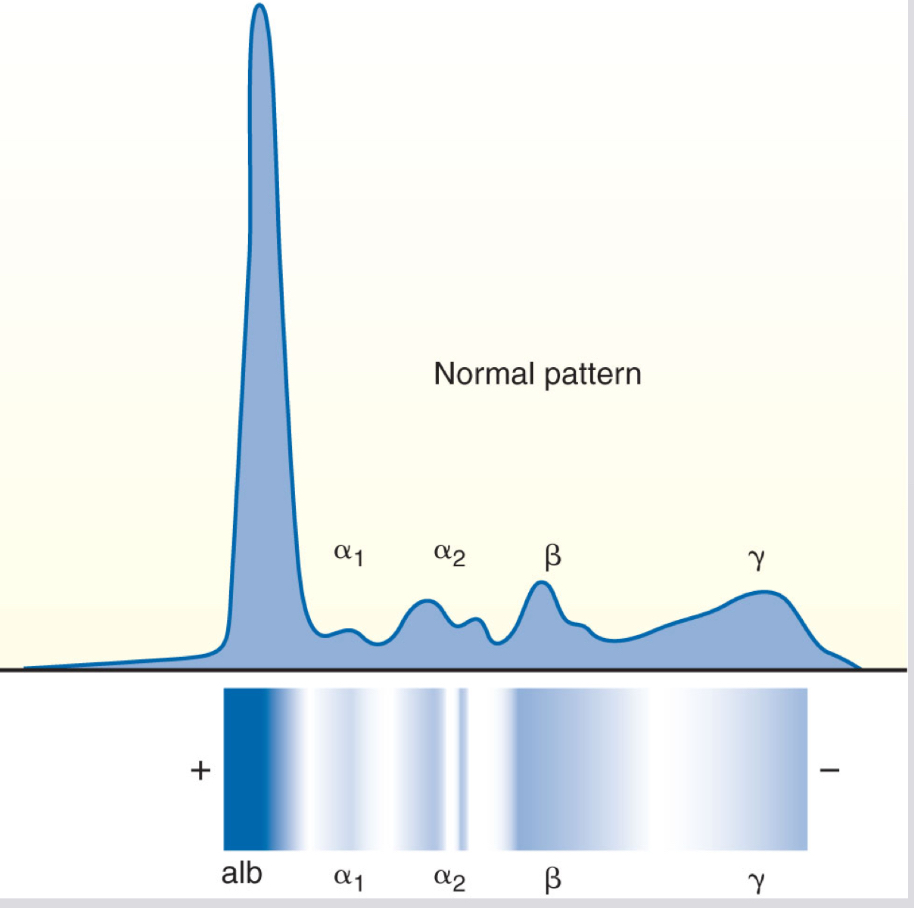
gammaglobulin is enriched with
antibody
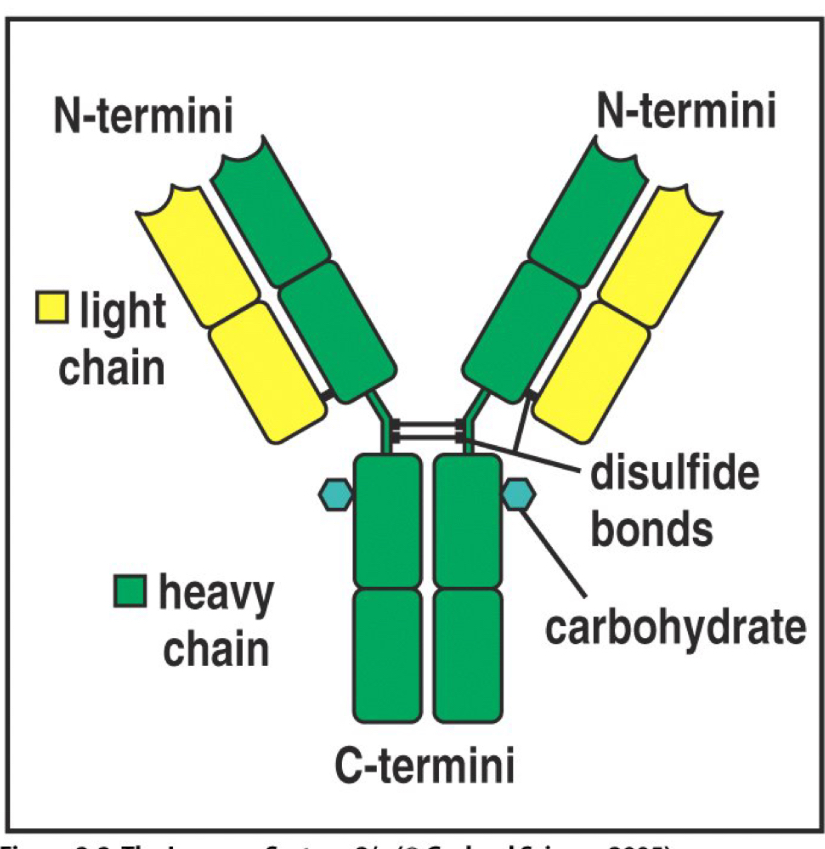
Basic structure of an antibody
Two heavy chains and two light chains held together by disulfide bonds, the chains are divided into domains
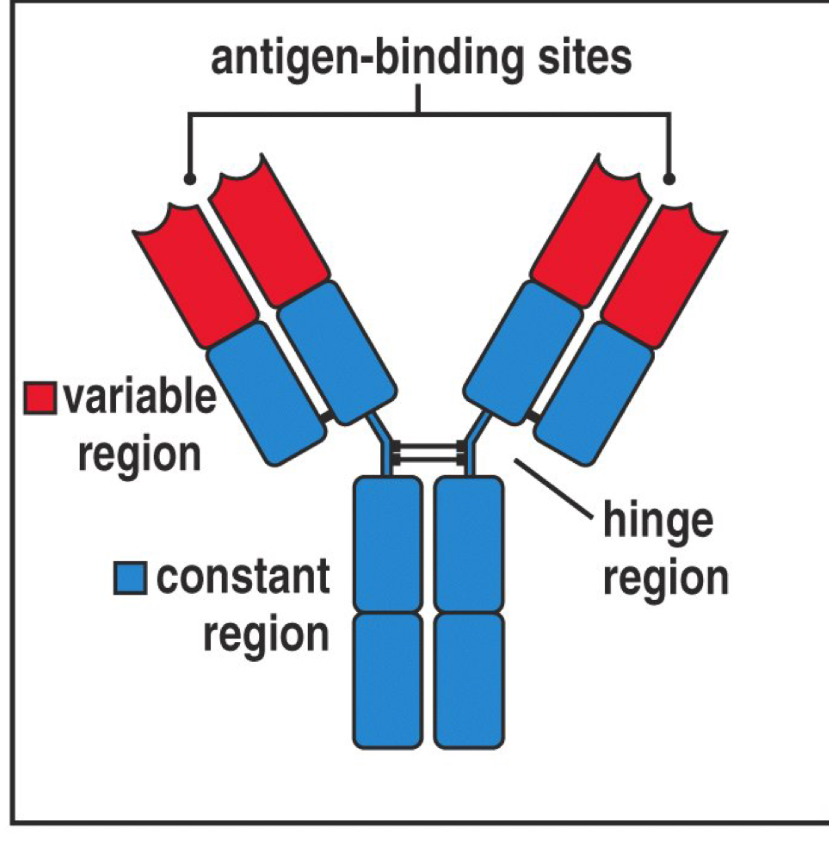
The variable and constant regions do what?
They function to specify the antibody
Variable region- binds to specific antigen
Constant region- determines Ab immunoglobin class
Types of light chains
Kappa and lambda
Light chains are secreted by what type of cells?
