CHE102B Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry - Carbonyl Chemistry
1/9
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts from the lecture on carbonyl chemistry, focusing on functional groups, nucleophilic additions, and related organic chemistry principles.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
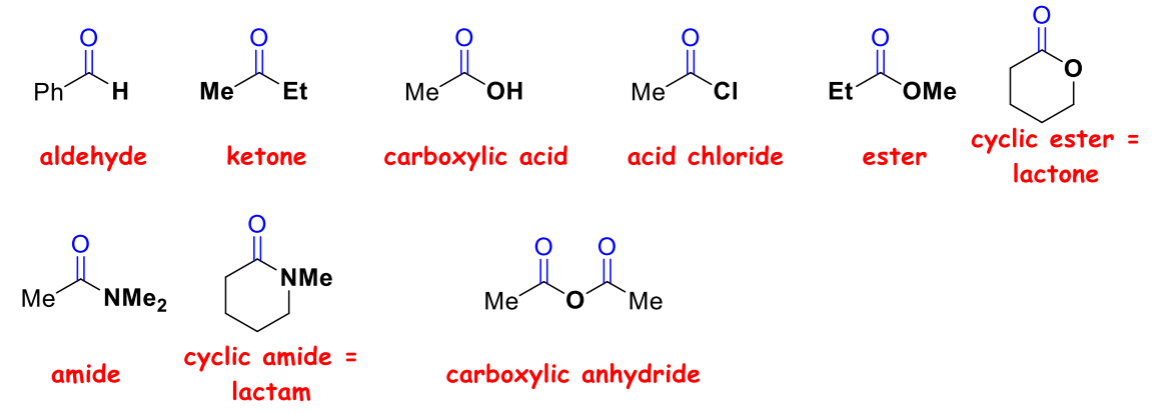
What are carbonyl functional groups that you should know?
What defines a nucleophile in organic chemistry?
Nucleophiles are electron pair donors, often containing a lone pair of electrons.
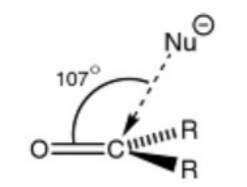
What is the Bürgi–Dunitz angle in relation to nucleophilic attack?
The optimum angle of attack by a nucleophile on a carbonyl compound is approximately 107 degrees.
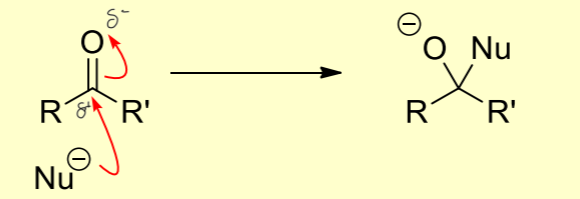
How do electrophiles interact with nucleophiles in a nucleophilic addition?
The nucleophile donates electrons to the electrophile, resulting in the formation of a new sigma bond and breaking the C-O pi bond.
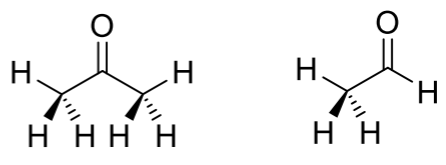
What is the difference in reactivity between aldehydes and ketones regarding nucleophilic attack?
Aldehydes are generally more reactive than ketones towards nucleophilic attack due to less steric hindrance.
What happens to the carbonyl group during nucleophilic addition?
A nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, leading to the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate.
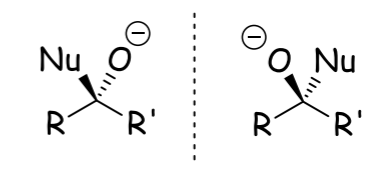
What is the role of electron-withdrawing and electron-donating groups in determining the reactivity of carbonyls?
Electron-withdrawing groups increase reactivity of the carbonyl, while electron-donating groups decrease it.
How does the presence of solvent affect the nucleophilic addition of water to a carbonyl compound?
The position of the equilibrium can depend on the nature of the carbonyl and the hydration level.
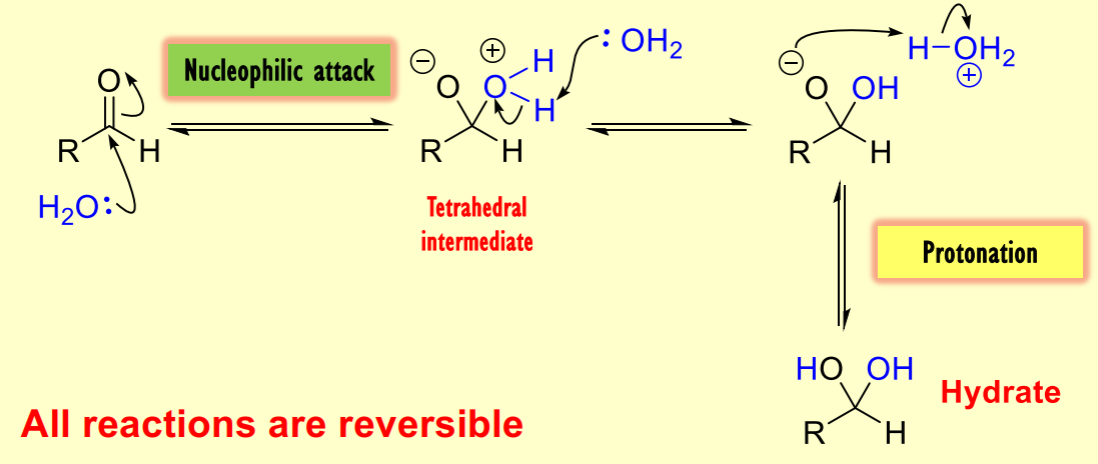
What occurs in the reaction of water with a carbonyl compound during nucleophilic addition?
The reaction is reversible, leading to the formation of a hydrate as a potential product.
Why is π* orbital significant in carbonyl chemistry?
It is the highest occupied molecular orbital that a nucleophile attacks during nucleophilic addition to the carbonyl.