Biology Term 2
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Nitrogen Cycle, Carbon Cycle, Plant cells, Animal Cells, Specialized cells, Human Impact
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
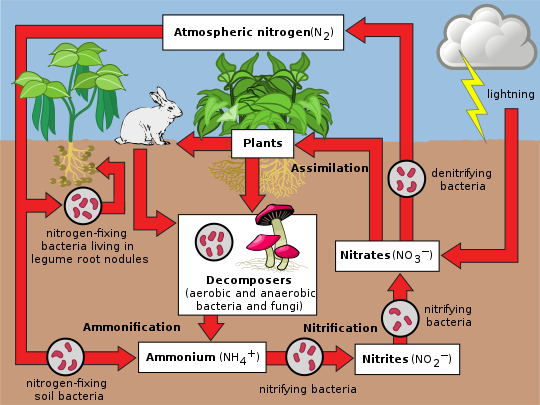
How much nitrogen is in the air?
78%
Why is Nitrogen needed?
Its needed for organism to make protein
Is nitrogen reactive?
No. Atmospheric Nitrogen is inert or unreactive.
What do nitrogen fixing Bacteria do ?
They convert atmospheric nitrogen into to nitrates ( NO 3)
What are some ways Nitrogen can be converted?
Lightning, fertilizers, Nitrogen Fixing Bacteria
How do plants use Nitrogen
They absorb a more reactive form of nitrogen called nitrates from the soil to make plant proteins.
How do animals use Nitrogen
They would eat plants or other animals that have already eaten plants to get it.
What is the purpose of Decomposers in the Nitrogen Cycle
They break down the bodies of dead plants and animals and there waste products like urine feaces etc.
What do decomposer break them down into?
Ammonia Compounds
What happens to the ammonia compounds after this decomposition.
The ammonia compounds are broken down by nitrifying bacteria to form nitrites then nitrates. Which can be absorbed by plants.
What happens to Nitrates in poorly aerated soil
Denitrifying Bacteria will use the oxygen from the nitrates and will release it back into the atmosphere.
Diagram of Nitrogen Cyclee
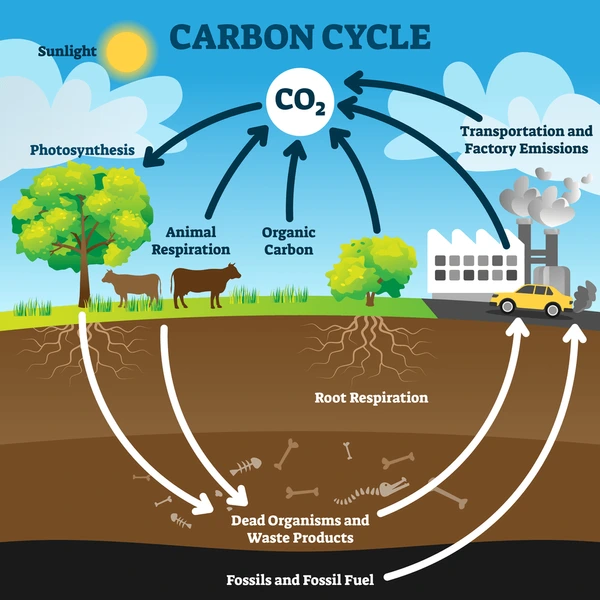
How much carbon is in the air
0.04%
What is carbon needed to make?
Carbohydrates, Protein, and Fats
How do plants use carbon dioxide
Plants use carbon dioxide to make food during photosynthesis. The carbon becomes a part of the plant
What happens to the carbon when plants and animals die
Their bodies are first decomposed by decomposers and their waste and absorb the carbon atoms
What factors can cause plants and animals to not decompose
-Lack of oxygen
-High salinity
- ocean floor
How does carbon return to the atmosphere
-When Decomposers respire
-Respiration
-Combustion
What process is carbon removed from the atmosphere
Photosynthesis
Diagram showing Carbon Cycle
What is the type of energy absorbed by producers during photosynthesis
Sunlight energy
What is the type of energy stored in food
Chemical Energy
What are some ways on which energy in the food chain is lost
Respiration, feaces, and movement
Why does energy flow in one direction in a food chain
Because energy flows from producers to consumers
What percent of energy is passed on from each trophic level?
10 %
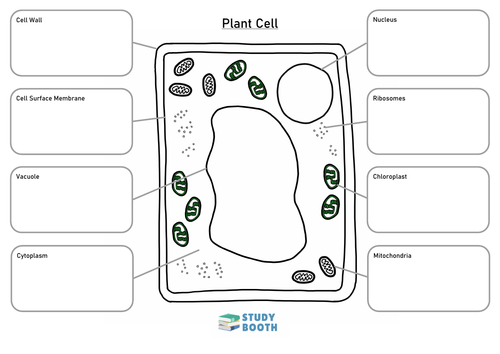
What are some distinguishing factors of Plant cells
Have a large vacuole
They have a cell wall made up of cellulose
Chloroplast with chlorophyll
Starch grain
What does the large vacuole and chloroplast do?