Malignant plasma cells
Type of heavy chains determines
The class of antibody
IgG: γ chain IgM: μ chain IgA: α chain IgD: δ chain IgE: ε chain

Match the immunoglobulin type to their heavy chain
IgG: gamma chain
IgM: mu (ul) chain
IgA: alpha chain
IgD: delta chain
IgE: epsilon chain
Isotype Definition
A unique amino acid sequence that is common to all immunoglobulin molecules of a given class in a given species
Define Allotypes
Minor variations of isotype sequences that are present in some individuals but not others
Idiotype Definition
Variations in variable regions that give individual antibody molecules specificity it is located on the antibody’s variable region or on the T cell receptor
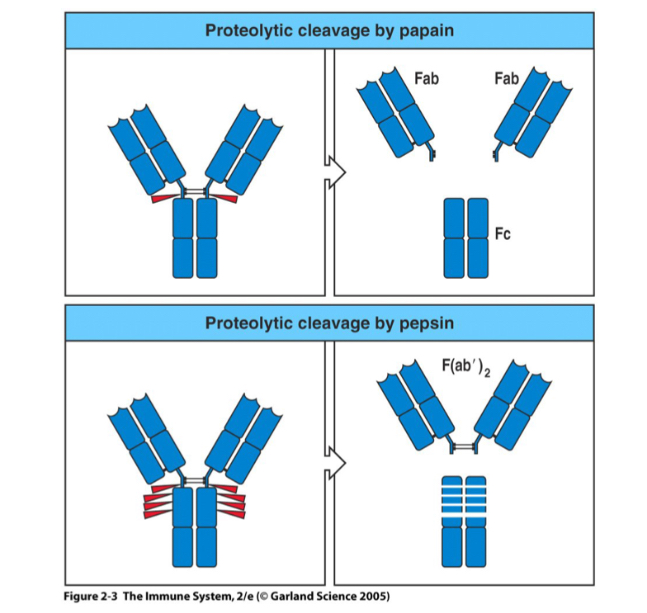
Compare the difference between the different proteolytic cleavages by papain and pepsin
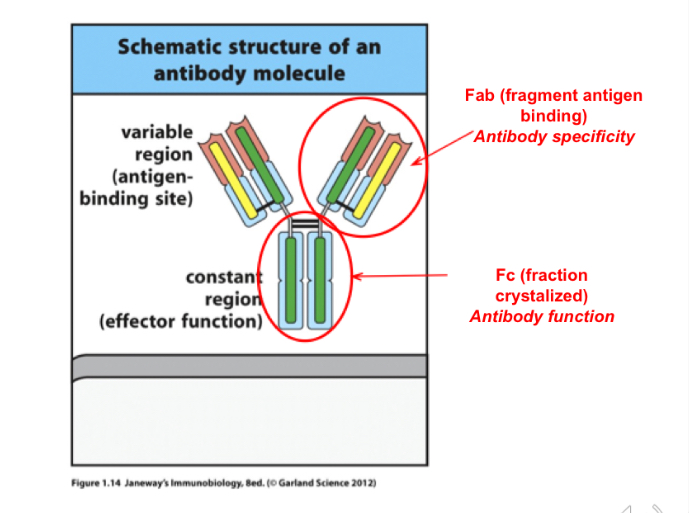
Fab stands for? Location? What does it do
Fragment antigen binding ; variable region; antibody specificity
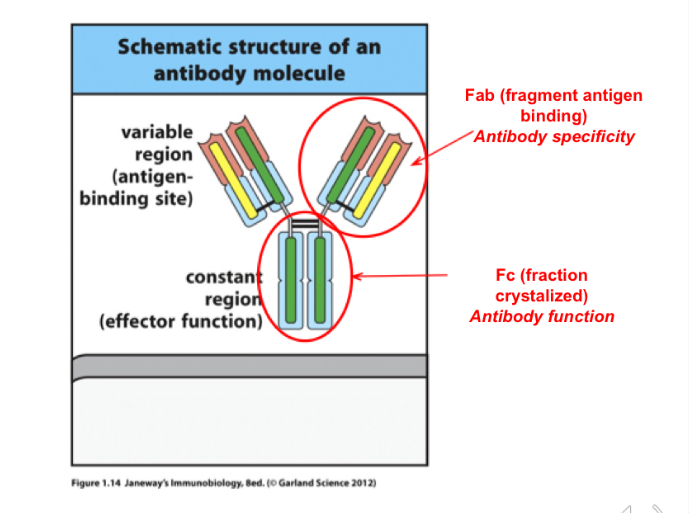
Fc stands for? Function?
fraction Crystallized, the constant region, confirms the antibody function
Provide two examples of the clinical usefulness of Fab fragments
• Neutralizing antibodies
(Rattlesnake venom, Digoxin overdose)
• Small and pass through the kidneys
(eliminated in urine)
Which antibody classes are found in monomers?
