QCE psychology units 3 & 4
1/199
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
200 Terms
cognitive dissonance
unpleasant feelings when beliefs are inconsistent with behaviours
ways to reduce prejudice
-education, interaction, sustained contact, mutual interdependence
fundamental attribution error
tendency to attribute others' behavior to their dispositions and our own behaviors to our situations
stereotype
A generalized belief about a group of people
explicit racism
overt racism, e.g slurs
implicit racism
racism that operates unconsciously and unintentionally, e.g pulling over a black person
Ethnocentrism
Belief in the superiority of one's nation or ethnic group.
Racism
Belief that race is the primary determinant of human traits and capacities and that racial differences produce an inherent superiority of a particular race.
xenophobia
dislike of or prejudice against people from other countries
Culture
Beliefs, customs, and traditions of a specific group of people.
Culture shock
personal disorientation when experiencing an unfamiliar way of life/culture
Assimilation
completely adapting to another culture
Acculturation
the adoption of the behavior patterns of the surrounding culture whilst retaining previous cultures
Multiculturalism
multiple cultures coexisting collectively; some aspects removed for collectivism.
Community
group of people with common characteristics
Pluralism
Multiple cultures coexisting separately
Scapegoating
The tendency for individuals, when frustrated or unhappy, to displace aggression onto groups that are disliked, visible, and relatively powerless
Ageism
Discrimination based on age
Sexism
prejudice, stereotyping, or discrimination, typically against women, on the basis of sex.
Tokenism
the practice of making only a perfunctory or symbolic effort to do a particular thing, especially by recruiting a small number of people from underrepresented groups in order to give the appearance of sexual or racial equality within a workforce.
self-serving bias
the tendency to perceive oneself favorably
confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that supports our beliefs
Bias
prejudice in favor of or against one thing, person, or group compared with another, usually in a way considered to be unfair.
attribution
the process of explaining one's own behavior and the behavior of others
dispositional attribution
attributing behavior to the person's disposition and traits
situational attribution
attributing behavior to the environment
social identity
person's sense of whom they are based on their group memberships. The central hypothesis is that group members of an in-group will seek to find negative aspects of an out-group, thus enhancing their self-image.
social identity theory
theory in which the formation of a person's identity within a particular social group is explained by social categorization, social identity, and social comparison
hazing
requiring a person to do humiliating acts in order to join a group
explicit attitude
an attitude that a person is consciously aware of and can report
implicit attitude
an attitude, such as prejudice, that one is not aware of having
General Aggression Model
a modern theory of aggression suggesting that aggression is triggered by a wide range of input variables that influence arousal, affective stages, and cognitions
hostile aggression
aggression stemming from feelings of anger and aimed at inflicting pain or injury
instrumental aggression
aggression motivated by the desire to obtain a concrete goal
Groupthink
the mode of thinking that occurs when the desire for harmony in a decision-making group overrides a realistic appraisal of alternatives
bystander effect
the tendency for any given bystander to be less likely to give aid if other bystanders are present
Cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body; largest part of the brain
Thalamus
the brain's sensory control center
Hypothalamus
maintains homeostasis
Hippocampus
regulation and expression of emotion, spatial awareness, consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory
Amygdala
involved in memory and emotion, particularly fear and aggression.
basal ganglia
structures in the forebrain that help to control movement
Cerebellum
Balance and coordination; coordinates motor skills required for muscle contraction
primary motor cortex
the section of the frontal lobe responsible for voluntary movement
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter that affects hunger, sleep, arousal, and mood.