The chloroplast contains chlorophyll and this is where photosynthesis takes place.
The large vacuole stores nutrients, waste, and regulates water. They also store toxins to deter herbivores but to attract polinators
Label this generalized plant cell
How do you tell the difference between mitochondria and chloroplast
Chloroplast has vertical lines and Mitochondria has horizontal lines
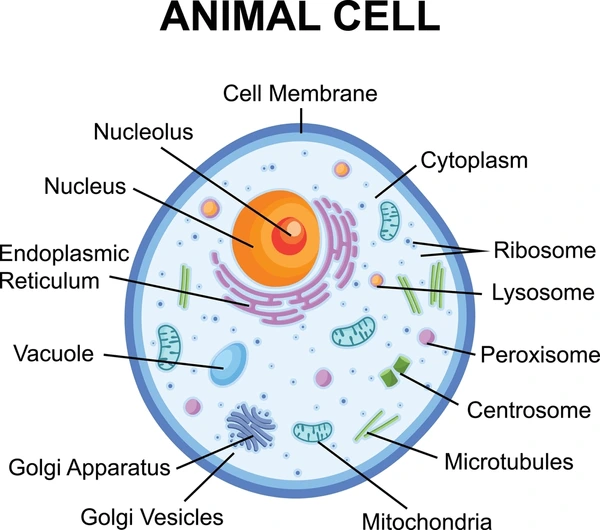
what are some distinguishing factors of a generalized animal cell
They don’t have a cell wall, chloroplast , or chlorophyll
They can be a variety of different shapes
they have glycogen granules as food stores
Diagram of generalized animal cell
What are specialized animal cells
Cells designed to carry out a specific role in the body of organisms in Kingdom Animalia
Name some examples of specialized animal cells
Nerve cells
Muscle Cells
Sperm and Egg cells
Ciliated Cells
What are Muscle Cells
Muscles cells are found in bundles which make up our muscles. These cells are able to contract (get shorter) and relax (return to original length). There are different types of muscle cell, each perfectly adapted to its function:
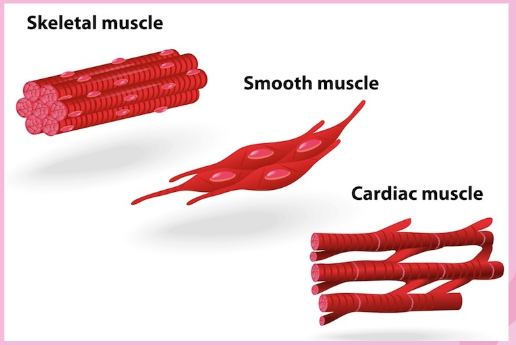
What are some types of muscle cells and what do they do
Cardiac cells- They contract and relax to pump blood around or bodies
Smooth cells-Smooth muscle cells make up thin sheets of muscle, such as the stomach lining. They can also be arranged in bundles, or rings, like that in the anus.
Skeletal Cell- Skeletal muscles are connected to bones. Its cells contract to make muscles move.
What is the function of chloroplast
²
This contains chlorophyll and this is where photosynthesis .
Compare and contrast animal and plant cells
Animal cells have no cell wall. Plants do
Animal cells have no chlorophyll. Plants do
Animal Cells have no chloroplast. Plants do
Plants have a large vacuole. Animals don’t
Microbes include members of what kingdoms
All the members of Kingdom Prokaryote, many members of kingdom Protoctista, and some members of Kingdom of Fungi
What are some examples of specialized plant cells
Xylem, Phloem, Epidermal, Root hair cells
What does the epidermal cell do?
They are the outermost layer of the cell, they protect the plant from any infection and prevents water loss by secreting a waxy layer called the cuticle.
What does the root hair cells do?
They are known was the nutrient absorbers. They absorb water, dissolve nutrients and minerals.
What does the Xylem do?
The xylem cells transport water and dissolved minerals from the roots to other parts of the plant.
What makes the Xylem cell suitable for this function
The xylems has a hollow interior and strong walls made out of lignin.
What does the Phloem do?
The phloem is the food distributor. This cell transports sugars and proteins.
What is diffusion
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. It does not required a semi permeable membrane.
Why is diffusion important to living things?
To gain Oxygen during aerobic respiration and to get rid of Carbon dioxide during the same process.