IgG and IgE
Which antibody classes are found in multimers held together by J chain?
IgM and IgA
Which antibody class is found in pentamers and monomers?
IgM
Which antibody is found in multimers made up of dimers and monomers?
IgA
B cell receptor Is _______ with membrane component
monomeric
Predominant immunoglobulin in humans percentages (75% to 80% of the total serum immunoglobulins)
Four subclasses:
IgG1: 66%
IgG2: 23%
IgG3: 7%
IgG4: 4%
Which antibody has the longest half life
IgG has longest half life, 23 days
Major Functions of IgG
Providing immunity for the newborn (because IgG can cross the placenta)
• Fixing complement
• Coating antigen for enhanced
phagocytosis (opsonization)
• Binding to cells for antibody- dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) by NK and other cells
• Neutralizing toxins and viruses
• Participating in agglutination and precipitation reactions
IgG role with toxins, it’s relationship with blood cells
All subclasses can cross the placenta
• Macrophages, monocytes, and neutrophils have Fc receptors specific to the Fc region of IgG, increasing the efficiency of phagocytosis
• A high diffusion coefficient allows IgG to enter extravascular spaces more readily than other immunoglobulin types
• IgG plays a major role in neutralizing toxins and viruses
What Trait of IgG allows it to enter extravascular spaces more readily than other immunoglobulin types?
It has a high diffusion coefficient
IgM Characteristics
Known as a macroglobulin
Has a molecular weight of about 900,000 d
Accounts for 5% to 10% of all serum immunoglobulins
No memory cells
Synthesized as long as antigen is present
Has half-life of 6 days (much shorter than that of IgG)
Can exist as:
Monomer (on surface of B cells) Pentamer (found in secretions)
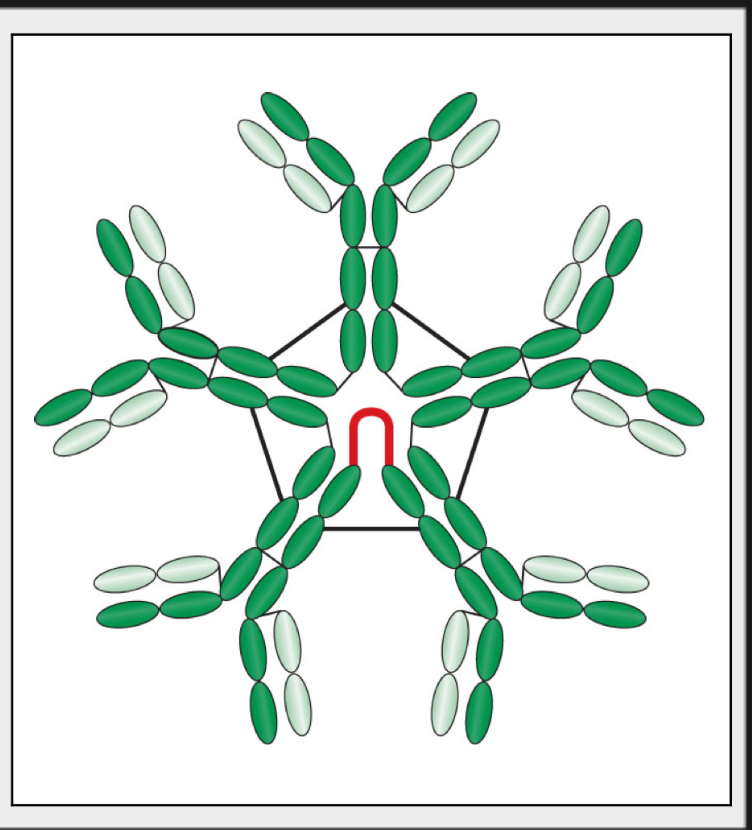
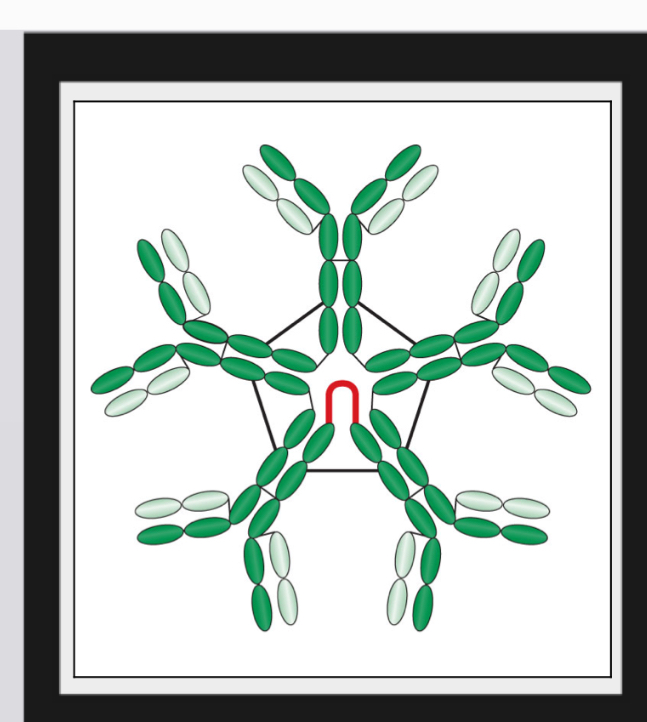
what best describes the IgM’s form and structure
Pentamer form
Held together by J chains, which are linkage points for disulfide bonds between two adjacent monomers
Has a star-like shape with 10 antigen-binding sites
Where is IgM mainly found?
Intravascular pool
Can IgM cross the placenta?
No
Which immunoglobulin appears first after antigenic stimulation?
IgM
Which antibody is also known as the primary response antibody?