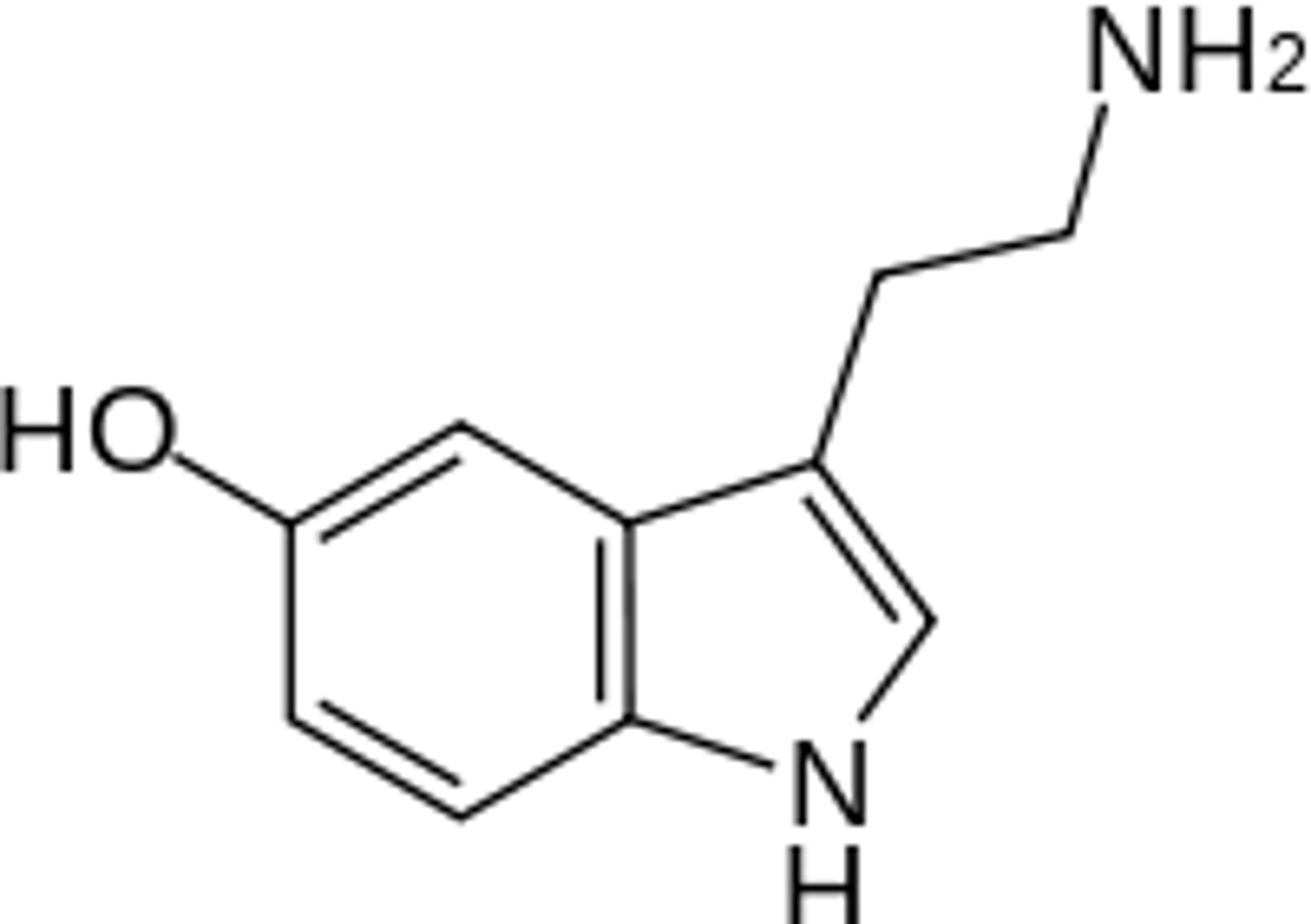
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter associated with movement, attention and learning and the brain's pleasure and reward system.
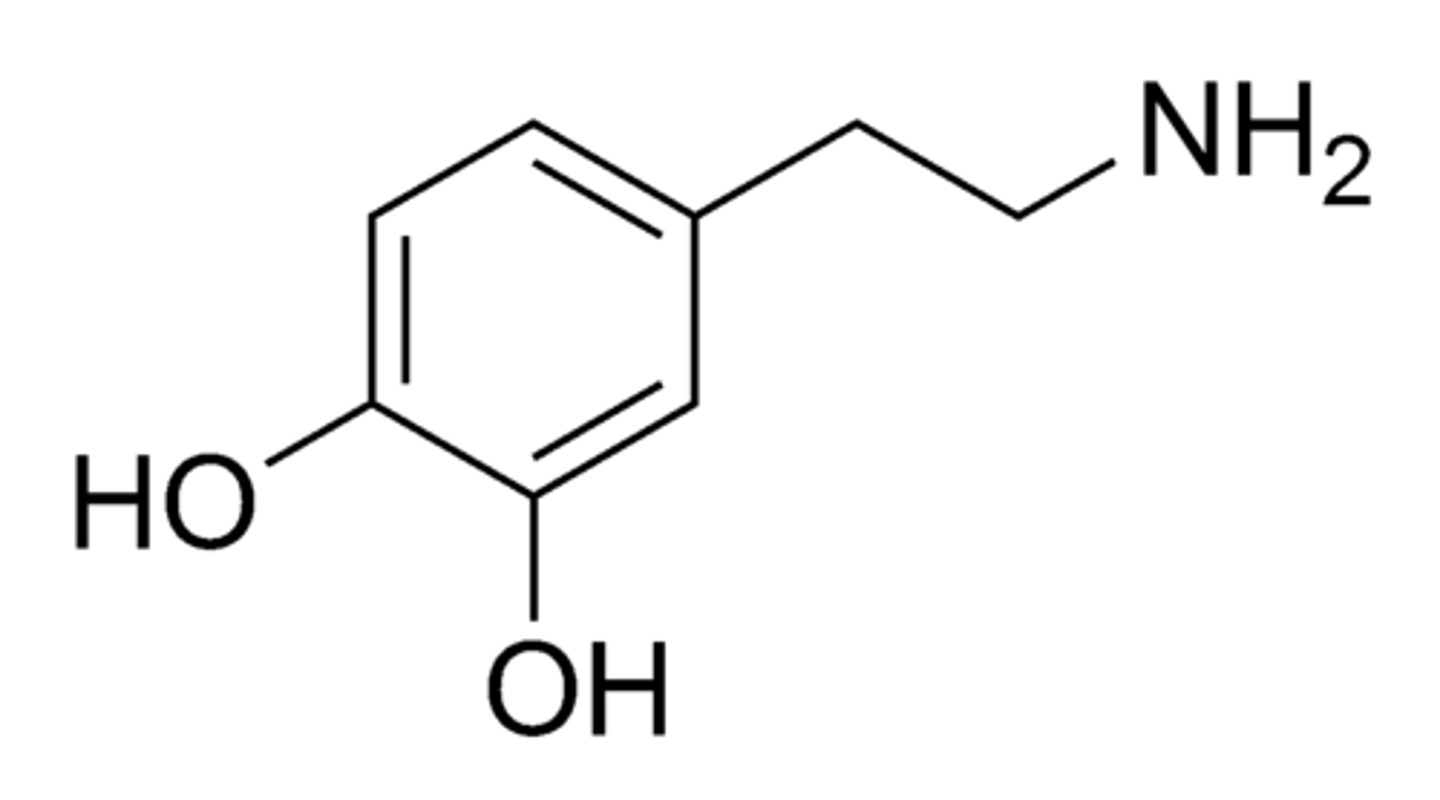
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction
Parkinson's disease
Breakdown of substantia nigra which stops production of dopamine, affecting movement, often including tremors in arms/legs etc.
Alzheimer's disease
a progressive and irreversible brain disorder caused by Acetylcholine deficit, characterized by gradual deterioration of memory, reasoning, language, and, finally, physical functioning
Conformity
Adjusting one's behavior or thinking to coincide with a group standard.
gender schema
a set of behaviors organized around how either a male or female should think and behave
primary socialisation
the process of learning that begins at birth and occurs in the home and family
secondary socialisation
process of learning appropriate behavior within smaller sections of the larger society
Ames room illusion
shape constancy > size constancy
Muller-Lyer Illusion
two vertical lines of the same length appear different due to inverted arrow heads
Ponzo illusion
railroad track, horizontal lines look different
floaters
caused by age, gel clumps that speck our vision
age-related macular degeneration
ARMD; griany deposits in macula
Congenital Visual Disorders
inherited, present at birth
photoreceptors
Cones = interpret color and bright light; Rods = Interpret dim light and greys
frontal lobe
associated with reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving
parietal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch and spatial awareness.
occipital lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
temporal lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.
Broca's area
speech production (left frontal lobe)
Broca's aphasia
inability to produce speech
Wernicke's area
language comprehension (temporal lobe)
Wernicke's aphasia
inability to comprehend speech
autonomic nervous system
The part of the PNS that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs.
sympathetic nervous system
fight or flight
parasympathetic nervous system
rest and digest
somatic nervous system
