Lecture 17 | Fossil Fuels
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Peak Oil, Fossil Fuel Formation, Biomass, Location of Coal/Natural Gas/Oil Formations, Extractions, Clathrates, Coal Burning & Pollution
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
Biomass
mass of some living organism
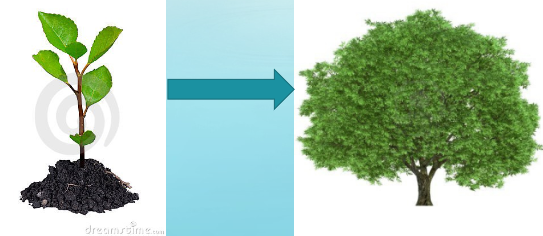
A tree can go from a 1g seed to over 100 kg as a massive tree. Where does this biomass come from?
co2, water, photosynthesis, thin air
Describe how primary producers make biomass:
e- from water and c from co2 to make glucose
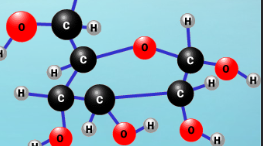
How do carbohydrates like glucose store energy?
chemical bonds, more bonds = more potential energy
How can we tap into the energy stored in primary producers?
break bonds: eat plant material & use e, burn biomass and release heat
How can you increase the energy you get from eating or burning biomass?
break more bonds
What are two paths that biomass can follow after an organism dies?
decomposed and e goes to decomposer, gets buried and e locked away
What happens when biomass gets buried under sediment?
gets compressed, can turn into fossil fuels
Compression
packs a lot of chemical bonds into a smaller volume
When you compress biomass, the ____ changes, but _____ stays the same
volume, mass

What volume of leaves could 1 piece of coal contain?
a full room
How does compression make biomass more useful?
portable, energy-dense materials
How old is the biomass that formed the fossil fuels we use today?
350-500 million years
Where does most of the biomass in fossil fuels come from? Why?
plants, low trophic level, more primary producers than apex predators
What does the amount of compression that biomass experiences depend on?
how deep its buried, deeper = more compression
In order from most shallow to deepest, list the formation of fossil fuels that occurs on land:
plba: peat, lignite, bituminous coal, anthracite

Peat
few 100 feet down, soft, squishy, barely compressed

Lignite
brown coal, hard, not dense, few 1000 feet down

Bituminous Coal
nearly 1 mile down, very hard, dense, burns well

Anthracite
several miles down, very rare, extremely energy rich, under mountains
Which type of coal yields the most energy when burned (per size)? Why?
anthracite, more compression fits more bonds per size
Peat Formation Conditions
low temp, low pressure
Coal/Anthracite Formation Conditions
low temp, high pressure
Natural Gas Formation Conditions
high temp, low pressure
Oil Formation Conditions
high temp, high pressure
In the formation of fossil fuels, what does low temperature mean?
formed on land
In the formation of fossil fuels, what does high temperature mean? Why?
formed under ocean, closer to mantle & warmer
In the formation of fossil fuels, what does high pressure mean?
buried deeper, could be under mountain or far under ocean
Because oil and gas are compressed, they are also ____ ______
under pressure
How do compressed oil and gas relieve the pressure they’re under? Provide an example:
find ways to get to the surface, coal oil point
What are two ways oil and natural gas can get trapped in rock formations?
anticlines, transform faults
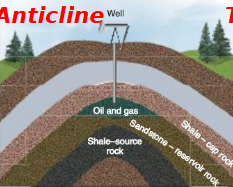
Anticline
upside down bowl, soft pore rock stuck beneath curved/hard cap rock
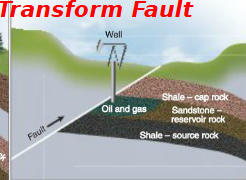
Transform Fault
two plates sliding past, cap rock slid over porous rock that traps oil & gas
What places do petroleum geologists look for to determine where to drill for oil & gas?
aged rocked, soft pore rock with cap rock on top
What are the two extraction methods to retrieve oil & gas?
primary production, enhanced production/recovery
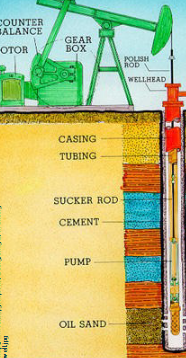
Primary Production
sink a well, pump oil whatever you can, 20% recovery
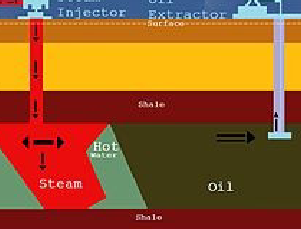
Enhanced Production/Recovery
inject co2 or n2 to force oil towards pumping well, 60% recovery, costs more
Where are most of the oil formations, and who used the most oil?
middle east, NA & europe, developed
Natural Gas provides _____ energy than oil
less
What does higher compression lead to for natural gas?
longer c chains, more energy
Natural gas still emits CO2 when burned. Why is it considered cleaner than coal?
no nox, sox, or mercury
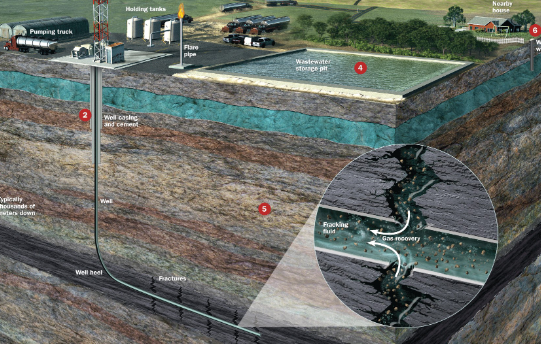
Hydraulic Fracturing (Fracking)
high pressure water & chemicals injected to burst fractures wider, makes pumping natural gas easier
What is a danger associated with fracking?
fracture cap rock, gas & chemicals leak into aquifers & drinking water
Methane Clathrates/Hydrates
gel-like deposits of methane gas trapped in water molecule cages
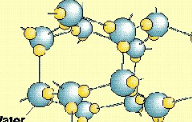
How and where do methane clathrates form?
hexagon lattice of water, methane fits in cage, specific temp & pressures in ocean

What is the issue with using methane clathrates?
unstable, release heat, chain reaction of destabilizing, methane bubble
Coal is the _____ and _____ fossil fuel used
most common, dirtiest
What three impurities does coal release, and what is their effects (4 things)?
sox & nox acid rain, mercury in aquatic food chain, particulate matter smog & breathing, co2 emissions climate change
Where are coal deposits commonly found?
north america, asia, europe
What is the most common coal types found in the US? Where is anthracite only found?
lignite & bituminous, anthracite in pennsylvania mountains
What are 3 technologies to treat coal pollution?
high efficiency filters, catalytic converters, flue gas desulfurization
High Efficiency Filter/Bag House Purpose
remove particulate matter
Catalytic Converter Reduction Purpose
turn nox into n2 and o2 gas
Flue Gas Desulfurization Purpose
combine sox, mercury, & limestone to make gypsum