IgM
Can IgM cross placenta? Does it have memory cells?
No bc it’s too large, no memory cells
Known as the primary response antibody
IgM, Appears first after antigenic stimulation and in the maturing infant
Synthesized only as long as antigen remains present due to lack of memory cells so it cannot make a secondary response
Functions of IgM
• Complement fixation
• Helps with opsonization due to it’s ability to activate complement.
• Some complement components are opsonins, e.g. C3b
• Agglutination
• Toxin neutralization
IgA characteristics in serum
Accounts for 10% to 15% of all circulating immunoglobulins in serum
One variable and three constant regions
Serum IgA: Appears as a monomer with a molecular weight of approximately 160,000
Secretory IgA (sIgA)
Is synthesized in plasma cells found mainly in mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue and beneath mucosal epithelium.
Is released in dimeric form
Is captured by poly-Ig receptor which transports it across epithelial cells.
When released, the IgA has part of the poly-Ig receptor still attached.
The part derived from receptor remaining is called secretory component (SC)
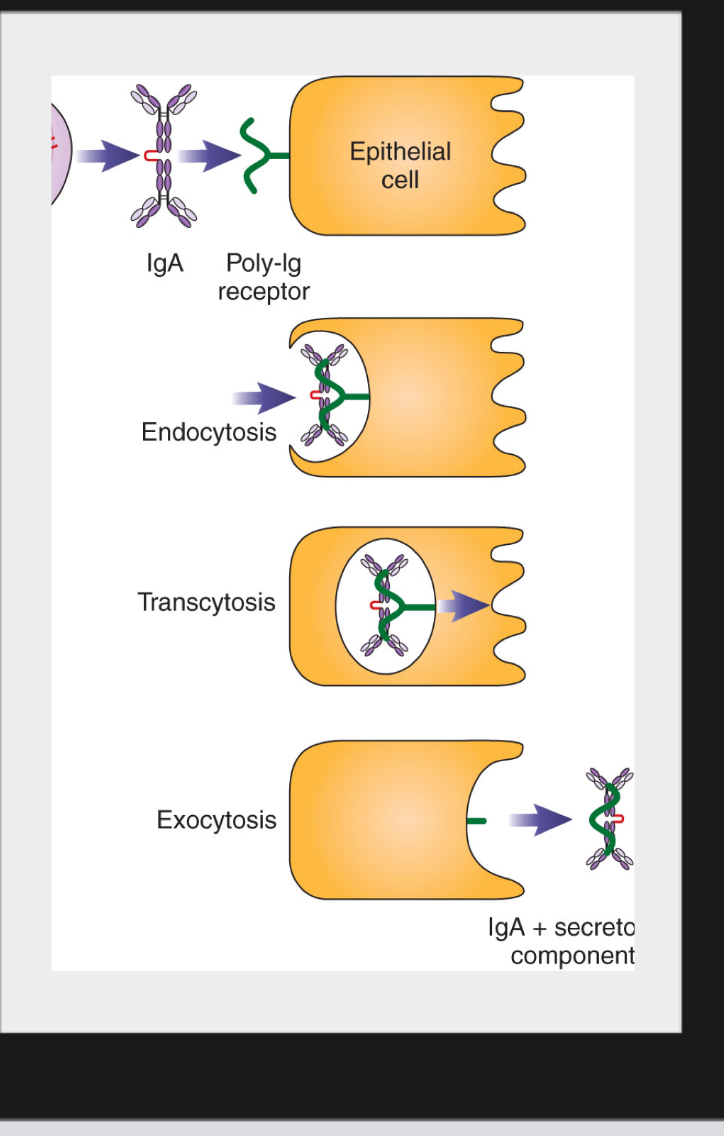
Function of IgA
Patrols and acts as the first line of defense in mucosal surfaces
Neutralizes toxins produced by microorganisms
Prevents bacterial adherence to mucosal surfaces
Found in breast milk and passively transfers immunity to newborn during breastfeeding
What antibody is found in breast milk?
IgA
IgD Characteristics in serum
Extremely scarce in the serum
Found on the surface of immunocompetent but unstimulated B lymphocytes
Appears second (after IgM)
May play a role in B-cell activation
Plays a role in regulating B-cell maturation and differentiation
Secreted form in serum does not appear to serve a protective function
Does not bind complement
Does not bind to neutrophils or macrophages Does not cross the placenta
IgE characteristics
0.0005 % of total serum immunoglobulins
• Produced by plasma cells that are located
primarily in the lungs, gut and skin
• Does not participate in complement fixation, agglutination, or opsonization
• Is incapable of crossing the placenta
• Attaches to basophils, eosinophils and tissue mast cells through high-affinity Fc ε RI