Division of the PNS that controls the body's skeletal muscles.
central nervous system
consists of the brain and spinal cord, controls most functions of the body and mind, connects brain to body
spinal reflexes
simple, automatic behaviours that are processed in the spinal cord independent of the brain for quick reflexes e.g stepping on something sharp
reflex arc
the nerve pathway involved in a reflex action including at its simplest a sensory nerve and a motor nerve with a synapse between.
retroactive interference
the disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old info
proactive interference
the disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of new info
classical conditioning
a type of learning in which one learns to link two or more stimuli and anticipate events
operant conditioning
a type of learning in which behavior is strengthened if followed by a reinforcer or diminished if followed by a punisher
social learning
Learning through observing others.
context-dependent retrieval
the improved ability to retrieve information when the conditions of the original learning are reproduced
state-dependent retrieval
the tendency for information to be better recalled when the person is in the same state during encoding and retrieval
levels of processing
a continuum of memory processing from shallow to intermediate to deep, with deeper processing producing better memory: sensory stores, short-term memory (STM) and long-term memory (LTM)
Working model of Memory
Baddeley and Hitch 1974
Split into three stores:
Central Executive function, visuo-spatial sketchboard and phonological loop. (Episodic buffer added in 2000)
procedural memory
implicit LTM: the gradual acquisition of skills as a result of practice, or "knowing how" to do things
declarative memory
It refers to memories which can be consciously recalled such as facts and events.
episodic memory
type of explicit long term memory for declarative, personal information
semantic memory
type of explicit long term memory for knowledge about the world
short-term memory
activated memory that holds a few items briefly, 12-30 seconds, 5-9 capacity
long-term memory
the relatively permanent and limitless storehouse of the memory system. Includes knowledge, skills, and experiences.