receptors
IgE Function: Allergic Reactions
Two adjacent IgE molecules on a mast cell bind a specific antigen
Cascade of cellular events results in degranulation of mast cells and release of vasoactive amines (such as histamine and heparin)
Induce allergic type reactions Helps expel parasites
Type I immediate hypersensitivity results in what conditions
Hay fever, asthma, vomiting and diarrhea, hives, life-threatening anaphylactic shock
IgE Involvement in Parasitic Infections
Eosinophils play a major part in the destruction of large antigens, such as parasitic worms, that cannot be easily phagocytized. Eosinophils recognize IgE bound to parasite
Which immunoglobulin is involved in type I immediate hypersensitivity reactions?
IgE
B cell receptor
• Antibody monomer has transmembrane anchor
• Igβ & Igα transmit signal
• Can have heavy chains from any of the antibody classes.
• Doesn’t matter what the class, B cell receptor is still a monomer
Affinity Definition
binding strength between an antibody and a single antigenic determinant (epitope)
Avidity Definition
number of antibody-combining sites and the number of epitopes in a single antigen
Monoclonal Antibodies
Mainly used for diagnostic testing and therapeutic purposes
In vitro diagnostic testing
Delivery of therapeutic agents in diseases
Developed based on knowledge that B cells are genetically preprogrammed to synthesize very specific antibody
Are derived from a single parent antibody- producing cell that has reproduced many times
Hybridoma
Fusion of plasma cell with a laboratory-grown myeloma cell deficient in Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT)
The myeloma cells require special medium to grow, but the plasma cells have a functional HGPRT gene.
Hybridoma will be immortal and will not need special medium
Hybridoma produces antibody with the specificity of the plasma cells indefinitely
Hybridoma Production involves
Immunizing a mouse with a certain antigen
Harvesting spleen cells
Spleen cells are fused with myeloma cells using polyethylene glycol (PEG)
Selecting fused cells and screening for presence of desired antibody
High affinity Vs Low affinity:
High affinity: tightly bind antigen at lower concentration
Low affinity: better when a large amount of antigen is present)