Epinephrine
Excitatory neurotransmitter, another term for adrenaline; raises heart rate and cardiac output
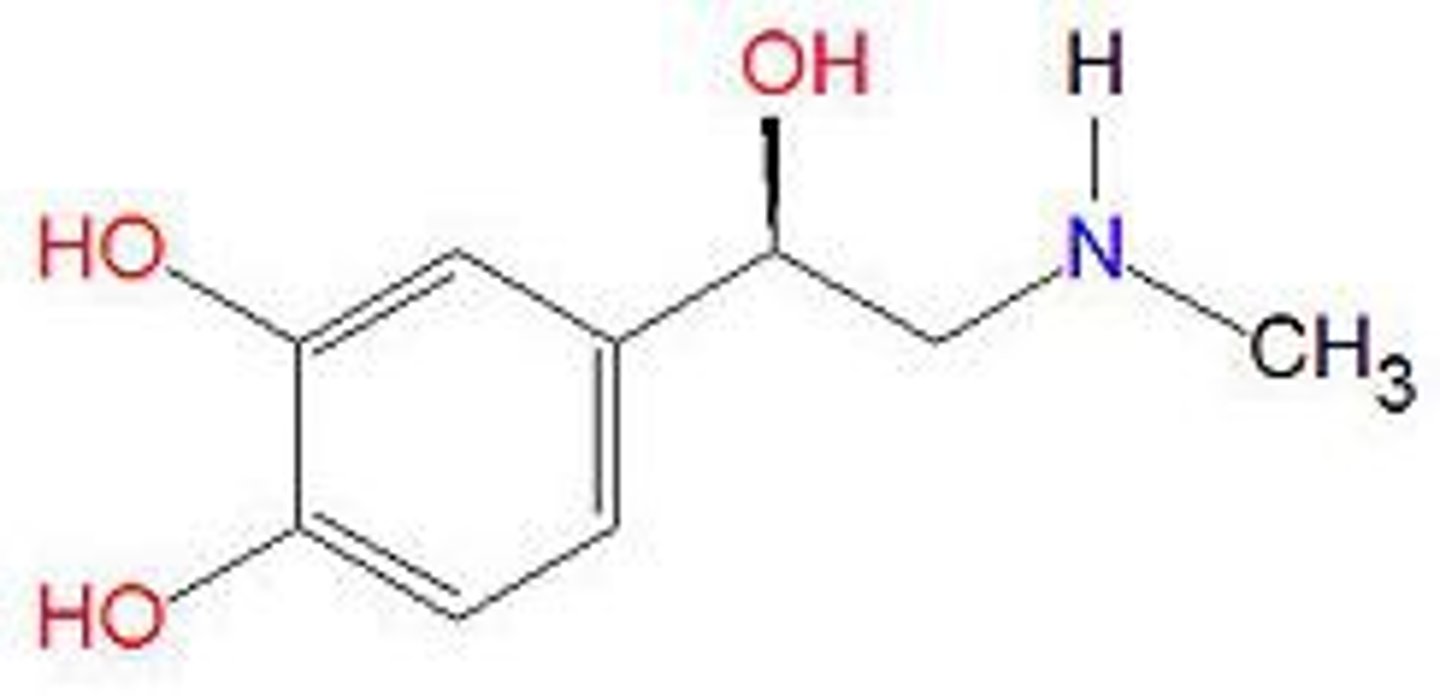
Norepinephrine
Excitatory neurotransmitter helps control alertness and arousal; undersupply can depress mood; maintains BP
limitations of social identity theory
limited explanatory power for prejudice formation toward out-groups
monosynaptic reflex
Reflex pathway with only one synapse between the sensory and motor neurons (ex: knee-jerk).
polysynaptic reflex
at least one interneuron between sensory neuron and motor neuron
axon terminal
The endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons
receptors
parts of the cell membrane that receive the neurotransmitter and initiate or prevent a new electric signal
subordinate goals
shared goals that override differences among people and require their cooperation
central executive
the part of working memory that directs attention and processing